Abstract
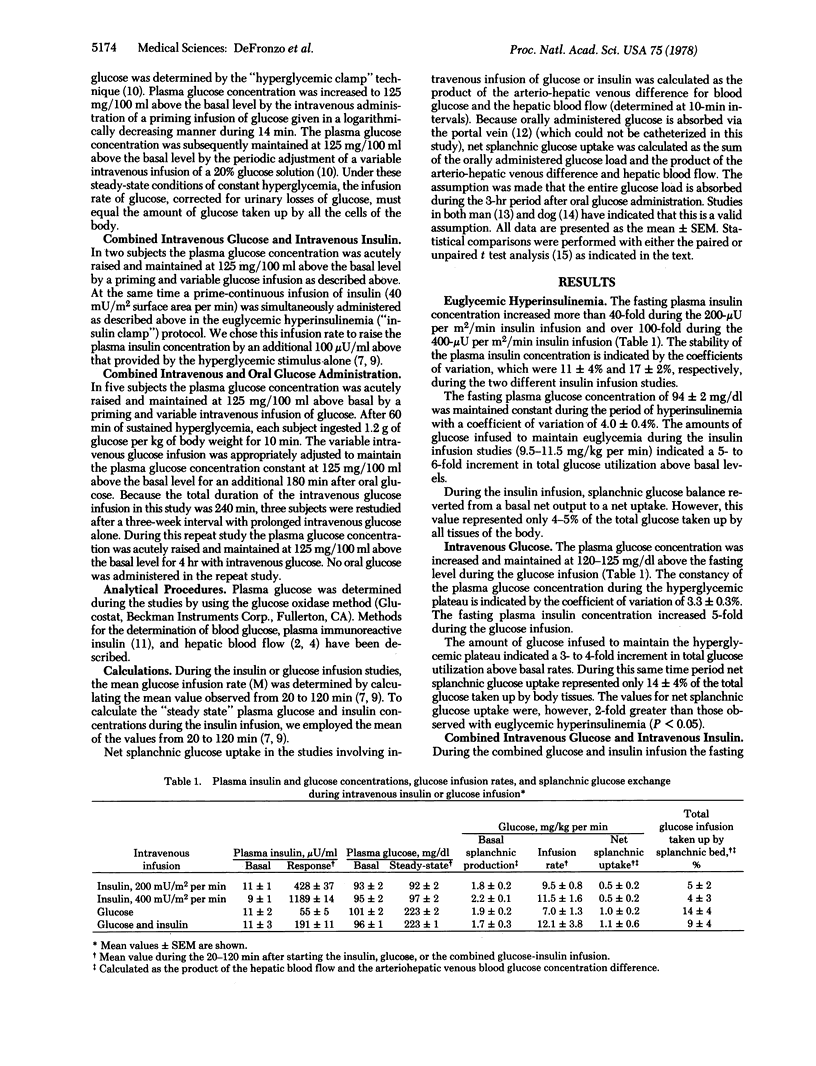
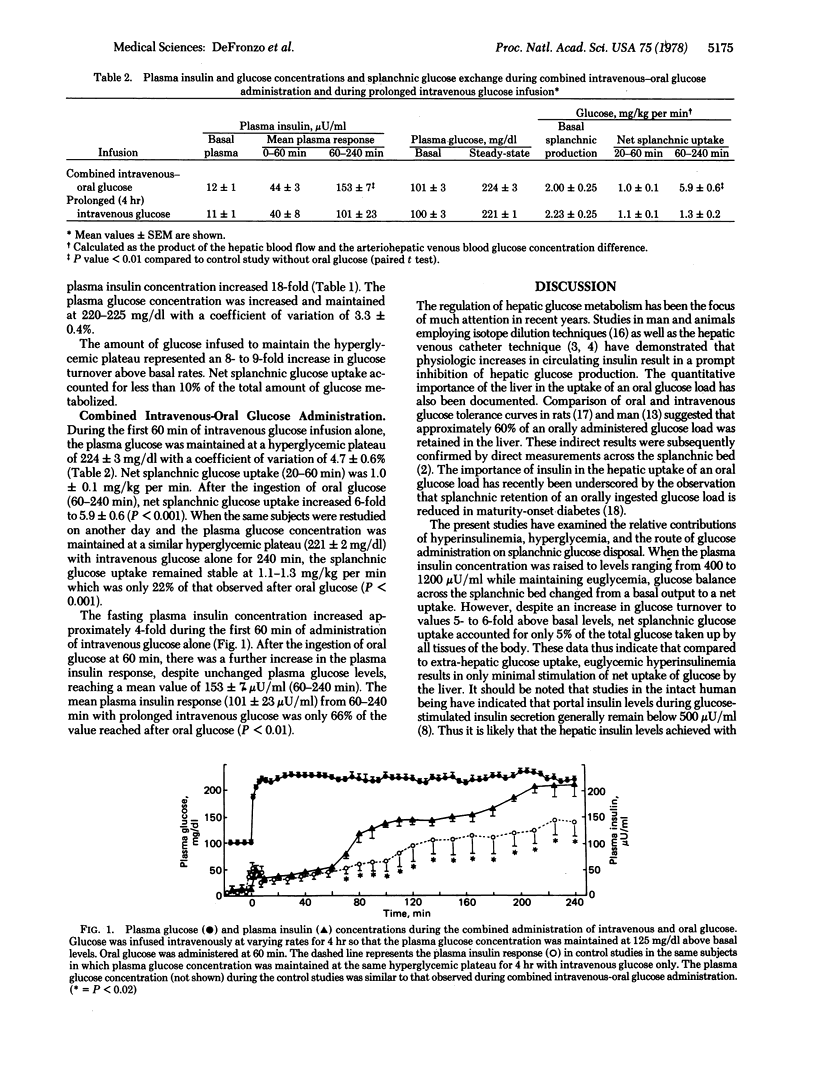
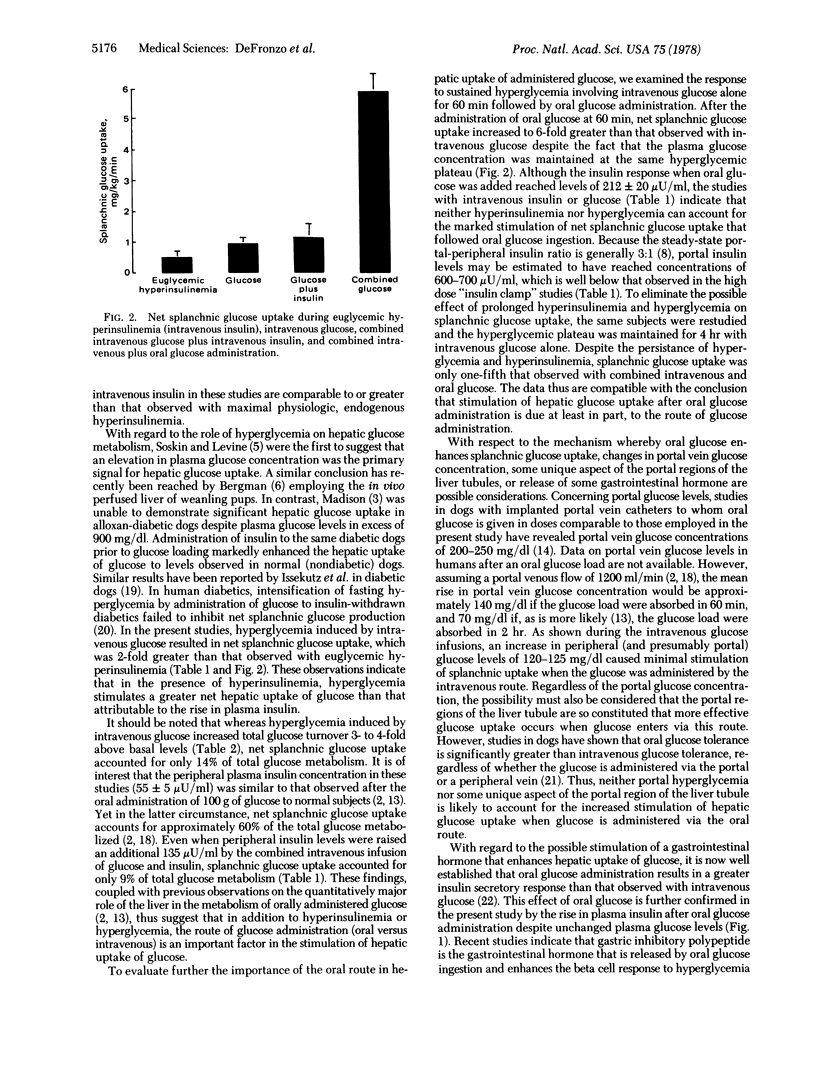
The effects of hyperinsulinemia, hyperglycemia, and the route of glucose administration on total glucose utilization and on net splanchnic glucose exchange were studied in 20 normal volunteers with the hepatic venous catheter technique. Euglycemic hyperinsulinemia [induced by a priming plus continuous infusion of insulin resulting in plasma insulin levels of 400-1200 μunits (international)/ml and a variable glucose infusion] caused a 5- to 6-fold increase above basal in total glucose turnover. However, net splanchnic glucose uptake (0.5 ± 0.2 mg/kg per min) accounted for only 4-5% of total glucose utilization. When hyperglycemia (223 ± 1 mg/dl) was induced in addition to hyperinsulinemia by the intravenous infusion of glucose, splanchnic glucose uptake increased 100% to 1.0-1.1 mg/kg per min but was still responsible for only 10-14% of total glucose utilization. In other studies hyperglycemia (223 ± 2 mg/dl) was maintained constant by a variable intravenous infusion of glucose for 4 hr and oral glucose (1.2 gm/kg) was administered at 1 hr. After the oral glucose, net splanchnic glucose uptake increased to values 6-fold higher than with intravenous glucose despite unchanged plasma glucose levels and plasma insulin concentrations well below those observed in the studies with euglycemic hyperinsulinemia. The results indicate that hyperinsulinemia or hyperglycemia induced by intravenous infusion of glucose or insulin causes minimal net uptake of glucose by the splanchnic bed despite marked stimulation of total glucose turnover. In contrast, administration of glucose by the oral route has a marked stimulatory effect on net splanchnic glucose uptake. These findings suggest that orally consumed glucose causes the release of a gastrointestinal factor that enhances insulin-mediated glucose uptake by the liver.
Keywords: liver, glucose uptake, gut factors
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergman R. N. Integrated control of hepatic glucose metabolism. Fed Proc. 1977 Feb;36(2):265–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackard W. G., Nelson N. C. Portal and peripheral vein immunoreactive insulin concentrations before and after glucose infusion. Diabetes. 1970 May;19(5):302–306. doi: 10.2337/diab.19.5.302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bondy P. K., James D. F., Farrar B. W. STUDIES OF THE ROLE OF THE LIVER IN HUMAN CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM BY THE VENOUS CATHETER TECHNIC. I. NORMAL SUBJECTS UNDER FASTING CONDITIONS AND FOLLOWING THE INJECTION OF GLUCOSE. J Clin Invest. 1949 Mar;28(2):238–244. doi: 10.1172/JCI102065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Soman V., Sherwin R. S., Hendler R., Felig P. Insulin binding to monocytes and insulin action in human obesity, starvation, and refeeding. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jul;62(1):204–213. doi: 10.1172/JCI109108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- DeFronzo R. A., Tobin J. D., Rowe J. W., Andres R. Glucose intolerance in uremia. Quantification of pancreatic beta cell sensitivity to glucose and tissue sensitivity to insulin. J Clin Invest. 1978 Aug;62(2):425–435. doi: 10.1172/JCI109144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felig P., Wahren J., Hendler R. Influence of maturity-onset diabetes on splanchnic glucose balance after oral glucose ingestion. Diabetes. 1978 Feb;27(2):121–126. doi: 10.2337/diab.27.2.121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felig P., Wahren J., Hendler R. Influence of oral glucose ingestion on splanchnic glucose and gluconeogenic substrate metabolism in man. Diabetes. 1975 May;24(5):468–475. doi: 10.2337/diab.24.5.468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felig P., Wahren J. Influence of endogenous insulin secretion on splanchnic glucose and amino acid metabolism in man. J Clin Invest. 1971 Aug;50(8):1702–1711. doi: 10.1172/JCI106659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issekutz B., Jr, Issekutz T. B., Elahi D., Borkow I. Effect of insulin infusions on the glucose kinetics in alloxan-steptozotocin diabetic dogs. Diabetologia. 1974 Aug;10(4):323–328. doi: 10.1007/BF02627734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lickley H. L., Chisholm D. J., Rabinovitch A., Wexler M., Dupre J. Effects of portacaval anastomosis on glucose tolerance in the dog: evidence of an interaction between the gut and the liver in oral glucose dosposal. Metabolism. 1975 Oct;24(10):1157–1168. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(75)90152-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison L. L. Role of insulin in the hepatic handling of glucose. Arch Intern Med. 1969 Mar;123(3):284–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pederson R. A., Schubert H. E., Brown J. C. Gastric inhibitory polypeptide. Its physiologic release and insulinotropic action in the dog. Diabetes. 1975 Dec;24(12):1050–1056. doi: 10.2337/diab.24.12.1050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perley M. J., Kipnis D. M. Plasma insulin responses to oral and intravenous glucose: studies in normal and diabetic sujbjects. J Clin Invest. 1967 Dec;46(12):1954–1962. doi: 10.1172/JCI105685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosselin G., Assan R., Yalow R. S., Berson S. A. Separation of antibody-bound and unbound peptide hormones labelled with iodine-131 by talcum powder and precipitated silica. Nature. 1966 Oct 22;212(5060):355–357. doi: 10.1038/212355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCOW R. O., CORNFIELD J. Quantitative relations between the oral and intravenous glucose tolerance curves. Am J Physiol. 1954 Dec;179(3):435–438. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1954.179.3.435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHOEMAKER W. C., YANOF H. M., TURK L. N., 3rd, WILSON T. H. Glucose and fructose absorption in the unanesthetized dog. Gastroenterology. 1963 May;44:654–663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEELE R., BISHOP J. S., DUNN A., ALTSZULER N., RATHBEB I., DEBODO R. C. INHIBITION BY INSULIN OF HEPATIC GLUCOSE PRODUCTION IN THE NORMAL DOG. Am J Physiol. 1965 Feb;208:301–306. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.208.2.301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwin R. S., Kramer K. J., Tobin J. D., Insel P. A., Liljenquist J. E., Berman M., Andres R. A model of the kinetics of insulin in man. J Clin Invest. 1974 May;53(5):1481–1492. doi: 10.1172/JCI107697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahren J., Felig P., Cerasi E., Luft R. Splanchnic and peripheral glucose and amino acid metabolism in diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jul;51(7):1870–1878. doi: 10.1172/JCI106989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



