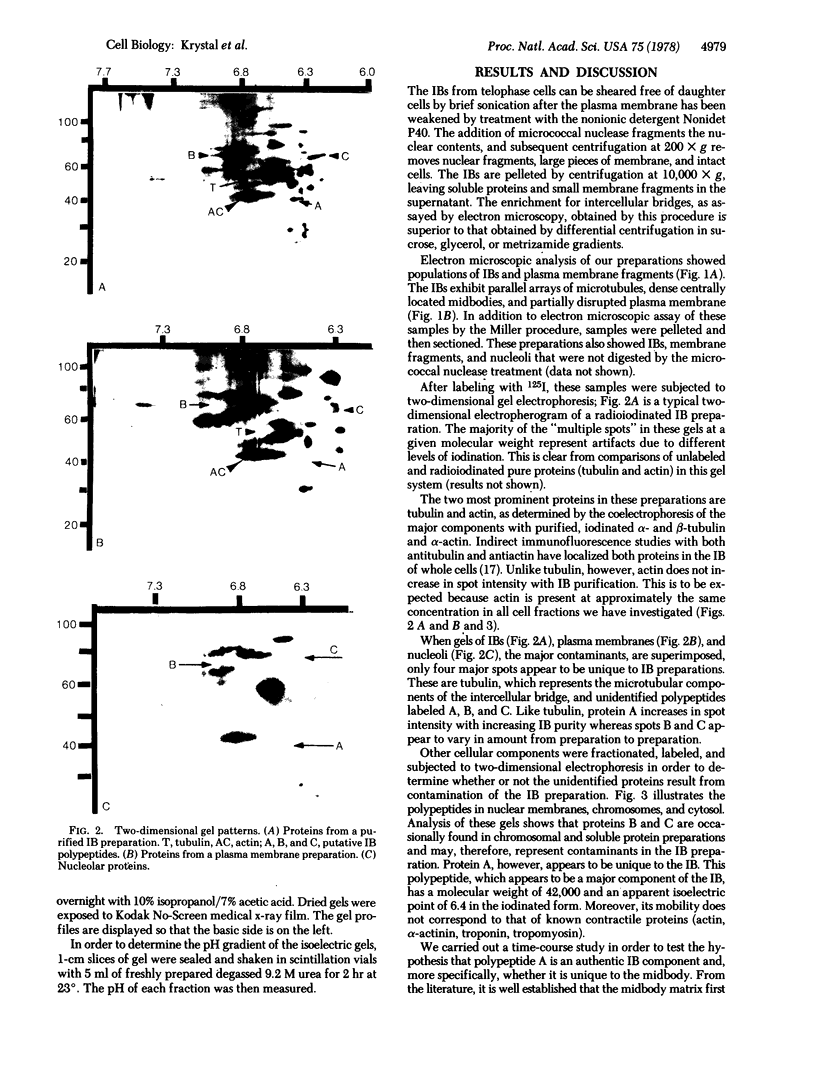
Abstract
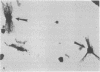
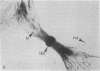
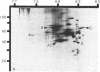
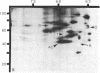
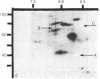
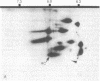
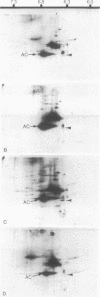
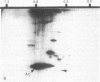
At the completion of mitosis, the two daughter cells are connected by a channel of membrane-bound cytoplasm, the intercellular bridge. This structure contains parallel arrays of spindle microtubules which are associated, at the bridge midline, with a metallophilic band called the midbody. In an effort to characterize midbody components, intercellular bridges were partially purified. The purification consisted of brief sonication of telophase populations of mouse L929 cells in order to shear intercellular bridges from daughter cells, digestion of chromatin by an excess of micrococcal nuclease, and differential centrifugation to enrich for intercellular bridges. Electron microscopy of these preparations substantiated the identity of the bulk of material as intercellular bridges. After solubilization with sodium dodecyl sulfate, the protein components of these preparations were iodinated with Na125I and separated by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. From these analyses, the major polypeptide components of intercellular bridges appear to be tubulin, varying amounts of plasma membrane proteins, and a polypeptide with an apparent molecular weight of 42,000. Time-course studies reveal that this polypeptide is first detectable in a pelletable form approximately 30 min after cells are released from metaphase block, reaches maximal spot intensity in late telophase, and is no longer detectable in G1 populations. We interpret these data to suggest that the 42,000-dalton polypeptide is a component of the midbody.
Keywords: midbody, electron microscopy, two-dimensional gel electrophoresis, tubulin
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allenspach A. L., Roth L. E. Structural variations during mitosis in the chick embryo. J Cell Biol. 1967 Apr;33(1):179–196. doi: 10.1083/jcb.33.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUCK R. C., TISDALE J. M. The fine structure of the mid-body of the rat erythroblast. J Cell Biol. 1962 Apr;13:109–115. doi: 10.1083/jcb.13.1.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cande W. Z., Lazarides E., McIntosh J. R. A comparison of the distribution of actin and tubulin in the mammalian mitotic spindle as seen by indirect immunofluorescence. J Cell Biol. 1977 Mar;72(3):552–567. doi: 10.1083/jcb.72.3.552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlandson R. A., de Harven E. The ultrastructure of synchronized HeLa cells. J Cell Sci. 1971 Mar;8(2):353–397. doi: 10.1242/jcs.8.2.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepler P. K., Jackson W. T. Microtubules and early stages of cell-plate formation in the endosperm of Haemanthus katherinae Baker. J Cell Biol. 1968 Aug;38(2):437–446. doi: 10.1083/jcb.38.2.437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones O. P. Elimination of midbodies from mitotic erythroblasts and their contribution to fetal blood plasma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1969 May;42(5):753–759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRISHAN A., BUCK R. C. STRUCTURE OF THE MITOTIC SPINDLE IN L STRAIN FIBROBLASTS. J Cell Biol. 1965 Mar;24:433–444. doi: 10.1083/jcb.24.3.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller O. L., Jr, Bakken A. H. Morphological studies of transcription. Acta Endocrinol Suppl (Copenh) 1972;168:155–177. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.071s155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller O. L., Jr, Beatty B. R. Visualization of nucleolar genes. Science. 1969 May 23;164(3882):955–957. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3882.955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller O. L., Jr, Hamkalo B. A., Thomas C. A., Jr Visualization of bacterial genes in action. Science. 1970 Jul 24;169(3943):392–395. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3943.392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins J. M., Biesele J. J. Cytokinetic activities in a human cell line: the midbody and intercellular bridge. Tissue Cell. 1973;5(1):47–61. doi: 10.1016/s0040-8166(73)80005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins J. M., Biesele J. J. Terminal phase of cytokinesis in D-98s cells. J Cell Biol. 1977 Jun;73(3):672–684. doi: 10.1083/jcb.73.3.672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paweletz N. Zur Funktion des "Flemming-Körpers" bei der Teilung tierischer Zellen. Naturwissenschaften. 1967 Oct;54(20):533–535. doi: 10.1007/BF00627210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBBINS E., GONATAS N. K. THE ULTRASTRUCTURE OF A MAMMALIAN CELL DURING THE MITOTIC CYCLE. J Cell Biol. 1964 Jun;21:429–463. doi: 10.1083/jcb.21.3.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rattner J. B., Krystal G., Hamkalo B. A. Selective digestion of mouse metaphase chromosomes. Chromosoma. 1978 Apr 25;66(3):259–268. doi: 10.1007/BF00330554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rattner J. B. Nuclear shaping in marsupial spermatids. J Ultrastruct Res. 1972 Sep;40(5):498–512. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(72)80038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]