Abstract
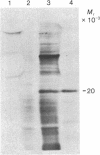
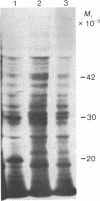
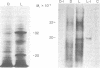
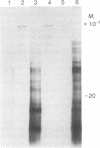
Polyadenylated RNA was isolated from Lemna gibba L. G-3 and translated in a cell-free system from wheat germ. When plants were placed into complete darkness for 4 days, then returned to light for 18 hr, increased amounts of polyadenylated mRNA for at least two polypeptides were detected by in vitro translation over those amounts present in the dark. These two polypeptides have molecular weights of 32,000 and 20,000. The 20,000 dalton polypeptide was identified by immunoprecipitation as the precursor to the small subunit of the photosynthetic enzyme ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase [3-phospho-D-glycerate carboxy-lyase (dimerizing), EC 4.1.1.39]. The polyadenylated mRNA that codes for the small subunit is not detectable by immunoprecipitation of translation products in the dark-treated tissue. Plants growing in the light actively synthesize both subunits of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase, but synthesis of these proteins was found to be greatly diminished in plants placed in darkness for 4 days. These results indicate that white light can dramatically affect the steady-state levels of specific polyadenylated mRNAs.
Keywords: polyadenylated mRNA; immunoprecipitation of translation products; precursor to small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase (EC 4.1.1.39); protein synthesis
Full text
PDF


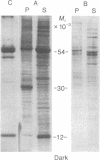
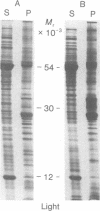
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apel K., Kloppstech K. The plastid membranes of barley (Hordeum vulgare). Light-induced appearance of mRNA coding for the apoprotein of the light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b protein. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Apr 17;85(2):581–588. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12273.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair G. E., Ellis R. J. Protein synthesis in chloroplasts. I. Light-driven synthesis of the large subunit of fraction I protein by isolated pea chloroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Aug 24;319(2):223–234. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90013-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashmore A. R., Broadhurst M. K., Gray R. E. Cell-free synthesis of leaf protein: Identification of an apparent precursor of the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):655–659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashmore A. R. Protein synthesis in plant leaf tissue. The sites of synthesis of the major proteins. J Biol Chem. 1976 May 10;251(9):2848–2853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan P. H., Wildman S. G. Chloroplast DNA codes for the primary structure of the large subunit of fraction I protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 14;277(3):677–680. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90115-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleland C. F., Briggs W. S. Gibberellin and CCC Effects on Flowering and Growth in the Long-day Plant Lemna gibba G3. Plant Physiol. 1969 Apr;44(4):503–507. doi: 10.1104/pp.44.4.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobberstein B., Blobel G., Chua N. H. In vitro synthesis and processing of a putative precursor for the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1082–1085. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg R. B., Hoschek G., Kamalay J. C., Timberlake W. E. Sequence complexity of nuclear and polysomal RNA in leaves of the tobacco plant. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):123–131. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90307-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldthwaite J. J., Bogorad L. A one-step method for the isolation and determination of leaf ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase. Anal Biochem. 1971 May;41(1):57–66. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90191-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray J. C., Kekwick R. G. The synthesis of the small subunit of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase in the french bean Phaseolus vulgaris. Eur J Biochem. 1974 May 15;44(2):491–500. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03507.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson A. O., Larkins B. A. Influence of Ionic Strength, pH, and Chelation of Divalent Metals on Isolation of Polyribosomes from Tobacco Leaves. Plant Physiol. 1976 Jan;57(1):5–10. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.1.5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawashima N., Wildman S. G. Studies on fraction I protein. IV. Mode of inheritance of primary structure in relation to whether chloroplast or nuclear DNA contains the code for a chloroplast protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 23;262(1):42–49. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90217-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengyel J. A., Penman S. Differential stability of cytoplasmic RNA in a Drosophila cell line. Dev Biol. 1977 Jun;57(2):243–253. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90212-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts B. E., Paterson B. M. Efficient translation of tobacco mosaic virus RNA and rabbit globin 9S RNA in a cell-free system from commercial wheat germ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosner A., Jakob K. M., Gressel J., Sagher D. The early synthesis and possible function of a 0.5 X 10(6) Mr RNA after transfer of dark-grown Spirodela plants to light. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Nov 3;67(1):383–391. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90327-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy H., Patterson R., Jagendorf A. T. Identification of the small subunit of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase as a product of wheat leaf cytoplasmic ribosomes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Jan;172(1):64–73. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R., Stinchcomb D., Losick R. Antibody directed against Bacillus subtilis rho factor purified by sodium dodecyl sulfate slab gel electrophoresis. Effect on transcription by RNA polymerase in crude extracts of vegetative and sporulating cells. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 25;250(22):8824–8828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobin E. M., Klein A. O. Isolation and translation of plant messenger RNA. Plant Physiol. 1975 Jul;56(1):88–92. doi: 10.1104/pp.56.1.88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]