Abstract
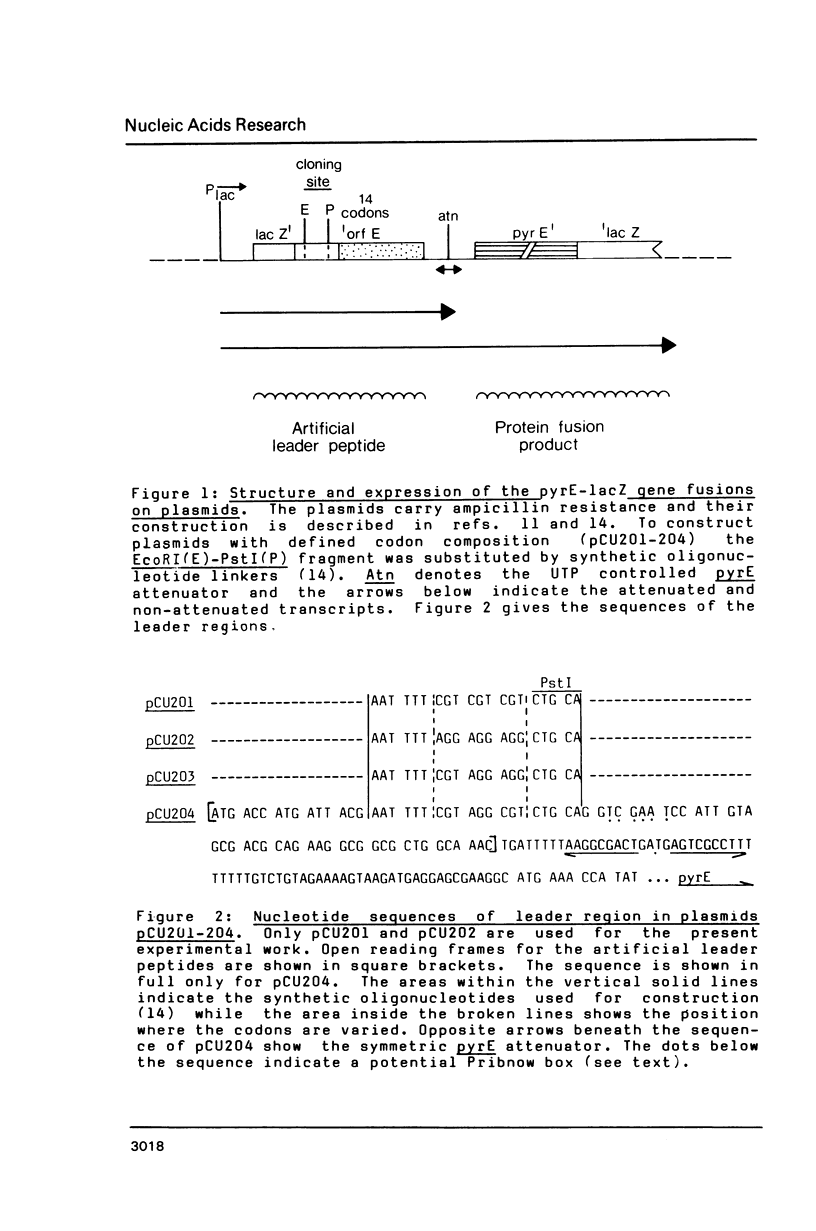
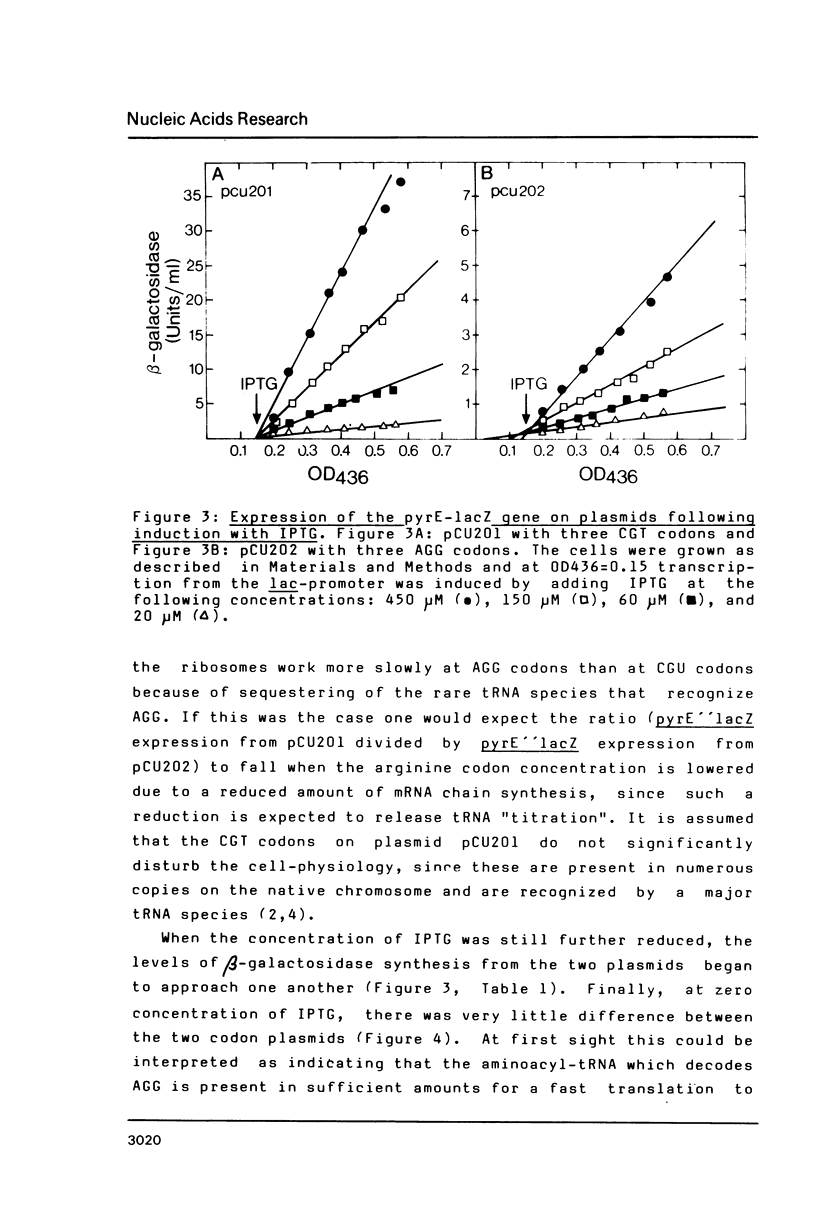
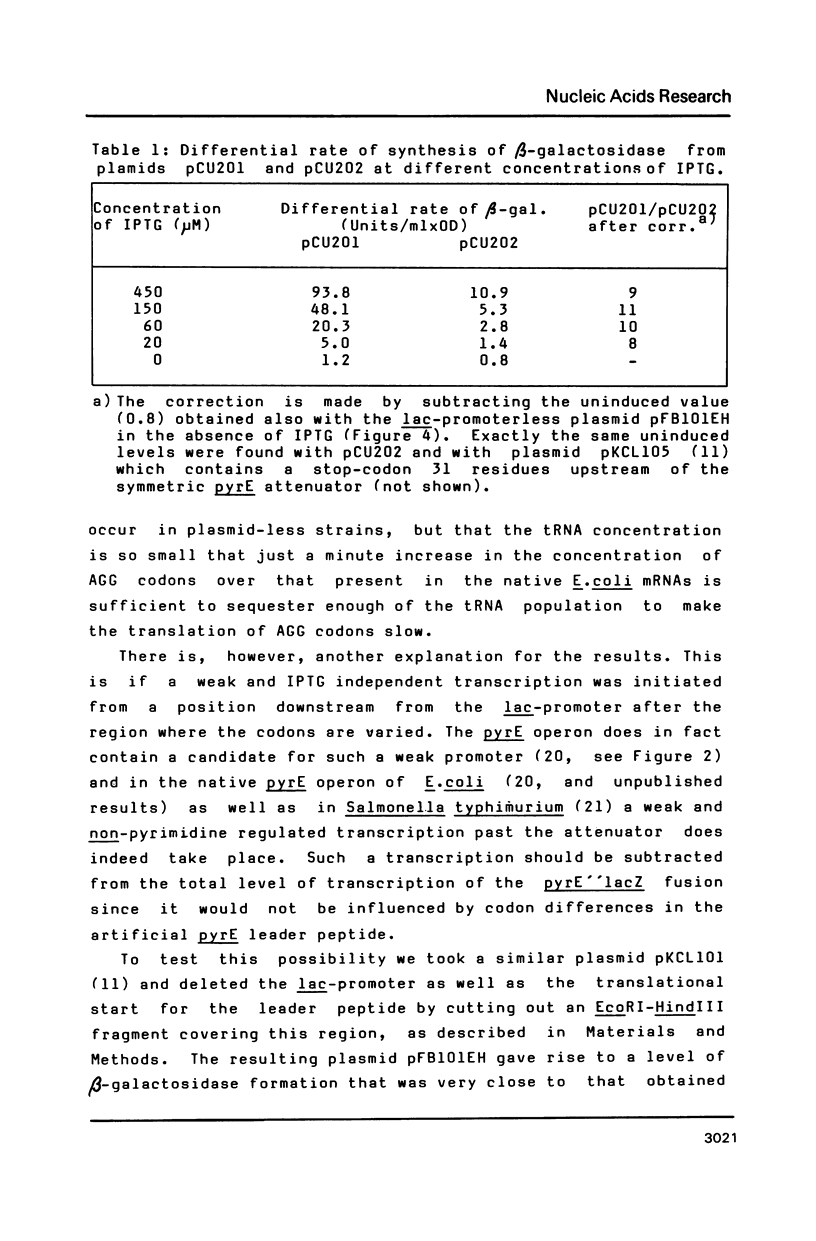
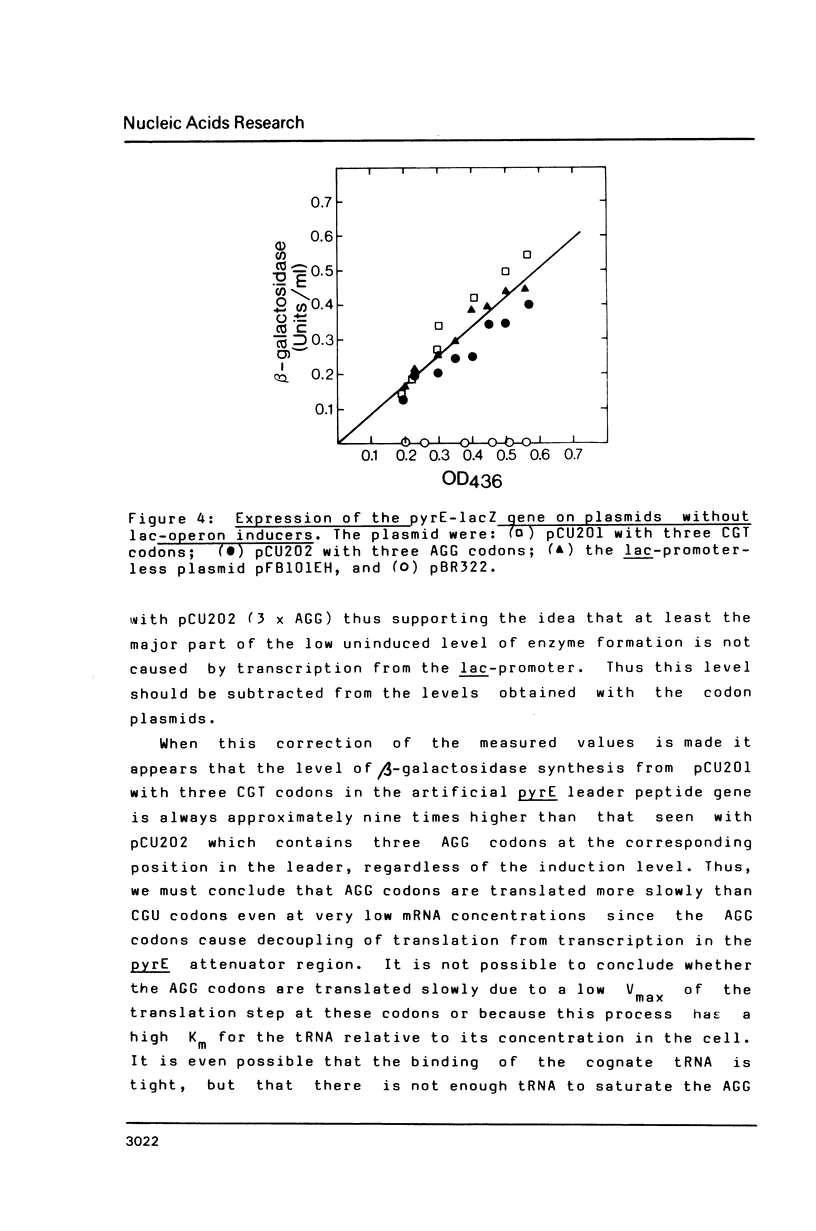
Data are presented which indicate that AGG codons for arginine are translated significantly more slowly than the CGU codons for the same amino acid even when their expression level from the probe is very low. The two types of codons were inserted (three in tandem) on a multicopy plasmid in an artificial leader peptide gene in front of the pyrE attenuator where the frequency of transcription termination is regulated by the degree of coupling between transcription and translation. Transcription of the operon is initiated from the lac-promoter dependent on the concentration of the lac-operon inducer IPTG. At all induction levels it was found that the frequency of transcription past the pyrE attenuator was approximately nine times lower when the AGG codons were present in the leader than with CGT codons present. This shows that AGG codons decouple translation from transcription in the pyrE attenuator region even when the concentration of this codon is not increased significantly relative to that in the unperturbed wild type strain. Thus the results indicate that AGG codons are always slowly translated in Escherichia coli.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennetzen J. L., Hall B. D. Codon selection in yeast. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3026–3031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonekamp F., Andersen H. D., Christensen T., Jensen K. F. Codon-defined ribosomal pausing in Escherichia coli detected by using the pyrE attenuator to probe the coupling between transcription and translation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 11;13(11):4113–4123. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.11.4113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonekamp F., Clemmesen K., Karlström O., Jensen K. F. Mechanism of UTP-modulated attenuation at the pyrE gene of Escherichia coli: an example of operon polarity control through the coupling of translation to transcription. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2857–2861. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02220.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulmer M. Coevolution of codon usage and transfer RNA abundance. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):728–730. doi: 10.1038/325728a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosjean H., Fiers W. Preferential codon usage in prokaryotic genes: the optimal codon-anticodon interaction energy and the selective codon usage in efficiently expressed genes. Gene. 1982 Jun;18(3):199–209. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90157-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T. Codon usage and tRNA content in unicellular and multicellular organisms. Mol Biol Evol. 1985 Jan;2(1):13–34. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T. Correlation between the abundance of Escherichia coli transfer RNAs and the occurrence of the respective codons in its protein genes: a proposal for a synonymous codon choice that is optimal for the E. coli translational system. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 25;151(3):389–409. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T. Correlation between the abundance of yeast transfer RNAs and the occurrence of the respective codons in protein genes. Differences in synonymous codon choice patterns of yeast and Escherichia coli with reference to the abundance of isoaccepting transfer RNAs. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jul 15;158(4):573–597. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90250-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen K. F., Fast R., Karlström O., Larsen J. N. Association of RNA polymerase having increased Km for ATP and UTP with hyperexpression of the pyrB and pyrE genes of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):857–865. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.857-865.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen K. F., Neuhard J., Schack L. RNA polymerase involvement in the regulation of expression of Salmonella typhimurium pyr genes. Isolation and characterization of a fluorouracil-resistant mutant with high, constitutive expression of the pyrB and pyrE genes due to a mutation in rpoBC. EMBO J. 1982;1(1):69–74. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01126.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuhard J., Stauning E., Kelln R. A. Cloning and characterization of the pyrE gene and of PyrE::Mud1 (Ap lac) fusions from Salmonella typhimurium. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Feb 1;146(3):597–603. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08693.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen S. Escherichia coli ribosomes translate in vivo with variable rate. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2895–2898. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02227.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulsen P., Jensen K. F. Effect of UTP and GTP pools on attenuation at the pyrE gene of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Jun;208(1-2):152–158. doi: 10.1007/BF00330436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulsen P., Jensen K. F., Valentin-Hansen P., Carlsson P., Lundberg L. G. Nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli pyrE gene and of the DNA in front of the protein-coding region. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Sep 15;135(2):223–229. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07641.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson M., Lilley R., Little S., Emtage J. S., Yarranton G., Stephens P., Millican A., Eaton M., Humphreys G. Codon usage can affect efficiency of translation of genes in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 11;12(17):6663–6671. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.17.6663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varenne S., Buc J., Lloubes R., Lazdunski C. Translation is a non-uniform process. Effect of tRNA availability on the rate of elongation of nascent polypeptide chains. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 15;180(3):549–576. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90027-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



