Abstract
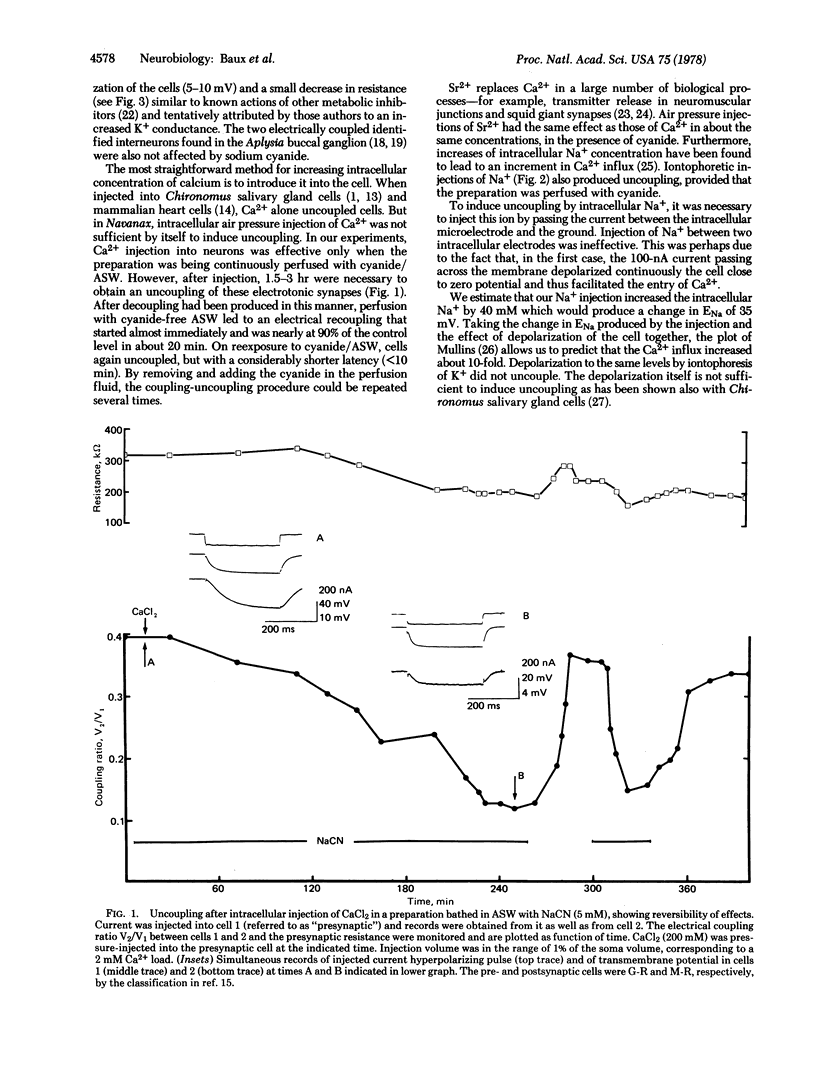
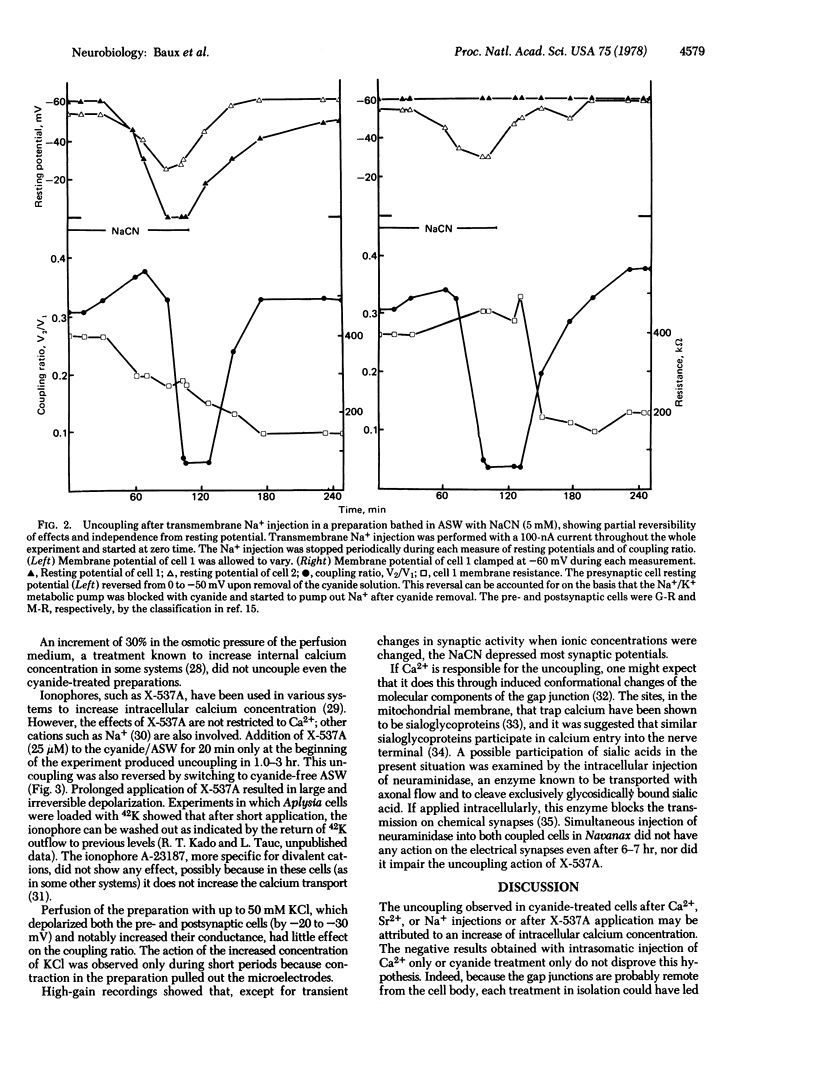
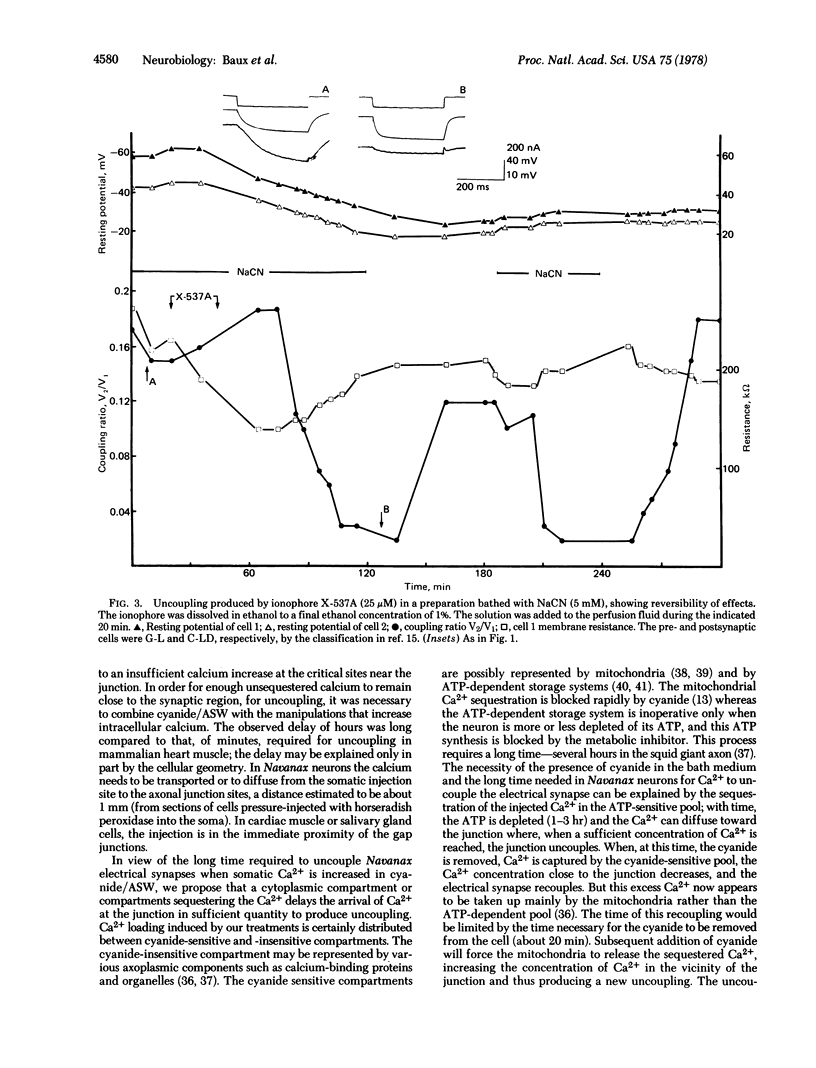
The degree of axo-axonal synaptic coupling between nerve cells in the buccal ganglion of Navanax was investigated in relation to intracellular ionic calcium. Increasing intracellular Ca2+ by injection of Ca2+, injection of Na+, or application of ionophore X537A produced uncoupling after at least 90 min, if metabolic inhibitor was present in the medium. Subsequent removal of the metabolic inhibitor reestablished the coupling in less than 30 min. Injected Sr2+ also mimicked the uncoupling action of Ca2+. The presence of a metabolic inhibitor alone had no effect on the coupling. These results lead to the following conclusions: (i) Uncoupling is due to an increased free Ca2+ concentration at the junctions. (ii) The liberation of endogenous sequestered Ca2+ is not sufficient to produce uncoupling except if an excess Ca2+ had been previously sequestered. The electrical synapses in the buccal ganglion of Navanax thus appear to be affected by Ca2+ in a similar way as gap junctions studied in non-neural tissues.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alnaes E., Rahamimoff R. On the role of mitochondria in transmitter release from motor nerve terminals. J Physiol. 1975 Jun;248(2):285–306. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F. Transport and metabolism of calcium ions in nerve. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1972;24:177–223. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(72)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker R., Llinás R. Electrotonic coupling between neurones in the rat mesencephalic nucleus. J Physiol. 1971 Jan;212(1):45–63. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker J. L., Levitan H. Mitochondrial uncoupling agents. Effects on membrane permeability of molluscan neurons. J Membr Biol. 1975;25(3-4):361–380. doi: 10.1007/BF01868584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. V. Function of electrotonic junctions in embryonic and adult tissues. Fed Proc. 1973 Jan;32(1):65–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinley F. J., Jr, Tiffert T., Scarpa A., Mullins L. J. Intracellular calcium buffering capacity in isolated squid axons. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Sep;70(3):355–384. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.3.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carafoli E. In vivo effect of uncoupling agents on the incorporation of calcium and strontium into mitochondria and other subcellular fractions of rat liver. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Aug;50(7):1849–1864. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.7.1849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspar D. L., Goodenough D. A., Makowski L., Phillips W. C. Gap junction structures. I. Correlated electron microscopy and x-ray diffraction. J Cell Biol. 1977 Aug;74(2):605–628. doi: 10.1083/jcb.74.2.605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Mello W. C. Effect of intracellular injection of calcium and strontium on cell communication in heart. J Physiol. 1975 Sep;250(2):231–245. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devore D. I., Nastuk W. L. Effects of 'calcium ionophore' X537A on frog skeletal muscle. Nature. 1975 Feb 20;253(5493):644–646. doi: 10.1038/253644a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodge F. A., Jr, Miledi R., Rahamimoff R. Strontium and quantal release of transmitter at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1969 Jan;200(1):267–283. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner D. Bilateral symmetry and interneuronal organization in the buccal ganglia of Aplysia. Science. 1971 Aug 6;173(3996):550–553. doi: 10.1126/science.173.3996.550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner D. Interconnections of identified multiaction interneurons in buccal ganglia of Aplysia. J Neurophysiol. 1977 Mar;40(2):349–361. doi: 10.1152/jn.1977.40.2.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Puyou A., De Gomez-Puyou M. T., Becker G., Lehninger A. L. An insoluble Ca 2+ -binding factor from rat liver mitochondria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 May 26;47(4):814–819. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90565-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendrick N. C., Blaustein M. P., Fried R. C., Ratzlaff R. W. ATP-dependent calcium storage in presynaptic nerve terminals. Nature. 1977 Jan 20;265(5591):246–248. doi: 10.1038/265246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn H., Sotelo C., Crepel F. Electronic coupling between neurons in the rat lateral vestibular nucleus. Exp Brain Res. 1973 Jan 29;16(3):255–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehninger A. Receptor biophysics and biochemistry. Mitochondria. Neurosci Res Program Bull. 1973 Jun;11(3):185–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitan H., Tauc L., Segundo J. P. Electrical transmission among neurons in the buccal ganglion of a mollusc, Navanax inermis. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Apr;55(4):484–496. doi: 10.1085/jgp.55.4.484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinas R., Baker R., Sotelo C. Electrotonic coupling between neurons in cat inferior olive. J Neurophysiol. 1974 May;37(3):560–571. doi: 10.1152/jn.1974.37.3.560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewenstein W. R. Permeable junctions. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:49–63. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe D. A., Richardson N. P., Taylor P., Donatsch P. Increasing intracellular sodium triggers calcium release from bound pools. Nature. 1976 Mar 25;260(5549):337–338. doi: 10.1038/260337a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makowski L., Caspar D. L., Phillips W. C., Goodenough D. A. Gap junction structures. II. Analysis of the x-ray diffraction data. J Cell Biol. 1977 Aug;74(2):629–645. doi: 10.1083/jcb.74.2.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W., Thomas R. C. The effect of calcium injection on the intracellular sodium and pH of snail neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Mar;265(3):867–879. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R. Transmitter release induced by injection of calcium ions into nerve terminals. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1973 Jul 3;183(1073):421–425. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1973.0026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins L. J. Steady-state calcium fluxes: membrane versus mitochondrial control of ionized calcium in axoplasm. Fed Proc. 1976 Dec;35(14):2583–2588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordmann J. J., Currell G. A. The mechanism of calcium ionophore-induced secretion from the rat neurohypophysis. Nature. 1975 Feb 20;253(5493):646–647. doi: 10.1038/253646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peracchia C. Calcium effects on gap junction structure and cell coupling. Nature. 1978 Feb 16;271(5646):669–671. doi: 10.1038/271669a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pressman B. C. Biological applications of ionophores. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:501–530. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.002441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahamimoff R., Erulkar S. D., Alnaes E., Meiri H., Rotshenker S., Rahamimoff H. Modulation of transmitter release by calcium ions and nerve impulses. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:107–116. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Requena J., DiPolo R., Brinley F. J., Jr, Mullins L. J. The control of ionized calcium in squid axons. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Sep;70(3):329–353. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.3.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose B., Loewenstein W. R. Permeability of a cell junction and the local cytoplasmic free ionized calcium concentration: a study with aequorin. J Membr Biol. 1976 Aug 27;28(1):87–119. doi: 10.1007/BF01869692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimoni Y., Alnaes E., Rahamimoff R. Is hyperosmotic neurosecretion from motor nerve endings a calcium-dependent process? Nature. 1977 May 12;267(5607):170–172. doi: 10.1038/267170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauc L., Hinzen D. H. Neuraminidase: its effect on synaptic transmission. Brain Res. 1974 Nov 15;80(2):340–344. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90697-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauc L., Hoffmann A., Tsuji S., Hinzen D. H., Faille L. Transmission abolished on a cholinergic synapse after injection of acetylcholinesterase into the presynaptic neurone. Nature. 1974 Aug 9;250(5466):496–498. doi: 10.1038/250496a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turin L., Warner A. Carbon dioxide reversibly abolishes ionic communication between cells of early amphibian embryo. Nature. 1977 Nov 3;270(5632):56–57. doi: 10.1038/270056a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


