Abstract
It is now universally recognized that neonates can experience considerable pain. While spinal lamina I neurons projecting to the brain contribute to the generation of hyperalgesia, nothing is known about their electrophysiological properties during early life. Here we have used in vitro whole cell patch-clamp recordings in rat spinal cord slices to determine whether the intrinsic membrane properties of lamina I projection neurons, as well as their synaptic inputs, are developmentally regulated during the early postnatal period. Projection neurons were identified via retrograde transport of DiI injected into the parabrachial nucleus (PB) or periaqueductal gray (PAG) and characterized at postnatal days (P)2–5, P10–12, P19–23, and P30–32. Both spino-PB and spino-PAG neurons demonstrated an age-dependent reduction in spike threshold and duration at room temperature, which was accompanied by a developmental increase in the frequency of miniature excitatory and inhibitory postsynaptic currents. Notably, in both groups, age-dependent changes in the passive membrane properties or rheobase only occurred after the third postnatal week. However, spontaneous activity was significantly more prevalent within the developing spino-PB population and was dominated by an irregular pattern of discharge. In addition, while the instantaneous firing frequency remained unaltered in spino-PB neurons during the first weeks of life, spino-PAG cells fired at a higher rate at P19–23 compared with younger groups, suggesting that the gain of parallel ascending nociceptive pathways may be independently regulated during development. Overall, these results demonstrate that intrinsic membrane excitability is modulated in a cell type-specific manner within developing spinal nociceptive circuits.
Keywords: dorsal horn, neonate, patch clamp
growing awareness that even the youngest infants can experience pain has driven increased efforts to understand the maturation of nociceptive pathways at cellular and molecular levels. As a result, it is now clear that pain networks in the CNS undergo considerable reorganization during the early postnatal period. In the superficial dorsal horn (SDH) of the rodent spinal cord, this includes age-dependent alterations in the pattern and strength of primary afferent input (Baccei et al. 2003; Beggs et al. 2002) as well as significant changes in the properties of local synaptic inhibition (Baccei and Fitzgerald 2004; Bremner and Fitzgerald 2008; Cordero-Erausquin et al. 2005; Keller et al. 2001). In addition, the morphology (Bicknell and Beal 1984) and intrinsic membrane properties (Walsh et al. 2009) of SDH neurons are known to be developmentally regulated. However, nociceptive processing within the immature SDH cannot be fully understood without specific knowledge of how the excitability of ascending projection neurons, which are responsible for the output of the spinal pain circuit, is modulated during early life.
Unfortunately, little is known about the electrophysiological properties of these projection neurons during the neonatal period, as numerous lines of evidence suggest that the information gained from prior studies of the general population of lamina I–II neurons cannot be extrapolated to immature projection neurons. First, since the vast majority of SDH neurons consist of propriospinal or local circuit interneurons (Bice and Beal 1997a, 1997b) and ascending projection neurons comprise only ∼5% of all lamina I cells (Spike et al. 2003), projection neurons undoubtedly represent an extremely small fraction of the neurons sampled when recording from unidentified cells in the developing SDH. In addition, examination of identified lamina I projection neurons in the young adult rat has demonstrated that these cells possess distinct passive and active membrane properties compared with adjacent, unidentified lamina I neurons, including unique intrinsic firing patterns (Ruscheweyh et al. 2004), greater levels of spontaneous synaptic input (Dahlhaus et al. 2005), and an enhanced propensity for activity-dependent synaptic plasticity (Ikeda et al. 2003).
Lamina I projection neurons target multiple supraspinal sites including the parabrachial nucleus (PB), periaqueductal gray (PAG), caudal ventrolateral medulla (CVLM), and thalamus, with the majority of neurons that project to the PAG, CVLM, and thalamus also projecting to the PB (Hylden et al. 1989; Spike et al. 2003). Despite this anatomical overlap, recent studies have demonstrated clear differences in the spino-PB and spino-PAG populations based on their firing patterns (Ruscheweyh et al. 2004), synaptic inputs (Dahlhaus et al. 2005), and characteristics of long-term potentiation (Ikeda et al. 2006). Our previous work suggests that functional differences between these groups may also exist during the neonatal period, as spino-PB neurons exhibited a significantly higher prevalence of spontaneous firing compared with the spino-PAG group (Li and Baccei 2011). Nonetheless, the extent to which the intrinsic membrane properties of these different populations change during early postnatal development remains unknown. These properties, along with the level of excitatory and inhibitory synaptic input to these cells, will clearly impact signal integration within lamina I projection neurons.
Given that an estimated 80–85% of all lamina I projection neurons target the PB (Hylden et al. 1989; Spike et al. 2003) and that spino-PB and spino-PAG cells are known to exhibit important functional differences later in life (Ikeda et al. 2006; Ruscheweyh et al. 2004), the goal of the present study was to characterize the intrinsic excitability of these two populations during early postnatal development. The results demonstrate that although lamina I neurons projecting to the PB and PAG exhibit similar developmental changes in many of their active membrane properties, spino-PB neurons exhibit higher levels of spontaneous activity throughout the postnatal period and only spino-PAG neurons undergo an age-dependent increase in firing frequency. Interestingly, the passive membrane properties of both groups remained stable over the first 3 wk of life, while a significant increase in both excitatory and inhibitory synaptic input occurred over this period. Collectively, these changes are expected to shape the transmission of nociceptive signals within ascending pain pathways during postnatal development.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Ethical approval.
All experiments were reviewed and approved by the University of Cincinnati Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee.
DiI injections.
Sprague-Dawley rats were anesthetized via intraperitoneal injection of a mixture of ketamine (90 mg/kg) and xylazine (10 mg/kg) on postnatal days (P)0–1 and placed in a plaster body mold that was secured in a stereotaxic apparatus (World Precision Instruments, Sarasota, FL) as described previously (Hoorneman 1985). The scalp was incised, and a small hole was made in the skull with a 30-gauge needle. The pup received a single injection (50–100 nl) of FAST DiI oil (2.5 mg/ml; Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) into either the PB or the PAG with a Hamilton microsyringe (62RN) equipped with a 28-gauge needle. Stereotaxic coordinates were based on an atlas of the E22 (i.e., P0) rat brain (Altman and Bayer 1995) as follows (in mm; relative to lambda): PB: 2.7 caudal, 1.0 lateral, and 3.3 ventral; PAG: 1.9 caudal, 0.60 lateral, and 2.9 ventral. The skin was closed with Vetbond, and the pups were returned to the home cage until the beginning of the electrophysiological experiments or the age of weaning. After euthanasia, the brain was harvested and immersed in 4% paraformaldehyde, and 30-μm coronal sections were cut on a cryostat and examined with a light microscope in order to verify the accuracy of the injection site.
Preparation of spinal cord slices.
Rats (at P2–5, P10–12, P19–23, or P30–32) were deeply anesthetized with pentobarbital sodium (30 mg/kg ip), perfused with ice-cold dissection solution consisting of (in mM) 250 sucrose, 2.5 KCl, 25 NaHCO3, 1.0 NaH2PO4, 6 MgCl2, 0.5 CaCl2, and 25 glucose continuously bubbled with 95% O2-5% CO2, and decapitated. The lumbar spinal cord was isolated and immersed in low-melting point agarose (3% in above solution; Invitrogen), and parasagittal slices (350–400 μm) were cut from the contralateral side with a Vibroslice tissue slicer (HA-752; Campden Instruments, Lafayette, IN). The slices were placed in a chamber filled with oxygenated dissection solution for 30 min and then allowed to recover in an oxygenated artificial cerebrospinal fluid (aCSF) solution containing (in mM) 125 NaCl, 2.5 KCl, 25 NaHCO3, 1.0 NaH2PO4, 1.0 MgCl2, 2.0 CaCl2, and 25 glucose for ≥1 h at room temperature.
Patch-clamp recordings.
After recovery, slices were transferred to a submersion-type recording chamber (RC-22; Warner Instruments, Hamden, CT) and mounted on the stage of an upright microscope (BX51WI; Olympus, Center Valley, PA) that was equipped with fluorescence to allow for the identification of DiI-labeled neurons. Slices were then perfused at room temperature with oxygenated aCSF at a rate of 1.5–6 ml/min.
Patch electrodes were constructed from thin-walled single-filamented borosilicate glass (1.5-mm outer diameter; World Precision Instruments) with a microelectrode puller (P-97; Sutter Instruments, Novato, CA). Pipette resistances ranged from 4 to 6 MΩ, and seal resistances were >1 GΩ. For current-clamp experiments, patch electrodes were filled with a solution containing the following (in mM): 130 K-gluconate, 10 KCl, 10 HEPES, 10 Na-phosphocreatine, 4 MgATP, and 0.3 Na2GTP, pH 7.2 (305 mosM). Voltage-clamp recordings used an intracellular solution containing the following (in mM): 130 Cs-gluconate, 10 CsCl, 10 HEPES, 11 EGTA, 1.0 CaCl2, and 2.0 MgATP, pH 7.2 (300–305 mosM).
Projection neurons were located under epifluorescence (Fig. 1) and visualized with infrared differential interference contrast optics, and patch-clamp recordings were obtained with a Multiclamp 700B amplifier (Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA). Approximately 1 min after establishment of the whole cell configuration, the spontaneous firing patterns of dorsal horn neurons were classified at the resting membrane potential (Vrest). Membrane capacitance (Cm) was calculated with the built-in pCLAMP membrane test (applied at 33.3 Hz), while membrane resistance (Rm) was measured with the hyperpolarization produced by a −20 pA current injection from Vrest. To characterize the properties of evoked action potential (AP) discharge, intracellular current injections (from −10 to +70 pA in 5-pA increments; 800-ms duration) were applied from Vrest. AP amplitude was measured as the difference between AP threshold and the peak amplitude, while the spike duration at 50% of the peak amplitude was used to calculate AP half-width. Instantaneous firing frequency (IF) was calculated as 1/interspike interval (ISI), while the degree of spike frequency adaptation (SFA) was measured as the following ratio: (IF using last ISI)/(IF using first ISI). Rheobase was defined as the minimum current step (delivered in 2.5-pA increments at 50-ms duration) that evoked AP discharge.
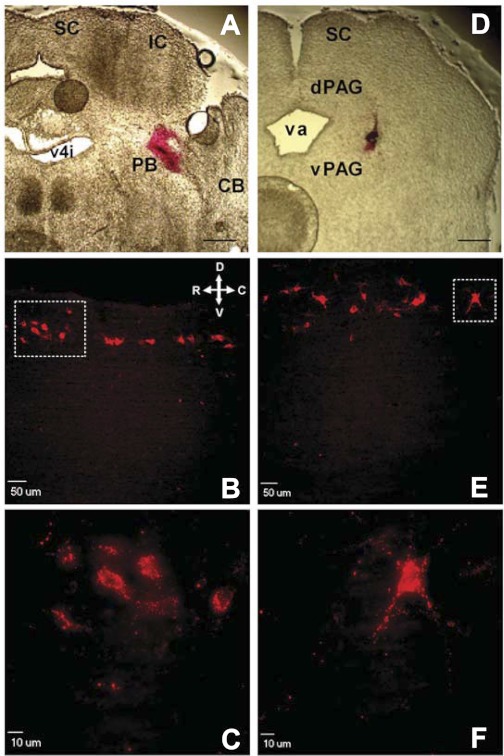
Fig. 1.
Retrograde labeling of developing lamina I neurons which project to the parabrachial nucleus (PB) or periaqueductal gray (PAG). A: section of rat brain at postnatal day (P)3 illustrating site where DiI was injected into PB at birth. SC, superior colliculus; IC, inferior colliculus; CB, cerebellum; v4i, fourth ventricle (isthmal). Scale bar, 400 μm. B: sagittal spinal cord section illustrating narrow band of retrogradely labeled neurons within lamina I at P21 after injection of DiI into PB at birth. Orientation arrows indicate dorsal (D), ventral (V), rostral (R), and caudal (C) axes. C: higher magnification of boxed region in B. D: P3 brain section demonstrating location of DiI injection into PAG at birth. dPAG, dorsal PAG; vPAG, ventral PAG; va, aqueduct. Scale bar, 400 μm. E: example of lamina I neurons fluorescently labeled at P21 after injections of DiI into PAG at birth. Same orientation as in B. F: higher magnification of boxed region in E.
Voltage-clamp experiments included the bath application of 500 nM TTX, in order to record miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents (mEPSCs) from a holding potential of −70 mV and miniature inhibitory postsynaptic currents (mIPSCs) from a holding potential of 0 mV in the same lamina I projection neurons.
Membrane voltages were adjusted for liquid junction potentials calculated with JPCalc software (P. Barry, University of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia; modified for Molecular Devices) unless otherwise specified. Currents were filtered at 4–6 kHz through a −3 dB, four-pole low-pass Bessel filter, digitally sampled at 20 kHz, and stored on a personal computer (ICT, Cincinnati, OH) with a commercially available data acquisition system (Digidata 1440A with pCLAMP 10.0 software; Molecular Devices).
Data analysis and statistics.
Miniature postsynaptic currents were analyzed via visual inspection with Mini Analysis (version 6.0.3; Synaptosoft, Decatur, GA), while AP properties were analyzed with Clampfit (Molecular Devices) software. The threshold for miniature postsynaptic current detection was set at twice the mean amplitude of the background noise. Nonparametric statistical tests (Mann-Whitney test for 2 groups; Kruskal-Wallis test for >2 groups; Prism 5.0 software, GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA) were used in cases in which the distribution of data failed the D'Agostino and Pearson normality test or when the number of observations was insufficient (n < 24) to definitively conclude that data were distributed in a Gaussian manner. Where parametric tests were appropriate, one-way ANOVAs (with Tukey posttests) or two-way ANOVAs (with Bonferroni posttests) were used unless otherwise stated. The χ2-test was used to determine whether the fraction of neurons exhibiting spontaneous activity (SA) or afterdepolarizations changed significantly with age. n refers to the number of neurons sampled in a given group. Data are expressed as means ± SE.
RESULTS
Passive membrane properties of lamina I projection neurons remain stable during early postnatal development.
Lamina I projection neurons were identified via the retrograde transport of DiI injected into either the PB or PAG at birth (Fig. 1). Spinal cord slices were subsequently prepared at P2–5, P10–12, P19–23, or P30–32, and whole cell patch-clamp recordings were obtained from spino-PB (n = 116) or spino-PAG (n = 97) neurons. As illustrated in Table 1, we failed to observe significant changes in Vrest, Cm, or Rm in either spino-PB or spino-PAG populations during the first three postnatal weeks (P > 0.05; 1-way ANOVA). However, Vrest did become significantly more negative in both groups between P19–23 and P30–32 (Table 1).
Table 1.
Passive membrane properties of developing lamina I projection neurons
| P2–5 | P10–12 | P19–23 | P30–32 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spino-PB (n = 27–33) | ||||
| Resting potential, mV | −69.4 ± 1.1 | −67.5 ± 1.4 | −71.5 ± 1.3 | −80.1 ± 1.4† |
| Membrane capacitance, pF | 72.0 ± 3.3 | 72.6 ± 3.3 | 83.3 ± 5.5 | 64.6 ± 3.9* |
| Membrane resistance, MΩ | 1,012 ± 69 | 1,083 ± 82 | 892 ± 52 | 845 ± 55 |
| No. of animals | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Spino-PAG (n = 17–28) | ||||
| Resting potential, mV | −68.4 ± 1.4 | −71.6 ± 1.4 | −70.1 ± 1.3 | −78.8 ± 1.8‡§ |
| Membrane capacitance, pF | 77.3 ± 3.3 | 79.3 ± 5.3 | 85.0 ± 5.0 | 74.0 ± 7.3 |
| Membrane resistance, MΩ | 755 ± 61 | 828 ± 63 | 818 ± 77 | 787 ± 101 |
| No. of animals | 4 | 4 | 5 | 3 |
Values are means ± SE. Data were obtained with the potassium gluconate-based intracellular solution. See materials and methods for calculations. PB, parabrachial nucleus; PAG, periaqueductal gray; P, postnatal day.
P < 0.01 vs. P19–23,
P < 0.001 vs. all other ages,
P < 0.01 vs. P10–12,
P < 0.001 vs. P2–5 and P19–23; 1-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparison test.
Spontaneous and evoked firing in developing projection neurons.
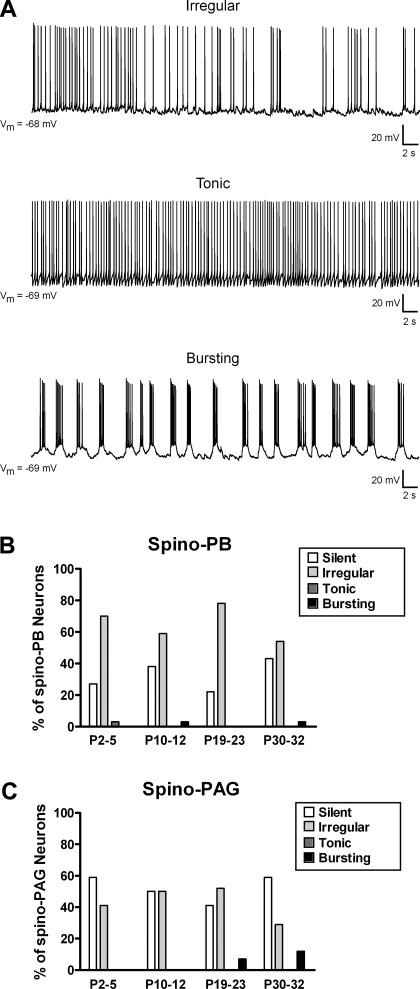
We previously classified the spontaneous firing patterns of newborn lamina I neurons as “silent,” “irregular,” “tonic,” or “bursting” and demonstrated that neither spino-PB nor spino-PAG projection neurons exhibit rhythmic burst-firing during the first days of life (Li and Baccei 2011). To determine whether these patterns of SA are developmentally regulated in ascending projection neurons, we recorded spontaneous AP discharge in these cells from Vrest (Fig. 2A) in the four postnatal age groups. Within the spino-PB population, the majority of neurons fired APs in an irregular manner regardless of age, with the remainder of neurons generally failing to show SA (Fig. 2B). Interestingly, the percentage of spino-PB neurons that exhibited some form of SA was not significantly different between age groups (P = 0.325; χ2-test). Although spino-PAG neurons were more likely to be silent at Vrest (Fig. 2C; P = 0.006 compared with spino-PB cells; Fisher's exact test), the overall prevalence of SA in this population was similarly independent of postnatal age (P = 0.514; χ2-test). In addition, while we again failed to observe spontaneous burst-firing in newborn lamina I projection neurons, a small number of spino-PB (n = 2) and spino-PAG (n = 4) cells generated rhythmic bursting at later ages (Fig. 2, B and C).
Fig. 2.
Spontaneous firing patterns in developing lamina I projection neurons. A: spino-PB and spino-PAG neurons located in lamina I of rat spinal cord were classified as irregular (exhibiting intermittent spike activity; top), tonic (continuous firing at a relatively constant frequency; middle), bursting (demonstrating rhythmic burst-firing; bottom), or silent (lack of action potential discharge; not shown). Vm, membrane potential. B and C: patterns of spontaneous activity (SA) in spino-PB (B) and spino-PAG (C) neurons at different postnatal ages, illustrating predominance of irregular spike discharge in both groups throughout development and greater overall prevalence of SA in the spino-PB population. Data for spino-PB group: P2–5: n = 33 cells from 3 rats; P10–12: n = 29 cells from 3 rats; P19–23: n = 27 cells from 4 rats; P30–32: n = 28 cells from 4 rats. Data for spino-PAG group: P2–5: n = 27 cells from 4 rats; P10–12: n = 28 cells from 4 rats; P19–23: n = 27 cells from 5 rats; P30–32: n = 17 cells from 3 rats.
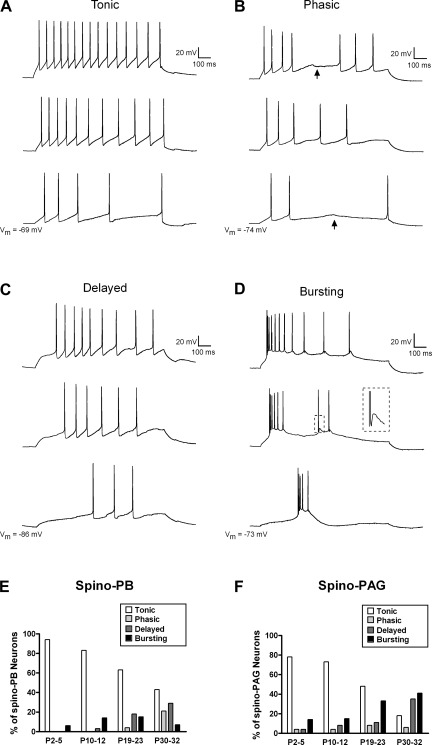
To examine the patterns of evoked AP discharge in developing projection neurons, intracellular current injections (800 ms) of increasing intensity were applied from Vrest via the patch electrode. Previous examinations of rat lamina I neurons (Prescott and De Koninck 2002; Ruscheweyh et al. 2004) have identified up to seven patterns of evoked firing (tonic, delayed, initial bursting, single spike, phasic, gap firing, and bursting firing). However, the present study (Fig. 3, A–D) classified evoked discharge into four categories (tonic, phasic, delayed, and bursting) since we failed to observe single-spike, initial bursting, or gap firing patterns in the sampled populations. As illustrated in Fig. 3, E and F, tonic firing predominated throughout the first three postnatal weeks in spino-PB and spino-PAG neurons, although in both groups the prevalence of tonic discharge appeared to decrease with age and a more even distribution of firing patterns was observed by P30–32. Phasic and delayed firing were notably absent in the newborn spino-PB group and rarely seen in spino-PAG cells at the same time point. In addition, despite the lack of spontaneous burst-firing in neonatal lamina I projection neurons, a small percentage of both the spino-PB and spino-PAG populations exhibited bursting in response to intracellular current injection at P2–5. This fraction did not change significantly with postnatal development in either the spino-PB (P = 0.606; χ2-test) or the spino-PAG (P = 0.103) group.
Fig. 3.
Evoked action potential (AP) discharge in ascending projection neurons during the early postnatal period. Direct current injection through the patch electrode at increasing intensities (bottom to top) revealed 4 firing patterns in developing spino-PB and spino-PAG lamina I neurons. A: tonic neurons fired APs throughout the 800-ms depolarizations. All traces in panel originate from the same lamina I projection neuron. B: phasic neurons exhibited APs at the beginning of the current step but did not discharge spikes throughout the prolonged depolarization, as irregular gaps in their firing were evident at many stimulus intensities (arrows). C: delayed neurons were distinguished by a long latency to the first spike that varied with stimulus intensity. D: bursting neurons were identified by their slow plateau potentials with superimposed bursts of high-frequency AP discharge. Inset, example of spike afterdepolarization (see boxed region). E and F: when APs were evoked by intracellular current injection from the resting membrane potential, the majority of both spino-PB (E) and spino-PAG (F) neurons exhibited tonic firing during the first 3 postnatal weeks, while a more even distribution of firing patterns was evident by P30–32. Sample sizes were the same as described in Fig. 2.
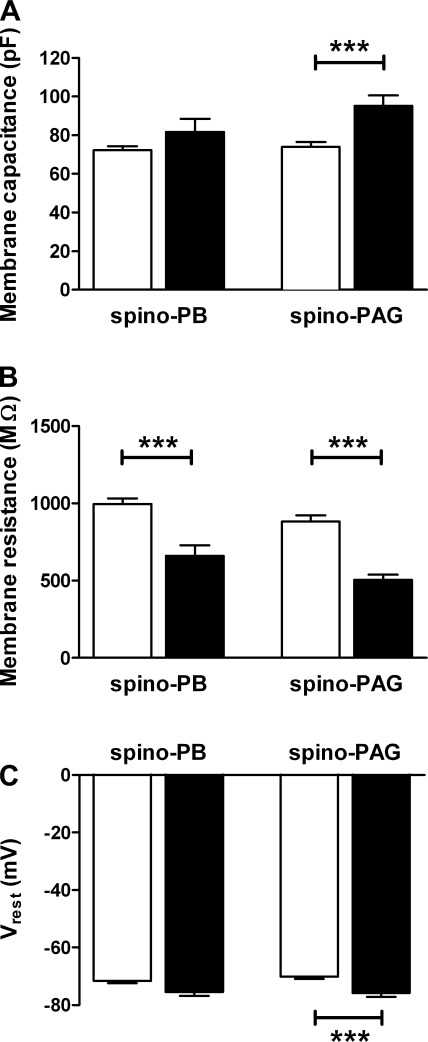
Lamina I interneurons that exhibit spontaneous bursting are characterized by significantly lower Cm and higher Rm compared with adjacent, nonbursting neurons (Li and Baccei 2011). To determine whether spinal projection neurons showing evoked burst-firing (Fig. 3D) are similarly distinguished by their passive membrane properties, we compared Cm, Rm, and Vrest between bursting and nonbursting neurons with projections to the PB or PAG (pooled across ages). Surprisingly, spino-PAG neurons that demonstrated bursting in response to current injection (n = 24) had a significantly higher Cm compared with spino-PAG cells that lacked burst-firing (n = 73; P = 0.0002; Mann-Whitney test; Fig. 4A, right), as well as a lower Rm (P < 0.0001; Mann-Whitney; Fig. 4B, right) and a more hyperpolarized Vrest (P = 0.0009; unpaired t-test; Fig. 4C, right). A decreased Rm in bursting (n = 12) relative to nonbursting (n = 101) cells was also observed within the spino-PB population (P = 0.0008; Fig. 4B, left). In addition, rheobase levels were significantly higher in bursting neurons compared with cells exhibiting other patterns of evoked discharge in both the spino-PB (bursting: 48.8 ± 5.2 pA; nonbursting: 29.7 ± 2.4 pA; P = 0.0015; Mann-Whitney test) and spino-PAG (bursting: 47.8 ± 4.9 pA; nonbursting: 32.3 ± 2.7 pA; P = 0.006; data not shown) groups.
Fig. 4.
Distinct passive membrane properties of ascending projection neurons that demonstrate evoked burst-firing. A: average membrane capacitance of bursting (filled bars) spino-PAG neurons was higher compared with nonbursting cells (open bars) in this population (***P = 0.0002; Mann-Whitney test; right), while no significant differences were noted in the spino-PB group (P = 0.141; left). B: bursting neurons (filled bars) exhibited significantly lower membrane resistance compared with other projection neurons (open bars) in both the spino-PB (***P = 0.0008; Mann-Whitney test; left) and spino-PAG (***P < 0.0001; right) populations. C: resting membrane potential (Vrest) was more hyperpolarized in spino-PAG neurons showing burst-firing in response to current injection compared with spino-PAG cells showing other patterns of evoked discharge (***P = 0.0009; right). Data on bursting neurons originate from 5 rats for the spino-PB group and 12 rats for the spino-PAG population.
We next examined the relationship between spontaneous AP discharge and evoked firing patterns within individual spino-PB and spino-PAG lamina I neurons. In the spino-PB group, a significantly higher fraction of cells exhibiting irregular SA fired tonically in response to direct current injection (63/75, 84%) compared with neurons that were silent at rest (18/38, 47%; P = 0.001; Fisher's exact test; Table 2). A similar relationship was observed in the spino-PAG population, as 77% (33/43) of irregular neurons and 46% (23/50) of silent cells (P = 0.003) demonstrated tonic firing in response to intracellular current injection. Strikingly, the vast majority of cells that were capable of burst-firing during current injection lacked SA in both the spino-PB (10/12) and spino-PAG (18/24) populations within lamina I.
Table 2.
Spontaneous versus evoked firing patterns in developing projection neurons
| Spino-PB Spontaneous Discharge |
Spino-PAG Spontaneous Discharge |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Evoked Discharge | Silent | Irregular | Tonic | Bursting | Silent | Irregular | Tonic | Bursting |
| Tonic | 18 | 63 | 1 | 1 | 23 | 33 | 0 | 0 |
| Phasic | 5 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| Delayed | 5 | 8 | 0 | 1 | 7 | 4 | 0 | 1 |
| Burst | 10 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 18 | 3 | 0 | 3 |
| Total | 38 | 75 | 1 | 2 | 50 | 43 | 0 | 4 |
Values represent the number of neurons exhibiting the indicated pattern of action potential discharge.
Parallel developmental changes in action potential properties in spino-PB and spino-PAG lamina I neurons.
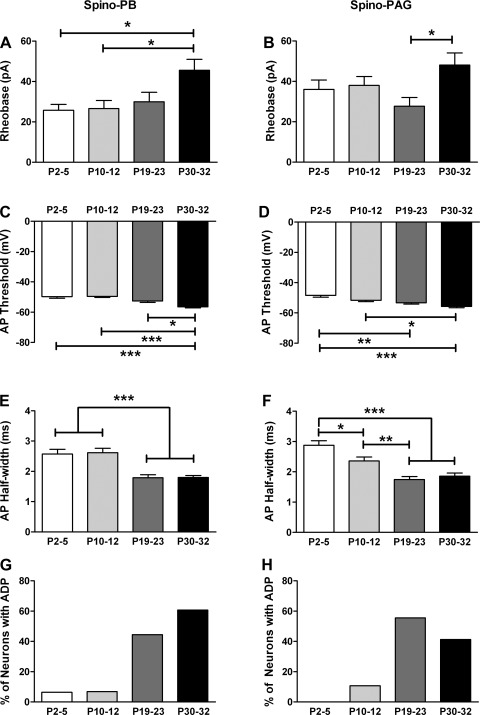
To investigate whether the different populations of lamina I projection neurons exhibit distinct age-dependent changes in their active membrane properties, we first measured the rheobase in spino-PB and spino-PAG neurons at various times during postnatal development. Rheobase levels did not significantly change over the first three postnatal weeks in either the spino-PB (n = 27–32 in each age group; P > 0.05; Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn's multiple comparison test; Fig. 5A) or spino-PAG (n = 17–28; Fig. 5B) population, although significantly higher rheobase levels were observed in the P30–32 group (P < 0.05). Meanwhile, AP threshold significantly decreased between P2–5 and P19–23 in spino-PAG neurons (P < 0.01; 1-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparison test; Fig. 5D) and was also lower in spino-PB cells at P30–32 compared with younger ages (P < 0.05; Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn's multiple comparison test; Fig. 5C). Spike duration (as measured by AP half-width) significantly decreased during postnatal development in both populations of projection neurons (Fig. 5, E and F), while AP amplitude depended on age in spino-PB neurons (P2–5: 75.3 ± 2.0 mV; P10–12: 73.3 ± 1.8 mV; P19–23: 79.4 ± 1.7 mV; P30–32: 82.2 ± 1.7 mV; P < 0.05 for P2–5 vs. P30–32; P < 0.01 for P10–12 vs. P30–32; 1-way ANOVA) but not in the spino-PAG group (P2–5: 70.6 ± 1.7 mV; P10–12: 76.8 ± 1.6 mV; P19–23: 75.2 ± 1.8 mV; P30–32: 77.9 ± 2.4 mV; P > 0.05; data not shown). Finally, in both the spino-PB and spino-PAG populations, afterdepolarizations following an AP (see Fig. 3D, inset) were rarely observed in the first days of life and were significantly upregulated during postnatal development (P < 0.0001; χ2-test, Fig. 5, G and H).
Fig. 5.
Age-dependent modulation of membrane excitability in developing spinal projection neurons. A and B: minimum current needed to evoke an AP (i.e., rheobase) did not change significantly during early postnatal development in either the spino-PB (A) or spino-PAG (B) population of lamina I neurons, although higher rheobase levels were seen in the P30–32 group (*P < 0.05; Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn's multiple comparison test). C and D: however, an age-related reduction in AP threshold was observed in both spino-PB (C; *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001; Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn's posttest) and spino-PAG (D; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001; 1-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparison test) neurons. E and F: both groups of projection neurons exhibited a developmental decrease in spike duration (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001; Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn's posttest). G and H: spino-PB (G) and spino-PAG (H) cells also demonstrated an increased prevalence of spike afterdepolarizations (ADPs) with age (P < 0.0001; χ2-test). Sample sizes were the same as described in Fig. 2.
Target-specific changes in firing frequency in developing lamina I projection neurons.
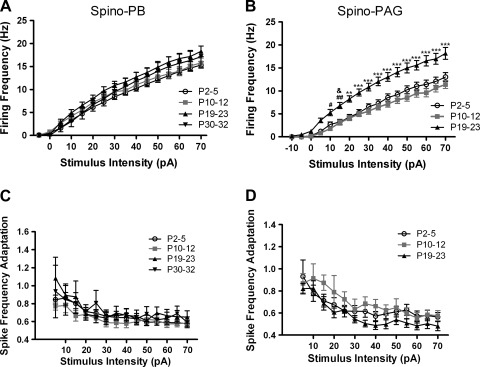
To examine whether the ability of lamina I projection neurons to fire repetitively was significantly altered during early postnatal development, we measured the mean IF (see materials and methods) in response to current injections of increasing intensity (−10 to +70 pA) in tonically firing spino-PB and spino-PAG neurons at different ages. We failed to observe significant age-related changes in the stimulus-response relationship within the spino-PB group (P > 0.05; 2-way ANOVA with Bonferroni posttest; Fig. 6A). However, spino-PAG neurons increased their rate of AP discharge after the second postnatal week (Fig. 6B), as the mean IF of the P19–23 group was significantly higher than that at the younger ages (P < 0.05; 2-way ANOVA with Bonferroni posttest). Despite this developmental increase in average firing frequency, the degree of SFA in spino-PAG neurons did not change significantly with age (P > 0.05; 2-way ANOVA; Fig. 6D). The population of spino-PB neurons also exhibited a similar degree of SFA throughout development (Fig. 6C).
Fig. 6.
Firing rate of spino-PAG, but not spino-PB, projection neurons accelerates during postnatal development. A: plot of mean instantaneous firing frequency as a function of stimulus intensity in spino-PB neurons reveals no significant differences in repetitive firing between age groups (P > 0.05; 2-way ANOVA; n = 12–30 in each group). B: in contrast, P19–23 spino-PAG neurons fired at a significantly higher frequency compared with younger ages (#P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 vs. P10–12; &P < 0.05 vs. P2–5; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs. both ages; 2-way ANOVA with Bonferroni posttests; n = 14–20 in each group). Spino-PAG neurons were not analyzed at P30–32 because of the low number (n = 3) of tonically firing neurons observed at this age. C and D: the degree of spike frequency adaptation across a range of stimulus intensities did not change significantly with age in either population of lamina I projection neurons (P > 0.05; 2-way ANOVA). The numbers of animals used were the same as described in Fig. 2.
Strengthening of excitatory and inhibitory synaptic input onto ascending projection neurons during early postnatal development.
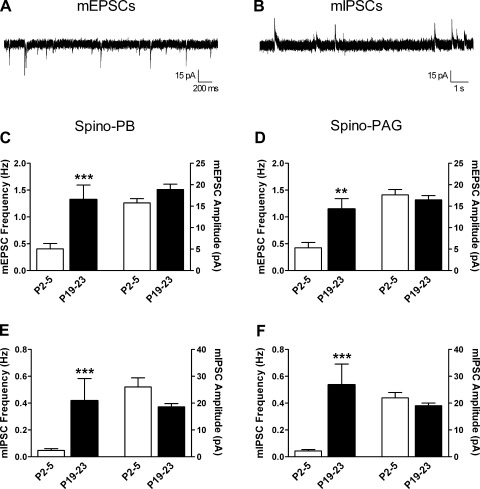
We previously reported a developmental increase in both spontaneous excitatory and inhibitory transmission onto lamina II neurons in the rat spinal cord (Baccei and Fitzgerald 2004; Li et al. 2009). To determine whether the efficacy of synaptic inputs to lamina I projection neurons undergoes a similar modulation during the first 3 wk of life, we recorded mEPSCs (Fig. 7A) and mIPSCs (Fig. 7B) in spino-PB and spino-PAG cells at P2–5 and P19–23.
Fig. 7.
Developmental increase in the efficacy of spontaneous excitatory and inhibitory synaptic transmission onto spinal projection neurons. A: example of miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents (mEPSCs) isolated at a holding potential of −70 mV in an immature lamina I projection neuron identified by retrograde transport of DiI. B: example of miniature inhibitory postsynaptic currents (mIPSCs) recorded in the same neuron from a holding potential of 0 mV. C and D: frequency of mEPSCs increased with age in both spino-PB (***P = 0.0003; Mann-Whitney test; C, left) and spino-PAG (**P = 0.0013; D, left) neurons without a significant change in mEPSC amplitude (right). E and F: similarly, mIPSC frequency was significantly higher at P19–23 compared with P2–5 in the same populations of spino-PB (***P < 0.0001; Mann-Whitney; E, left) and spino-PAG neurons (***P = 0.0002; F, left), while mIPSC amplitude was unaltered (right). Data for spino-PB group are derived from 3 rats at P2–5 and 4 rats at P19–23. Data for spino-PAG group are derived from 3 rats at P2–5 and 4 rats at P19–23.
As illustrated in Fig. 7C, spino-PB neurons showed a clear age-dependent increase in the frequency of mEPSCs (n = 18–22 at each age; P = 0.0003; Mann-Whitney test; Fig. 7C, left), while mEPSC amplitude was not significantly altered (P = 0.059; Fig. 7C, right). Likewise, mIPSC frequency markedly increased with age in the same neurons (P < 0.0001; Mann-Whitney; Fig. 7E, left) without statistically significant changes in mIPSC amplitude (P = 0.066; Fig. 7E, right). A similar developmental trend was observed in the spino-PAG group, as the frequency of both mEPSCs (P = 0.0013; Mann-Whitney; Fig. 7D, left) and mIPSCs (P = 0.0002; Fig. 7F, left) were significantly elevated by the end of the third postnatal week, with no accompanying changes in the mean amplitude of these currents (n = 20–26 at each age; Fig. 7, D and F, right).
DISCUSSION
The present study characterizes, for the first time, the electrophysiological properties of identified lamina I projection neurons during early postnatal development. When considered alongside prior investigations of the developing SDH, our results suggest that the maturation of intrinsic membrane properties within ascending projection neurons may occur with a distinct time course compared with the surrounding population of interneurons within the SDH. For example, neither the spino-PB nor the spino-PAG group showed age-dependent shifts in Vrest (Table 1), Rm, Cm, or rheobase (Fig. 5) during the first 3 wk of life. Interestingly, significant changes in Vrest and rheobase were observed after P23 (Fig. 5 and Table 1), suggesting that a subset of electrophysiological properties may be slow to mature within the population of lamina I projection neurons. In contrast, previous studies have documented age-dependent hyperpolarization of Vrest, decrease in Rm, and elevation in rheobase across the general population of lamina I (Li and Baccei 2011) and lamina II (Walsh et al. 2009) neurons in the rodent spinal cord during the first three postnatal weeks. In addition, while the prevalence of SA in unidentified lamina I neurons (the vast majority of which correspond to interneurons) clearly decreases during early life (Li and Baccei 2011), the level of SA in both the spino-PB and spino-PAG populations remained unchanged during the course of development. Finally, while the firing frequency of unidentified SDH neurons does not appear to depend on age (Baccei and Fitzgerald 2005), lamina I neurons projecting to the PAG (but not PB) discharged APs at a significantly higher rate after the second postnatal week (Fig. 6, A and B). The selective effect of age on the firing rate of spino-PAG cells suggests that the gain of ascending nociceptive pathways may be differentially regulated during the postnatal period. Collectively, the available evidence strongly suggests that neuronal excitability may be modulated in a cell type-specific manner within the developing SDH.
Given their dependence on the surface area of the membrane (Hille 1992), the passive membrane properties (such as Rm and Cm) of a neuron will be significantly influenced by its morphological properties including the relative size and complexity of the dendritic compartment (Rall and Rinzel 1973). As a result, it is notable that the anatomical maturation of SDH neurons occurs in two distinct phases. Supraspinal projection neurons are generated before local circuit interneurons in the embryonic dorsal horn (Nandi et al. 1993), regardless of their target in the brain (Bice and Beal 1997a; Bicknell and Beal 1984) or whether they project ipsilaterally or contralaterally (Nandi et al. 1991). Importantly, their axonal and dendritic development predominantly occurs prior to birth (Bicknell and Beal 1984). Meanwhile, presumptive interneurons within the SDH undergo a dramatic growth and reorganization of their dendritic trees during the early postnatal period (Bicknell and Beal 1984). This may explain the observations that the passive membrane properties of ascending projection neurons remain stable during the first three postnatal weeks (Table 1) while those of unidentified SDH neurons (i.e., interneurons) exhibit significant developmental changes (Li and Baccei 2011; Walsh et al. 2009). However, the potential mechanisms that contribute to the delayed changes in Vrest and rheobase within projection neurons remain unclear.
Despite the fact that the morphological development of lamina I projection neurons occurs before birth, our results clearly demonstrate that the maturation of excitatory and inhibitory synaptic inputs onto these cells continues throughout the first three postnatal weeks (Fig. 7). The selective elevation in the frequency of the miniature postsynaptic currents predicts a developmental increase in the number of synapses onto ascending projection neurons and/or an enhanced probability of transmitter release at these synapses. However, we cannot completely exclude the possibility that the age-related facilitation in mEPSC frequency reflects a conversion from “silent” (i.e., pure NMDA receptor only) to functional glutamatergic synapses via the insertion of AMPA receptors into the postsynaptic membrane (Bardoni et al. 1998; Li and Zhuo 1998; Torsney 2011). It is also presently unclear whether the changes in glutamatergic input onto projection neurons reflect an increased efficacy of synapses formed by primary afferents (Todd 2002), local excitatory interneurons (Cordero-Erausquin et al. 2009), or other lamina I projection neurons (Luz et al. 2010; Szucs et al. 2010).
As a result, it will be important to characterize the nature of primary afferent synaptic input to spino-PB and spino-PAG neurons at various stages of early postnatal development. Previous studies have demonstrated that low-threshold Aβ-fiber input to the SDH is more pronounced during the neonatal period (Beggs et al. 2002; Daniele and MacDermott 2009; Jennings and Fitzgerald 1996) and becomes subject to tight inhibitory control at later ages (Torsney and MacDermott 2006). However, since primary afferents may target subtypes of SDH neurons in a highly selective manner (Lu and Perl 2003, 2005; Zheng et al. 2010), it remains to be determined whether newborn spinal projection neurons do in fact receive enhanced low-threshold sensory input. It should also be noted that low-threshold input to adult lamina I projection neurons can also arise from C-fiber mechanoreceptors (Andrew 2010).
Overall, our results also suggest that spino-PB and spino-PAG neurons exhibit many similar developmental changes in their active membrane properties. Both groups demonstrate an age-dependent reduction in AP threshold, which would be predicted to facilitate synaptic potential-spike coupling (Andersen et al. 1980; Sharifullina et al. 2004) and thus enhance the effectiveness of nociceptive inputs to these neurons. Spike duration also decreased with age in both groups (Fig. 4), which may allow developing projection neurons to respond with high fidelity to a progressively higher frequency of presynaptic input. In addition, neither population exhibited significant developmental changes in the degree of SFA (Fig. 6) or the distribution of spontaneous firing patterns, as irregular neurons represented the majority of spontaneously active cells throughout the postnatal period (Fig. 2, B and C). Interestingly, spontaneous burst-firing was observed in a small percentage of spino-PB and spino-PAG neurons at later ages. Future experiments are required to determine whether this rhythmic bursting represents the emergence of intrinsic “pacemaker” activity, as has been documented in lamina I interneurons during the neonatal period (Li and Baccei 2011), or is instead driven by synaptic transmission within the SDH network. A larger number of projection neurons appear capable of bursting after intracellular current injection (Fig. 3, D–F), but the vast majority of these neurons are silent at their Vrest (Table 2). Notably, bursting spino-PAG neurons exhibit significantly lower Rm, larger Cm, and a more hyperpolarized Vrest compared with other spino-PAG cells that fail to show evoked burst-firing (Fig. 4). Since pacemaker neurons within lamina I appear to be distinguished by their high Rm (Li and Baccei 2011), the passive membrane properties of developing projection neurons may suppress spontaneous burst-firing by making it more difficult to achieve sufficient membrane depolarization to activate the voltage-gated conductances (such as persistent Na+ and high-threshold Ca2+ currents) that drive burst generation. Clearly, it will also be important to characterize in detail the expression of the membrane currents that underlie the observed firing patterns within developing lamina I projection neurons.
At first glance, the patterns of evoked AP discharge reported here (tonic, phasic, delayed, and bursting) differ from a previous study of rat spino-PB and spino-PAG lamina I neurons at ∼3–4 wk of age (Ruscheweyh et al. 2004). For example, we failed to observe gap firing (characterized by a long first ISI followed by tonic discharge) in projection neurons at any stage of postnatal development (Fig. 3), while Ruscheweyh et al. (2004) found that ∼75% of spino-PAG and ∼45% of spino-PB neurons exhibited this pattern at room temperature. Instead, we observed a high incidence of tonic firing in both the spino-PB and spino-PAG populations throughout development. This apparent discrepancy is likely explained by differences in experimental approach between the two studies. Specifically, we classified evoked firing patterns from Vrest, which averaged approximately −70 mV after correction for liquid junction potentials (see materials and methods). Meanwhile, Ruscheweyh et al. (2004) employed multiple holding potentials, including voltages that were significantly more negative (less than −80 mV without correction for liquid junction potentials) than those used in the present study. This is noteworthy because gap firing is only observed at holding potentials more negative than −75 mV, because of the need to remove the steady-state inactivation of a slow A-type K+ current (Ruscheweyh et al. 2004). Indeed, the authors reported that the use of a more depolarized holding potential could convert neurons from gap firing to tonic firing. Similar reasons could explain why we alone observed delayed firing in projection neurons, as this pattern only requires holding potentials below −60 mV and reflects the voltage-dependent properties of a fast A-type K+ current (Ruscheweyh and Sandkühler 2002; Ruscheweyh et al. 2004). Meanwhile, our results (Fig. 3) are in general agreement with previous findings that lamina I projection neurons do not exhibit the initial burst pattern of discharge and are rarely single-spiking (Ruscheweyh et al. 2004).
Different firing patterns may be observed within projection neurons with the use of an elevated temperature, which has been reported to decrease input resistance and reduce the excitability of subsets of SDH neurons (Graham et al. 2008). Thus it is possible that the use of higher recording temperatures may reveal a decreased prevalence of spontaneous activity (Fig. 2) and the appearance of single-spiking (or “reluctant firing”) within projection neurons, although it should be noted that the prevalence of tonic firing cells was unaltered by changes in temperature (Graham et al. 2008). Importantly, these patterns of AP discharge may correlate with distinct types of signal processing within lamina I neurons, as tonic and delayed neurons have been proposed to act as integrators of sensory information while phasic and single-spiking neurons are well-suited to function as coincidence detectors (Prescott and De Koninck 2002). Therefore, the predominance of tonic firing in lamina I projection neurons throughout early life (Fig. 3) may reflect their responsibility for integrating signals from a complex interneuronal network in order to govern the output of the spinal nociceptive circuit.
In conclusion, the present study provides the first electrophysiological characterization of spinal lamina I projection neurons during early life, which has important functional implications for nociceptive processing in the neonate. For example, the fact that these neurons possess relatively stable intrinsic membrane properties during the neonatal period may facilitate the faithful transmission of noxious stimuli to the immature brain, as nociceptive-specific cortical potentials have been observed as early as 25 gestational weeks in humans (Slater et al. 2006), thus leading to an appropriate behavioral response that alerts a caregiver that a potential injury has occurred. Meanwhile, the persistence of spontaneous activity within lamina I projection neurons throughout the first weeks of life could provide an endogenous excitatory drive to ascending pain pathways, thereby promoting the maturation of supraspinal nociceptive circuits as well as descending modulatory pathways from the brain stem, which appear to develop gradually during the postnatal period (Fitzgerald and Koltzenburg 1986; Hathway et al. 2009). Finally, since lamina I projection neurons are known to be involved in the generation of chronic pain states (Mantyh et al. 1997; Nichols et al. 1999; Suzuki et al. 2002), a more complete understanding of how membrane excitability is regulated within this population may yield insight into novel, age-specific strategies to modulate the ascending flow of noxious information, and thus pain perception, in infants and children.
GRANTS
This study was supported by National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke Grant NS-072202 (M. L. Baccei).
DISCLOSURES
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the author(s).
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Author contributions: J.L. and M.L.B. conception and design of research; J.L. performed experiments; J.L. and M.L.B. analyzed data; J.L. and M.L.B. interpreted results of experiments; J.L. and M.L.B. prepared figures; J.L. and M.L.B. edited and revised manuscript; J.L. and M.L.B. approved final version of manuscript; M.L.B. drafted manuscript.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors thank Meredith Blankenship for technical assistance during this project.
REFERENCES
- Altman and Bayer, 1995. Altman J, Bayer SA. Atlas of Prenatal Rat Brain Development. Boca Raton, FL: CRC, 1995 [Google Scholar]
- Andersen et al., 1980. Andersen P, Sundberg SH, Sveen O, Swann JW, Wigstrom H. Possible mechanisms for long-lasting potentiation of synaptic transmission in hippocampal slices from guinea-pigs. J Physiol 302: 463–482, 1980 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrew, 2010. Andrew D. Quantitative characterization of low-threshold mechanoreceptor inputs to lamina I spinoparabrachial neurons in the rat. J Physiol 588: 117–124, 2010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baccei et al., 2003. Baccei ML, Bardoni R, Fitzgerald M. Development of nociceptive synaptic inputs to the neonatal rat dorsal horn: glutamate release by capsaicin and menthol. J Physiol 549: 231–242, 2003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baccei and Fitzgerald, 2004. Baccei ML, Fitzgerald M. Development of GABAergic and glycinergic transmission in the neonatal rat dorsal horn. J Neurosci 24: 4749–4757, 2004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baccei and Fitzgerald, 2005. Baccei ML, Fitzgerald M. Intrinsic firing properties of developing rat superficial dorsal horn neurons. Neuroreport 16: 1325–1328, 2005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardoni et al., 1998. Bardoni R, Magherini PC, MacDermott AB. NMDA EPSCs at glutamatergic synapses in the spinal cord dorsal horn of the postnatal rat. J Neurosci 18: 6558–6567, 1998 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beggs et al., 2002. Beggs S, Torsney C, Drew LJ, Fitzgerald M. The postnatal reorganization of primary afferent input and dorsal horn cell receptive fields in the rat spinal cord is an activity-dependent process. Eur J Neurosci 16: 1249–1258, 2002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bice and Beal, 1997a. Bice TN, Beal JA. Quantitative and neurogenic analysis of neurons with supraspinal projections in the superficial dorsal horn of the rat lumbar spinal cord. J Comp Neurol 388: 565–574, 1997a [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bice and Beal, 1997b. Bice TN, Beal JA. Quantitative and neurogenic analysis of the total population and subpopulations of neurons defined by axon projection in the superficial dorsal horn of the rat lumbar spinal cord. J Comp Neurol 388: 550–564, 1997b [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bicknell and Beal, 1984. Bicknell HR, Jr, Beal JA. Axonal and dendritic development of substantia gelatinosa neurons in the lumbosacral spinal cord of the rat. J Comp Neurol 226: 508–522, 1984 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremner and Fitzgerald, 2008. Bremner LR, Fitzgerald M. Postnatal tuning of cutaneous inhibitory receptive fields in the rat. J Physiol 586: 1529–1537, 2008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordero-Erausquin et al., 2009. Cordero-Erausquin M, Allard S, Dolique T, Bachand K, Ribeiro-da-Silva A, De Koninck Y. Dorsal horn neurons presynaptic to lamina I spinoparabrachial neurons revealed by transynaptic labeling. J Comp Neurol 517: 601–615, 2009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordero-Erausquin et al., 2005. Cordero-Erausquin M, Coull JA, Boudreau D, Rolland M, De Koninck Y. Differential maturation of GABA action and anion reversal potential in spinal lamina I neurons: impact of chloride extrusion capacity. J Neurosci 25: 9613–9623, 2005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlhaus et al., 2005. Dahlhaus A, Ruscheweyh R, Sandkühler J. Synaptic input of rat spinal lamina I projection and unidentified neurones in vitro. J Physiol 566: 355–368, 2005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniele and MacDermott, 2009. Daniele CA, MacDermott AB. Low-threshold primary afferent drive onto GABAergic interneurons in the superficial dorsal horn of the mouse. J Neurosci 29: 686–695, 2009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald and Koltzenburg, 1986. Fitzgerald M, Koltzenburg M. The functional development of descending inhibitory pathways in the dorsolateral funiculus of the newborn rat spinal cord. Brain Res 389: 261–270, 1986 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham et al., 2008. Graham BA, Brichta AM, Callister RJ. Recording temperature affects the excitability of mouse superficial dorsal horn neurons, in vitro. J Neurophysiol 99: 2048–2059, 2008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathway et al., 2009. Hathway GJ, Koch S, Low L, Fitzgerald M. The changing balance of brainstem-spinal cord modulation of pain processing over the first weeks of rat postnatal life. J Physiol 587: 2927–2935, 2009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille, 1992. Hille B. Ionic Channels of Excitable Membranes (2nd ed.). Sunderland, MA: Sinauer, 1992 [Google Scholar]
- Hoorneman, 1985. Hoorneman EM. Stereotaxic operation in the neonatal rat; a novel and simple procedure. J Neurosci Methods 14: 109–116, 1985 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hylden et al., 1989. Hylden JL, Anton F, Nahin RL. Spinal lamina I projection neurons in the rat: collateral innervation of parabrachial area and thalamus. Neuroscience 28: 27–37, 1989 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda et al., 2003. Ikeda H, Heinke B, Ruscheweyh R, Sandkühler J. Synaptic plasticity in spinal lamina I projection neurons that mediate hyperalgesia. Science 299: 1237–1240, 2003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda et al., 2006. Ikeda H, Stark J, Fischer H, Wagner M, Drdla R, Jager T, Sandkühler J. Synaptic amplifier of inflammatory pain in the spinal dorsal horn. Science 312: 1659–1662, 2006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings and Fitzgerald, 1996. Jennings E, Fitzgerald M. C-fos can be induced in the neonatal rat spinal cord by both noxious and innocuous peripheral stimulation. Pain 68: 301–306, 1996 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller et al., 2001. Keller AF, Coull JA, Chery N, Poisbeau P, De Koninck Y. Region-specific developmental specialization of GABA-glycine cosynapses in laminas I–II of the rat spinal dorsal horn. J Neurosci 21: 7871–7880, 2001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li and Baccei, 2011. Li J, Baccei ML. Pacemaker neurons within newborn spinal pain circuits. J Neurosci 31: 9010–9022, 2011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li et al., 2009. Li J, Walker SM, Fitzgerald M, Baccei ML. Activity-dependent modulation of glutamatergic signaling in the developing rat dorsal horn by early tissue injury. J Neurophysiol 102: 2208–2219, 2009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li and Zhuo, 1998. Li P, Zhuo M. Silent glutamatergic synapses and nociception in mammalian spinal cord. Nature 393: 695–698, 1998 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu and Perl, 2003. Lu Y, Perl ER. A specific inhibitory pathway between substantia gelatinosa neurons receiving direct C-fiber input. J Neurosci 23: 8752–8758, 2003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu and Perl, 2005. Lu Y, Perl ER. Modular organization of excitatory circuits between neurons of the spinal superficial dorsal horn (laminae I and II). J Neurosci 25: 3900–3907, 2005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luz et al., 2010. Luz LL, Szucs P, Pinho R, Safronov BV. Monosynaptic excitatory inputs to spinal lamina I anterolateral-tract-projecting neurons from neighbouring lamina I neurons. J Physiol 588: 4489–4505, 2010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantyh et al., 1997. Mantyh PW, Rogers SD, Honore P, Allen BJ, Ghilardi JR, Li J, Daughters RS, Lappi DA, Wiley RG, Simone DA. Inhibition of hyperalgesia by ablation of lamina I spinal neurons expressing the substance P receptor. Science 278: 275–279, 1997 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nandi et al., 1991. Nandi KN, Knight DS, Beal JA. Neurogenesis of ascending supraspinal projection neurons: ipsi- versus contralateral projections. Neurosci Lett 131: 8–12, 1991 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nandi et al., 1993. Nandi KN, Knight DS, Beal JA. Spinal neurogenesis and axon projection: a correlative study in the rat. J Comp Neurol 328: 252–262, 1993 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols et al., 1999. Nichols ML, Allen BJ, Rogers SD, Ghilardi JR, Honore P, Luger NM, Finke MP, Li J, Lappi DA, Simone DA, Mantyh PW. Transmission of chronic nociception by spinal neurons expressing the substance P receptor. Science 286: 1558–1561, 1999 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott and De Koninck, 2002. Prescott SA, De Koninck Y. Four cell types with distinctive membrane properties and morphologies in lamina I of the spinal dorsal horn of the adult rat. J Physiol 539: 817–836, 2002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall and Rinzel, 1973. Rall W, Rinzel J. Branch input resistance and steady attenuation for input to one branch of a dendritic neuron model. Biophys J 13: 648–687, 1973 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruscheweyh et al., 2004. Ruscheweyh R, Ikeda H, Heinke B, Sandkühler J. Distinctive membrane and discharge properties of rat spinal lamina I projection neurones in vitro. J Physiol 555: 527–543, 2004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruscheweyh and Sandkühler, 2002. Ruscheweyh R, Sandkühler J. Lamina-specific membrane and discharge properties of rat spinal dorsal horn neurones in vitro. J Physiol 541: 231–244, 2002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharifullina et al., 2004. Sharifullina E, Ostroumov K, Nistri A. Activation of group I metabotropic glutamate receptors enhances efficacy of glutamatergic inputs to neonatal rat hypoglossal motoneurons in vitro. Eur J Neurosci 20: 1245–1254, 2004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater et al., 2006. Slater R, Cantarella A, Gallella S, Worley A, Boyd S, Meek J, Fitzgerald M. Cortical pain responses in human infants. J Neurosci 26: 3662–3666, 2006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spike et al., 2003. Spike RC, Puskar Z, Andrew D, Todd AJ. A quantitative and morphological study of projection neurons in lamina I of the rat lumbar spinal cord. Eur J Neurosci 18: 2433–2448, 2003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki et al., 2002. Suzuki R, Morcuende S, Webber M, Hunt SP, Dickenson AH. Superficial NK1-expressing neurons control spinal excitability through activation of descending pathways. Nat Neurosci 5: 1319–1326, 2002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szucs et al., 2010. Szucs P, Luz LL, Lima D, Safronov BV. Local axon collaterals of lamina I projection neurons in the spinal cord of young rats. J Comp Neurol 518: 2645–2665, 2010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd, 2002. Todd AJ. Anatomy of primary afferents and projection neurones in the rat spinal dorsal horn with particular emphasis on substance P and the neurokinin 1 receptor. Exp Physiol 87: 245–249, 2002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torsney, 2011. Torsney C. Inflammatory pain unmasks heterosynaptic facilitation in lamina I neurokinin 1 receptor-expressing neurons in rat spinal cord. J Neurosci 31: 5158–5168, 2011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torsney and MacDermott, 2006. Torsney C, MacDermott AB. Disinhibition opens the gate to pathological pain signaling in superficial neurokinin 1 receptor-expressing neurons in rat spinal cord. J Neurosci 26: 1833–1843, 2006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh et al., 2009. Walsh MA, Graham BA, Brichta AM, Callister RJ. Evidence for a critical period in the development of excitability and potassium currents in mouse lumbar superficial dorsal horn neurons. J Neurophysiol 101: 1800–1812, 2009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng et al., 2010. Zheng J, Lu Y, Perl ER. Inhibitory neurones of the spinal substantia gelatinosa mediate interaction of signals from primary afferents. J Physiol 588: 2065–2075, 2010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]