Abstract
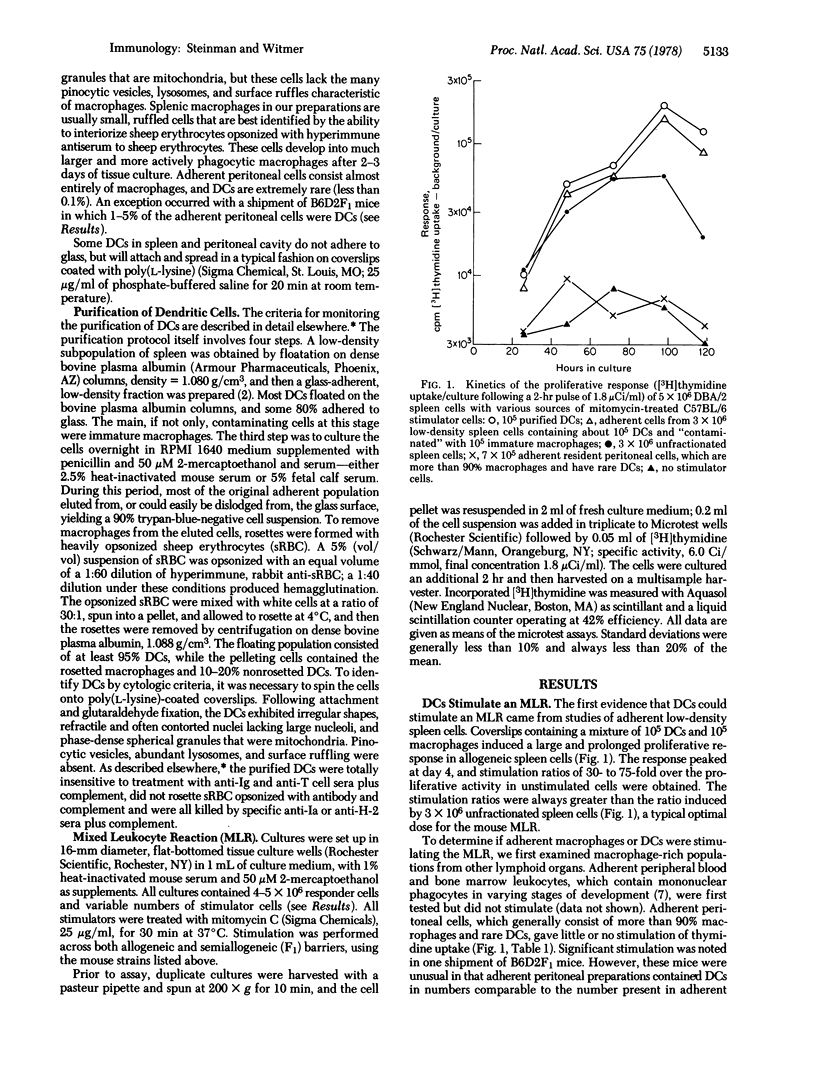
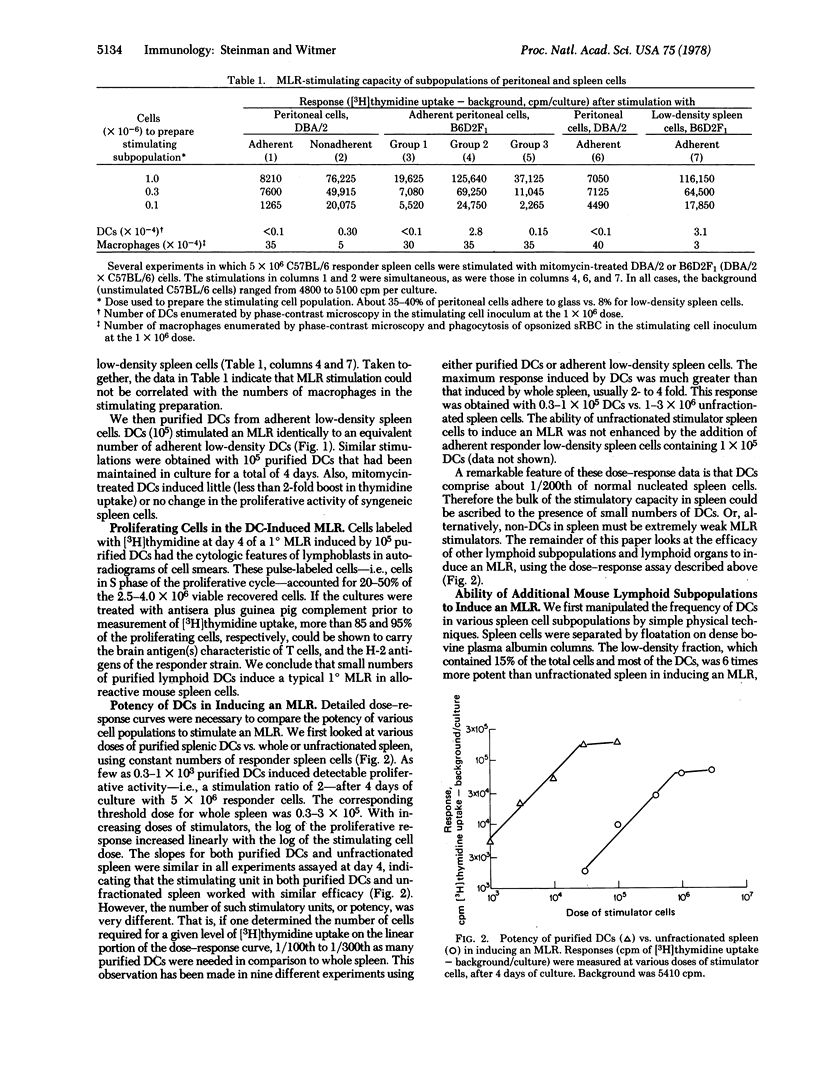
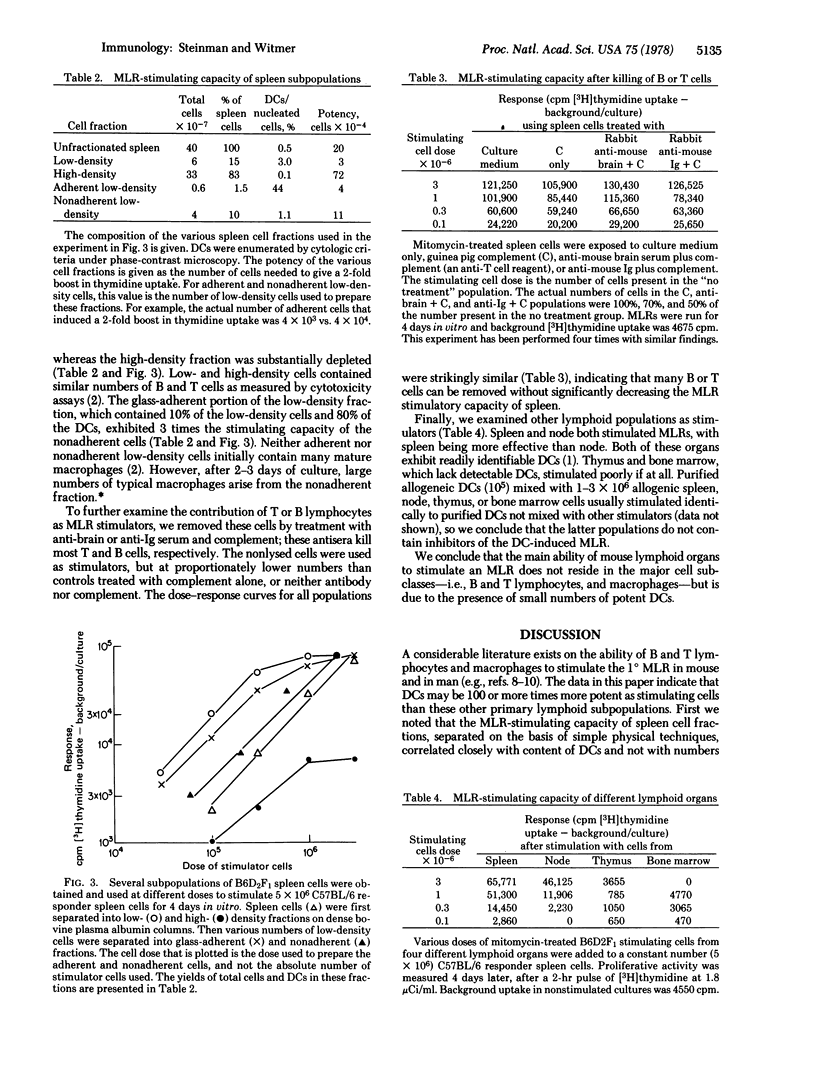
Dendrite cells (DCs) are a new cell type initially identified in mouse lymphoid organs. Recently, DCs have been purified from mouse spleen. This paper demonstrates a functional role of DCs: they are potent stimulators of the primary mixed leukocytes reaction (MLR). As few as 300-1000 DCs doubled the proliferative activity of 5 X 10(6) allogeneic responder spleen cells, while 0.3-1.0 X 10(5) DCs induced a maximal stimulation of 30- to 80-fold. Between these extremes, the log of the MLR response increased linearly with the log of DC numbers. This dose-response assay was then used to compare the potency of purified DCs with that of other heterogeneous lymphoid populations, many of which gave dose-response curves with similar slopes. The potency of purified DCs as MLR stimulators was 100-300 times greater than that of unfractionated spleen cells. When spleen cells were fractionated by simple physical techniques, MLR-stimulating capacity in the subpopulations correlated closely with DC numbers. Removal of splenic B or T lymphocytes, by anti-immunoglobulin or anti-brain serum plus complement, did not reduce MLR-stimulating capacity. Finally, several populations, enriched in mononuclear phagocytes but lacking in DCs, stimulated weakly if at all. We conclude that DCs are a potent stimulating cell and are at least 100 times more effective than other major cell subclasses--i.e., B and T lymphocytes and macrophages.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bach F. H., Bach M. L., Sondel P. M. Differential function of major histocompatibility complex antigens in T-lymphocyte activation. Nature. 1976 Jan 29;259(5541):273–281. doi: 10.1038/259273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach F. H., Widmer M. B., Bach M. L., Klein J. Serologically defined and lymphocyte-defined components of the major histocompatibility complex in the mouse. J Exp Med. 1972 Dec 1;136(6):1430–1444. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.6.1430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billingham R. E. The passenger cell concept in transplantation immunology. Cell Immunol. 1971 Feb;2(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(71)90022-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor H., Boyse E. A. Functional subclasses of T lymphocytes bearing different Ly antigens. II. Cooperation between subclasses of Ly+ cells in the generation of killer activity. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1390–1399. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fathman C. G., Handwerger B. S., Sachs D. H. Evidence for a role of Ir-associated alloantigens in mixed lymphocyte culture stimulation. J Exp Med. 1974 Sep 1;140(3):853–858. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.3.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greineder D. K., Rosenthal A. S. Macrophage activation of allogeneic lymphocyte proliferation in the guinea pig mixed leukocyte culture. J Immunol. 1975 May;114(5):1541–1547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz D. H., Graves M., Dorf M. E., Dimuzio H., Benacerraf B. Cell interactions between histoincompatible T and B lymphocytes. VII. Cooperative responses between lymphocytes are controlled by genes in the I region of the H-2 complex. J Exp Med. 1975 Jan 1;141(1):263–268. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.1.263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz D. H., Unanue E. R. Critical role of determinant presentation in the induction of specific responses in immunocompetent lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1973 Apr 1;137(4):967–990. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.4.967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal A. S., Shevach E. M. Function of macrophages in antigen recognition by guinea pig T lymphocytes. I. Requirement for histocompatible macrophages and lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1973 Nov 1;138(5):1194–1212. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. H., Yano A., Paul W. E. Interaction between antigen-presenting cells and primed T lymphocytes: an assessment of Ir gene expression in the antigen-presenting cell. Immunol Rev. 1978;40:153–180. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1978.tb00405.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shevach E. M., Rosenthal A. S. Function of macrophages in antigen recognition by guinea pig T lymphocytes. II. Role of the macrophage in the regulation of genetic control of the immune response. J Exp Med. 1973 Nov 1;138(5):1213–1229. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.5.1213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson E. Stimulation of mixed lymphocyte cultures and cytotoxic responses: evidence that T cells express SD but not LD antigens, whereas B cells express both. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Jul;5(7):456–461. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer A., Cowing C., Hathcock K. S., Dickler H. B., Hodes R. J. Cellular and genetic control of antibody responses in vitro. III. Immune response gene regulation of accessory cell function. J Exp Med. 1978 Jun 1;147(6):1611–1620. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.6.1611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M., Adams J. C., Cohn Z. A. Identification of a novel cell type in peripheral lymphoid organs of mice. IV. Identification and distribution in mouse spleen. J Exp Med. 1975 Apr 1;141(4):804–820. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M., Blumencranz S. J., Machtinger B. G., Fried J., Cohn Z. A. Mouse spleen lymphoblasts generated in vitro. Their replication and differentiation in vitro. J Exp Med. 1978 Feb 1;147(2):297–315. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.2.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M., Cohn Z. A. Identification of a novel cell type in peripheral lymphoid organs of mice. I. Morphology, quantitation, tissue distribution. J Exp Med. 1973 May 1;137(5):1142–1162. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.5.1142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M., Cohn Z. A. Identification of a novel cell type in peripheral lymphoid organs of mice. II. Functional properties in vitro. J Exp Med. 1974 Feb 1;139(2):380–397. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.2.380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M., Lustig D. S., Cohn Z. A. Identification of a novel cell type in peripheral lymphoid organs of mice. 3. Functional properties in vivo. J Exp Med. 1974 Jun 1;139(6):1431–1445. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.6.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M., Machtinger B. G., Fried J., Cohn Z. A. Mouse spleen lymphoblasts generated in vitro. Recovery in high yield and purity after floatation in dense bovine plasma albumin solutions. J Exp Med. 1978 Feb 1;147(2):279–296. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.2.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Doherty P. C. H-2 compatability requirement for T-cell-mediated lysis of target cells infected with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. Different cytotoxic T-cell specificities are associated with structures coded for in H-2K or H-2D;. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1427–1436. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Furth R., Hirsch J. G., Fedorko M. E. Morphology and peroxidase cytochemistry of mouse promonocytes, monocytes, and macrophages. J Exp Med. 1970 Oct 1;132(4):794–812. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.4.794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



