Abstract
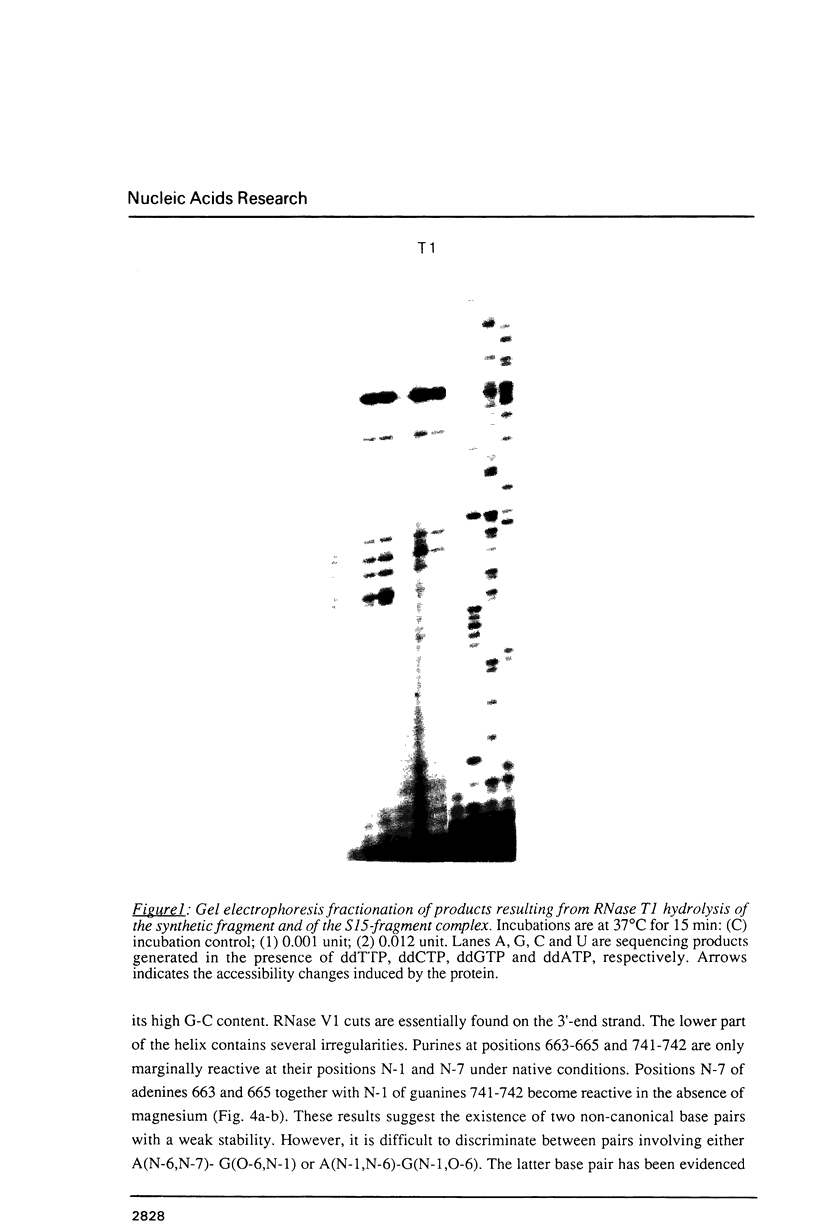
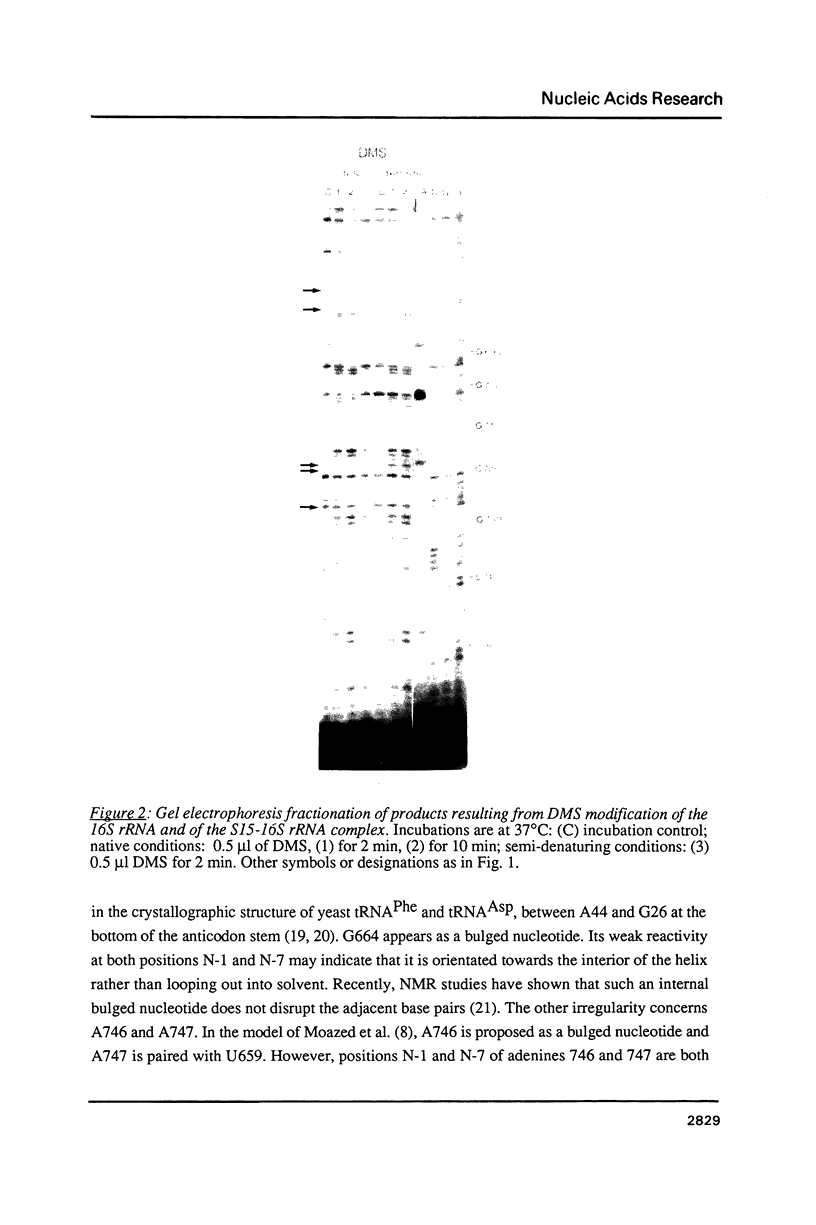
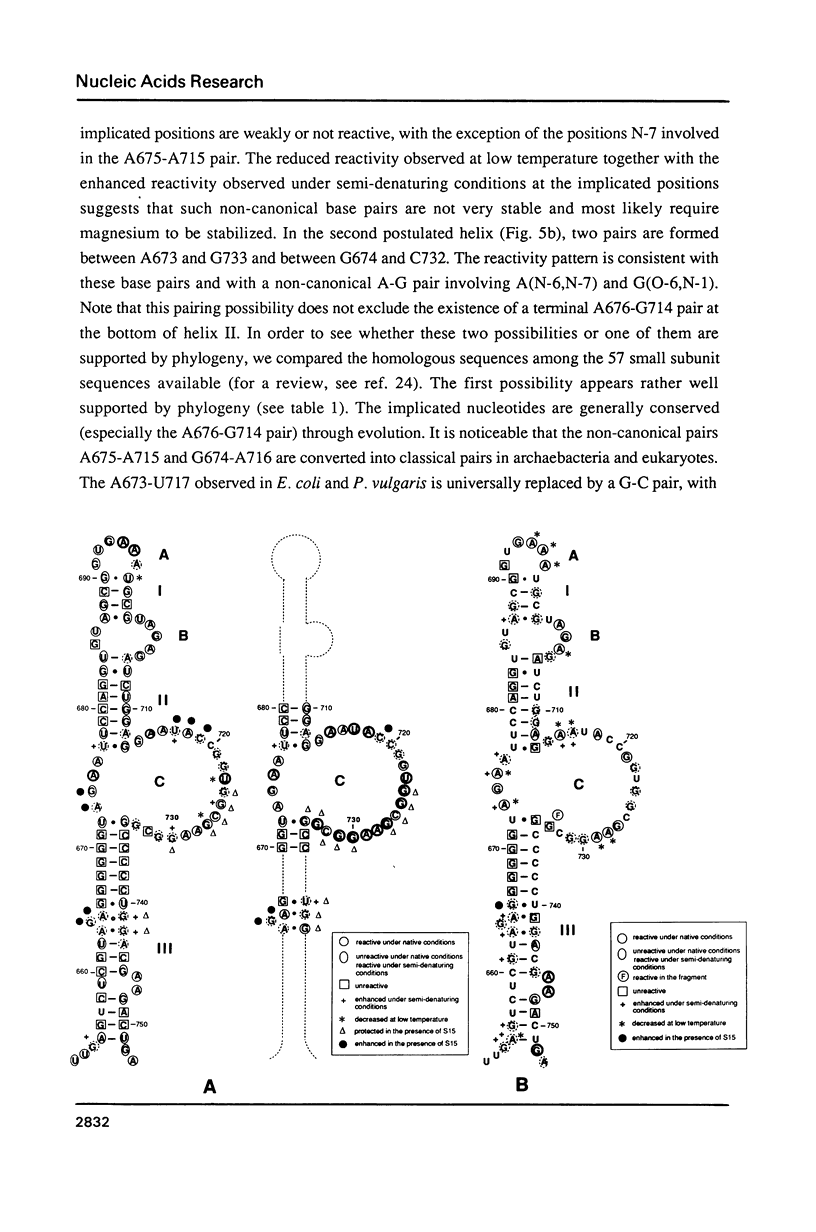
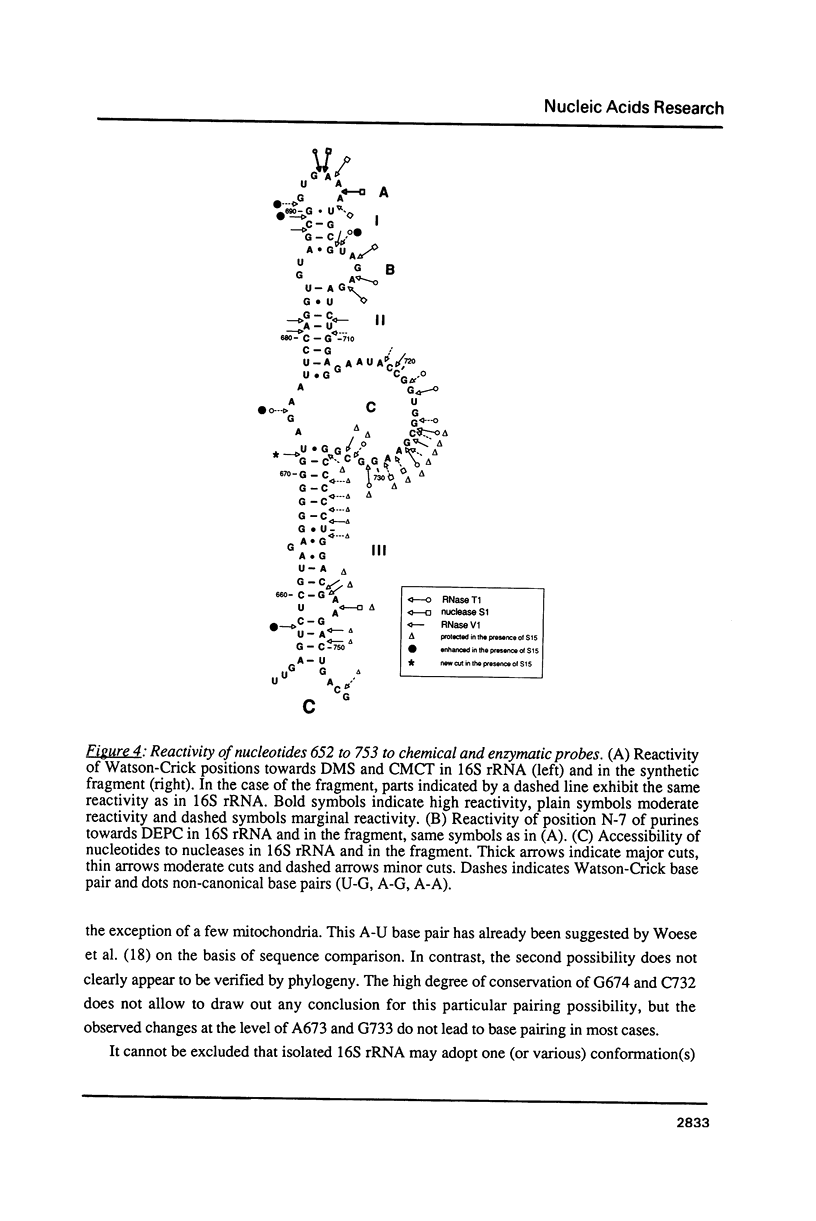
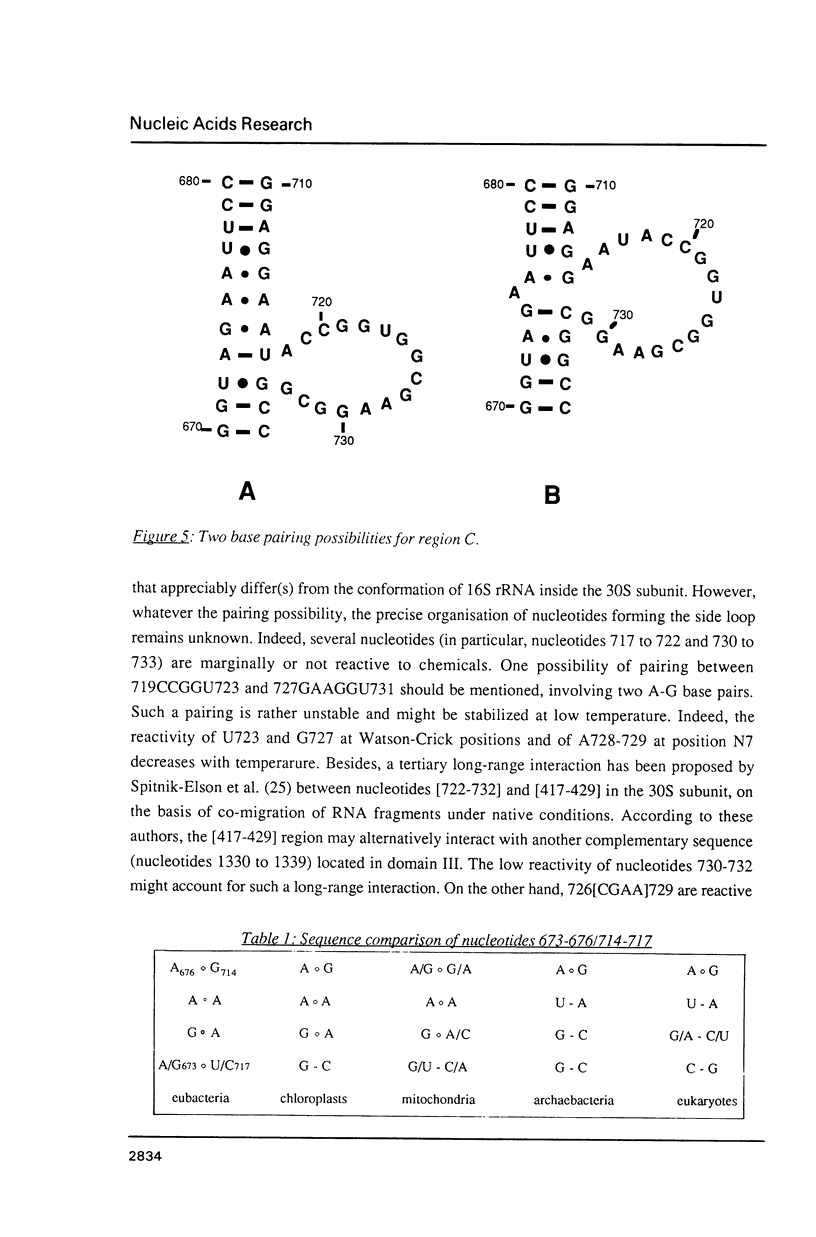
We have investigated in detail the secondary and tertiary structures of E. coli 16S rRNA binding site of protein S15 using a variety of enzymatic and chemical probes. RNase T1 and nuclease S1 were used to probe unpaired nucleotides and RNase V1 to monitor base-paired or stacked nucleotides. Bases were probed with dimethylsulfate (at A(N-1), C(N-3) and G(N-7)), with 1-cyclohexyl-3 (2-(1-methylmorpholino)-ethyl)-carboiimide-p- toluenesulfonate (at U(N-3) and G(N-1)) and with diethylpyrocarbonate (at A(N-7)). The RNA region corresponding to nucleotides 652 to 753 was tested within: (1) the complete 16S rRNA molecule; (2) a 16S rRNA fragment corresponding to nucleotides 578 to 756 obtained by transcription in vitro; (3) the S15-16S rRNA complex; (4) the S15-fragment complex. Cleavage and modification sites were detected by primer extension with reverse transcriptase. Our results show that: (1) The synthetized fragment folds into the same overall secondary structure as in the complete 16S rRNA, with the exception of the large asymmetrical internal loop (nucleotides 673-676/714-733) which is fully accessible in the fragment while it appears conformationally heterogeneous in the 16S rRNA; (2) the reactivity patterns of the S15-16S rRNA and S15-fragment complexes are identical; (3) the protein protects defined RNA regions, located in the large interior loop and in the 3'-end strand of helix [655-672]-[734-751]; (4) the protein also causes enhanced chemical reactivity and enzyme accessibility interpreted as resulting from a local conformational rearrangement, induced by S15 binding.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Capel M. S., Engelman D. M., Freeborn B. R., Kjeldgaard M., Langer J. A., Ramakrishnan V., Schindler D. G., Schneider D. K., Schoenborn B. P., Sillers I. Y. A complete mapping of the proteins in the small ribosomal subunit of Escherichia coli. Science. 1987 Dec 4;238(4832):1403–1406. doi: 10.1126/science.3317832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egebjerg J., Leffers H., Christensen A., Andersen H., Garrett R. A. Structure and accessibility of domain I of Escherichia coli 23 S RNA in free RNA, in the L24-RNA complex and in 50 S subunits. Implications for ribosomal assembly. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 5;196(1):125–136. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90515-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehresmann C., Baudin F., Mougel M., Romby P., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann B. Probing the structure of RNAs in solution. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 25;15(22):9109–9128. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.22.9109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flamion P. J., Schreiber J. P. Ionic-exchange high-performance liquid chromatography of Escherichia coli ribosomal small-subunit proteins. Anal Biochem. 1985 Jun;147(2):458–461. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90298-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory R. J., Zeller M. L., Thurlow D. L., Gourse R. L., Stark M. J., Dahlberg A. E., Zimmermann R. A. Interaction of ribosomal proteins S6, S8, S15 and S18 with the central domain of 16 S ribosomal RNA from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1984 Sep 15;178(2):287–302. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90145-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greuer B., Osswald M., Brimacombe R., Stöffler G. RNA-protein cross-linking in Escherichia coli 30S ribosomal subunits; determination of sites on 16S RNA that are cross-linked to proteins S3, S4, S7, S9, S10, S11, S17, S18 and S21 by treatment with bis-(2-chloroethyl)-methylamine. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 24;15(8):3241–3255. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.8.3241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutell R. R., Weiser B., Woese C. R., Noller H. F. Comparative anatomy of 16-S-like ribosomal RNA. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1985;32:155–216. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60348-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Held W. A., Ballou B., Mizushima S., Nomura M. Assembly mapping of 30 S ribosomal proteins from Escherichia coli. Further studies. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 25;249(10):3103–3111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Chapman N. M., Noller H. F. Mechanism of ribosomal subunit association: discrimination of specific sites in 16 S RNA essential for association activity. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jun 5;130(4):433–449. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90433-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter W. N., Brown T., Kennard O. Structural features and hydration of d(C-G-C-G-A-A-T-T-A-G-C-G); a double helix containing two G.A mispairs. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1986 Oct;4(2):173–191. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1986.10506338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huysmans E., De Wachter R. Compilation of small ribosomal subunit RNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986;14 (Suppl):r73–118. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.suppl.r73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kean J. M., Draper D. E. Secondary structure of a 345-base RNA fragment covering the S8/S15 protein binding domain of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 10;24(19):5052–5061. doi: 10.1021/bi00340a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyriatsoulis A., Maly P., Greuer B., Brimacombe R., Stöffler G., Frank R., Blöcker H. RNA-protein cross-linking in Escherichia coli ribosomal subunits: localization of sites on 16S RNA which are cross-linked to proteins S17 and S21 by treatment with 2-iminothiolane. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 11;14(3):1171–1186. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.3.1171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Noller H. F. Transfer RNA shields specific nucleotides in 16S ribosomal RNA from attack by chemical probes. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):985–994. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90813-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Stern S., Noller H. F. Rapid chemical probing of conformation in 16 S ribosomal RNA and 30 S ribosomal subunits using primer extension. J Mol Biol. 1986 Feb 5;187(3):399–416. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90441-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Van Stolk B. J., Douthwaite S., Noller H. F. Interconversion of active and inactive 30 S ribosomal subunits is accompanied by a conformational change in the decoding region of 16 S rRNA. J Mol Biol. 1986 Oct 5;191(3):483–493. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90143-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mougel M., Eyermann F., Westhof E., Romby P., Expert-Bezançon A., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann B., Ehresmann C. Binding of Escherichia coli ribosomal protein S8 to 16 S rRNA. A model for the interaction and the tertiary structure of the RNA binding site. J Mol Biol. 1987 Nov 5;198(1):91–107. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90460-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Garrett R. A., Noller H. F. The structure of the RNA binding site of ribosomal proteins S8 and S15. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):3873–3878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osswald M., Greuer B., Brimacombe R., Stöffler G., Bäumert H., Fasold H. RNA-protein cross-linking in Escherichia coli 30S ribosomal subunits; determination of sites on 16S RNA that are cross-linked to proteins S3, S4, S5, S7, S8, S9, S11, S13, S19 and S21 by treatment with methyl p-azidophenyl acetimidate. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 24;15(8):3221–3240. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.8.3221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitnik-Elson P., Elson D., Avital S., Abramowitz R. Long range RNA-RNA interactions in the 30 S ribosomal subunit of E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 11;13(13):4719–4738. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.13.4719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark M. J., Gregory R. J., Gourse R. L., Thurlow D. L., Zwieb C., Zimmermann R. A., Dahlberg A. E. Effects of site-directed mutations in the central domain of 16 S ribosomal RNA upon ribosomal protein binding, RNA processing and 30 S subunit assembly. J Mol Biol. 1984 Sep 15;178(2):303–322. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90146-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern S., Wilson R. C., Noller H. F. Localization of the binding site for protein S4 on 16 S ribosomal RNA by chemical and enzymatic probing and primer extension. J Mol Biol. 1986 Nov 5;192(1):101–110. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90467-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub W., Sussman J. L. Adenine-guanine base pairing ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Apr 24;10(8):2701–2708. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.8.2701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ungewickell E., Garrett R., Ehresmann C., Stiegler P., Fellner P. An investigation of the 16-S RNA binding sites of ribosomal proteins S4, S8, S15, and S20 FROM Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Feb 3;51(1):165–180. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb03917.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westhof E., Dumas P., Moras D. Crystallographic refinement of yeast aspartic acid transfer RNA. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jul 5;184(1):119–145. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90048-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Gutell R., Gupta R., Noller H. F. Detailed analysis of the higher-order structure of 16S-like ribosomal ribonucleic acids. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Dec;47(4):621–669. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.4.621-669.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann R. A., Mackie G. A., Muto A., Garrett R. A., Ungewickell E., Ehresmann C., Stiegler P., Ebel J. P., Fellner P. Location and characteristics of ribosomal protein binding sites in the 16S RNA of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Feb;2(2):279–302. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.2.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann R. A., Singh-Bergmann K. Binding sites for ribosomal proteins S8 and S15 in the 16 S RNA of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jul 26;563(2):422–431. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(79)90061-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






