Abstract
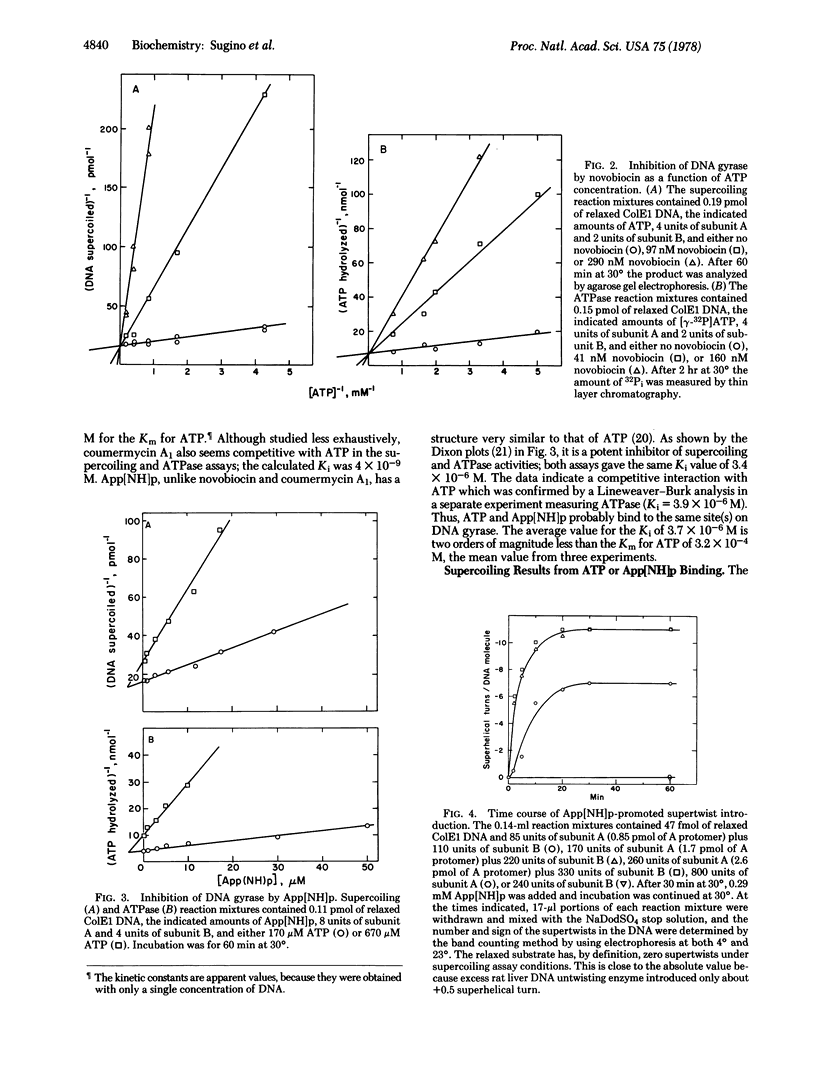
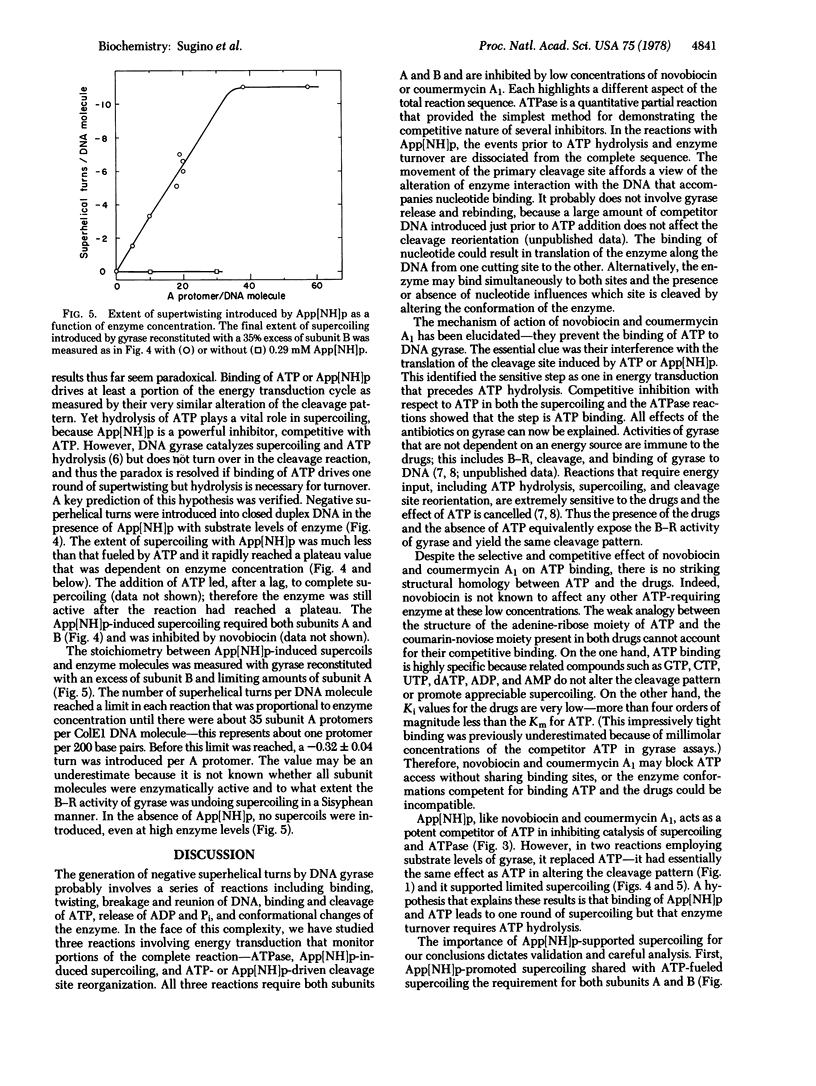
Escherichia coli DNA gyrase catalyzes negative supercoiling of closed duplex DNA at the expense of ATP. Two additional activities of the enzyme that have illuminated the energy coupling component of the supercoiling reaction are the DNA-dependent hydrolysis of ATP to ADP and Pi and the alteration by ATP of the DNA site specificity of the gyrase cleavage reaction. This cleavage of both DNA strands results from treatment with sodium dodecyl sulfate of the stable gyrase-DNA complex that is trapped by the inhibitor oxolinic acid. Either ATP or a nonhydrolyzable analogue, adenyl-5′-yl-imidodiphosphate (App[NH]p), shifts the primary cleavage site on ColE1 DNA. The prevention by novobiocin and coumermycin A1 of this cleavage rearrangement places the site of action of the antibiotics at a reaction step prior to ATP hydrolysis. The step blocked is the binding of ATP because coumermycin A1 and novobiocin interact competitively with ATP in the ATPase and supercoiling assays; the Ki values are more than four orders of magnitude less than the Km for ATP. This simple mechanism accounts for all effects of the drugs on DNA gyrase. Studies with App[NH]p, another potent competitive inhibitor of reactions catalyzed by gyrase, show that cleavage of a high energy bond is not required for driving DNA into the higher energy supercoiled form. With substrate levels of gyrase, App[NH]p induces supercoiling that is proportional to the amount of enzyme; a -0.3 superhelical turn was introduced per gyrase protomer A. We postulate that ATP and App[NH]p are allosteric effectors of a conformational change of gyrase that leads to one round of supercoiling. Nucleotide dissociation favored by hydrolysis of ATP returns gyrase to its original conformation and thereby permits enzyme turnover. Such cyclic conformational changes accompanying alteration in nucleotide affinity also seem to be a common feature of energy transduction in other diverse processes including muscle contraction, protein synthesis, and oxidative phosphorylation.
Keywords: coumermycin A1, oxolinic acid, site-specific DNA cleavage, DNA supercoiling, ATPase
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bourguignon G. J., Levitt M., Sternglanz R. Studies on the mechanism of action of nalidixic acid. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Oct;4(4):479–486. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.4.479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champoux J. J. Strand breakage by the DNA untwisting enzyme results in covalent attachment of the enzyme to DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3800–3804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cozzarelli N. R. The mechanism of action of inhibitors of DNA synthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:641–668. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.003233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON M. The determination of enzyme inhibitor constants. Biochem J. 1953 Aug;55(1):170–171. doi: 10.1042/bj0550170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depew R. E., Liu L. F., Wang J. C. Interaction between DNA and Escherichia coli protein omega. Formation of a complex between single-stranded DNA and omega protein. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 25;253(2):511–518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Itoh T., Tomizawa J. I. Nalidixic acid resistance: a second genetic character involved in DNA gyrase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4772–4776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Nash H. A. DNA gyrase: an enzyme that introduces superhelical turns into DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3872–3876. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., O'Dea M. H., Itoh T., Tomizawa J. Novobiocin and coumermycin inhibit DNA supercoiling catalyzed by DNA gyrase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4474–4478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins N. P., Peebles C. L., Sugino A., Cozzarelli N. R. Purification of subunits of Escherichia coli DNA gyrase and reconstitution of enzymatic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1773–1777. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. L. A proposed common allosteric mechanism for active transport, muscle contraction, and ribosomal translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Sep;64(1):267–274. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.1.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue-Yokosawa N., Ishikawa C., Kaziro Y. The role of guanosine triphosphate in translocation reaction catalyzed by elongation factor G. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4321–4323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller W. Determination of the number of superhelical turns in simian virus 40 DNA by gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4876–4880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg A., Scott J. F., Bertsch L. L. ATP utilization by rep protein in the catalytic separation of DNA strands at a replicating fork. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 10;253(9):3298–3304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Wang J. C. Micrococcus luteus DNA gyrase: active components and a model for its supercoiling of DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2098–2102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett M. A., Katz L., Helinski D. R. Unidirectional replication of plasmid ColE1 DNA. Nature. 1974 Sep 27;251(5473):337–340. doi: 10.1038/251337a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marians K. J., Ikeda J. E., Schlagman S., Hurwitz J. Role of DNA gyrase in phiX replicative-form replication in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):1965–1968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan M. J. Coumermycin A1: A preferential inhibitor of replicative DNA synthesis in Escherichia coli. I. In vivo characterization. Biochemistry. 1976 Aug 24;15(17):3769–3777. doi: 10.1021/bi00662a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shure M., Vinograd J. The number of superhelical turns in native virion SV40 DNA and minicol DNA determined by the band counting method. Cell. 1976 Jun;8(2):215–226. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90005-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugino A., Peebles C. L., Kreuzer K. N., Cozzarelli N. R. Mechanism of action of nalidixic acid: purification of Escherichia coli nalA gene product and its relationship to DNA gyrase and a novel nicking-closing enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yount R. G., Babcock D., Ballantyne W., Ojala D. Adenylyl imidodiphosphate, an adenosine triphosphate analog containing a P--N--P linkage. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2484–2489. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]