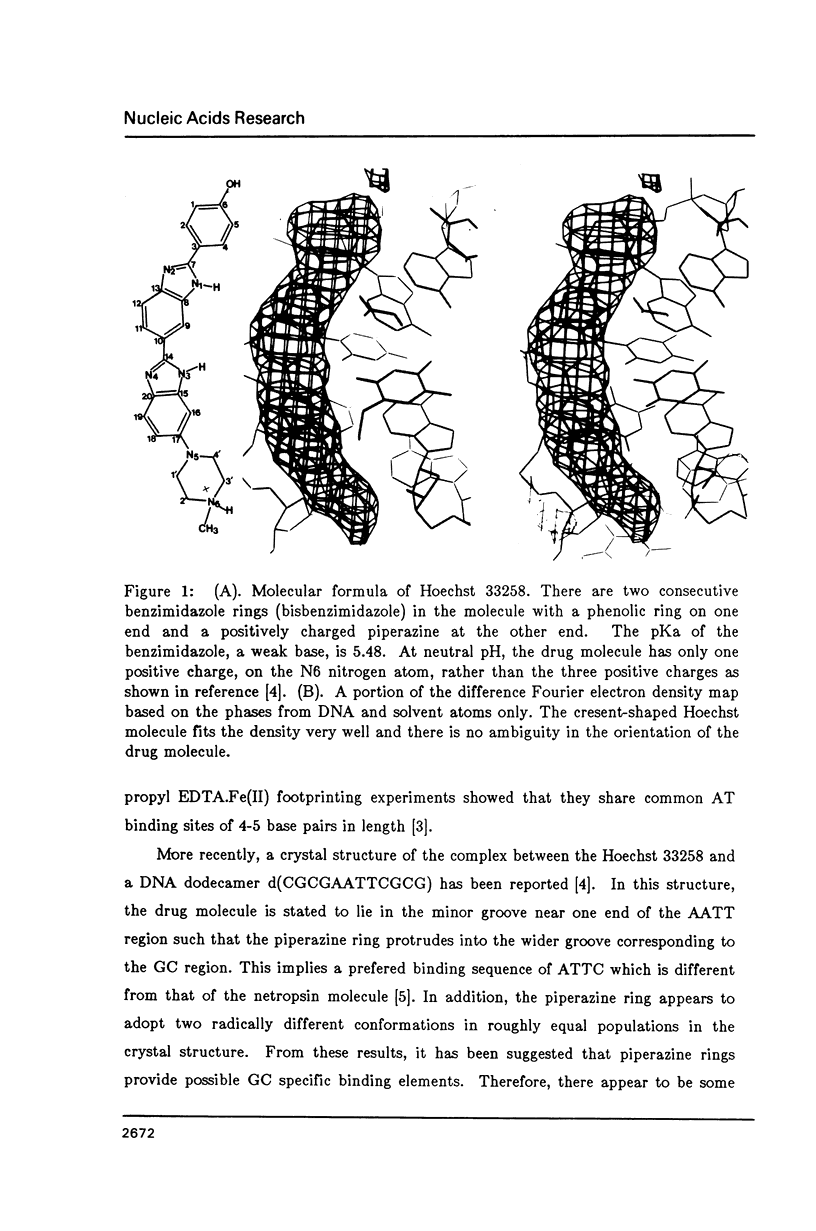
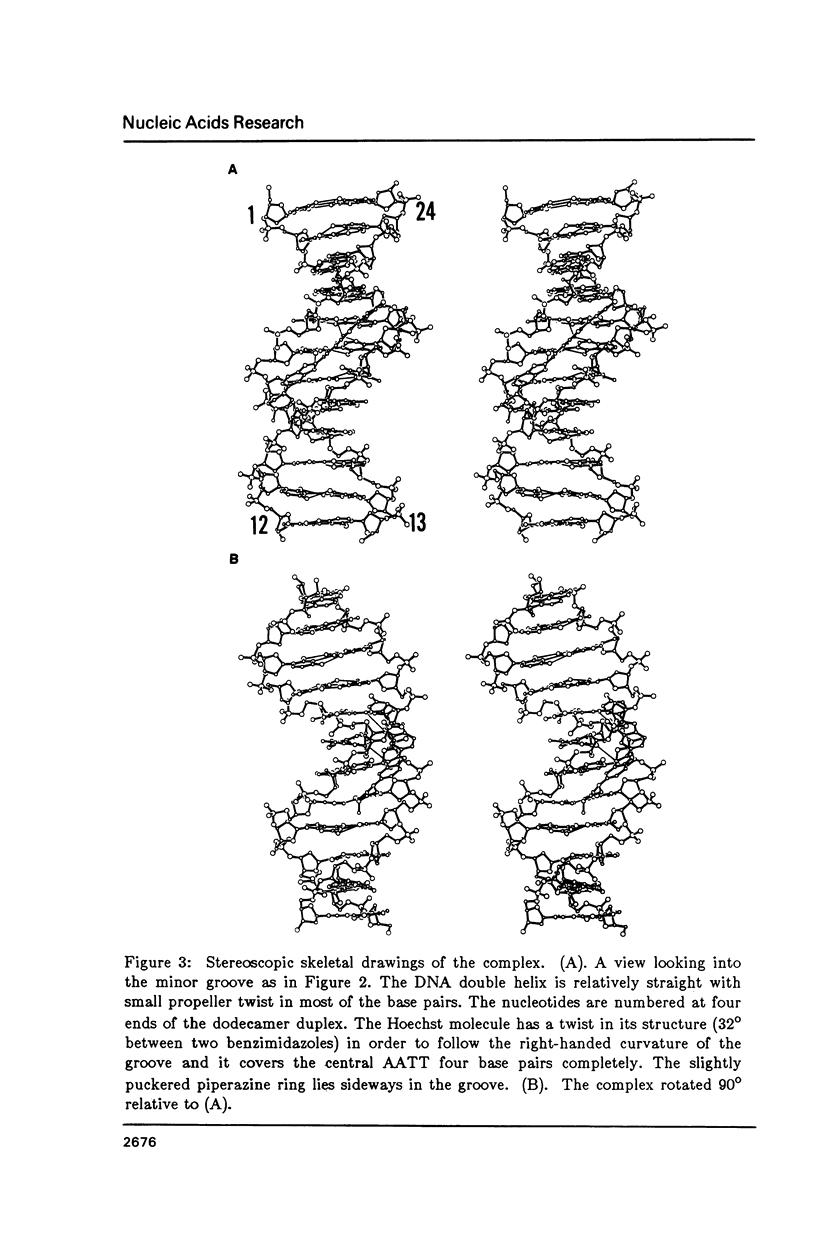
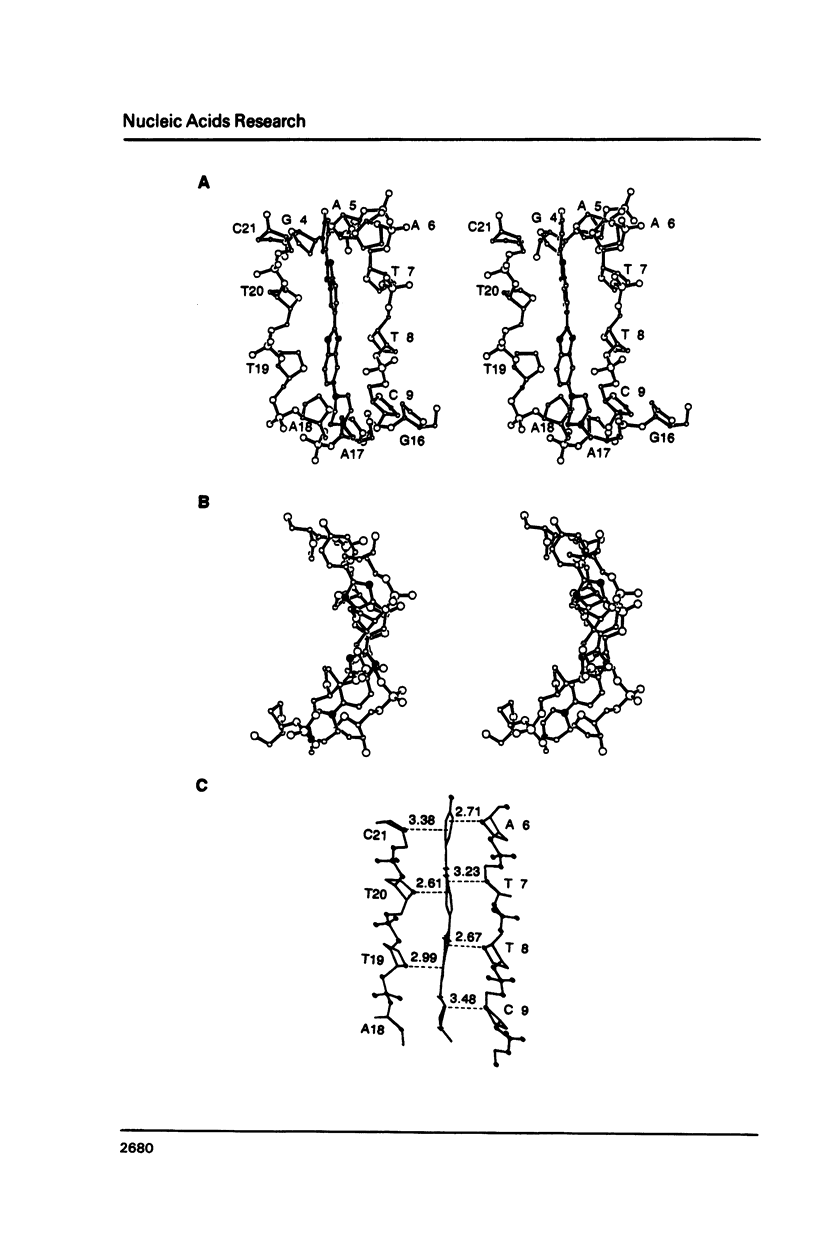
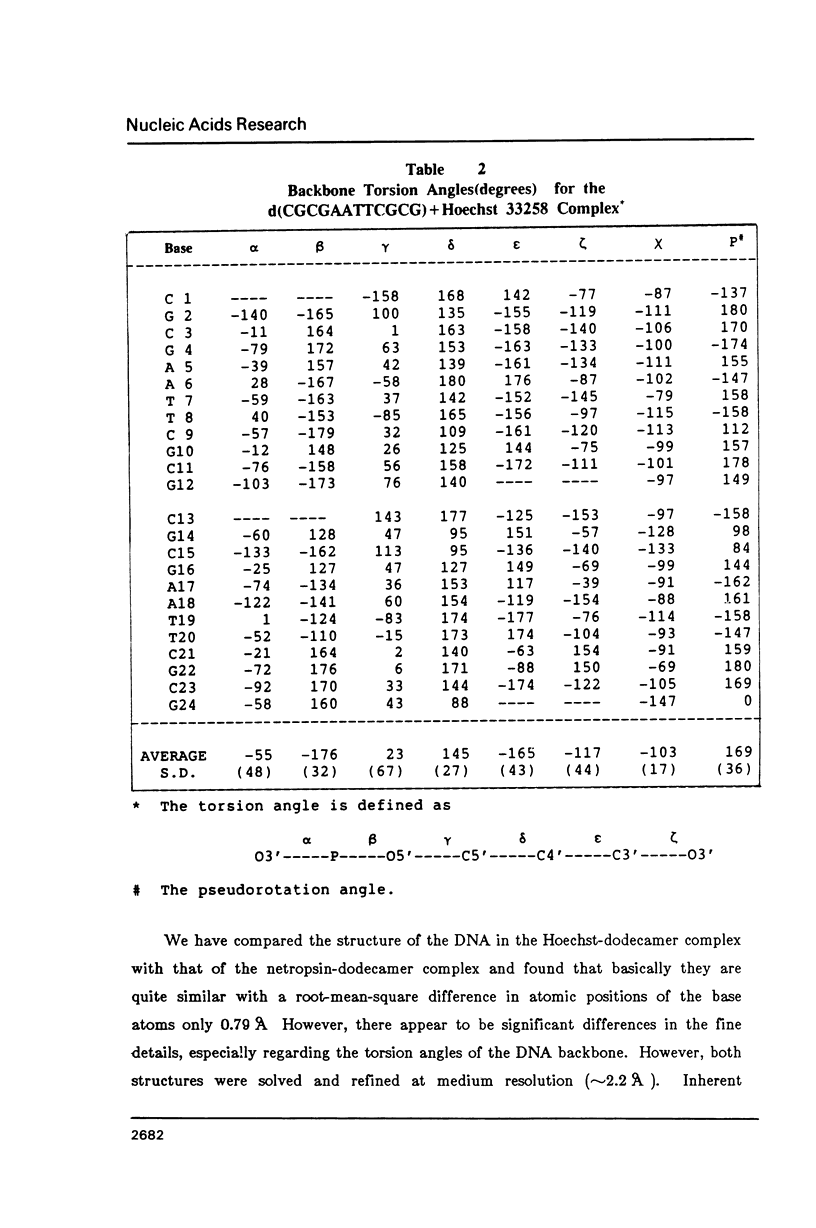
Abstract
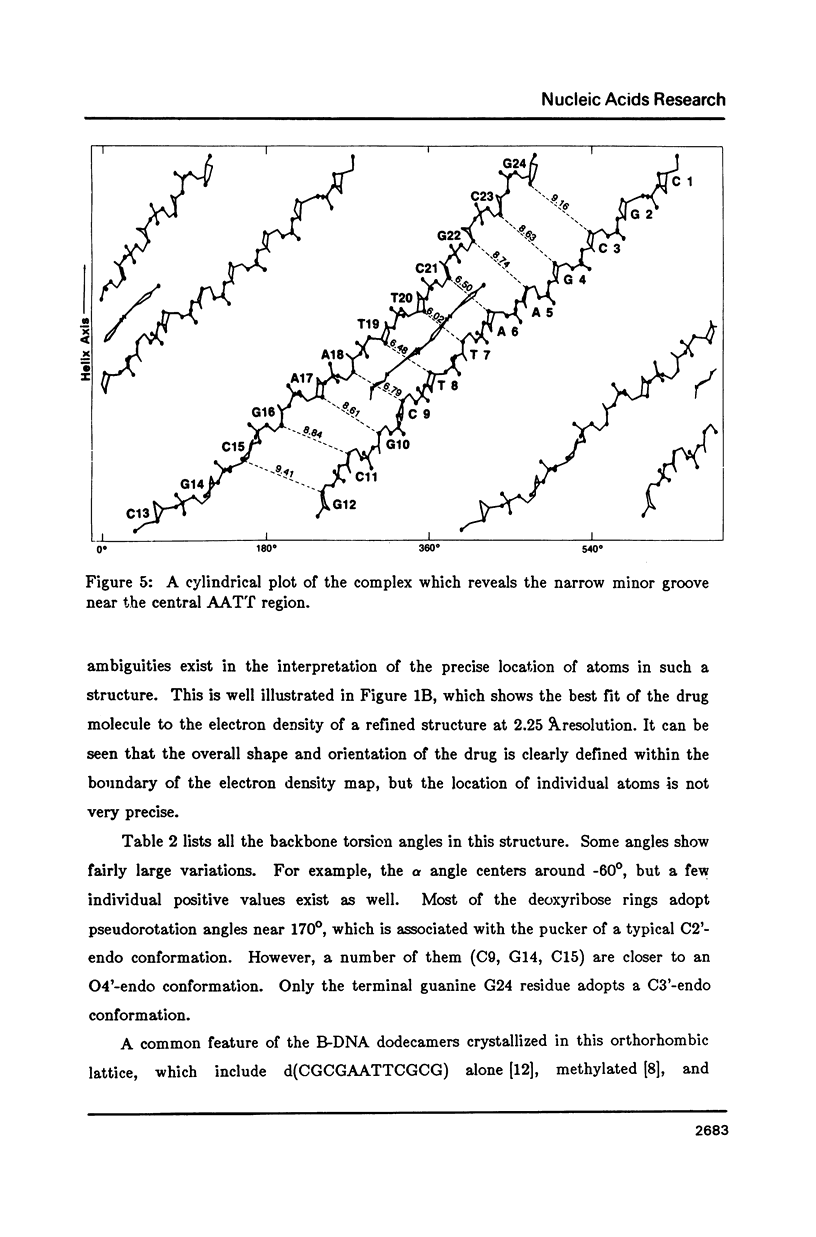
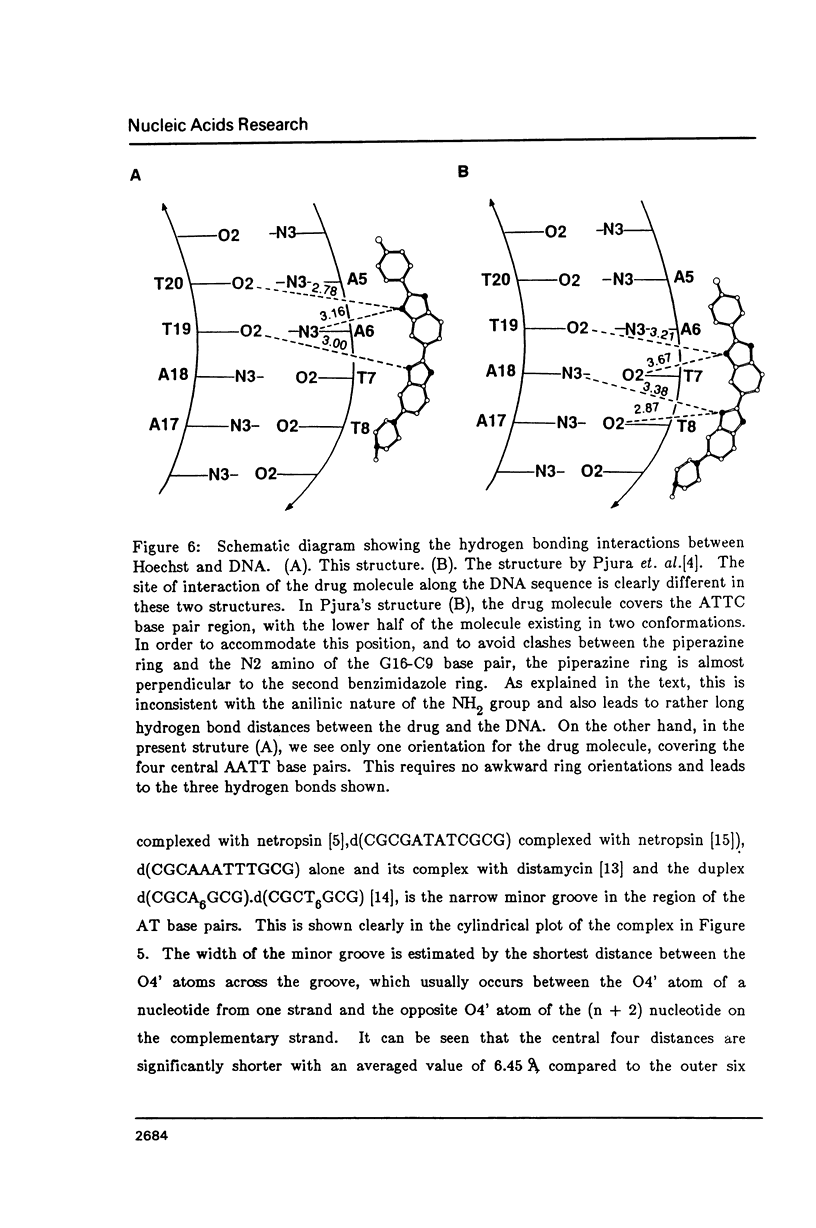
The crystal structure of the complex between the dodecamer d(CGCGAATTCGCG) and a synthetic dye molecule Hoechst 33258 was solved by X-ray diffraction analysis and refined to an R-factor of 15.7% at 2.25 A resolution. The crescent-shaped Hoechst compound is found to bind to the central four AATT base pairs in the narrow minor groove of the B-DNA double helix. The piperazine ring of the drug has its flat face almost parallel to the aromatic bisbenzimidazole ring and lies sideways in the minor groove. No evidence of disordered structure of the drug is seen in the complex. The binding of Hoechst to DNA is stabilized by a combination of hydrogen bonding, van der Waals interaction and electrostatic interactions. The binding preference for AT base pairs by the drug is the result of the close contact between the Hoechst molecule and the C2 hydrogen atoms of adenine. The nature of these contacts precludes the binding of the drug to G-C base pairs due to the presence of N2 amino groups of guanines. The present crystal structural information agrees well with the data obtained from chemical footprinting experiments.
Full text
PDF













Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burley S. K., Wang A. H., Votano J. R., Rich A. Antigelling and antisickling bisphenyl oligopeptides and peptide analogues have similar structural features. Biochemistry. 1987 Aug 11;26(16):5091–5099. doi: 10.1021/bi00390a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coll M., Frederick C. A., Wang A. H., Rich A. A bifurcated hydrogen-bonded conformation in the d(A.T) base pairs of the DNA dodecamer d(CGCAAATTTGCG) and its complex with distamycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8385–8389. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene P. H., Poonian M. S., Nussbaum A. L., Tobias L., Garfin D. E., Boyer H. W., Goodman H. M. Restriction and modification of a self-complementary octanucleotide containing the EcoRI substrate. J Mol Biol. 1975 Dec 5;99(2):237–261. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80143-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harshman K. D., Dervan P. B. Molecular recognition of B-DNA by Hoechst 33258. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 11;13(13):4825–4835. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.13.4825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopka M. L., Yoon C., Goodsell D., Pjura P., Dickerson R. E. The molecular origin of DNA-drug specificity in netropsin and distamycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1376–1380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lämmler G., Herzog H., Saupe E., Schütze H. R. Chemotherapeutic studies on Litomosoides carinii infection of Mastomys natalensis. 1. The filaricidal action of 2,6-bis-benzimidazoles. Bull World Health Organ. 1971;44(6):751–756. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson H. C., Finch J. T., Luisi B. F., Klug A. The structure of an oligo(dA).oligo(dT) tract and its biological implications. Nature. 1987 Nov 19;330(6145):221–226. doi: 10.1038/330221a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pjura P. E., Grzeskowiak K., Dickerson R. E. Binding of Hoechst 33258 to the minor groove of B-DNA. J Mol Biol. 1987 Sep 20;197(2):257–271. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90123-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. H., Fujii S., van Boom J. H., Rich A. Molecular structure of the octamer d(G-G-C-C-G-G-C-C): modified A-DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):3968–3972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.3968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. H., Quigley G. J., Kolpak F. J., Crawford J. L., van Boom J. H., van der Marel G., Rich A. Molecular structure of a left-handed double helical DNA fragment at atomic resolution. Nature. 1979 Dec 13;282(5740):680–686. doi: 10.1038/282680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wing R., Drew H., Takano T., Broka C., Tanaka S., Itakura K., Dickerson R. E. Crystal structure analysis of a complete turn of B-DNA. Nature. 1980 Oct 23;287(5784):755–758. doi: 10.1038/287755a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakrzewska K., Lavery R., Pullman B. Theoretical studies of the selective binding to DNA of two non-intercalating ligands: netropsin and SN 18071. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 20;11(24):8825–8839. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.24.8825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer C., Wähnert U. Nonintercalating DNA-binding ligands: specificity of the interaction and their use as tools in biophysical, biochemical and biological investigations of the genetic material. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1986;47(1):31–112. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(86)90005-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



