Abstract
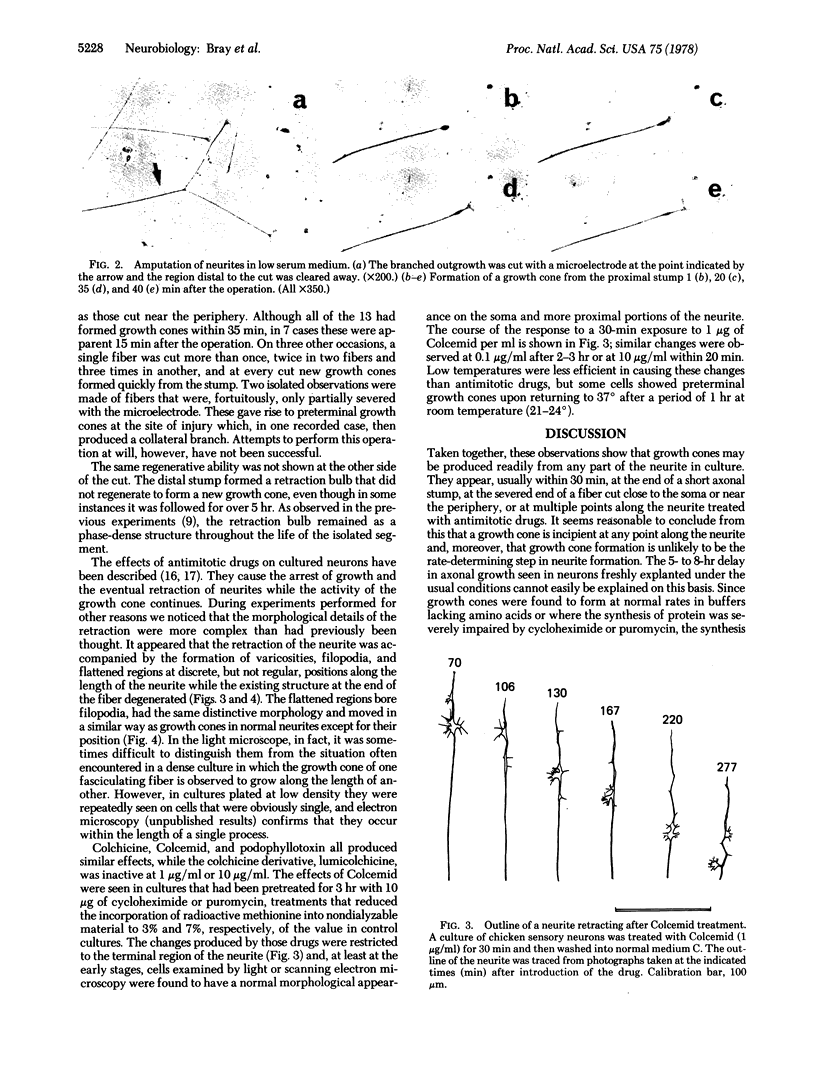
Three experimental situations have been found in which cultured sensory neurons from embryonic chicken will form growth cones from positions along the length of the neurite. If the neurons are dissected with a remaining short axonal stump and plated into serum-free medium, they can form a morphologically normal growth cone from the stump within 15 min, even in the presence of cycloheximide or puromycin. When neurites growing in culture media with low levels of serum are cut at any point with microneedles, growth cones are produced quickly from the amputated stump, usually within 20 min. Treatment of growing neurons with low concentrations of colchicine, Colcemid, or podophyllotoxin results in the progressive appearance of lateral filopodia and regions of flattened cytoplasm that closely resemble growth cones except for their preterminal positions. These observations show that the potential to form growth cones is distributed throughout the neuron and suggest that this normally repressed in some way by the neuronal microtubules.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albrecht-Buehler G., Goldman R. D. Microspike-mediated particle transport towards the cell body during early spreading of 3T3 cells. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Feb;97(2):329–339. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90624-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray D. Branching patterns of individual sympathetic neurons in culture. J Cell Biol. 1973 Mar;56(3):702–712. doi: 10.1083/jcb.56.3.702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray D. Surface movements during the growth of single explanted neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Apr;65(4):905–910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.4.905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunge M. B. Fine structure of nerve fibers and growth cones of isolated sympathetic neurons in culture. J Cell Biol. 1973 Mar;56(3):713–735. doi: 10.1083/jcb.56.3.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunge M. B. Initial endocytosis of perioxidase or ferritin by growth cones of cultured nerve cells. J Neurocytol. 1977 Aug;6(4):407–439. doi: 10.1007/BF01178226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels M. P. Colchicine inhibition of nerve fiber formation in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1972 Apr;53(1):164–176. doi: 10.1083/jcb.53.1.164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDDS M. V., Jr Collateral nerve regeneration. Q Rev Biol. 1953 Sep;28(3):260–276. doi: 10.1086/399699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVI-MONTALCINI R., ANGELETTI P. U. Essential role of the nerve growth factor in the survival and maintenance of dissociated sensory and sympathetic embryonic nerve cells in vitro. Dev Biol. 1963 Mar;6:653–659. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(63)90149-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letourneau P. C. Cell-to-substratum adhesion and guidance of axonal elongation. Dev Biol. 1975 May;44(1):92–101. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(75)90379-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letourneau P. C. Possible roles for cell-to-substratum adhesion in neuronal morphogenesis. Dev Biol. 1975 May;44(1):77–91. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(75)90378-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludueña M. A. Nerve cell differentiation in vitro. Dev Biol. 1973 Aug;33(2):268–284. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(73)90137-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludueña M. A. The growth of spinal ganglion neurons in serum-free medium. Dev Biol. 1973 Aug;33(2):470–476. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(73)90152-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morest D. K. The differentiation of cerebral dendrites: A study of the post-migratory neuroblast in the medial nucleus of the trapezoid body. Z Anat Entwicklungsgesch. 1969;128(4):271–289. doi: 10.1007/BF00522528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAKAI J. Dissociated dorsal root ganglia in tissue culture. Am J Anat. 1956 Jul;99(1):81–129. doi: 10.1002/aja.1000990105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrick J., Heinemann S., Schubert D. Biology of cultured nerve and muscle. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1978;1:417–443. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.01.030178.002221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulson J. C., McClure W. O. Microtubules and axoplasmic transport. Inhibition of transport by podophyllotoxin: an interaction with microtubule protein. J Cell Biol. 1975 Nov;67(2PT1):461–467. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.2.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajaraman R., Rounds D. E., Yen S. P., Rembaum A. A scanning electron microscope study of cell adhesion and spreading in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Oct;88(2):327–339. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90248-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Bray D. Movement and extension of isolated growth cones. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Jan;104(1):55–62. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90068-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varon S., Nomura J., Shooter E. M. Subunit structure of a high-molecular-weight form of the nerve growth factor from mouse submaxillary gland. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jun;57(6):1782–1789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.6.1782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasiliev J. M., Gelfand I. M., Domnina L. V., Ivanova O. Y., Komm S. G., Olshevskaja L. V. Effect of colcemid on the locomotory behaviour of fibroblasts. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1970 Nov;24(3):625–640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughn J. E., Peters A. Electron microscopy of the early postnatal development of fibrous astrocytes. Am J Anat. 1967 Jul;121(1):131–152. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001210109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson L., Friedkin M. The biochemical events of mitosis. I. Synthesis and properties of colchicine labeled with tritium in its acetyl moiety. Biochemistry. 1966 Jul;5(7):2463–2468. doi: 10.1021/bi00871a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M., Spooner B. S., Wessells N. K. Axon growth: roles of microfilaments and microtubules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Aug;66(4):1206–1212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.4.1206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M., Spooner B. S., Wessells N. K. Ultrastructure and function of growth cones and axons of cultured nerve cells. J Cell Biol. 1971 Jun;49(3):614–635. doi: 10.1083/jcb.49.3.614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]