Abstract
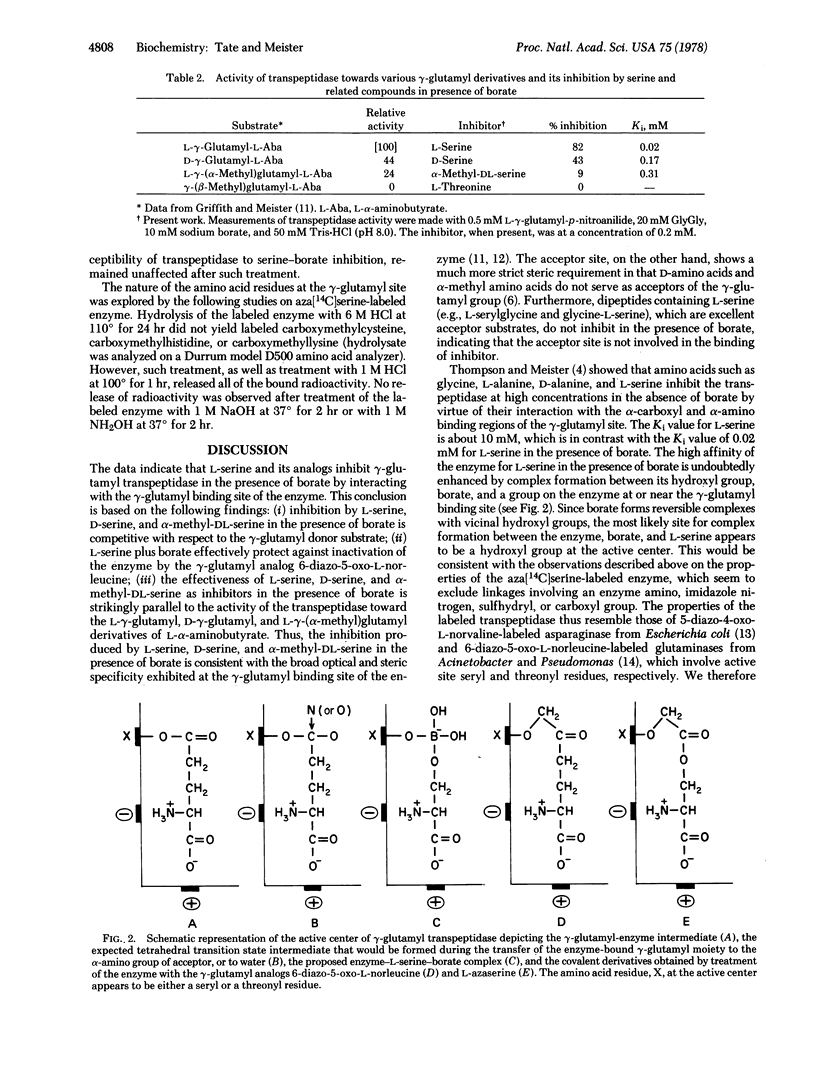
gamma-Glutamyl transpeptidase, a membrane-bound enzyme, functions in the gamma-glutamyl cycle to catalyze utilization of glutathione. It has been postulated that the amino-acid-stimulated utilization of glutathione by gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase reflects an aspect of amino acid translocation. As one approach to the effective in vivo inhibition of this enzyme, the inhibition of the enzyme by L-serine in the presence of borate buffers [Revel, J.P. & Ball, E.G. (1959) J. Biol. Chem. 234, 577-582] was reinvestigated. Inhibition by L-serine, D-serine, and alpha-methyl-DL-serine in the presence of borate is competitive with respect to gamma-glutamyl substrate and such inhibition is parallel to the activity of transpeptidase toward L-gamma-glutamyl, D-gamma-glutamyl, and L-gamma-(alpha-methyl)glutamyl derivatives. L-Serine and borate effectively protect against inactivation of the enzyme by the gamma-glutamyl analogs, 6-diazo-5-oxonorleucine and azaserine, which bind to the gamma-glutamyl site of the enzyme. These studies, kinetic investigations, equilibrium dialysis experiments, and other data support the view that inhibition is produced by formation of serine-borate complex which binds at the gamma-glutamyl binding site of the light subunit of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase. The data indicate that serine-borate complex is a transition state inhibitor of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antonov V. K., Ivanina T. V., Berezin I. V., Martinek K. n-Alkylboronic acids as bifunctional reversible inhibitors of alpha-chymotrypsin. FEBS Lett. 1970 Mar 16;7(1):23–25. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80607-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith O. W., Meister A. Selective inhibition of gamma-glutamyl-cycle enzymes by substrate analogs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3330–3334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holcenberg J. S., Ericsson L., Roberts J. Amino acid sequence of the diazooxonorleucine binding site of Acinetobacter and Pseudomonas 7A glutaminase--asparaginase enzymes. Biochemistry. 1978 Feb 7;17(3):411–417. doi: 10.1021/bi00596a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koehler K. A., Lienhard G. E. 2-phenylethaneboronic acid, a possible transition-state analog for chymotrypsin. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2477–2483. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MYER Y. P., SCHELLMAN J. A. The interaction of ribonuclease with purine and pyrimidine phosphates. I. Binding of adenosine 5'-monophosphate to ribonuclease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Mar 5;55:361–373. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90791-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews D. A., Alden R. A., Birktoft J. J., Freer S. T., Kraut J. X-ray crystallographic study of boronic acid adducts with subtilisin BPN' (Novo). A model for the catalytic transition state. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 25;250(18):7120–7126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister A., Tate S. S. Glutathione and related gamma-glutamyl compounds: biosynthesis and utilization. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:559–604. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.003015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson R. G., Richards F. F., Handschumacher R. E. Structure of peptide from active site region of Escherichia coli L-asparaginase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):2072–2076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipp M., Bender M. L. Inhibition of serine proteases by arylboronic acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):478–480. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REVEL J. P., BALL E. G. The reaction of glutathione with amino acids and related compounds as catalyzed by gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):577–582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szewczuk A., Connell G. E. The reaction of iodoacetamide with the active center of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Aug 24;105(2):352–367. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(65)80159-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate S. S., Meister A. Affinity labeling of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase and location of the gamma-glutamyl binding site on the light subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):931–935. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate S. S., Meister A. Identity of maleate-stimulated glutaminase with gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase in rat kidney. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 25;250(12):4619–4627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate S. S., Meister A. Interaction of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase with amino acids, dipeptides, and derivatives and analogs of glutathione. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 10;249(23):7593–7602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate S. S., Meister A. Stimulation of the hydrolytic activity and decrease of the transpeptidase activity of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase by maleate; identity of a rat kidney maleate-stimulated glutaminase and gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3329–3333. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate S. S., Meister A. Subunit structure and isozymic forms of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2599–2603. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson G. A., Meister A. Hydrolysis and transfer reactions catalyzed by gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase; evidence for separate substrate sites and for high affinity of L-cystine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jul 12;71(1):32–36. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90245-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson G. A., Meister A. Interrelationships between the binding sites for amino acids, dipeptides, and gamma-glutamyl donors in gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 10;252(19):6792–6798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



