Abstract
A method is described for the rapid purification of high quality lambda DNA. The method can be used from either liquid or plate lysates and on a small scale or a large scale. It relies on the preadsobtion of all polyanions present in the lysate to an "insoluble" anion-exchange matrix (DEAE or TEAE). Phage particles are then disrupted by combined treatment with EDTA/proteinase K and the resulting DNA is precipitated by the addition of the cationic detergent cetyl (or hexadecyl)-trimethyl ammonium bromide-CTAB ("soluble" anion-exchange matrix). The precipitated CTAB-DNA complex is then exchanged to Na-DNA and ethanol precipitated. The resultant purified DNA is suitable for enzymatic reactions and provides a high quality template for dideoxy-sequence analysis.
Full text
PDF



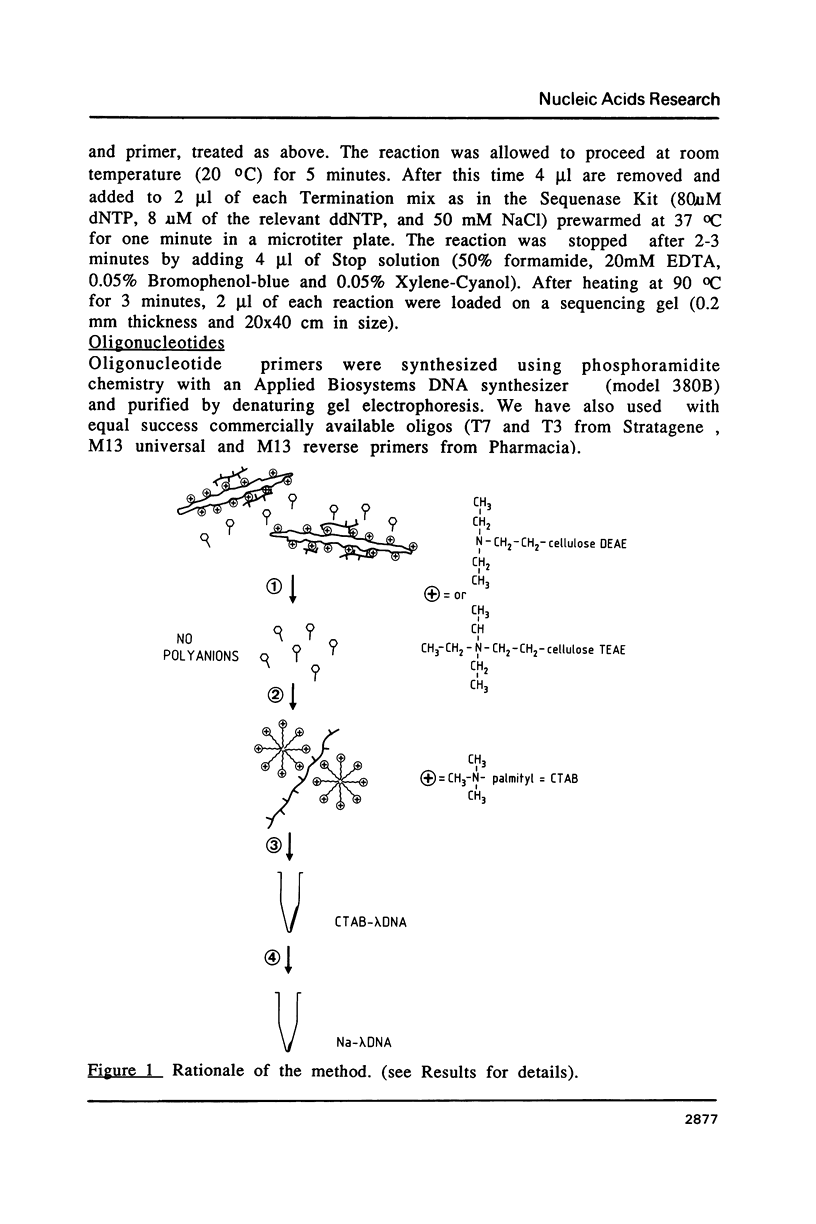

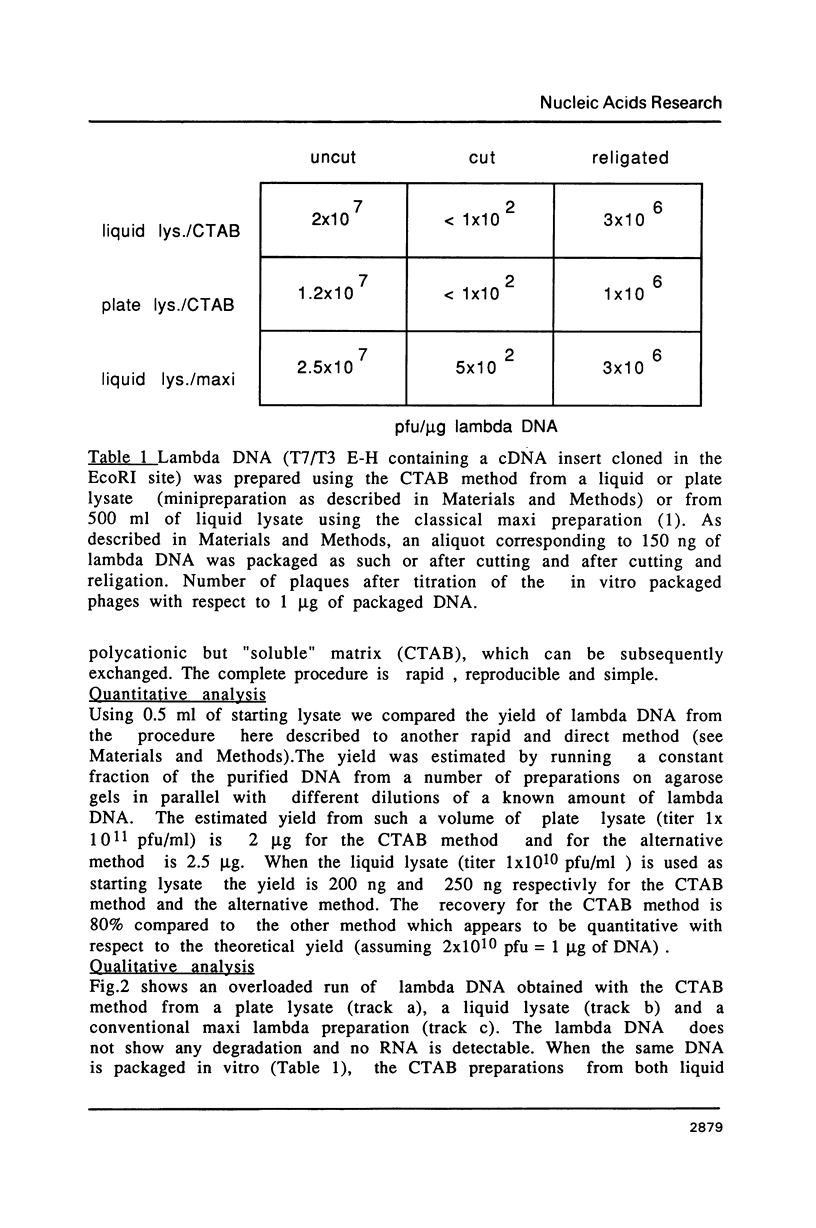





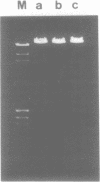
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Del Sal G., Schneider C. A simple and fast method for preparing single stranded DNA template suitable for sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 10;15(23):10047–10047. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.23.10047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi G., Manfioletti G., Schneider C. A lambda vector for directional cDNA cloning and in vitro transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 25;15(22):9608–9608. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.22.9608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helms C., Graham M. Y., Dutchik J. E., Olson M. V. A new method for purifying lambda DNA from phage lysates. DNA. 1985 Feb;4(1):39–49. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JONES A. S. USE OF ALKYLTRIMETHYLAMMONIUM BROMIDES FOR THE ISOLATION OF RIBO- AND DESOXYRIBO-NUCLEIC ACIDS. Nature. 1963 Jul 20;199:280–282. doi: 10.1038/199280b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. G., Thompson W. F. Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Oct 10;8(19):4321–4325. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.19.4321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scalenghe F., Turco E., Edström J. E., Pirrotta V., Melli M. Microdissection and cloning of DNA from a specific region of Drosophila melanogaster polytene chromosomes. Chromosoma. 1981;82(2):205–216. doi: 10.1007/BF00286105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker R. T., RajBhandary U. L. Formylatable methionine transfer RNA from Mycoplasma: purification and comparison of partial nucleotide sequences with those of other prokaryotic initiator tRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Jan;2(1):61–78. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]