Abstract
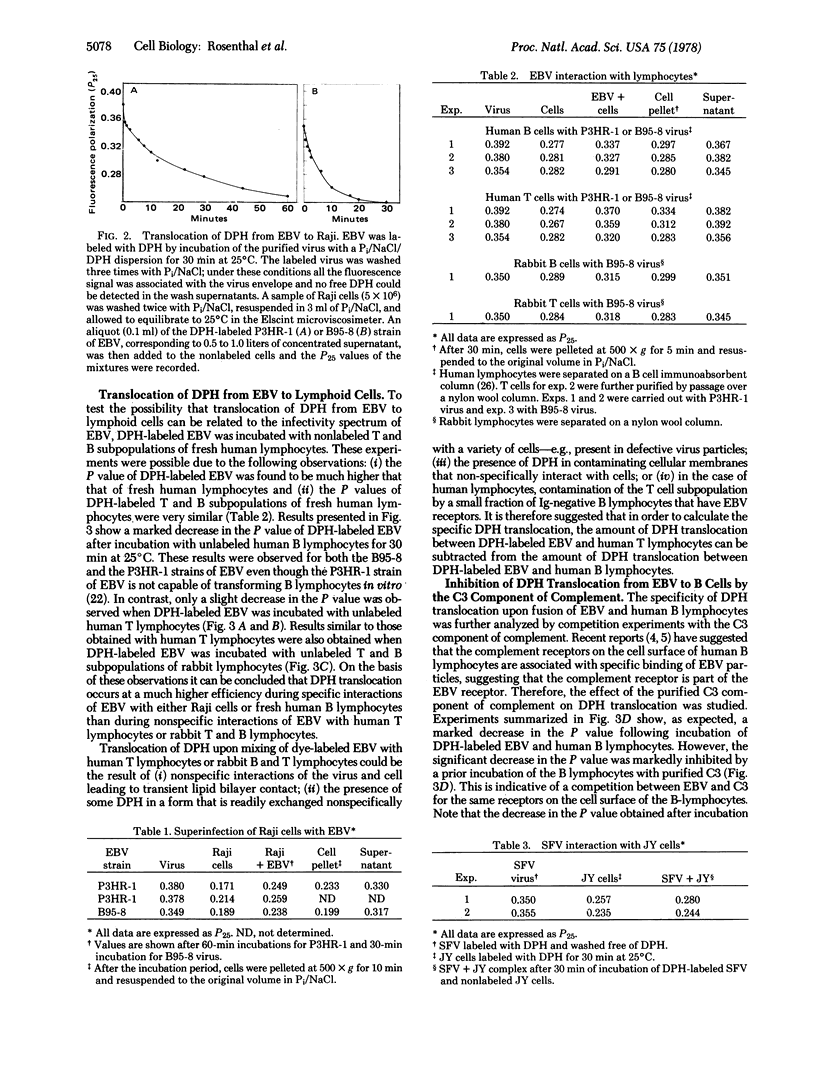
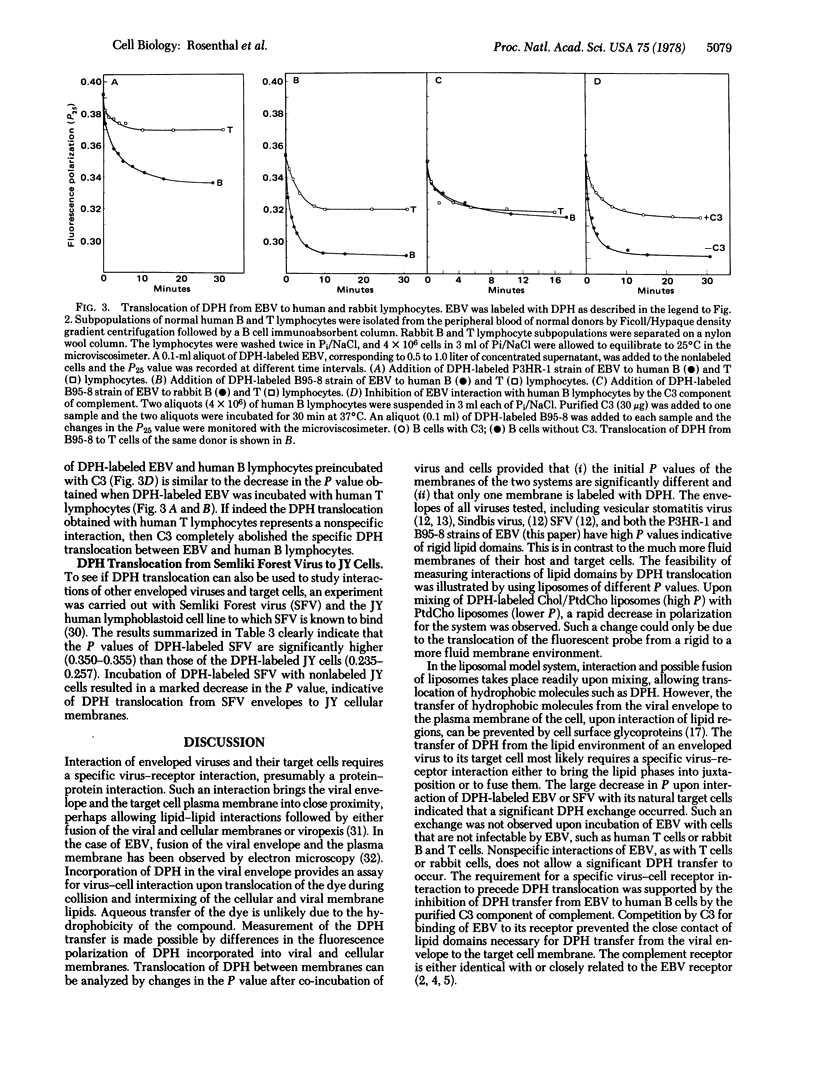
Translocation of the hydrocarbon fluorescent probe diphenylhexatriene (DPH) between membranes was studied by fluorescence polarization (P) analysis. First, using a model system, the high P value (0.324) of DPH-labeled cholesterol/phosphatidylcholine liposomes and the low P value (0.157) of DPH-labeled phosphatidylcholine liposomes allowed detection of DPH translocation between interacting liposomes. This was monitored by the change in P in either direction. Early events during cell-virus interactions were similarly studied by monitoring DPH translocation. The P value of DPH-labeled Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) was significantly higher (0.350-0.392) than the P value of DPH-labeled lymphoid cells (0.238-0.289). Hence, DPH translocation could be detected by changes in P following incubation of DPH-labeled EBV and nonlabeled cells. A marked decrease in P was observed after incubation of DPH-labeled EBV with either nonlabeled lymphoblastoid Raji cells or fresh human B lymphocytes. However, only a slight decrease in P was obtained when DPH-labeled EBV was incubated with either nonlabeled fresh human T lymphocytes or fresh T or B rabbit lymphocytes. Moreover, incubation of fresh human B lymphocytes with the purified C3 component of complement (a putative inhibitor for the EBV receptor) prior to the addition of DPH-labeled EBV abolished the observed decrease in the P value. Most of these experiments were carried out with both the P3HR-1 and the B95-8 strains of EBV. DPH translocation, as determined by fluorescence polarization analysis, is, therefore, measuring some early event during interaction of this enveloped virus and mammalian cells. The potential applicability of this technique to other viruses is illustrated by an experiment with Semliki Forest virus.
Keywords: liposomes, lymphocyte membranes, diphenylhexatriene, fluorescence polarization
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berke G., Tzur R., Inbar M. Changes in fluorescence polarization of a membrane probe during lymphocyte-target cell interaction. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1378–1384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collard J. G., de Wildt A., Inbar M. Translocation of a fluorescent lipid probe between contacting cells: evidence for membrane lipid interactions. FEBS Lett. 1978 Jun 1;90(1):24–28. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80290-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dales S. Early events in cell-animal virus interactions. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Jun;37(2):103–135. doi: 10.1128/br.37.2.103-135.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolyniuk M., Pritchett R., Kieff E. Proteins of Epstein-Barr virus. I. Analysis of the polypeptides of purified enveloped Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1976 Mar;17(3):935–949. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.3.935-949.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein M. A., Achong B. G. Recent progress in Epstein-Barr virus research. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:421–445. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.002225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs P., Parola A., Robbins P. W., Blout E. R. Fluorescence polarization and viscosities of membrane lipids of 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3351–3354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAGERMAN J. S., GOULD R. G. The in vitro interchange of cholesterol between plasma and red cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1951 Oct;78(1):329–332. doi: 10.3181/00379727-78-19064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Morein B., Fries E., Simons K., Robinson P., Schirrmacher V., Terhorst C., Strominger J. L. Human (HLA-A and HLA-B) and murine (H-2K and H-2D) histocompatibility antigens are cell surface receptors for Semliki Forest virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3846–3850. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Söderlund H. Stepwise dissociation of the Semliki Forest Virus membrane with trition X-100. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 May 11;307(2):287–300. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90096-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inbar M., Ben-Bassat H. Fluidity difference in the surface membrane lipid core of human lymphoblastoid and lymphoma cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1976 Sep 15;18(3):293–297. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910180305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inbar M., Shinitzky M. Cholesterol as a bioregulator in the development and inhibition of leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4229–4231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inbar M., Yuli I., Raz A. Contact-mediated changes in the fluidity of membrane lipids in normal and malignant transformed mammalian fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Mar 15;105(2):325–335. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90131-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M., Klein G. Surface markers on human B and T lymphocytes. II. Presence of Epstein-Barr virus receptors on B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1973 Dec 1;138(6):1365–1378. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.6.1365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenard J., Rothman J. E. Transbilayer distribution and movement of cholesterol and phospholipid in the membrane of influenza virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):391–395. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menezes J., Seigneurin J. M., Patel P., Bourkas A., Lenoir G. Presence of Epstein-Barr virus receptors, but absence of virus penetration, in cells of an Epstein-Barr virus genome-negative human lymphoblastoid T line (Molt 4). J Virol. 1977 Jun;22(3):816–821. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.3.816-821.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Robinson J., Heston L., Lipman M. Differences between laboratory strains of Epstein-Barr virus based on immortalization, abortive infection, and interference. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4006–4010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore N. F., Barenholz Y., Wagner R. R. Microviscosity of togavirus membranes studied by fluorescence depolarization: influence of envelope proteins and the host cell. J Virol. 1976 Jul;19(1):126–135. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.1.126-135.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pessin J. E., Salter D. W., Glaser M. Use of a fluorescent probe to compare the plasma membrane properties in normal and transformed cells. Evaluation of the interference by triacylglycerols and alkyldiacylglycerols. Biochemistry. 1978 May 16;17(10):1997–2004. doi: 10.1021/bi00603a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petitou M., Tuy F., Rosenfeld C., Mishal Z., Paintrand M., Jasnin C., Mathe G., Inbar M. Decreased microviscosity of membrane lipids in leukemic cells: two possible mechanisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2306–2310. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poznansky M. J., Lange Y. Transbilayer movement of cholesterol in phospholipid vesicles under equilibrium and non-equilibrium conditions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jan 19;506(2):256–264. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90396-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seigneurin J. M., Vuillaume M., Lenoir G., De-Thé G. Replication of Epstein-Barr virus: ultrastructural and immunofluorescent studies of P3HR1-superinfected Raji cells. J Virol. 1977 Dec;24(3):836–845. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.3.836-845.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinitzky M., Inbar M. Difference in microviscosity induced by different cholesterol levels in the surface membrane lipid layer of normal lymphocytes and malignant lymphoma cells. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jan 5;85(4):603–615. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90318-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinitzky M., Inbar M. Microviscosity parameters and protein mobility in biological membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 16;433(1):133–149. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90183-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubbs G. W., Litman B. J. Microviscosity of the hydrocarbon region of the bovine retinal rod outer segment disk membrane determined by fluorescent probe measurements. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 29;15(13):2766–2772. doi: 10.1021/bi00658a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeagle P. L., Martin R. B., Lala A. K., Lin H. K., Bloch K. Differential effects of cholesterol and lanosterol on artificial membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4924–4926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yefenof E., Klein G., Jondal M., Oldstone M. B. Surface markers on human B and T-lymphocytes. IX. Two-color immunofluorescence studies on the association between ebv receptors and complement receptors on the surface of lymphoid cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1976 Jun 15;17(6):693–700. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yefenof E., Klein G. Membrane receptor stripping confirms the association between EBV receptors and complement receptors on the surface of human B lymphoma lines. Int J Cancer. 1977 Sep 15;20(3):347–352. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910200305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Laat S. W., van der Saag P. T., Shinitzky M. Microviscosity modulation during the cell cycle of neuroblastoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4458–4461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



