Abstract
Developing effective and safe drugs is imperative for replacing antibiotics and controlling multidrug-resistant microbes. Nanoscale silicate platelet (NSP) and its nanohybrid, silver nanoparticle/NSP (AgNP/NSP), have been developed, and the nanohybrids show a strong and general antibacterial activity in vitro. Here, their efficacy for protecting Salmonella-infected chicks from fatality and septicemia was evaluated. Both orally administrated NSP and AgNP/NSP, but not AgNPs alone, effectively reduced the systemic Salmonella infection and mortality. In addition, quantitative Ag analyses demonstrated that Ag deposition from AgNP/NSP in the intestines was less than that from conventional AgNPs, indicating that the presence of NSP for immobilizing AgNPs reduced Ag accumulation in tissue and improved the safety of AgNPs. These in vivo results illustrated that both NSP and AgNP/NSP nanohybrid represent potential agents for controlling enteric bacterial infections.
Keywords: silver, nanoparticle, biocompatibility, infection, cytotoxicity
Introduction
Both soluble silver (Ag) ion species and colloidal silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) are well documented as effective antiseptics for controlling broad-spectrum microbes and antibiotic-resistant bacteria in vitro.1–4 Recently, some discoveries have also shown that AgNPs are superior to conventional Ag ions for inhibiting bacterial growth.5,6 Ag is extensively used in many commercial products, including medical devices, because of its relatively low toxicity. The guideline for maximal Ag dose in drinking water for humans by the US Environmental Protection Agency is 100 ppb. In addition, additives containing AgNPs have been considered in domestic animal diets.7 However, the efficacy of AgNPs or their derivatives for controlling microbial infections in the digestive tract of animals has not yet been reported.
In considering the relative toxicity of AgNPs and Ag ions in medicine, the former has been shown to be approximately three times less toxic than the latter in a human monocytic cell line and in zebrafish.8,9 Compared with Ag sulfadiazine, topical application of an AgNP complex on mouse skin showed significantly reduced Ag deposition in the blood, feces, and internal organs, demonstrating the lower percutaneous adsorption rate for AgNPs than for Ag ions.10
In spite of these advantages for AgNPs as a new antiseptic, metal nanoparticles have an inherent tendency for aggregation. The reduction in these nanoparticles’ reactive surfaces affects the efficacy for controlling pathogens in solution.11 In addition, for clinical application of AgNPs, especially for controlling internal organ infections, the cytotoxicity and the accumulation of Ag deposition in tissues are still the major safety concerns.12
The approach of using a high-aspect-ratio nanoscale silicate platelet (NSP) clay for supporting AgNPs has been taken.6 The NSP was fabricated by exfoliating the natural clay of sodium montmorillonite (Na+-MMT).13,14 The purified NSPs were negatively charged and existed in irregular polygonal shapes with extremely thin dimensions of 80 × 80 × 1 to 100 × 100 × 1 nm3 (1.0 nm thickness). The developed process yielded NSPs as randomized clay platelets with large surface areas (ca 750 m2/g) and strong ionic charges (ca 12,000–19,000 charges/platelet).14 These features enabled NSPs to attract metal ions, polar organic molecules, and microbial cell surfaces effectively.6,15,16 For instance, the use of NSP provides an extensive reactive surface for adhering spherical AgNPs fabricated by the in situ reduction of Ag ions with a reducing agent.6 Acting as a dispersant and a carrier, NSP immobilizes and concentrates AgNPs on an ultrathin platelet.
The strong attraction of NSP to microbes was demonstrated by treating NSP and its AgNP/NSP nanohybrid with Salmonella, which aggregated the bacterial cells into a small cluster.6 This bridging effect of the NSP was speculated to be caused by the extensive reactive surface of the nanomaterial. Examining the bacteria-NSP complex under a transmission electronic microscope revealed that the NSP primarily enwrapped the bacterial cell instead of penetrating into the cell.6,15,17,18 The AgNP/NSP nanohybrids were demonstrated to be an effective antibacterial agent mainly through the robust production of reactive oxygen species on the contacted bacterial membrane.6,18
Experimental results suggested that the NSP carriers might impede the accumulation of AgNPs when topically applied to cells and tissues. In addition, the unique characteristics of NSP may make the nanohybrid a potential drug to control bacterial infections in the body, such as in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, with an attenuated detrimental effect of Ag deposition. To test this hypothesis, NSP, AgNP/NSP, and AgNPs were orally administrated to Salmonella-infected chicks. The nanoparticles’ antibacterial efficacy was subsequently examined. In addition, the comparative safety of the fed Ag nanomaterials, including the cytotoxicity, Ag adsorption, and organ distribution in internal organs, was also evaluated.
Materials and methods
Preparation of NSP, AgNP/NSP, and AgNPs
NSPs were prepared from a Na+-form layered smectite clay, montmorillonite (Na+-MMT; Nanocor Inc, Hoffman Estates, IL), according to the reported exfoliation process.14 The procedures for preparing the AgNP/NSP nanohybrid have been described in detail previously.14 The formation of AgNPs was monitored by observing the color change and ultraviolet absorption at 414 nm. The particle sizes were measured by field emission scanning electronic microscopy (FE-SEM; Zeiss EM 902A) at 80 kV. The size distribution was estimated from 100 individual particles. The concentration of AgNP on NSP was determined by an atomic absorption spectrometer (iCE 3300; Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA).
The synthetic procedure for poly(styrene-co-maleic anhydrides) (SMA) has been described in a recent report.19 The SMA-AgNPs were prepared chemically by reducing Ag salts into NPs by NaBH4.16 The excess Ag ions and free SMA were further removed by dialysis.16 The particle sizes were estimated by transmission electronic microscope (200EX, JEOL, Tokyo, Japan) at 80 kV. The chemical composition was 17.5% Ag and 82.4% SMA, as determined by thermogravimetric analysis (PerkinElmer TGA7, Waltham, MA).
Determination of zeta potential
NSP, AgNP/NSP, and SMA-AgNPs were all dissolved and diluted in water. The zeta potential was measured five times by Laser Doppler Electrophoresis (Zetasizer Nano ZS, Malvern, UK) at 25°C ± 0.1°C and calculated using the Smoluchowski approximation.
Bacterial organisms
Two Salmonella enteric field isolates, serovar pullorum and typhimurium (S. pullorum and S. typhimurium), were provided by Dr Jun-Hong Lin at the Animal Technology Institute Taiwan. Specific pathogen-free (SPF) white Leghorn chicks were purchased from the Animal Health Research Institute in Taiwan. The animal use protocol was reviewed and approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at the National Chung Hsing University (NCHU, No 99-42).
Infection of Salmonella in chicks
The challenge procedure of Salmonella in SPF chicks was modified from the report described by Roy et al.20 Fresh S. pullorum were prepared in Luria-Bertani (LB) broth (OD600 0.4–0.6) (Difco Laboratories, Detroit, MI) and concentrated to make the stock at 5 × 1010 colony-forming units (CFU)/mL. One-day-old Leghorn chicks were fed with 0.1 mL bacterial stock six times within 3 days. During the period of challenges, the animals remained starved to help the colonization of Salmonella in the GI tract.
Detection of S. pullorum in blood
The blood was harvested from the heart of the sacrificed animal on day 5 under a sterilized operation. The Salmonella in the blood were amplified in buffered peptone water (Acumedia, Neogen Corporation, Lansing, MI) for 18 hours at 37°C, and a 50 μL aliquot was further streaked on blood agar for overnight culture. Single colonies were picked and grown in LB broth overnight. Finally, the amplified Salmonella were distinguished by the transparency of the colonies on MacConkey selective agar (Acumedia).
Detection of S. typhimurium in tissues
The isolation of S. typhimurium in tissues followed the reported method.21 Briefly, tissues (100–200 mg) from internal organs were homogenized, and the supernatants (100 μL) were aseptically inoculated into 5 mL buffered peptone water and grown overnight. Aliquots were further grown in Rappaport–Vassiliades broth (Acumedia) for enrichment and incubated at 37°C for 24 hours. A loop full of the Rappaport–Vassiliades broth was spread on to MacConkey agar and Salmonella–Shigella selective agar (Acumedia). Typical colonies of Salmonella showed transparency of colonies with black centers on the Salmonella–Shigella agar after overnight culture.
MTT viability assay
The LoVo and C2BBel cells, which were obtained from the Bioresource Collection and Research Center (BCRC) in Taiwan, were split into 24-well culture plates at a density of 5 × 104 cells/well in 1 mL culture medium and allowed to attach for 24 hours before treatment. After the medium was added with AgNP/NSP, the cells were incubated at 37°C under 5% CO2 for 24 hours. The cells were stained with methylthiazolyldiphenyl tetrazolium bromide (MTT) solution (500 μg/mL) at 37°C for 2 hours. After the removal of the supernatant, dimethyl sulfoxide was applied to dissolve the formazan crystals. The optical density was obtained on an ELISA reader at 595 nm (DV-990-BV, GDV, Rome, Italy).
Pathological and ICP-MS examinations
One-day-old SPF chicks (approximately 40 g) were fed NSP, AgNP/NSP, or AgNPs once with 200 μL tips. Before tissue collection, 1-week-old chicks fasted overnight and were subsequently anesthetized and sacrificed with CO2. Tissue samples (approximately 250 mg) from the gizzard (middle part), small intestine (middle part), large intestine (middle part), liver (median lobe), lungs (median lobe), kidney (whole), and heart (whole) were collected for later histopathological examination. The pathological report was issued by Animal Disease Diagnostic Center in NCHU.
The tissue samples subjected to inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) analysis were washed three times with phosphate buffered saline to remove any adherent nanomaterials. All oven-dried samples were digested with 65% nitric acid at 180°C for 30 minutes in a microwave oven (MARS-Xpress, CEM Corporation, Matthews, NC). The Ag concentration of the nanomaterial suspensions was determined using an ICP-MS (ELAN 6100 DRC, PE-SCIEX) in the Soil Survey and Testing Center at NCHU. The limit of detection was estimated at 0.7–2.0 ppb in the examined samples.
Statistical analysis
Each experiment was performed in duplicate or triplicate, and the derived data were presented as the mean ± standard deviation. Statistical analysis of the data was conducted using SPSS software (SPSS, Inc, Chicago, IL). Significance of differences was analyzed with one-way or two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Tukey’s post-hoc test using SPSS software. The statistical significance was set at P-value < 0.05.
To calculate the 50% lethal dose (LD50) of the tested nanomaterials in cultured cells, MTT data from three independent experiments were collected and fitted to a power curve trend and a four-parameter nonlinear logistic model. The LD50 values were estimated using a fit model (power series 550) and a predicted X model in XLfit 5.3 software (ID Business Solutions, Surrey, UK) (http://www.excelcurvefitting.com/index.html).
Results
Characterization of the NSP, AgNP/NSP, and AgNPs
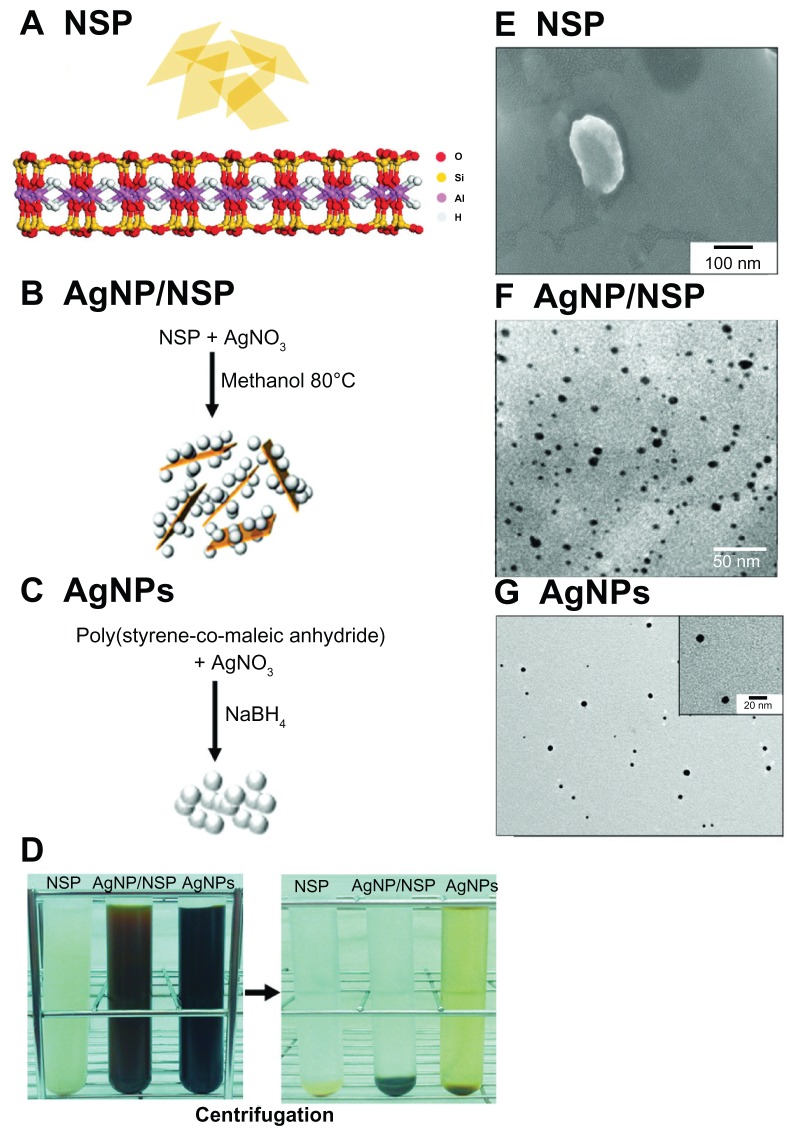
The method for fabrication of NSP and AgNP/NSP is briefly illustrated in Figure 1A and B.6,13,14,22 The AgNP/NSP was synthesized by the reduction of Ag nitrate in the presence of NSP. The morphology of NSP was examined under SEM (Figure 1E and F), showing an irregular polygonal shape with approximately 100 × 100 nm2 dimensions. Regarding the AgNP/NSP nanohybrid, the synthesized AgNPs were free of polymers and well dispersed on the NSP platelet. The spherical particle diameter was 7 ± 3 nm (Figure 1F), and the weight ratio of AgNPs to NSP was 1:11.5. The Ag content of 1.0 wt% AgNP/NSP was 650 ppm. The ICP-MS analysis showed that the dissolved Ag ion concentration of 1.0 wt% AgNP/NSP was 509 ppb, indicating that the applied Ag nitrate was almost completely reduced and less than 0.1% total Ag (0.509 ppm/650 ppm) was dissociated.
Figure 1.
The characteristics of the nanoscale silicate platelet (NSP), silver nanoparticle (AgNP)/NSP, and AgNPs. (A–C) The molecular structure of NSP produced by ChemDraw is illustrated (A). The shapes and fabrication procedures of NSP (A), AgNP/NSP (B), and AgNPs (C) are illustrated. (D) The synthesized nanomaterials were precipitated by the centrifugation at 140,000 × g for 20 hours at 20°C. (E–G) Scanning electronic microscopy pictures of the NSP (E), AgNP/NSP, (F) and AgNPs (G) are presented.
The zeta potential of 0.1 wt% NSP was −44.0 ± 1.2 mV and that of 0.1 wt% AgNP/NSP nanohybrid was −38.9 ± 0.3 mV. These results demonstrated that the immobilized AgNPs did not dramatically alter the electrical potential of the original NSP. The electrostatic stabilization of metal particles in solution generally requires a zeta potential above 30 mV or below −30 mV.23 The low Ag dissociation rate and the low zeta potential of AgNP/NSP both suggested that the AgNPs on the NSP carrier were stable in a reduced form and were well dispersed in water.
To generate size- and homogeneity-controlled AgNPs, the copolymer SMA was used as a steric stabilizer for AgNPs.16 SMA has already been applied for coating anticancer drugs to reduce drug release and toxicity in vivo.24,25 In addition, the SMA will probably not affect antibacterial tests due to its high biocompatibility and weak bactericidal effect.16,26 The SMA-AgNPs, designated AgNPs in the following text and graphs, were prepared chemically by reducing Ag nitrate with NaBH4 into NPs (Figure 1C). The particle size was estimated to be 8.6 ± 0.2 nm (Figure 1G), similar to the AgNP size of AgNP/NSP. The concentration of the SMA-coated AgNPs was determined by thermogravimetric analysis, and the weight ratio of AgNP to SMA was found to be 1:4.7. The Ag content in the stock AgNPs solution (0.37 wt%, 650 ppm Ag) was similar to that in the 1.0 wt% AgNP/NSP solution. After centrifuging the AgNPs at 140,000 × g for 20 hours at 20°C, the AgNPs solution appeared to be light brown in comparison with the clear supernatants of NSP and AgNP/NSP (Figure 1D). The supernatants of these nanomaterials were assumed to contain few AgNPs because this ultracentrifugation precipitates particles above 1 nm in diameter.27 ICP-MS revealed that the Ag ion concentration in the stock AgNPs solution was 30.0 ppm. To reduce the interference of Ag ions in the following tests, the fabricated AgNPs were dialyzed and ultracentrifuged before use. The supernatant of dialyzed SMA-AgNP was clear and showed no antibacterial activity in vitro. The resuspended AgNPs were well dispersed in water with a −32.1 ± 0.3 mV zeta potential.
Controlling Salmonella infection with NSP and AgNP/NSP
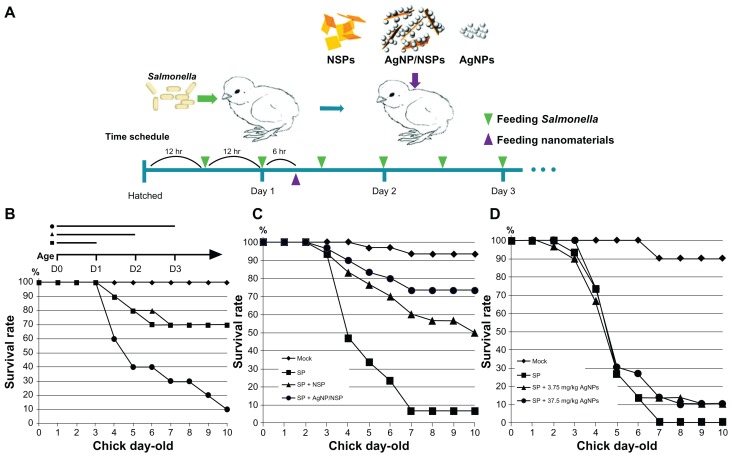
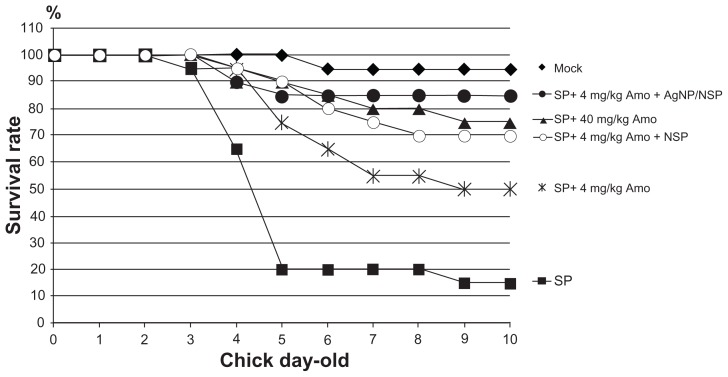
Salmonellosis is a severe threat to the poultry industry and public health. Eliminating Salmonella infection in chickens will reduce the bacterial pollution in meat and the infection risk to humans. In this study, newborn SPF chicks were used as the animal model for bacterial GI infection. No viable Salmonella were ever isolated from the recruited SPF chicks. The animals were starved for 3 days to help the colonization of exogenous Salmonella in the GI tract during the oral challenges (Figure 2A). Feeding of Salmonella enteric serovar pullorum (S. pullorum) (5 × 109 CFU), a lethal pathogen specifically for chicks,20 resulted in 30% mortality on day 10 after two or four oral challenges within the three fasting days (square and triangle, respectively, in Figure 2B). When the chicks were challenged six times during the 3-day fasting period, 90% mortality was achieved (dots in Figure 2B). This six-time challenge schedule was therefore applied in the following experiments.
Figure 2.
Controlling Salmonella infection with the investigated nanomaterials. (A) Experimental conditions in newborn chicks, including the feeding schedules of both Salmonella pullorum (SP) and the nanomaterials. (B) The chicks were orally challenged with Salmonella twice (within day 1, square), four times (within the first 2 days, triangle), or six times (dot). (C and D) The chicks were challenged with Salmonella pullorum six times within the first 3 days. The nanoscale silicate platelets (NSPs) (C), silver nanoparticle (AgNP)/NSPs (C), and AgNPs (D) were administrated once at postnatal 30 hours. Mock in (C and D), feeding water only.
Note: The data represent three independent experiments (n = 10 per group) and were analyzed by two-way analysis of variance.
Interestingly, feeding 10 mg/kg NSP (0.4 mg NSP to a 40 g chick) or 10 mg/kg AgNP/NSP once at postnatal 30 hours (6 hours after the second challenge) successfully improved the chicks’ mortality on day 10 from 6.7% ± 5.8% to 50.0% ± 17.3% (P < 0.05, two-way ANOVA test) or to 73.3% ± 5.8% (P < 0.01), respectively (Figure 2C). According to these results, the 50% effective dose (ED50) of NSP and AgNP/NSP for controlling Salmonella was approximately 10 mg/kg or less. Although 3-day starvation weakened the chicks during the bacterial challenges, most infected chicks were alive on day 3, and over 90% of the uninfected chicks survived to day 10. The endpoint of examination was on day 10 because the mortality of the chicks was generally not altered past this age.
Controlling Salmonella infection with AgNPs
We next examined the bactericidal activity of AgNPs on Salmonella in vitro and in vivo. The AgNPs effectively inhibited the growth of S. pullorum and Escherichia coli on agars and showed a similar potency to that of AgNP/NSP (Supplementary data Figure S1).16 The chicks were thus fed with 3.75 mg/kg (the same Ag content as the AgNP/NSP group in Figure 2C) and 37.5 mg/kg AgNPs following the schedule illustrated in Figure 2A. Surprisingly, mortality rates of both the 3.75 mg/kg and 37.5 mg/kg AgNP-treated chicks were 90% on day 10, indicating the incompetence on protecting the Salmonella infection. Even when a ten-fold dose of Ag was administered, the AgNPs did not exhibit a comparable effect with NSP or AgNP/NSP on clearing enteric Salmonella (Figure 2D).
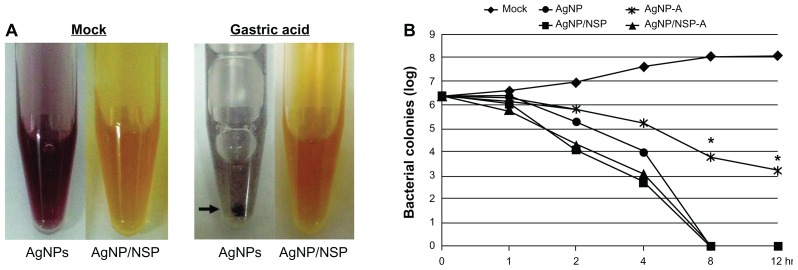
The environment of the GI tract of chicks, such as the low pH gastric juice, may reduce antibacterial potency of AgNPs in vivo. To investigate this possibility, both AgNP/NSP and AgNPs were treated with a simulated gastric juice at 37°C, which contained 3 mg/mL pepsin in a HCl adjusted saline (pH 3.0, 0.85% NaCl).28 Interestingly, at 30-minute treatment with gastric acid, the dark-brown AgNPs turned to gray, agglomerated, and precipitated (arrow in Figure 3A). In contrast, no gross change was observed for the acid-treated AgNP/NSP (Figure 3A). Examining the anti-Salmonella activity of the nanomaterials in LB broth further revealed that the gastric acid significantly reduced the biocidal effect of AgNPs (AgNP-A vs AgNP; P < 0.01 at 8 hours and 12 hours post-treatment; one-way ANOVA) but not that of AgNP/NSP (Figure 3B). This experiment suggested that AgNP/NSP was gastroresistant, and the stability of nanomaterials in gastric acid is a critical factor for antibacterial potency.
Figure 3.
The stability of the silver nanomaterials in gastric acid. (A) The colors of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) and AgNP/nanoscale silicate platelet (NSP) in water (mock) or in simulated chicken gastric juice at 30 minutes post-treatment are shown. The arrow indicates the precipitated colloidal AgNPs. (B) Approximately 5 × 106 Salmonella synchronized at the log phase of the growth curve were cultured in Luria-Bertani (LB) broth with 0.01 wt% nanomaterials. At the indicated times, aliquots of the mixtures were spread on to LB agar, and the surviving cells were estimated by counting the number of resulting colonies.
Notes: The gastric acid-treated AgNPs and AgNP/NSP were labeled AgNP-A and AgNP/NSP-A, respectively. *P < 0.01 (AgNP-A vs AgNP, one-way analysis of variance).
Preventing septicemia with NSP and AgNP/NSP
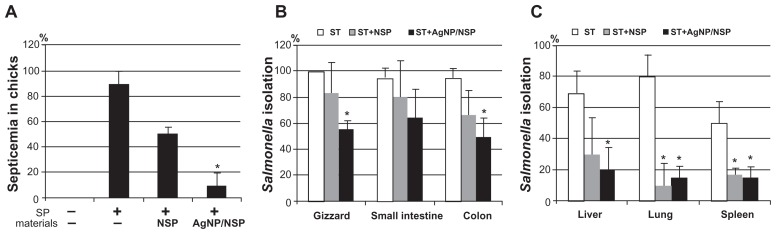
The occurrence of septicemia, caused by the spread of enteric Salmonella into the blood, primarily results in the fatality of infected newborn chicks.20 In addition to reduced mortality, AgNP/NSP also significantly prevented septicemia in the infected chicks (Figure 4A). To address this issue further, S. enteric serovar typhimurium (S. typhimurium) was also tested in this study. In contrast to the limited host of S. pullorum, S. typhimurium is a broad-spectrum zoonosis. In addition, S. typhimurium is featured with resistance to phagocytosis and causes systemic septicemia in infected animals.29
Figure 4.
Prevention of septicemia in the nanomaterial-treated chicks. (A) The blood was harvested from the Salmonella pullorum (SP)-dosed chicks (n = 10 per group) on day 5. (B and C) The isolation of S. typhimurium (ST) in tissues, including the gastrointestinal tract (B), liver, lung, and spleen (C) from Salmonella-fed chicks, was recorded. The infection and the treatment were performed under the same experimental conditions as in Figure 2A. Positive reactions of Salmonella were distinguished by the colony appearance on the MacConkey and the Salmonella–Shigella selective agars.
Notes: *P < 0.05, one-way analysis of variance. Each data represents three independent experiments.
Abbreviations: AgNP, silver nanoparticle; NSP, nanoscale silicate platelet.
One-day-old chicks were orally challenged with S. typhimurium once (106 CFU) and sacrificed at 24 hours postinfection. As expected, the Salmonella were consistently isolated from enteric organs, including the gizzard (100%), the small intestine (95%), and the colon (95%) (Figure 4B). For the liver, lung, and spleen, the isolation rates were 70%, 80%, and 50%, respectively (Figure 4C). Feeding 10 mg/kg NSP at 6 hours postinfection did not dramatically affect the isolation rate in enteric organs (Figure 4B) but inhibited the Salmonella spreading to the nonenteric organs (P < 0.05, one-way ANOVA) (Figure 4C). Notably, treating 10 mg/kg AgNP/NSP reduced the isolation rate of Salmonella from both the enteric and nonenteric organs (P < 0.05, one-way ANOVA) (Figure 4B and C). These results demonstrated that AgNP/NSP was effective in controlling Salmonella infection by preventing the transmission of enteric bacteria into the blood.
Additional effect of the nanomaterials with antibiotics
The increasing dosages of antibiotics required for effectiveness have motivated scientists to develop new strategies for controlling bacterial infections. With regard to this, 40 mg/kg amoxicillin once per day for three consecutive days was found to rescue the survival rate of S. pullorum-infected chicks from 15% to 75% (Figure 5). One-tenth of a usual amoxicillin dose (4 mg/kg) over three consecutive days provided 50% protection. Interestingly, adding NSP or AgNP/NSP with 4 mg/kg amoxicillin increased the survival rate from 50% to 70% or 85% (P < 0.05) on day 10, respectively (Figure 5). This result suggested that both nanomaterials have an additive antibacterial effect with antibiotics for Salmonella prevention.
Figure 5.
The additional effects of nanoscale silicate platelet (NSP) and silver nanoparticle (AgNP)/NSP with amoxicillin for Salmonella control.
Notes: The surviving rates of the S. pullorum (SP)-infected chicks (n = 10 per group) were recorded after treatment with amoxicillin (Amo) and the NSP (10 mg/kg) or AgNP/NSP (10 mg/kg). The amoxicillin was fed to chicks three times at 26 hours, 50 hours, and 74 hours after birth, and the nanomaterials were given once at postnatal 30 hours. The experiments were performed in duplicate.
The cytotoxicity of AgNP/NSP
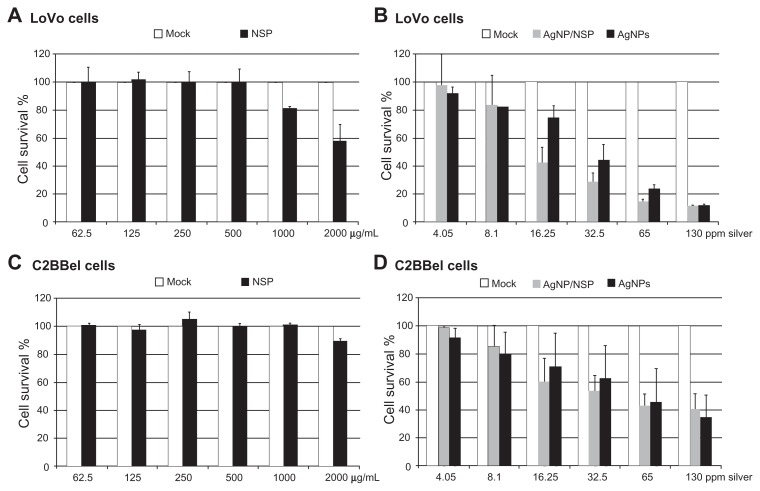
The cytotoxicity of NSP, AgNPs, and AgNP/NSP was tested in two common human intestinal epithelial cell lines, LoVo and C2BBel (a subclone of Caco-2) cells (Figure 6). In our previous study,13 treating Chinese hamster ovary cells with 500 μg/mL and 1000 μg/mL NSP for 24 hours resulted in 80% and 60% cell survival, respectively. Here, the study in LoVo cells revealed that 1000 μg/mL and 2000 μg/mL NSP gave 81.1% ± 1.2% and 57.6% ± 12.2% cell survival examined by the MTT assay (Figure 6A). The 50% lethal concentration (LC50) of NSP at 24 hours for LoVo cells was more than 2000 μg/mL, emphasizing the low toxicity of NSP to intestinal cells in vitro. This low toxicity of NSP was also recapitulated in a study with C2BBel cells (Figure 6C).
Figure 6.
The toxicity of the nanomaterials in vitro. (A–D) LoVo (A and B) and C2BBel cells (C and D) were cultured and treated with the nanoscale silicate platelet (NSP) (A and C) or the silver nanomaterials (B and D) for 24 hours.
Notes: The cytopathic effect of silver nanoparticle (AgNP)/NSP (62.5 μg/mL, 125 μg/mL, 250 μg/mL, 500 μg/mL, 1000 μg/mL, and 2000 μg/mL) and AgNPs (20.6 μg/mL, 41.25 μg/mL, 92.5 μg/mL, 185 μg/mL, 370 μg/mL, 740 μg/mL) was compared at the same silver concentrations (4.05 ppm, 8.1 ppm, 16.25 ppm, 32.5 ppm, 65 ppm, 130 ppm) in culture medium. The cytotoxicity was estimated by the methylthiazolyldiphenyl tetrazolium bromide assay in triplicate.
Compared with NSP, AgNP/NSP and AgNPs showed higher cytotoxicity to human colon cancer cells (Figure 6B and D). The LC50 of AgNP/NSP and AgNPs at 24 hours post-treatment was 341 μg/mL (22.1 ppm Ag) and 205 μg/mL (36.1 ppm Ag) in LoVo cells, respectively (Figure 6B). In addition, the LC50 of AgNP/NSP and AgNPs in C2BBel cells were 820 μg/mL (Ag, 53.3 ppm) and 318 μg/mL (Ag, 55.8 ppm), respectively (Figure 6D). The averaged LC50 doses of AgNP/NSP and AgNPs for intestinal cells were 37.7 ppm Ag and 46.0 ppm Ag, respectively. Notably, cytotoxicity assays in human HT29 colon cells showed that the LC50 of pure AgNPs (particle size, 10–15 nm) was 27 ppm at 12 hours post-treatment.30 These results suggested that AgNP/NSP and SMA-AgNPs were less cytotoxic than pure AgNPs on cultured intestinal cells.
The acute toxicity of the AgNP/NSP in vivo
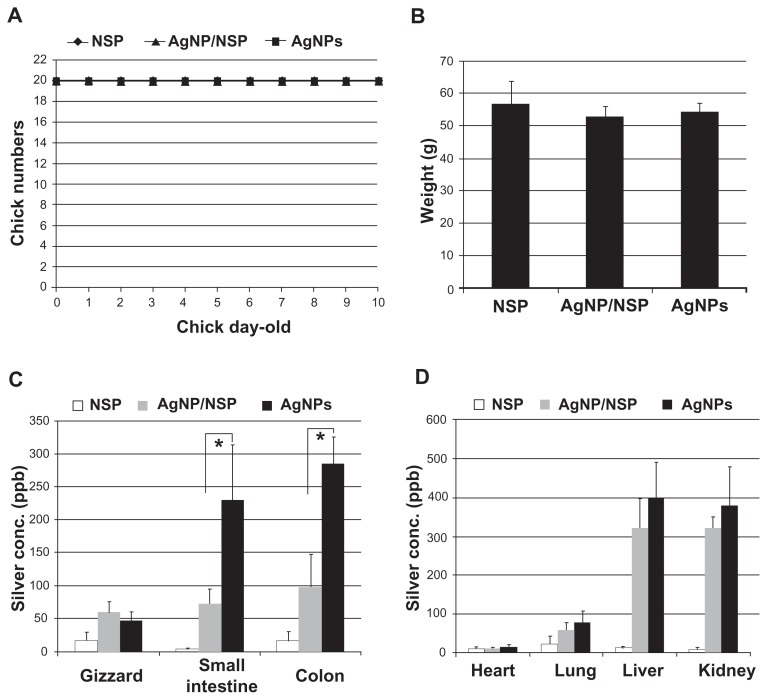
To evaluate the safety of AgNP/NSP in vivo, a 50-fold higher dose of the nanohybrids (500 mg/kg), compared with that used in the aforementioned studies, was given to the 1-day-old chicks. We found that during the first week, all examined chicks were healthy (Figure 7A) and showed no gross abnormality with respect to their appearance, appetite, and body weight (P > 0.05) (Figure 7B). The appearance of dark-brown feces from the chicks at 6 hours post-treatment of AgNP/NSP was observed, suggesting that fecal excretion was the primary excretion route for the orally applied nanomaterial. We observed that the feces returned to a normal gray color on day 3 post-treatment.
Figure 7.
The acute toxicity of the nanomaterials in vivo. The newborn chicks (n = 10 per group) were fed once with 500 mg/kg nanoscale silicate platelet (NSP), 500 mg/kg silver nanoparticle (AgNP)/NSP, or 187.5 mg/kg AgNPs at postnatal 12 hours. The silver nanomaterials were given at the same silver content. (A) The surviving animals were recorded, and the chicks were weighed every day until day 7. (B) The weight data on day 7 are shown. (C and D) The organs of 1-week-old chicks (n = 3) were collected and oven-dried, and their silver deposits were determined by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry.
Notes: The values indicate the silver concentrations in the wet tissues. The data represent two independent experiments. *P < 0.05 (one-way analysis of variance).
Feeding AgNPs (187.5 mg/kg), NSP (500 mg/kg), and AgNP/NSP (500 mg/kg) to 1-day-old chicks did not cause notable gross tissue damage in the examined internal organs. Histological examinations by experienced pathologists revealed that the epithelial cells of the GI tract were intact, and inflammatory cells were not detected in the collected tissues of the nanomaterial-treated chicks, including GI tract, heart, lung, liver, and kidney (Table S1). These experiments suggested that NSP and the AgNP/NSP nanohybrid were pharmacologically safe nanomaterials (therapeutic index, LD50/ED50 > 50) for controlling enteric bacterial infections.
In addition to histological examinations, tracing the nanosilver in the body is essential for evaluating the metabolism of the nanohybrids and their long-term safety. The NSP (500 mg/kg), AgNP/NSP (500 mg/kg), and AgNPs (187.5 mg/kg; same Ag content to AgNP/NSP) were fed to 1-day-old chicks, and the Ag distribution of nanomaterials in their organs was determined by ICP-MS. In the NSP control group, the detected Ag concentrations were all lower than 30 ppb in the wet tissues of NSP-treated chicks (Figure 7C and D). For AgNP/NSP, the average Ag deposits in the GI tract were below 100 ppb. Importantly, feeding AgNPs resulted in 231 ± 83 ppb Ag and 285 ± 41 ppb Ag ions in the small and large intestine, respectively. The accumulated Ag in AgNPs-dosed intestines showed significantly higher levels than those in the AgNP/NSP-treated group (P < 0.05, one-way ANOVA) (Figure 7C).
In the non-GI internal organs of AgNP/NSP- and AgNPs-treated chicks, the Ag concentrations in heart tissue were below 30 ppb (Figure 7D). We detected 61 ± 19 ppb and 82 ± 28 ppb in the lungs of AgNP/NSP and AgNPs groups, respectively. In the liver and kidney of AgNPs-treated chicks, 396 ± 95 ppb Ag and 378 ± 102 ppb Ag were found. Unexpectedly, 319 ± 80 ppb Ag and 315 ± 37 ppb Ag were detected in the liver and kidney of AgNP/NSP-treated chicks, respectively. These Ag concentrations in AgNP/NSP-dosed liver and kidney still exhibited a moderate, but not significant, reduction compared with the AgNP-treated group (P > 0.05) (Figure 7D).
Discussion
AgNPs have been proposed to be a potential drug for bacterial infection based on the strong bactericidal activity of AgNP in vitro. However, our study indicated that feeding AgNPs did not effectively rescue Salmonella-mediated mortality of the chicks. We further demonstrated that the AgNPs coated with SMA copolymer were acid-instable, and the NPs became agglomerated in the presence of gastric acid. This study emphasized that the stability and dispersion of nanomaterials in vivo are key factors for their antibacterial potency in GI infections.
In contrast, the NSP clay, showing barely antibacterial effects in protein-rich medium,6 protected 50% Salmonella-infected chicks from fatality. We speculate that the high cationic exchange capacity and the excellent dispersion enabled the NSP to be a potent adsorbent for enteric bacterial pathogens.14 NSP may encapsulate the bacteria and prevent the colonization of Salmonella on to the luminal epithelium of digestive tissues.6 Therefore, feeding NSP to chicks may not kill the colonized Salmonella but reduces bacterial mobility and brings the Salmonella or their released toxins away from the lumen of the intestines.
AgNP/NSP have been shown to be impressive antibacterials in vitro, including for Salmonella and Ag ion-resistant E. coli.6,18 Here, in vivo studies further emphasized that AgNP/NSP effectively controlled enteric Salmonella infection and prevented septicemia in infected chicks. Combined with AgNP/NSP, only one-tenth the normal dose of amoxicillin was required to achieve 80%–90% protection from Salmonellosis. The reduced dosage of applied antibiotics will reduce the risk of the emergence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in field. These data further suggested that the AgNP/NSP nanohybrid is a potential antimicrobial agent to treat infectious gastroenteritis in animals and humans.
Interestingly, significant Ag content in the liver and kidney was detected in AgNP/NSP-treated chicks. The high Ag content in the liver and kidney may be caused by the partial dissolution of Ag ions from the Ag nanomaterials under acidic or basic environment, such as in the stomach or intestine, respectively. The released Ag ions may subsequently be passively diffused from the GI tract into the blood and accumulate in the liver and kidney. In addition, although the geometric shape of NSP and its derivatives may hinder the direct diffusion of the nanomaterials from the intestinal lumen into the blood, AgNP/NSP may be engulfed by enterocytes or M cells residing in the lumen.31 Through endocytosis, intracellular transport, and excretion, the nanomaterials may be transported through the enterocytes to the blood and be systemically delivered to other organs.
Another interesting finding was that the Ag in the liver and kidney of AgNP/NSP-treated chicks was comparable with that in the intestines of AgNP-treated chicks. Previous studies demonstrated that the distribution of Ag in adult rats following AgNP feeding for 28 consecutive days resulted in ten-fold higher Ag accumulation in the intestine than in the liver and kidney.27 These explanations include a variable GI absorption rate, metabolism, and the excretion of the nanomaterial in different species and at different ages. For example, a dramatic difference was documented between the distribution of Ag granules in the kidney of rats and rabbits.32 The deposition of ingested Ag in rat kidney also exhibited a varied Ag density and Ag granule distribution between young and adult animals.33 Abundant Ag-binding substances in the liver and kidney or slow excretion of Ag through the bile duct or urine in chicks may also contribute to the high Ag deposition observed in both organs. Explaining this discrepancy requires a long-term toxicity evaluation of AgNP/NSP in rats and comparing the safety and organ distribution of the nanohybrid with that of pure AgNPs. In addition, further experiments are required to determine which form of Ag, such as Ag ions, intact AgNPs, or AgNP/NSPs, is absorbed and accumulated in the liver and kidney in the nanohybrid-treated animals.
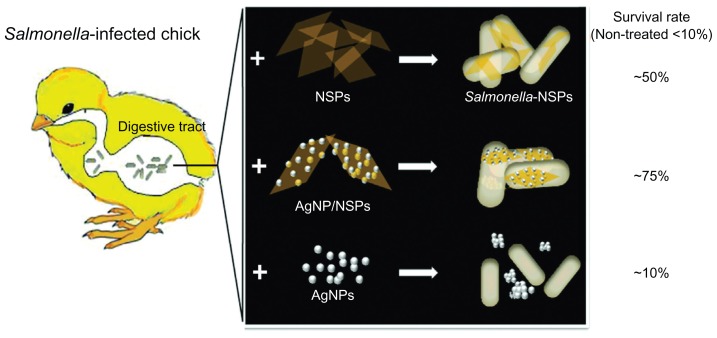
The efficacy of the tested nanomaterials on Salmonella infection and the postulated hypotheses are summarized in Figure 8. In addition, observation and quantitative Ag analyses indicated that orally administrated AgNP/NSP was mainly excreted from the body through the feces. The absorbed Ag from the nanohybrids was accumulated in the intestine, liver, and kidney, similar to the reported distribution of AgNPs fed to mice.27,34–36 The comparative tests between AgNP/NSP and AgNPs demonstrated that the Ag deposition from AgNP/NSP in the internal organs was less than that observed from conventional AgNPs.
Figure 8.
The nanoscale silicate platelet (NSP) and silver nanoparticle (AgNP)/NSP, but not AgNPs, are well dispersed in the digestive tract and effectively rescue Salmonella-infected chicks from death.
Conclusion
Our experiments demonstrated that NSP and AgNP/NSP, but not AgNPs alone, were potential antimicrobial agents for controlling enteric bacterial infection. In contrast to the considerable Ag deposits in the GI tract upon application of AgNPs, the Ag accumulation in digestive tissues from AgNP/NSP was significantly decreased, showing improved safety over conventional AgNPs in animals.
Supplementary materials
Table S1.
Histopathological findings in the nanomaterial-fed chicks
| Organs/degreea | Chicks | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
| Control | AgNP/NSP | NSP | AgNPs | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| 5 days old | 10 days old | 5 days old | 10 days old | 5 days old | 10 days old | 5 days old | 10 days old | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| Gizzard | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Proventriculus | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Small intestine | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Large intestine | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Lung | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Heart | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Liver | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Kidney | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
Notes: –No significant lesion.
Degree of lesions was graded from 1 to 4 depending on severity: 1 = minimal (<1%); 2: slight (1%–25%); 3 = moderate (26%–50%); 4 = moderate/severe (51%–75%); 5 = severe/high (76%–100%).
Abbreviations: AgNP, silver nanoparticle; NSP, nanoscale silicate platelet.
The antimicrobial effect of the silver nanoparticle (AgNPs). Approximately 1 × 103 Salmonella pullorum and Escherichia coli, synchronized at the log phase of the growth curve, were spread on Luria-Bertani agars where AgNPs or AgNP/nanoscale silicate platelet (NSP) were mixed with at the indicated concentrations.
Note: The numbers of colonies were counted after overnight incubation at 37°C.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Program for Nanoscience and Technology sponsored by the National Science Council (100-2120-M-002-006). The research was also funded in part by the Ministry of Education, Taiwan, Republic of China, under the ATU Plan. Assistance provided by Dr Cheng-Chung Lin at the Graduate Institute of Veterinary Pathobiology, NCHU is highly appreciated.
Footnotes
Disclosure
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
- 1.Jung WK, Koo HC, Kim KW, Shin S, Kim SH, Park YH. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of action of the silver ion in Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008;74(7):2171–2178. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02001-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kim JS, Kuk E, Yu KN, et al. Antimicrobial effects of silver nanoparticles. Nanomedicine. 2007;3(1):95–101. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2006.12.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lok CN, Ho CM, Chen R, et al. Silver nanoparticles: partial oxidation and antibacterial activities. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2007;12(4):527–534. doi: 10.1007/s00775-007-0208-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Shahverdi AR, Fakhimi A, Shahverdi HR, Minaian S. Synthesis and effect of silver nanoparticles on the antibacterial activity of different antibiotics against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Nanomedicine. 2007;3(2):168–171. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2007.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Choi O, Deng KK, Kim NJ, Ross L, Jr, Surampalli RY, Hu Z. The inhibitory effects of silver nanoparticles, silver ions, and silver chloride colloids on microbial growth. Water Res. 2008;42(12):3066–3074. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2008.02.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Su HL, Lin SH, Wei JC, et al. Novel nanohybrids of silver particles on clay platelets for inhibiting silver-resistant bacteria. PLoS One. 2011;6(6):e21125. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Fondevila M, Herrer R, Casallas MC, Abecia L, Ducha JJ. Silver nanoparticles as a potential antimicrobial additive for weaned pigs. Anim Feed Sci Technol. 2009;150:259–269. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Foldbjerg R, Olesen P, Hougaard M, Dang DA, Hoffmann HJ, Autrup H. PVP-coated silver nanoparticles and silver ions induce reactive oxygen species, apoptosis and necrosis in THP-1 monocytes. Toxicol Lett. 2009;190(2):156–162. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2009.07.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Bilberg K, Hovgaard MB, Besenbacher F, Baatrup E. In vivo toxicity of silver nanoparticles and silver ions in zebrafish (Danio rerio) J Toxicol. 2012 doi: 10.1155/2012:293784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Brandt O, Mildner M, Egger AE, et al. Nanoscalic silver possesses broad-spectrum antimicrobial activities and exhibits fewer toxicological side effects than silver sulfadiazine. Nanomedicine. 2011 doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2011.1007.1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Sondi I, Salopek-Sondi B. Silver nanoparticles as antimicrobial agent: a case study on E. coli as a model for Gram-negative bacteria. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2004;275(1):177–182. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2004.02.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Chaloupka K, Malam Y, Seifalian AM. Nanosilver as a new generation of nanoproduct in biomedical applications. Trends Biotechnol. 2010;28(11):580–588. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2010.07.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Li PR, Wei JC, Chiu YF, Su HL, Peng FC, Lin JJ. Evaluation on cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of the exfoliated silicate nanoclay. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2010;2(6):1608–1613. doi: 10.1021/am1001162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wei JC, Yen YT, Su HL, Lin JJ. Inhibition of bacterial growth by the exfoliated clays and observation of physical capturing mechanism. J Phys Chem C. 2011;115:18770–18775. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Wang MC, Lin JJ, Tseng HJ, Hsu SH. Characterization, antimicrobial activities, and biocompatibility of organically modified clays and their nanocomposites with polyurethane. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2011;4(1):338–350. doi: 10.1021/am2014103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Lin JJ, Lin WC, Dong RX, Hsu SH. The cellular responses and antibacterial activities of silver nanoparticles stabilized by different polymers. Nanotechnology. 2012;23(6):065102. doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/23/6/065102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hsu SH, Tseng HJ, Hung HS, et al. Antimicrobial activities and cellular responses to natural silicate clays and derivatives modified by cationic alkylamine salts. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2009;1(11):2556–2564. doi: 10.1021/am900479q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Su HL, Chou CC, Hung DJ, et al. The disruption of bacterial membrane integrity through ROS generation induced by nanohybrids of silver and clay. Biomaterials. 2009;30(30):5979–5987. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2009.07.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lin JJ, Hsu YC, Wei KL. Mechanistic aspects of clay intercalation with amphiphilic poly(styrene-co-maleic anhydride)-grafting polyamine salts. Macromolecules. 2007;40(5):1579–1584. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Roy P, Dhillon AS, Shivaprasad HL, Schaberg DM, Bandli D, Johnson S. Pathogenicity of different serogroups of avian salmonellae in specific-pathogen-free chickens. Avian Dis. 2001;45(4):922–937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Waltman WD, Mallinson ET. Isolation of Salmonella from poultry tissue and environmental samples: a nationwide survey. Avian Dis. 1995;39(1):45–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Chiu CW, Hong PD, Lin JJ. Clay-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles exhibiting low-temperature melting. Langmuir. 2011;27(18):11690–11696. doi: 10.1021/la202661n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Bihari P, Vippola M, Schultes S, et al. Optimized dispersion of nanoparticles for biological in vitro and in vivo studies. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2008;5:14. doi: 10.1186/1743-8977-5-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Maeda H, Ueda M, Morinaga T, Matsumoto T. Conjugation of poly(styrene-co-maleic acid) derivatives to the antitumor protein neocarzinostatin: pronounced improvements in pharmacological properties. J Med Chem. 1985;28(4):455–461. doi: 10.1021/jm00382a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Greish K, Sawa T, Fang J, Akaike T, Maeda H. SMA-doxorubicin, a new polymeric micellar drug for effective targeting to solid tumours. J Control Release. 2004;97(2):219–230. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2004.03.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Donati I, Gamini A, Vetere A, Campa C, Paoletti S. Synthesis, characterization, and preliminary biological study of glycoconjugates of poly(styrene-co-maleic acid) Biomacromolecules. 2002;3(4):805–812. doi: 10.1021/bm020018x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Loeschner K, Hadrup N, Qvortrup K, et al. Distribution of silver in rats following 28 days of repeated oral exposure to silver nanoparticles or silver acetate. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2011;8:18. doi: 10.1186/1743-8977-8-18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Musikasang H, Tani A, H-kittikun A, Maneerat S. Probiotic potential of lactic acid bacteria isolated from chicken gastrointestinal digestive tract. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2009;25:1337–1345. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Finlay BB, Brumell JH. Salmonella interactions with host cells: in vitro to in vivo. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2000;355(1397):623–631. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2000.0603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Gopinath P, Gogoi SK, Chattopadhyay A, Ghosh SS. Implications of silver nanoparticle induced cell apoptosis for in vitro gene therapy. Nanotechnology. 2008;19(7):075104. doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/19/7/075104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Florence AT. The oral absorption of micro- and nanoparticulates: neither exceptional nor unusual. Pharm Res. 1997;14(3):259–266. doi: 10.1023/a:1012029517394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Moffat DB, Creasey M. The distribution of ingested silver in the kidney of the rat and of the rabbit. Acta Anat (Basel) 1972;83(3):346–355. doi: 10.1159/000143868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Creasey M, Moffat DB. The deposition of ingested silver in the rat kidney at different ages. Experientia. 1973;29(3):326–327. doi: 10.1007/BF01926506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Park EJ, Bae E, Yi J, et al. Repeated-dose toxicity and inflammatory responses in mice by oral administration of silver nanoparticles. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2010;30(2):162–168. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2010.05.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kim YS, Kim JS, Cho HS, et al. Twenty-eight-day oral toxicity, genotoxicity, and gender-related tissue distribution of silver nanoparticles in Sprague-Dawley rats. Inhal Toxicol. 2008;20(6):575–583. doi: 10.1080/08958370701874663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Kim YS, Song MY, Park JD, et al. Subchronic oral toxicity of silver nanoparticles. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2010;7:20. doi: 10.1186/1743-8977-7-20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Table S1.
Histopathological findings in the nanomaterial-fed chicks
| Organs/degreea | Chicks | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
| Control | AgNP/NSP | NSP | AgNPs | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| 5 days old | 10 days old | 5 days old | 10 days old | 5 days old | 10 days old | 5 days old | 10 days old | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| Gizzard | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Proventriculus | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Small intestine | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Large intestine | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Lung | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Heart | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Liver | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Kidney | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
Notes: –No significant lesion.
Degree of lesions was graded from 1 to 4 depending on severity: 1 = minimal (<1%); 2: slight (1%–25%); 3 = moderate (26%–50%); 4 = moderate/severe (51%–75%); 5 = severe/high (76%–100%).
Abbreviations: AgNP, silver nanoparticle; NSP, nanoscale silicate platelet.
The antimicrobial effect of the silver nanoparticle (AgNPs). Approximately 1 × 103 Salmonella pullorum and Escherichia coli, synchronized at the log phase of the growth curve, were spread on Luria-Bertani agars where AgNPs or AgNP/nanoscale silicate platelet (NSP) were mixed with at the indicated concentrations.
Note: The numbers of colonies were counted after overnight incubation at 37°C.