Abstract
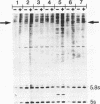
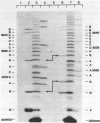
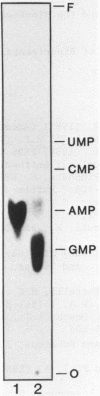
We have surveyed 14 different toxic and nontoxic ribosome-inactivating proteins from plants for the ability to act on the RNA of the eucaryotic 60 S ribosomal subunit. All of these proteins act to introduce a specific modification into 26-28 S RNA which renders the RNA sensitive to cleavage by aniline. Sequence analysis of the 5'-termini of the fragments produced by ricin and saporin following aniline cleavage indicate that both proteins possess identical specificity. Our observations support the conclusion of Endo and Tsurugi (J. Biol. Chem. 262, 8128-8130, 1987) that ricin is a specific N-glycosidase and we have located the site of this cleavage by direct sequence analysis. Our results further suggest that all plant ribosome-inactivating proteins function as specific N-glycosidases with the same specificity.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banerjee A. K. 5'-terminal cap structure in eucaryotic messenger ribonucleic acids. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Jun;44(2):175–205. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.2.175-205.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbieri L., Zamboni M., Lorenzoni E., Montanaro L., Sperti S., Stirpe F. Inhibition of protein synthesis in vitro by proteins from the seeds of Momordica charantia (bitter pear melon). Biochem J. 1980 Feb 15;186(2):443–452. doi: 10.1042/bj1860443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry M. J., Samuel C. E. Detection of subnanogram amounts of RNA in polyacrylamide gels in the presence and absence of protein by staining with silver. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jul 15;124(1):180–184. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90235-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H., Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Mapping adenines, guanines, and pyrimidines in RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2527–2538. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Mitsui K., Motizuki M., Tsurugi K. The mechanism of action of ricin and related toxic lectins on eukaryotic ribosomes. The site and the characteristics of the modification in 28 S ribosomal RNA caused by the toxins. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5908–5912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Tsurugi K. RNA N-glycosidase activity of ricin A-chain. Mechanism of action of the toxic lectin ricin on eukaryotic ribosomes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):8128–8130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassur S. M., Whitlock H. W., Jr UV shadowing--a new and convenient method for the location of ultraviolet-absorbing species in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1974 May;59(1):162–164. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofbauer R., Fessl F., Hamilton B., Ruis H. Preparation of a mRNA-dependent cell-free translation system from whole cells of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Feb;122(1):199–203. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb05867.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obrig T. G., Moran T. P., Colinas R. J. Ribonuclease activity associated with the 60S ribosome-inactivating proteins ricin A, phytolaccin and Shiga toxin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jul 31;130(2):879–884. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90498-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsnes S., Fernandez-Puentes C., Carrasco L., Vazquez D. Ribosome inactivation by the toxic lectins abrin and ricin. Kinetics of the enzymic activity of the toxin A-chains. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Dec 1;60(1):281–288. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb21001.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ready M. P., Adams R. P., Robertus J. D. Dodecandrin, a new ribosome-inhibiting protein from Phytolacca dodecandra. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Dec 21;791(3):314–319. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(84)90342-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. K., Selitrennikoff C. P. Plant proteins that inactivate foreign ribosomes. Biosci Rep. 1986 Jan;6(1):19–29. doi: 10.1007/BF01145175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. K., Stewart T. S. Purification and properties of a translation inhibitor from wheat germ. Biochemistry. 1979 Jun 12;18(12):2615–2621. doi: 10.1021/bi00579a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirpe F., Barbieri L., Battelli M. G., Falasca A. I., Abbondanza A., Lorenzoni E., Stevens W. A. Bryodin, a ribosome-inactivating protein from the roots of Bryonia dioica L. (white bryony). Biochem J. 1986 Dec 15;240(3):659–665. doi: 10.1042/bj2400659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirpe F., Barbieri L. Ribosome-inactivating proteins up to date. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jan 20;195(1-2):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80118-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirpe F., Gasperi-Campani A., Barbieri L., Falasca A., Abbondanza A., Stevens W. A. Ribosome-inactivating proteins from the seeds of Saponaria officinalis L. (soapwort), of Agrostemma githago L. (corn cockle) and of Asparagus officinalis L. (asparagus), and from the latex of Hura crepitans L. (sandbox tree). Biochem J. 1983 Dec 15;216(3):617–625. doi: 10.1042/bj2160617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirpe F., Olsnes S., Pihl A. Gelonin, a new inhibitor of protein synthesis, nontoxic to intact cells. Isolation, characterization, and preparation of cytotoxic complexes with concanavalin A. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6947–6953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirpe F., Williams D. G., Onyon L. J., Legg R. F., Stevens W. A. Dianthins, ribosome-damaging proteins with anti-viral properties from Dianthus caryophyllus L. (carnation). Biochem J. 1981 May 1;195(2):399–405. doi: 10.1042/bj1950399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veldman G. M., Klootwijk J., de Regt V. C., Planta R. J., Branlant C., Krol A., Ebel J. P. The primary and secondary structure of yeast 26S rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6935–6952. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziska P., Franz H., Kindt A. The lectin from viscum album L. purification by biospecific affinity chromatography. Experientia. 1978 Jan 15;34(1):123–124. doi: 10.1007/BF01921941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]