Abstract
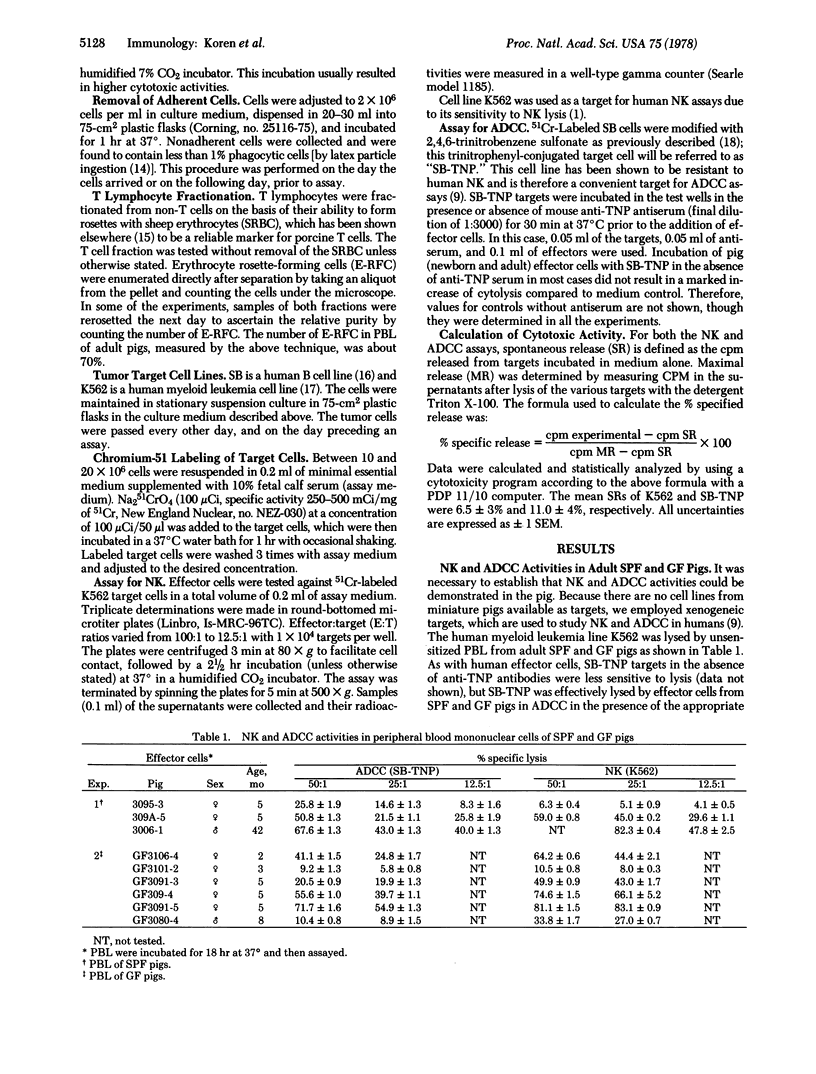
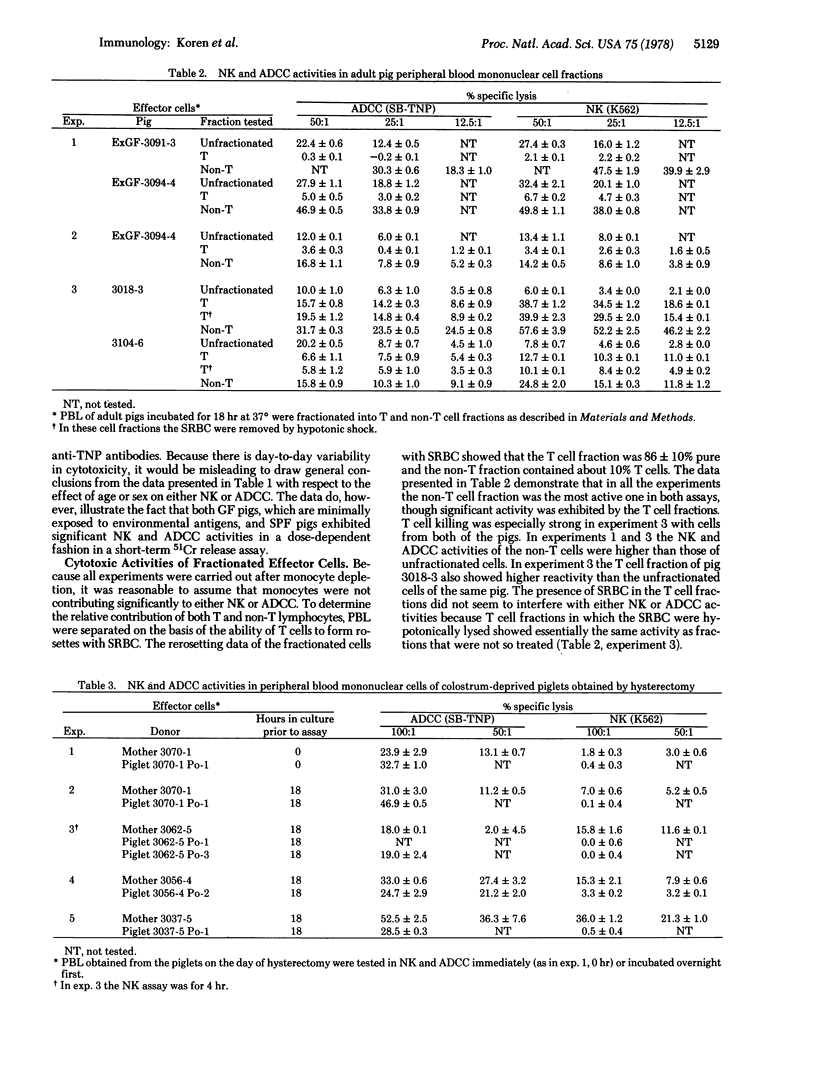
Peripheral blood lymphocytes from Minnesota miniature pigs were tested for natural killing (NK) and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) in a 2- to 4-hr 51Cr release assay against human myeloid and lymphoid tumor target cells. Adult specific pathogen-free and germfree animals exhibited normal levels of activity in both assays. In addition, the NK and ADCC activities of peripheral blood lymphocytes from colostrum-deprived newborn piglets were examined. These animals were obtained by hysterectomy and previously shown to be immunologically "virgin." We found that these newborn piglets exhibited normal ADCC but lacked NK activity. The differences in the ontogeny of the two activities suggest that they are distinct. Preliminary effector cell characterization studies suggest that: (i) NK and ADCC in the pig are physically not separable; (ii) the majority of the cytotoxic activity on a cell-per-cell basis is mediated by the non-T lymphocyte fraction; and (iii) the rosetted T cells, which account for about 60% of the total pig peripheral blood lymphocytes, have low but demonstrable cytotoxic activity as well.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akira D., Takasugi M. Loss of specific natural cell-mediated cytotoxicity with absorption of natural antibodies from serum. Int J Cancer. 1977 Jun 15;19(6):747–755. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910190603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baines M. G., Pross H. F., Millar K. G. Spontaneous human lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity against tumor target cells. IV. The suppressive effect of normal pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1978 Apr 1;130(7):741–744. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(78)90001-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakacs T., Gergely P., Klein E. Characterization of cytotoxic human lymphocyte subpopulations: the role of Fc-receptor-carrying cells. Cell Immunol. 1977 Aug;32(2):317–328. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90208-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haller O., Hansson M., Kiessling R., Wigzell H. Role of non-conventional natural killer cells in resistance against syngeneic tumour cells in vivo. Nature. 1977 Dec 15;270(5638):609–611. doi: 10.1038/270609a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M., Pross H. Surface markers on human b and t lymphocytes. VI. Cytotoxicity against cell lines as a functional marker for lymphocyte subpopulations. Int J Cancer. 1975 Apr 15;15(4):596–605. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910150409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay H. D., Bonnard G. D., West W. H., Herberman R. B. A functional comparison of human Fc-receptor-bearing lymphocytes active in natural cytotoxicity and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1977 Jun;118(6):2058–2066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiessling R., Hochman P. S., Haller O., Shearer G. M., Wigzell H., Cudkowicz G. Evidence for a similar or common mechanism for natural killer cell activity and resistance to hemopoietic grafts. Eur J Immunol. 1977 Sep;7(9):655–663. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830070915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiessling R., Klein E., Pross H., Wigzell H. "Natural" killer cells in the mouse. II. Cytotoxic cells with specificity for mouse Moloney leukemia cells. Characteristics of the killer cell. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Feb;5(2):117–121. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiessling R., Klein E., Wigzell H. "Natural" killer cells in the mouse. I. Cytotoxic cells with specificity for mouse Moloney leukemia cells. Specificity and distribution according to genotype. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Feb;5(2):112–117. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. B., Bradley S. G., Watson D. W. Ontogeny of the immune response. I. Development of immunoglobulins in germfree and conventional colostrum-deprived piglets. J Immunol. 1966 Jul;97(1):52–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. B. Developmental immunity in the piglet. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1975;11(1):549–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. B., Watson D. W. Role of antibodies in reactions to gram-negative bacterial endotoxins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jun 30;133(2):727–745. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb52402.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiuchi M., Takasugi M. The nonselective cytotoxic cell (N cell). J Natl Cancer Inst. 1976 Mar;56(3):575–582. doi: 10.1093/jnci/56.3.575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koide Y., Takasugi M. Distinct target determinants on two lymphoblastoid lines derived from the same individual1. J Immunol. 1976 Oct;117(4):1197–1202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koren H. S., Amos D. B., Buckley R. H. Natural killing in immunodeficient patients. J Immunol. 1978 Mar;120(3):796–799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozzio C. B., Lozzio B. B. Cytotoxicity of a factor isolated from human spleen. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Feb;50(2):535–538. doi: 10.1093/jnci/50.2.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. L., Bundy B. M., Strober W. Spontaneous cell-mediated cytotoxicity by human peripheral blood lymphocytes in vitro. J Immunol. 1977 Oct;119(4):1401–1405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunn M. E., Djeu J. Y., Glaser M., Lavrin D. H., Herberman R. B. Natural cytotoxic reactivity of rat lymphocytes against syngeneic Gross virus-induced lymphoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1976 Feb;56(2):393–399. doi: 10.1093/jnci/56.2.393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pape G. R., Troye M., Perlmann P. Characterization of cytolytic effector cells in peripheral blood of healthy individuals and cancer patients. II. Cytotoxicity to allogeneic or autochthonous tumor cells in tissue culture. J Immunol. 1977 Jun;118(6):1925–1930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack S. B., Kraft D. S. Effector cells which mediate antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. II. Ontogeny of effector activity in murine spleen. Cell Immunol. 1977 Nov;34(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90223-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph P., Nakoinz I., Cohn M. Antibody dependent cellular immunity in newborn mice. Nat New Biol. 1973 Oct 3;245(144):157–158. doi: 10.1038/newbio245157a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanal S. O., Buckley R. H. Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity in primary immunodeficiency diseases and with normal leukocyte subpopulations. Importance of the type of target. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jan;61(1):1–10. doi: 10.1172/JCI108907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setcavage T. M., Kim Y. B. Variability of the immunological state of germfree colostrum-deprived Minnesota miniature piglets. Infect Immun. 1976 Feb;13(2):600–607. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.2.600-607.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shellam G. R., Hogg N. Gross-virus-induced lymphoma in the rat. IV. Cytotoxic cells in normal rats. Int J Cancer. 1977 Feb 15;19(2):212–224. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910190211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



