Abstract
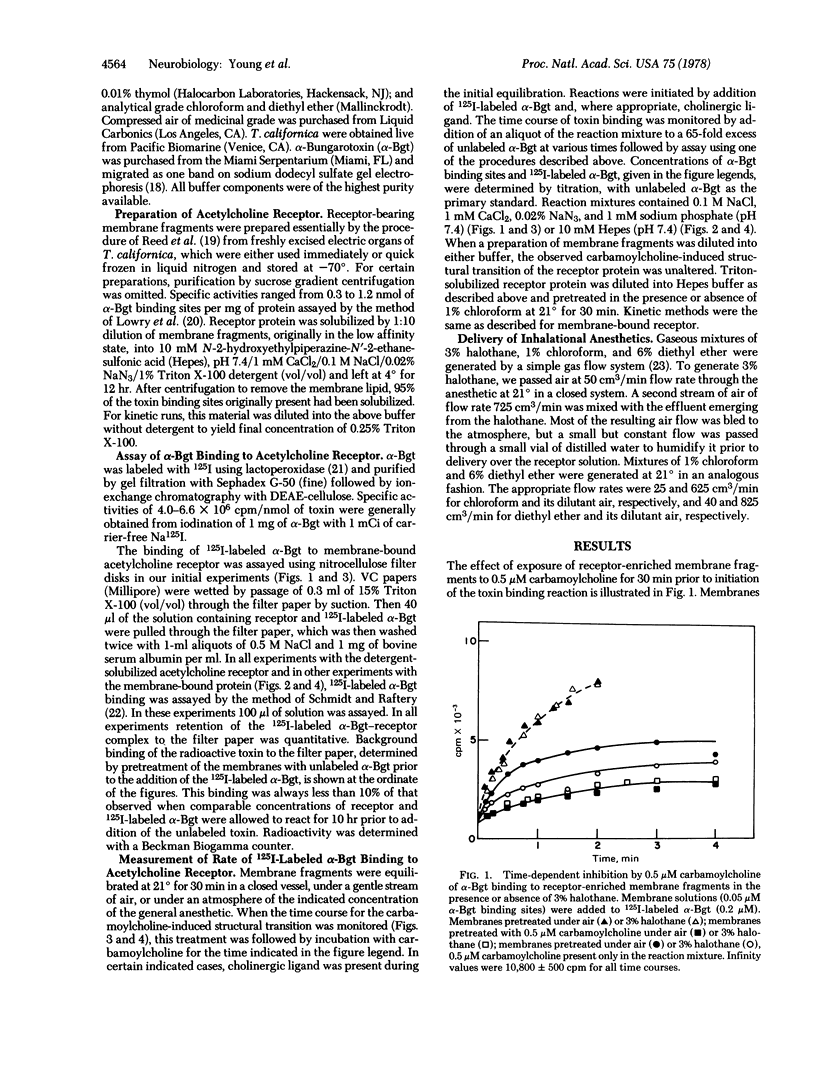
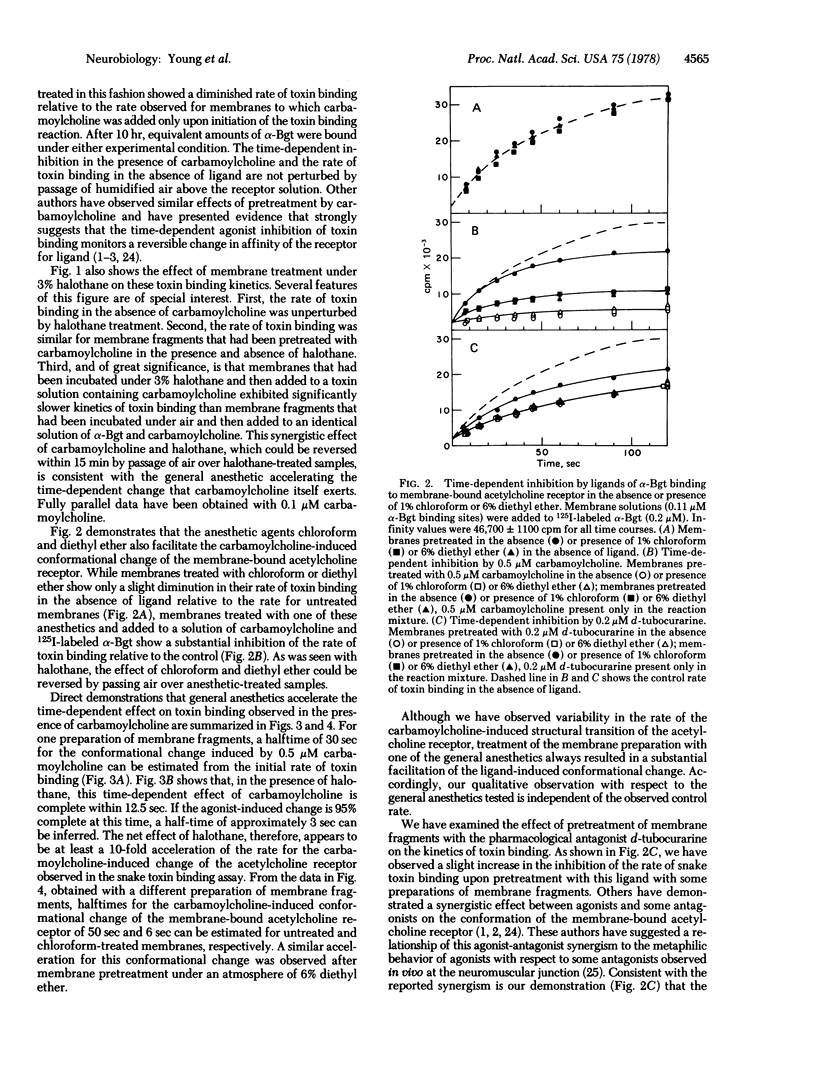
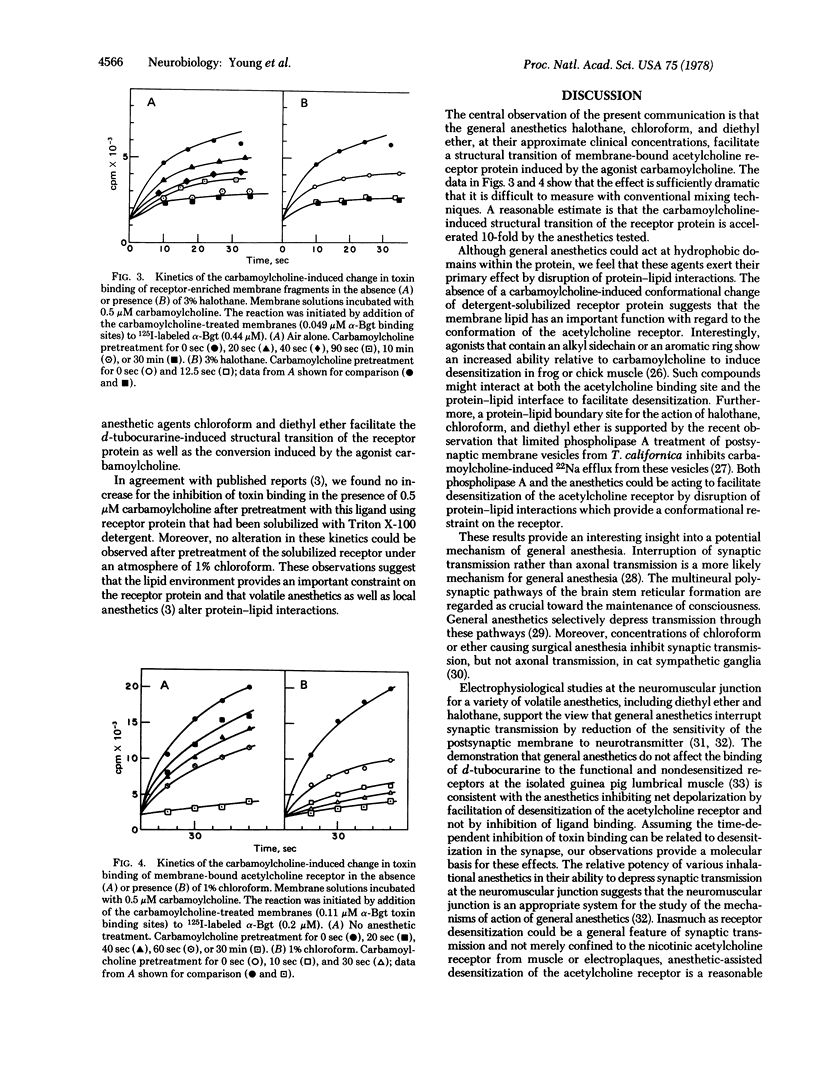
Incubation of membrane fragments bearing acetylcholine receptors from Torpedo californica under an atmosphere of 3% halothane, 1% chloroform, or 6% diethyl ether greatly facilitates the carbamoylcholine-induced structural transition of the acetylcholine receptor reflected by alterations in the rate of binding of 125I-labeled α-bungarotoxin. The half-time of this ligand-induced conformational change is decreased to 10% of the original value after incubation of the membranes with these volatile anesthetics at or near their clinical concentrations. The synergistic effects observed with the general anesthetics and carbamoylcholine are abolished if the membranes are incubated under a stream of air after exposure to the inhalational agents. The antagonist d-tubocurarine exerts a smaller yet measurable time-dependent effect on the toxin-binding properties of the membrane fragments. Treatment of membranes with general anesthetics facilitates this antagonist-induced conversion of the receptor protein as well. The synergism between ligands and general anesthetics may be due to the disruption by these inhalational agents of interactions at the protein-lipid interface, which may play a significant role in determination of receptor conformation. In addition, if the conformational change induced by carbamoylcholine observed in the snake toxin binding assay corresponds to desensitization of the receptor in vivo, facilitation of this conformational change by volatile anesthetics provides an attractive model for the pharmacological action of these compounds.
Keywords: mechanism of general anesthesia, ligand-induced conformational change, protein-lipid interactions
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreasen T. J., McNamee M. G. Phospholipase A inhibition of acetylcholine receptor function in Torpedo californica membrane vesicles. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Dec 7;79(3):958–965. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91203-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS H. S., COLLINS W. F., RANDT C. T., DILLON W. H. Effect of anesthetic agents on evoked central nervous system responses; gaseous agents. Anesthesiology. 1957 Jul-Aug;18(4):634–642. doi: 10.1097/00000542-195707000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldefrawi M. E., Eldefrawi A. T. Purification and molecular properties of the acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo electroplax. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Nov;159(1):362–373. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90462-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldefrawi M. E., Eldefrawi A. T., Wilson D. B. Tryptophan and cystein residues of the acetylcholine receptors of Torpedo species. Relationship to binding of cholinergic ligands. Biochemistry. 1975 Sep 23;14(19):4304–4310. doi: 10.1021/bi00690a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesketh T. R., Smith G. A., Houslay M. D., McGill K. A., Birdsall N. J., Metcalfe J. C., Warren G. B. Annular lipids determine the ATPase activity of a calcium transport protein complexed with dipalmitoyllecithin. Biochemistry. 1976 Sep 21;15(19):4145–4151. doi: 10.1021/bi00664a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., THESLEFF S. A study of the desensitization produced by acetylcholine at the motor end-plate. J Physiol. 1957 Aug 29;138(1):63–80. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LARRABEE M. G., POSTERNAK J. M. Selective action of anesthetics on synapses and axons in mammalian sympathetic ganglia. J Neurophysiol. 1952 Mar;15(2):91–114. doi: 10.1152/jn.1952.15.2.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T., Witzemann V., Schimerlik M., Raftery M. A. Cholinergic ligand-induced affinity changes in Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Sep;183(1):57–63. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90418-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester H. A., Changeux J. P., Sheridan R. E. Conductance increases produced by bath application of cholinergic agonists to Electrophorus electroplaques. J Gen Physiol. 1975 Jun;65(6):797–816. doi: 10.1085/jgp.65.6.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Carrion M., Raftery M. A. Use of a fluorescent probe for the study of ligand binding by the isolated cholinergic receptor of Torpedo californica. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Dec 19;55(4):1156–1164. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(73)80016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau M., Changeux J. P. Studies on the electrogenic action of acetylcholine with Torpedo marmorata electric organ. I. Pharmacological properties of the electroplaque. J Mol Biol. 1976 Sep 25;106(3):457–467. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90246-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien R. D., Gibson R. E. Conversion of high affinity acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica electroplax to an altered form. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Aug;169(2):458–463. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90188-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quast U., Schimerlik M., Lee T., Witzemann T. L., Blanchard S., Raftery M. A. Ligand-induced conformation changes in Torpedo californica membrane-bound acetylcholine receptor. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 13;17(12):2405–2414. doi: 10.1021/bi00605a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rang H. P., Ritter J. M. On the mechanism of desensitization at cholinergic receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1970 Jul;6(4):357–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rang H. P., Ritter J. M. The relationship between desensitization and the metaphilic effect at cholinergic receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1970 Jul;6(4):383–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K., Vandlen R., Bode J., Duguid J., Raftery M. A. Characterization of acetylcholine receptor-rich and acetylcholinesterase-rich membrane particles from Torpedo californica electroplax. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Mar;167(1):138–144. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90449-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J., Raftery M. A. A simple assay for the study of solubilized acetylcholine receptors. Anal Biochem. 1973 Apr;52(2):349–354. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90036-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama H., Changeux J. P. Interconversion between different states of affinity for acetylcholine of the cholinergic receptor protein from Torpedo marmorata. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jul 15;55(3):505–515. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02188.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama H., Popot J. L., Changeux J. P. Studies on the electrogenic action of acetylcholine with Torpedo marmorata electric organ. III. Pharmocological desensitization in vitro of the receptor-rich membrane fragments by cholinergic agonists. J Mol Biol. 1976 Sep 25;106(3):485–496. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90248-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorell J. I., Johansson B. G. Enzymatic iodination of polypeptides with 125I to high specific activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Dec 28;251(3):363–369. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90123-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waud B. E., Waud D. R. Comparison of the effects of general anesthethics on the end-plate of skeletal muscle. Anesthesiology. 1975 Nov;43(5):540–547. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197511000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waud B. E., Waud D. R. The effects of diethyl ether, enflurane, and isoflurane at the neuromuscular junction. Anesthesiology. 1975 Mar;42(3):275–280. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197503000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber M., Changeux J. P. Binding of Naja nigricollis (3H)alpha-toxin to membrane fragments from Electrophorus and Torpedo electric organs. 3. Effects of local anaesthetics on the binding of the tritiated alpha-neurotoxin. Mol Pharmacol. 1974 Jan;10(1):35–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber M., David-Pfeuty T., Changeux J. P. Regulation of binding properties of the nicotinic receptor protein by cholinergic ligands in membrane fragments from Torpedo marmorata. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3443–3447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiland G., Georgia B., Lappi S., Chignell C. F., Taylor P. Kinetics of agonist-mediated transitions in state of the cholinergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7648–7656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



