Abstract
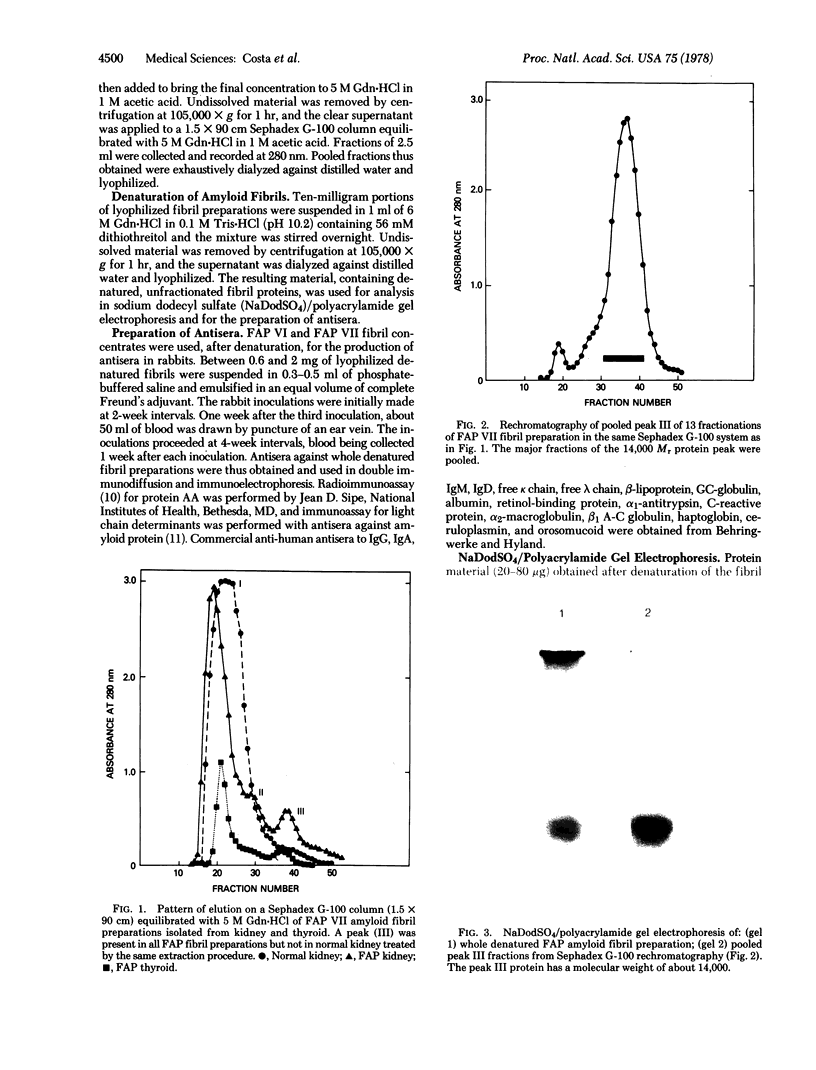
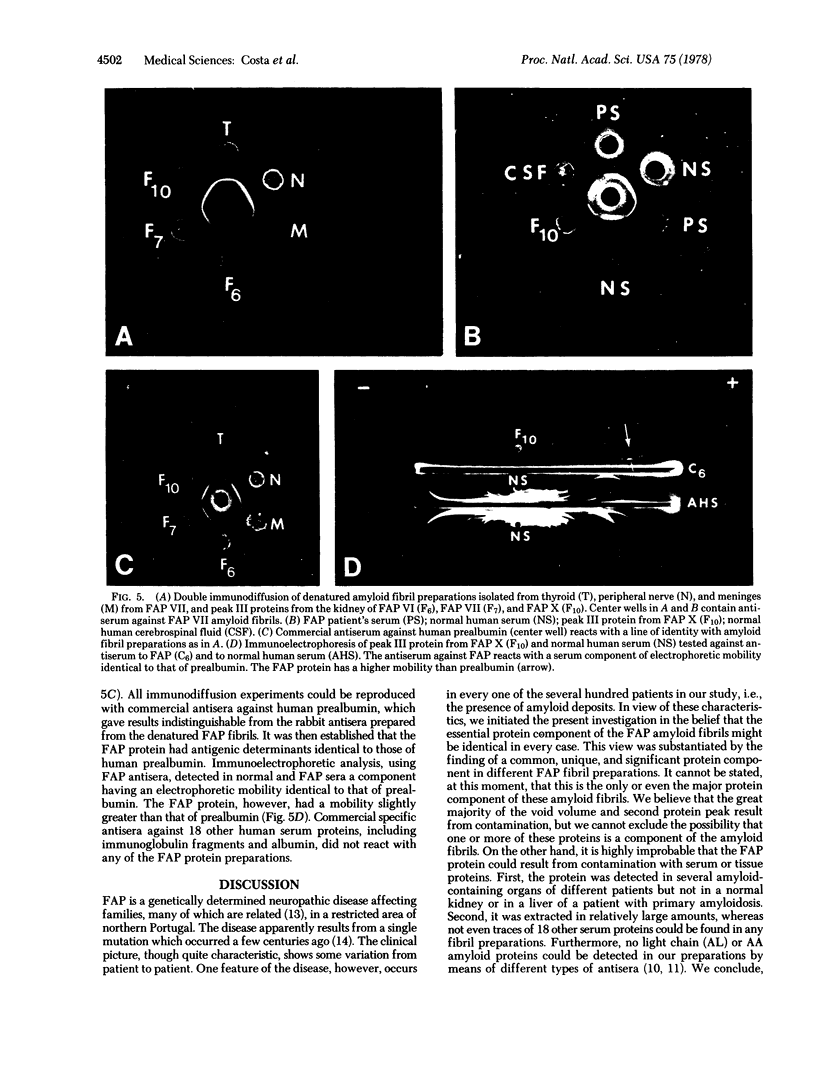
Amyloid fibrils were concentrated from the kidney, thyroid, and peripheral nerve of six patients with familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy (FAP). The fibril concentrates were solubilized in 6 M guanidine.HCl and fractionated on Sephadex G-100 columns. The elution profile of all FAP amyloid fibril concentrates revealed a protein of apparent Mr of 14,000, designated the FAP protein, that was absent from normal human tissues treated by the same procedure and from fibrils of a primary amyloidosis liver. Antisera against whole denatured fibril concentrates prepared in rabbits reacted with the FAP protein and a component in normal human serum corresponding to prealbumin. It was further established that the FAP protein shared common antigenic determinants with human prealbumin by its reaction of identity with normal prealbumin using commercial antisera against human prealbumin. Amyloid AL or AA proteins could not be identified in FAP fibrils by sensitive immunochemical assay methods. These results suggest that the FAP protein is a unique and significant component of the FAP amyloid fibrils and that it is closely related to the 13,745 Mr prealbumin subunit.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDRADE C. A peculiar form of peripheral neuropathy; familiar atypical generalized amyloidosis with special involvement of the peripheral nerves. Brain. 1952 Sep;75(3):408–427. doi: 10.1093/brain/75.3.408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrade C., Canijo M., Klein D., Kaelin A. The genetic aspect of the familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy. Portuguese type of paramyloidosis. Humangenetik. 1969;7(2):163–175. doi: 10.1007/BF00287080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake C. C., Geisow M. J., Swan I. D., Rerat C., Rerat B. Strjcture of human plasma prealbumin at 2-5 A resolution. A preliminary report on the polypeptide chain conformation, quaternary structure and thyroxine binding. J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 5;88(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90291-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Cuatrecasas P., Isersky C., Bladen H. A., Eanes E. D. Physical and chemical properties of amyloid fibers. II. Isolation of a unique protein constituting the major component from human splenic amyloid fibril concentrates. J Histochem Cytochem. 1969 Dec;17(12):769–780. doi: 10.1177/17.12.769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Eanes E. D., Bladen H. A., Linke R. P., Termine J. D. Beta-pleated sheet fibrils. A comparison of native amyloid with synthetic protein fibrils. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Dec;22(12):1141–1158. doi: 10.1177/22.12.1141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Harada M., Isersky C. The purification of amyloid fibril proteins. Prep Biochem. 1972;2(1):39–51. doi: 10.1080/00327487208061451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Page D. L. Amyloid, amyloidosis, and amyloidogenesis. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1976;15:1–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isersky C., Ein D., Page D. L., Harada M., Glenner G. G. Immunochemical cross-reactions of human amyloid proteins with human immunoglobulin light polypeptide chains. J Immunol. 1972 Feb;108(2):486–493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanai M., Raz A., Goodman D. S. Retinol-binding protein: the transport protein for vitamin A in human plasma. J Clin Invest. 1968 Sep;47(9):2025–2044. doi: 10.1172/JCI105889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanda Y., Goodman D. S., Canfield R. E., Morgan F. J. The amino acid sequence of human plasma prealbumin. J Biol Chem. 1974 Nov 10;249(21):6796–6805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahloudji M., Teasdall R. D., Adamkiewicz J. J., Hartmann W. H., Lambird P. A., McKusick V. A. The genetic amyloidoses with particular reference to hereditary neuropathic amyloidosis, type II (Indiana or Rukavina type). Medicine (Baltimore) 1969 Jan;48(1):1–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer J. H. Role of plasma proteins in the binding, distribution and metabolism of the thyroid hormones. N Engl J Med. 1968 May 23;278(21):1153–1162. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196805232782107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pras M., Schubert M., Zucker-Franklin D., Rimon A., Franklin E. C. The characterization of soluble amyloid prepared in water. J Clin Invest. 1968 Apr;47(4):924–933. doi: 10.1172/JCI105784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro A. L., Viñuela E., Maizel J. V., Jr Molecular weight estimation of polypeptide chains by electrophoresis in SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Sep 7;28(5):815–820. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90391-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sipe J. D., Ignaczak T. F., Pollock P. S., Glenner G. G. Amyloid fibril protein AA: purification and properties of the antigenically related serum component as determined by solid phase radioimmunoassay. J Immunol. 1976 Apr;116(4):1151–1156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]