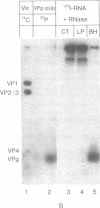
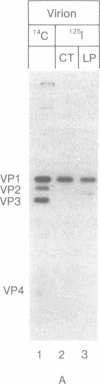
Abstract
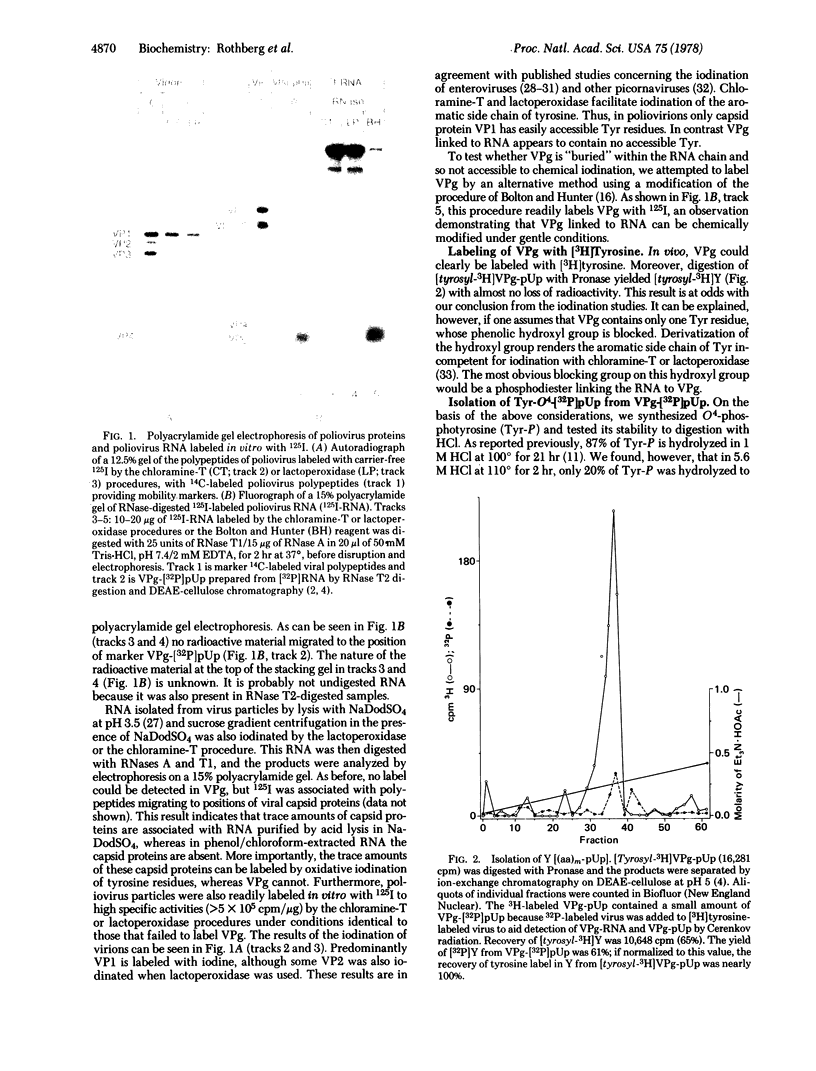
Virion RNA of poliovirus type 1 has been analyzed for the linkage between genome-protein VPg and the polyribonucleotide chain. Hydrolysis of the linkage with acid or alkali and enzymatic degradation lead to the conclusion that the bond is neither a phosphodiester such as nucleotidyl-(P-O)-serine (or threonine) nor a phosphoramidate such as nucleotidyl-(P-N)-amino acid. VPg-RNA can be iodinated by the Bolton and Hunter reagent [iodinated 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propionic acid N-hydroxysuccinimide ester] but not by the chloramine-T or lactoperoxidase procedures, an observation suggesting that VPg does not contain accessible tyrosine. However, VPg can be labeled with [3H]tyrosine in vivo. Hydrolysis of VPg-[32P]pUp with 5.6 M HCl at 110 degrees yielded 32P-labeled O4-(3'-phospho-5'-uridylyl)tyrosine that could be cleaved with micrococcal nuclease to O4-[32P]phosphotyrosine and uridine 3'-[32P]phosphate. These data establish that VPg is linked to the poliovirus genome by a bond between the O4 of tyrosine and the 5'-P atom of the terminal uridylic acid residue. The 5' end of polio genome RNA can now be described as VPg(Tyr-O)-pU-U-A-A-A-A-C-A-G.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler S. P., Purich D., Stadtman E. R. Cascade control of Escherichia coli glutamine synthetase. Properties of the PII regulatory protein and the uridylyltransferase-uridylyl-removing enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 25;250(16):6264–6272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambros V., Baltimore D. Protein is linked to the 5' end of poliovirus RNA by a phosphodiester linkage to tyrosine. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 10;253(15):5263–5266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray D., Brownlee S. M. Peptide mapping of proteins from acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1973 Sep;55(1):213–221. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90306-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carthew P., Martin S. J. The iodination of bovine enterovirus particles. J Gen Virol. 1974 Sep;24(3):525–534. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-24-3-525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champoux J. J. Mechanism of the reaction catalyzed by the DNA untwisting enzyme: attachment of the enzyme to 3'-terminus of the nicked DNA. J Mol Biol. 1978 Jan 25;118(3):441–446. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90238-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole C. N., Smoler D., Wimmer E., Baltimore D. Defective interfering particles of poliovirus. I. Isolation and physical properties. J Virol. 1971 Apr;7(4):478–485. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.4.478-485.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depew R. E., Liu L. F., Wang J. C. Interaction between DNA and Escherichia coli protein omega. Formation of a complex between single-stranded DNA and omega protein. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 25;253(2):511–518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S., Griffith J., Kornberg A. phiX174 cistron A protein is a multifunctional enzyme in DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3198–3202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldmann H., Falter H. Transfer ribonucleic acid from Mycoplasma laidlawii A. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Feb;18(4):573–581. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01278.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanegan J. B., Petterson R. F., Ambros V., Hewlett N. J., Baltimore D. Covalent linkage of a protein to a defined nucleotide sequence at the 5'-terminus of virion and replicative intermediate RNAs of poliovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):961–965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golini F., Nomoto A., Wimmer E. The genome-linked protein of picornaviruses. IV. Difference in the VPg's of encephalomyocarditis virus and poliovirus as evidence that the genome-linked proteins are virus-coded. Virology. 1978 Aug;89(1):112–118. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90045-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guiney D. G., Helinski D. R. Relaxation complexes of poasmid DNA and protein. III. Association of protein with the 5' terminus of the broken DNA strand in the relaxed complex of plasmid ColE1. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 25;250(22):8796–8803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gumport R. I., Lehman I. R. Structure of the DNA ligase-adenylate intermediate: lysine (epsilon-amino)-linked adenosine monophosphoramidate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Oct;68(10):2559–2563. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.10.2559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzer H., Wohlhueter R. (Glutamine synthetase) tyrosyl-O-adenylate: a new energy-rich phosphate bond. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1972;10:121–132. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(72)90009-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruby D. E., Roberts W. K. Encephalomyocarditis virus RNA. III. Presence of a genome-associated protein. J Virol. 1978 Jan;25(1):413–415. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.1.413-415.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasamatsu H., Wu M. Structure of a nicked DNA-protein complex isolated from simian virus 40: covalent attachment of the protein to DNA and nick specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1945–1949. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krystal G., Winn P., Millward S., Sakuma S. Evidence for phosphoproteins in reovirus. Virology. 1975 Apr;64(2):505–512. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90127-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. F., Nomoto A., Detjen B. M., Wimmer E. A protein covalently linked to poliovirus genome RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):59–63. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. F., Nomoto A., Wimmer E. The genome of poliovirus is an exceptional eukaryotic mRNA. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1976;19:89–96. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60910-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonberg-Holm K., Butterworth B. E. Investigation of the structure of polio- and human rhinovirions through the use of selective chemical reactivity. Virology. 1976 May;71(1):207–216. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90106-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund G. A., Ziola B. R., Salmi A., Scraba D. G. Structure of the Mengo virion. V. Distribution of the capsid polypeptides with respect to the surface of the virus particle. Virology. 1977 May 1;78(1):35–44. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90076-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDEL B. THE EXTRACTION OF RIBONUCLEIC ACID FROM POLIOVIRUS BY TREATMENT WITH SODIUM DODECYL SULFATE. Virology. 1964 Mar;22:360–367. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90026-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHELL H. K., LUNAN K. D. TYROSINE-O-PHOSPHATE IN DROSOPHILA. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Jul 20;106:219–222. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(64)90179-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura S. Minor components in transfer RNA: their characterization, location, and function. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1972;12:49–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto A., Detjen B., Pozzatti R., Wimmer E. The location of the polio genome protein in viral RNAs and its implication for RNA synthesis. Nature. 1977 Jul 21;268(5617):208–213. doi: 10.1038/268208a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto A., Kitamura N., Golini F., Wimmer E. The 5'-terminal structures of poliovirion RNA and poliovirus mRNA differ only in the genome-linked protein VPg. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5345–5349. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto A., Lee Y. F., Wimmer E. The 5' end of poliovirus mRNA is not capped with m7G(5')ppp(5')Np. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):375–380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson R. F., Flanegan J. B., Rose J. K., Baltimore D. 5'-Terminal nucleotide sequences of polio virus polyribosomal RNA and virion RNA are identical. Nature. 1977 Jul 21;268(5617):270–272. doi: 10.1038/268270a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plimmer R. H. Esters of phosphoric acid: Phosphoryl hydroxyamino-acids. Biochem J. 1941 Apr;35(4):461–469. doi: 10.1042/bj0350461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rekosh D. M., Russell W. C., Bellet A. J., Robinson A. J. Identification of a protein linked to the ends of adenovirus DNA. Cell. 1977 Jun;11(2):283–295. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90045-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowlands D. J., Shirley M. W., Sangar D. V., Brown F. A high density component in several vertebrate enteroviruses. J Gen Virol. 1975 Nov;29(2):223–234. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-29-2-223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salas M., Mellado R. P., Viñuela E. Characterization of a protein covalently linked to the 5' termini of the DNA of Bacillus subtilis phage phi29. J Mol Biol. 1978 Feb 25;119(2):269–291. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90438-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sangar D. V., Rowlands D. J., Harris T. J., Brown F. Protein covalently linked to foot-and-mouth disease virus RNA. Nature. 1977 Aug 18;268(5621):648–650. doi: 10.1038/268648a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot P., Rowlands D. J., Burroughs J. N., Sangar D. V., Brown F. Evidence for a group protein in foot-and-mouth disease virus particles. J Gen Virol. 1973 Jun;19(3):369–380. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-19-3-369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorell J. I., Johansson B. G. Enzymatic iodination of polypeptides with 125I to high specific activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Dec 28;251(3):363–369. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90123-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimmer E., Reichmann M. E. Two 3'-terminal sequences in satellite tobacco necrosis virus RNA. Nature. 1969 Mar 22;221(5186):1122–1126. doi: 10.1038/2211122a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]