Abstract
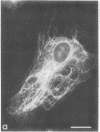
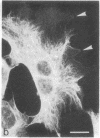
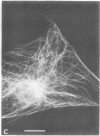
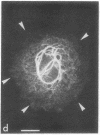
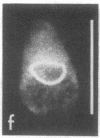
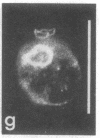
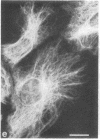
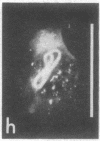
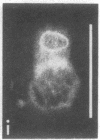
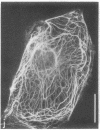
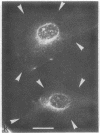
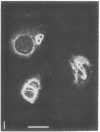
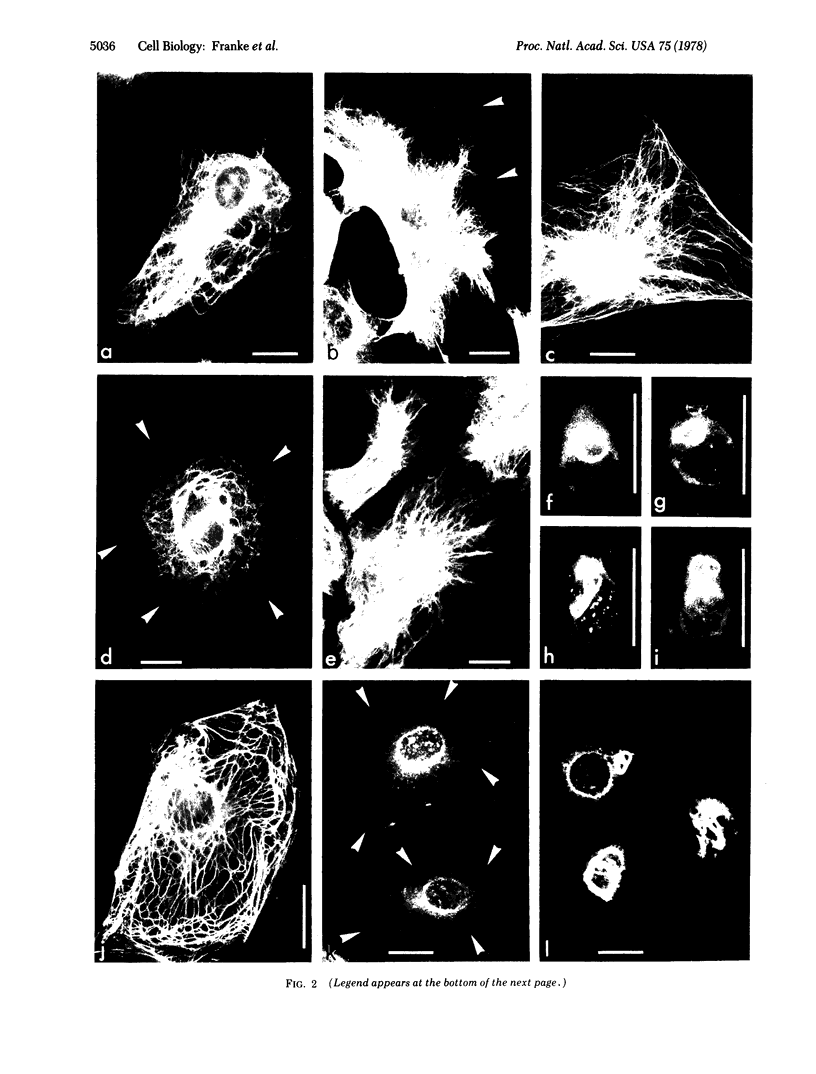
The major protein of intermediate-sized filaments in mouse 3T3 cells, for which the name vimentin is proposed, has a molecular weight of 57,000. Antibodies against vimentin and antibodies against prekeratin have been used in parallel in immunofluorescence microscopy on a variety of cultured cells as well as on frozen tissue sections. Both antibodies decorate extended wavy arrays of filaments that are different from microfilaments and microtubules. Intermediate filament bundles decorated by antibodies against prekeratin are predominant in many epithelial cells, including epithelia-derived tumor cells, and are not decorated by antibodies to vimentin. In contrast, intermediate filaments decorated by antibodies against vimentin are widespread among nonmuscle cells of mesenchymal origin, including transformed cells, and also occur in other cells. Perinuclear whorls of aggregates of intermediate filaments induced by prolonged treatment with Colcemid generally show strong decoration with antibodies against vimentin. No significant reaction with either antiserum has been observed in muscle structures or in brain nerve tissue. These observations show that intermediate filaments with similar ultrastructure and solubility characteristics can be distinguished immunologically.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blose S. H., Shelanski M. L., Chacko S. Localization of bovine brain filament antibody on intermediate (100 A) filaments in guinea pig vascular endothelial cells and chick cardiac muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):662–665. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S., Levinson W., Spudich J. A. Cytoskeletal elements of chick embryo fibroblasts revealed by detergent extraction. J Supramol Struct. 1976;5(2):119–130. doi: 10.1002/jss.400050203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dau P. C. Chromatin proteins from human lymphocytes: a gel electrophoretic comparison between normal, mitogen-stimulated, cell-line, and chronic lymphocytic leukemia lymphocytes. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Jan;54(1):37–48. doi: 10.1093/jnci/54.1.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison P. F., Hong B. S., Cooke P. Classes of distinguishable 10 nm cytoplasmic filaments. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Oct 15;109(2):471–474. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Grund C., Osborn M., Weber K. The intermediate-sized filaments in rat kangaroo PtK2 cells. I. Morphology in situ. Cytobiologie. 1978 Aug;17(2):365–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schmid E., Osborn M., Weber K. The intermediate-sized filaments in rat kangaroo PtK2 cells. II. Structure and composition of isolated filaments. Cytobiologie. 1978 Aug;17(2):392–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. D. The role of three cytoplasmic fibers in BHK-21 cell motility. I. Microtubules and the effects of colchicine. J Cell Biol. 1971 Dec;51(3):752–762. doi: 10.1083/jcb.51.3.752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon W. E., 3rd, Bushnell A., Burridge K. Characterization of the intermediate (10 nm) filaments of cultured cells using an autoimmune rabbit antiserum. Cell. 1978 Feb;13(2):249–261. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90194-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O., Destree A. T. 10 nm filaments in normal and transformed cells. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):151–163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90146-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa H., Bischoff R., Holtzer H. Mitosis and intermediate-sized filaments in developing skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol. 1968 Sep;38(3):538–555. doi: 10.1083/jcb.38.3.538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen A. O., Subrahmanyan L., Turnbull C., Kalnins V. I. Localization of the neurofilament protein in neuroblastoma cells by immunofluorescent staining. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3192–3196. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurki P., Linder E., Virtanen I., Stenman S. Human smooth muscle autoantibodies reacting with intermediate (100 A) filaments. Nature. 1977 Jul 21;268(5617):240–241. doi: 10.1038/268240a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E., Hubbard B. D. Immunological characterization of the subunit of the 100 A filaments from muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4344–4348. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E. The distribution of desmin (100 A) filaments in primary cultures of embryonic chick cardiac cells. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Mar 15;112(2):265–273. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90209-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E., Weber K. Actin antibody: the specific visualization of actin filaments in non-muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2268–2272. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M., Weber K. The detertent-resistant cytoskeleton of tissue culture cells includes the nucleus and the microfilament bundles. Exp Cell Res. 1977 May;106(2):339–349. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90179-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small J. V., Sobieszek A. Studies on the function and composition of the 10-NM(100-A) filaments of vertebrate smooth muscle. J Cell Sci. 1977 Feb;23:243–268. doi: 10.1242/jcs.23.1.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starger J. M., Goldman R. D. Isolation and preliminary characterization of 10-nm filaments from baby hamster kidney (BHK-21) cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2422–2426. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Bibring T., Osborn M. Specific visualization of tubulin-containing structures in tissue culture cells by immunofluorescence. Cytoplasmic microtubules, vinblastine-induced paracrystals, and mitotic figures. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Oct 1;95(1):111–120. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90615-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Pollack R., Bibring T. Antibody against tuberlin: the specific visualization of cytoplasmic microtubules in tissue culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):459–463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]