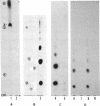
Abstract
Large-scale purification of translational inhibitors present in interferon-treated mouse L cells, but not in untreated cells, led to the isolation of two interferon-induced activities. One is a protein kinase system that is activatable by double-stranded RNA and ATP and that phosphorylates a Mr 67,000 protein and the smallest subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor-2. The purified protein kinase is a strong translational inhibitor. The second activity is an enzyme that, with double-stranded RNA, slowly polymerizes ATP into oligoadenylate with a 2'-5' phosphodiester linkage. The oligo-isoadenylate in turn activates a potent inhibitor of mRNA translation.
Full text
PDF
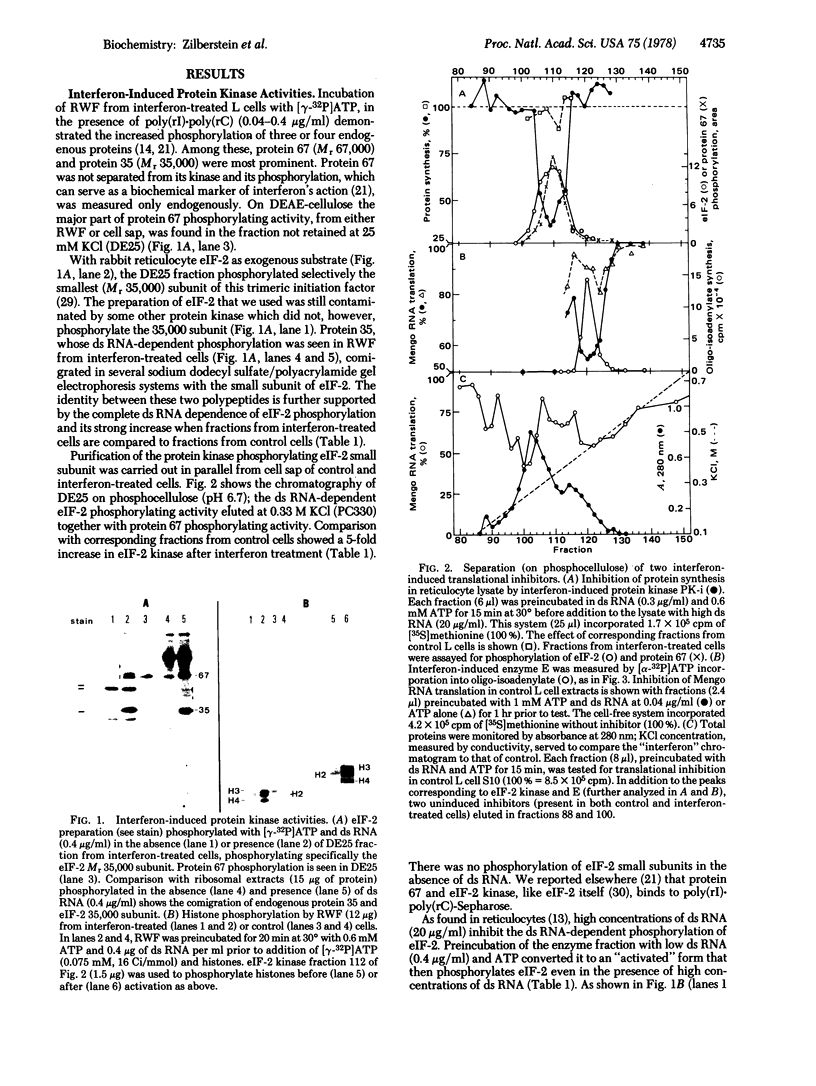



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clemens M. J., Williams B. R. Inhibition of cell-free protein synthesis by pppA2'p5'A2'p5'A: a novel oligonucleotide synthesized by interferon-treated L cell extracts. Cell. 1978 Mar;13(3):565–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90329-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Content J., Lebleu B., Nudel U., Zilberstein A., Berissi H., Revel M. Blocks in elongation and initiation of protein synthesis induced by interferon treatment in mouse L cells. Eur J Biochem. 1975 May;54(1):1–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04106.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Content J., Lebleu B., Zilberstein A., Berissi H., Revel M. Mechanism of the interferon-induced block of mRNA translation in mouse L cells: reversal of the block by transfer RNA. FEBS Lett. 1974 Apr 15;41(1):125–130. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80970-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Farrell P. J. Extracts of interferon-treated cells can inhibit reticulocyte lysate protein synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jul 11;77(1):124–131. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80173-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eppstein D. A., Samuel C. E. Mechanism of interferon action. Partial purification and characterization of a low-molecular-weight interferon-mediated inhibitor of translation with nucleolytic activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Nov 7;79(1):145–153. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90072-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falcoff E., Falcoff R., Lebleu B., Revel M. Correlation between the antiviral effect of interferon treatment and the inhibition of in vitro mRNA translation in noninfected L cells. J Virol. 1973 Sep;12(3):421–430. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.3.421-430.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. J., Balkow K., Hunt T., Jackson R. J., Trachsel H. Phosphorylation of initiation factor elF-2 and the control of reticulocyte protein synthesis. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):187–200. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90330-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. M., Metz D. H., Esteban R. M., Tovell D. R., Ball L. A., Kerr I. M. Mechanism of interferon action: inhibition of viral messenger ribonucleic acid translation in L-cell extracts. J Virol. 1972 Dec;10(6):1184–1198. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.6.1184-1198.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert J. M., Anderson W. F. Cell-free hemoglobin synthesis. II. Characteristics of the transfer ribonucleic acid-dependent assay system. J Biol Chem. 1970 May 10;245(9):2342–2349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S. L., Sopori M. L., Lengyel P. Inhibition of protein synthesis directed by added viral and cellular messenger RNAs in extracts of interferon-treated Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. Location and dominance of the inhibitor(s). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Sep 18;54(2):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91491-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johns E. W. Studies on histones. 7. Preparative methods for histone fractions from calf thymus. Biochem J. 1964 Jul;92(1):55–59. doi: 10.1042/bj0920055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr I. M., Brown R. E., Ball L. A. Increased sensitivity of cell-free protein synthesis to double-stranded RNA after interferon treatment. Nature. 1974 Jul 5;250(461):57–59. doi: 10.1038/250057a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr I. M., Brown R. E., Hovanessian A. G. Nature of inhibitor of cell-free protein synthesis formed in response to interferon and double-stranded RNA. Nature. 1977 Aug 11;268(5620):540–542. doi: 10.1038/268540a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr I. M., Brown R. E. pppA2'p5'A2'p5'A: an inhibitor of protein synthesis synthesized with an enzyme fraction from interferon-treated cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):256–260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr I. M., Friedman R. M., Brown R. E., Ball L. A., Brown J. C. Inhibition of Protein Synthesis in Cell-Free Systems from Interferon-Treated, Infected Cells: Further Characterization and Effect of Formylmethionyl-tRNA(F). J Virol. 1974 Jan;13(1):9–21. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.1.9-21.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebleu B., Sen G. C., Shaila S., Cabrer B., Lengyel P. Interferon, double-stranded RNA, and protein phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3107–3111. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayr U., Bermayer H. P., Weidinger G., Jungwirth C. Release of interferon-induced translation inhibition by tRNA in cell-free extracts from mouse erythroleukemia cells. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jun 15;76(2):541–551. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11624.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratner L., Sen G. C., Brown G. E., Lebleu B., Kawakita M., Cabrer B., Slattery E., Lengyel P. Interferon, double-stranded RNA and RNA degradation. Characteristics of an endonuclease activity. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Oct 3;79(2):565–577. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11841.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. K., Hovanessian A., Brown R. E., Clemens M. J., Kerr I. M. Interferon-mediated protein kinase and low-molecular-weight inhibitor of protein synthesis. Nature. 1976 Dec 2;264(5585):477–480. doi: 10.1038/264477a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sela I., Grossberg S. E., Sedmak J. J., Mehler A. H. Discharge of aminoacyl-viral RNA by a factor from interferon-treated cells. Science. 1976 Oct 29;194(4264):527–529. doi: 10.1126/science.973135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen G. C., Gupta S. L., Brown G. E., Lebleu B., Rebello M. A., Lengyel P. Interferon treatment of Ehrlich ascites tumor cells: effects on exogenous mRNA translation and tRNA inactivation in the cell extract. J Virol. 1975 Jan;17(1):191–203. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.1.191-203.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen G. C., Lebleu B., Brown G. E., Kawakita M., Slattery E., Lengyel P. Interferon, double-stranded RNA and mRNA degradation. Nature. 1976 Nov 25;264(5584):370–373. doi: 10.1038/264370a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen G. C., Shaila S., Lebleu B., Brown G. E., Desrosiers R. C., Lengyel P. Impairment of reovirus mRNA methylation in extracts of interferon-treated Ehrilich ascites tumor cells: further characteristics of the phenomenon. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):69–83. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.69-83.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh D. A., Ashby C. D., Gonzalez C., Calkins D., Fischer E. H. Krebs EG: Purification and characterization of a protein inhibitor of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 10;246(7):1977–1985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yakobson E., Prives C., Hartman J. R., Winocour E., Revel M. Inhibition of viral protein synthesis in monkey cells treated with interferon late in simian virus 40 lytic cycle. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):73–81. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90186-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberstein A., Dudock B., Berissi H., Revel M. Control of messenger RNA translation by minor species of leucyl-transfer RNA in extracts from interferon-treated L cells. J Mol Biol. 1976 Nov;108(1):43–54. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80093-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberstein A., Federman P., Shulman L., Revel M. Specific phosphorylation in vitro of a protein associated with ribosomes of interferon-treated mouse L cells. FEBS Lett. 1976 Sep 15;68(1):119–124. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80418-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Haro C., Datta A., Ochoa S. Mode of action of the hemin-controlled inhibitor of protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):243–247. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]