Abstract
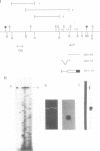
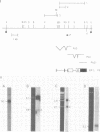
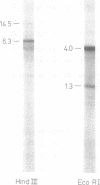
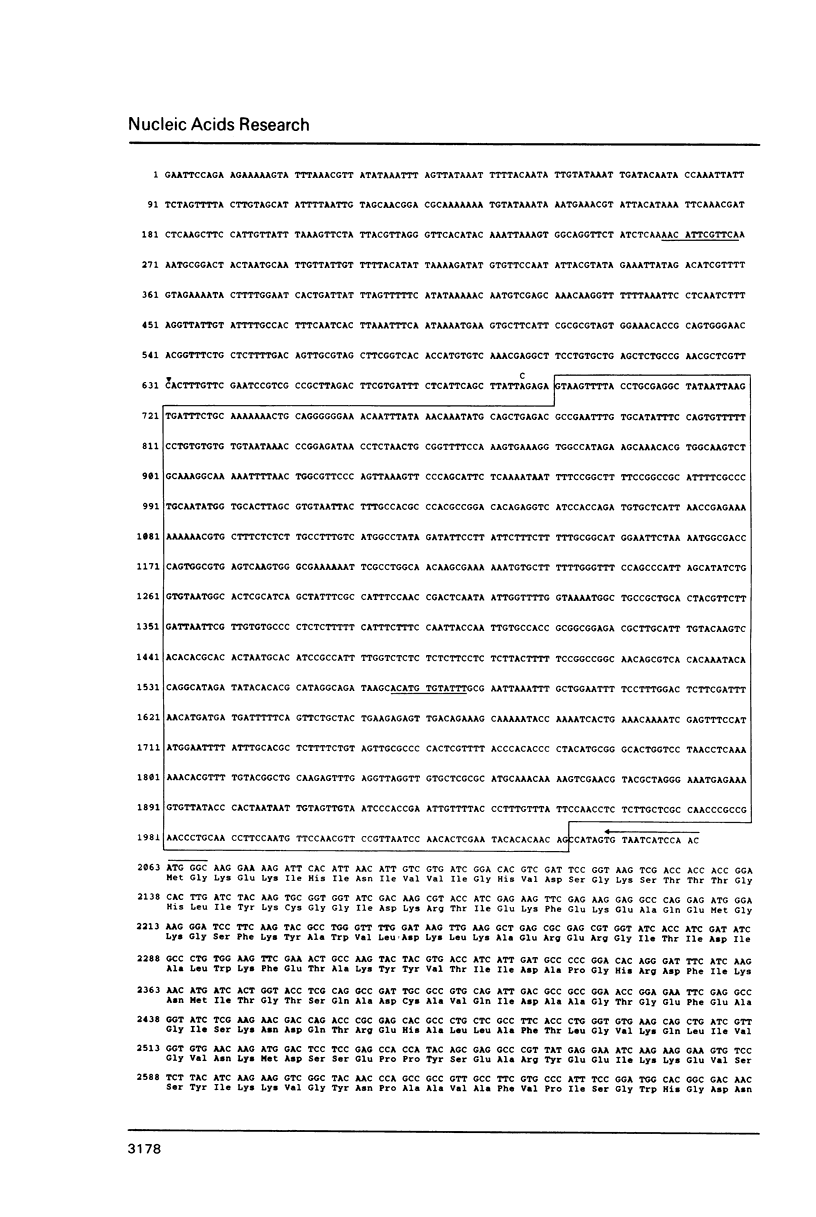
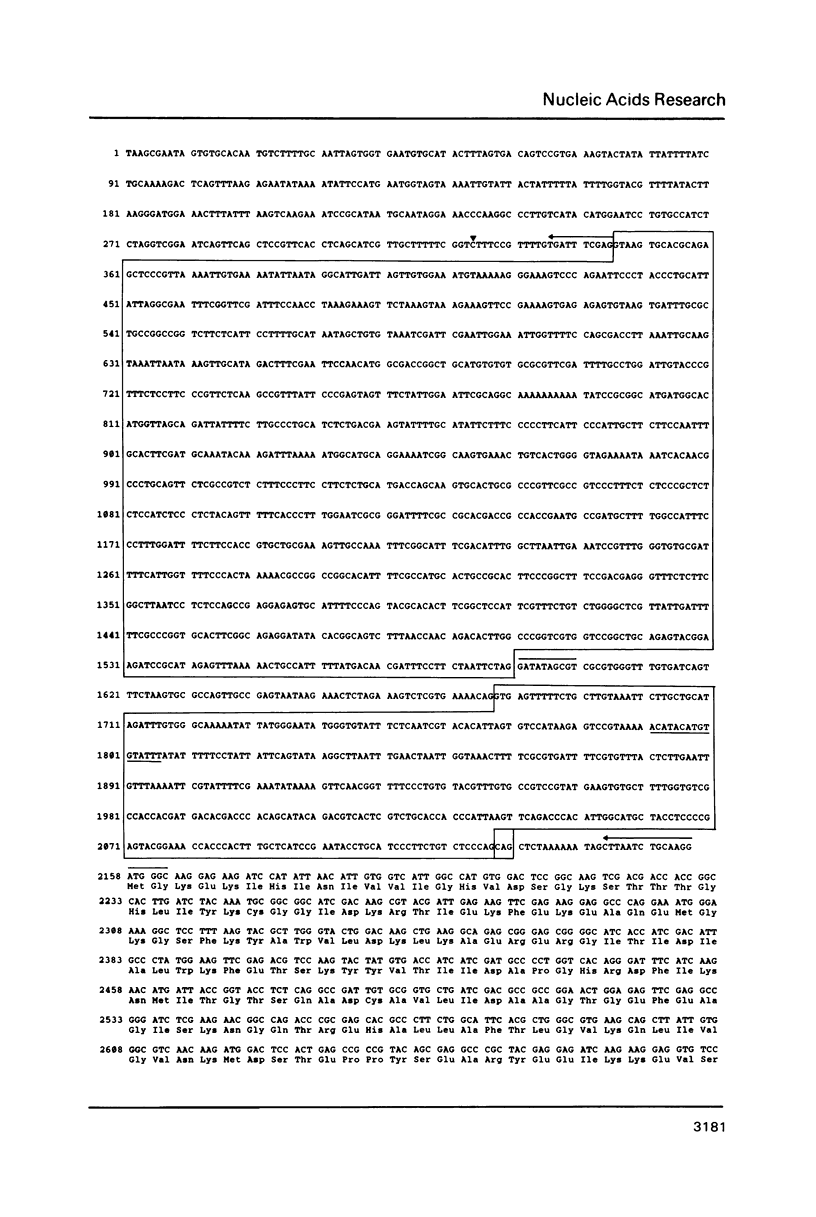
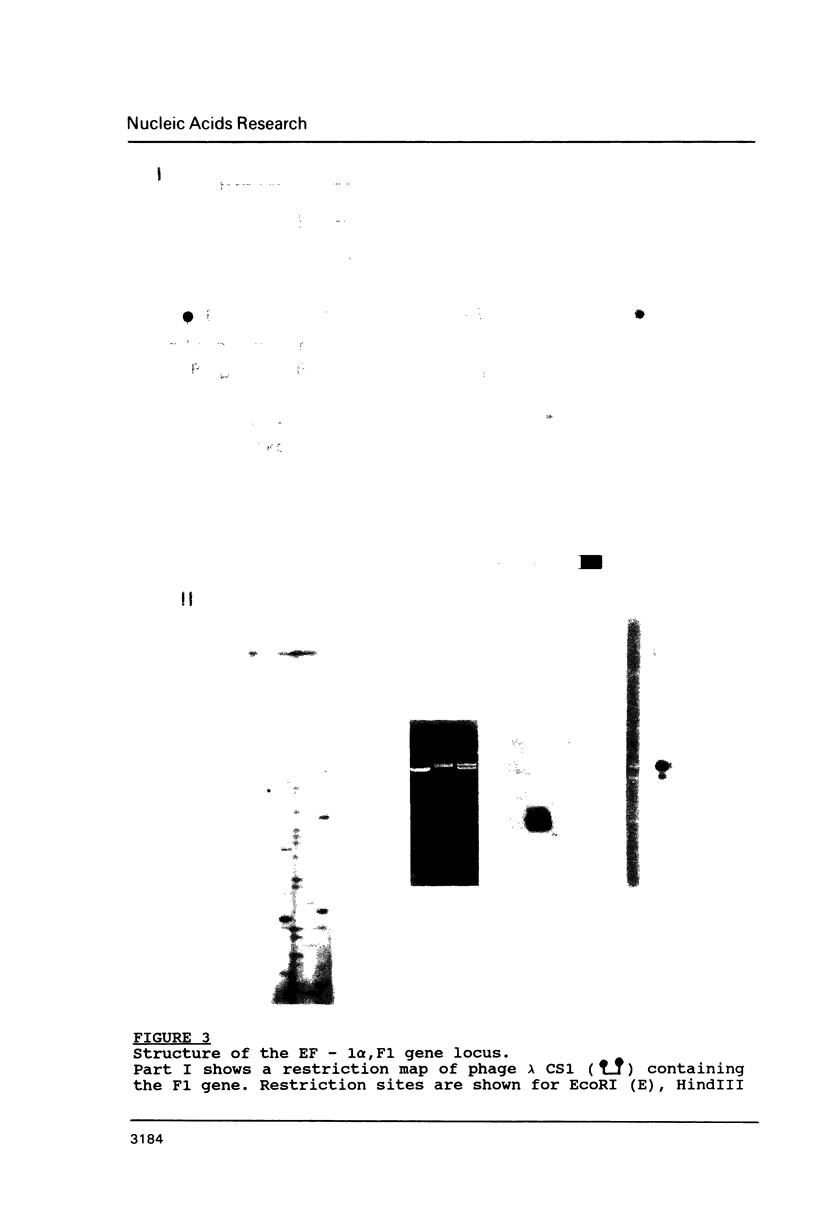
We have characterized two previously cloned genes, F1 and F2 (1) that code for elongation factor EF - 1 alpha of Drosophila melanogaster. Genomic Southern blot hybridization revealed that they are the only gene copies present. We isolated cDNA clones of both transcripts from embryonal and pupal stage of development that cover the entire transcription unit. The 5' ends of both genes have been determined by primer extension and for F1 also by RNA sequencing. These start sites have been shown to be used consistently during development. Comparison of cDNA and genomic sequences revealed that EF - 1 alpha,F1 consists of two and EF - 1 alpha,F2 of five exons. The two described elongation factor genes exhibit several regions of strong sequence conservation when compared to five recently cloned eucaryotic elongation factors.
Full text
PDF
















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballinger D. G., Pardue M. L. The control of protein synthesis during heat shock in Drosophila cells involves altered polypeptide elongation rates. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90339-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brands J. H., Maassen J. A., van Hemert F. J., Amons R., Möller W. The primary structure of the alpha subunit of human elongation factor 1. Structural aspects of guanine-nucleotide-binding sites. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Feb 17;155(1):167–171. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09472.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cottrelle P., Thiele D., Price V. L., Memet S., Micouin J. Y., Marck C., Buhler J. M., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression of one of two genes coding for yeast elongation factor 1 alpha. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):3090–3096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crechet J. B., Canceill D., Bocchini V., Parmeggiani A. Characterization of the elongation factors from calf brain. 1. Purification, molecular and immunological properties. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Dec 15;161(3):635–645. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10488.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dever T. E., Glynias M. J., Merrick W. C. GTP-binding domain: three consensus sequence elements with distinct spacing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1814–1818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drews J., Bednarik K., Grasmuk H. Elongation factor 1 from Krebs II mouse ascites cells. Purification, structure and enzymatic properties. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jan 16;41(2):217–227. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03263.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geliebter J., Zeff R. A., Melvold R. W., Nathenson S. G. Mitotic recombination in germ cells generated two major histocompatibility complex mutant genes shown to be identical by RNA sequence analysis: Kbm9 and Kbm6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3371–3375. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet J., Cottrelle P., Cool M., Vignais M. L., Thiele D., Marck C., Buhler J. M., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. A general upstream binding factor for genes of the yeast translational apparatus. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3539–3547. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04114.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaziro Y. The role of guanosine 5'-triphosphate in polypeptide chain elongation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 21;505(1):95–127. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(78)90009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller E. B., Noon W. A. Intron splicing: a conserved internal signal in introns of Drosophila pre-mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 11;13(13):4971–4981. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.13.4971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemper W. M., Merrick W. C., Redfield B., Liu C. K., Weissbach H. Purification and properties of rabbit reticulocyte elongation factor 1. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Jun;174(2):603–612. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90389-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauer S. J., Burks E., Irvin J. D., Ravel J. M. Purification and characterization of three elongation factors, EF-1 alpha, EF-1 beta gamma, and EF-2, from wheat germ. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1644–1648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leberman R., Egner U. Homologies in the primary structure of GTP-binding proteins: the nucleotide-binding site of EF-Tu and p21. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):339–341. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01808.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenstra J. A., Van Vliet A., Arnberg A. C., Van Hemert F. J., Möller W. Genes coding for the elongation factor EF-1 alpha in Artemia. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Mar 17;155(3):475–483. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09514.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linz J. E., Katayama C., Sypherd P. S. Three genes for the elongation factor EF-1 alpha in Mucor racemosus. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):593–600. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linz J. E., Lira L. M., Sypherd P. S. The primary structure and the functional domains of an elongation factor-1 alpha from Mucor racemosus. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 15;261(32):15022–15029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., Coppard N. J., Brown R. S., Clark B. F., De Robertis E. M. 42S p48--the most abundant protein in previtellogenic Xenopus oocytes--resembles elongation factor 1 alpha structurally and functionally. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2409–2413. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02519.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami K., Miyamoto K. Polypeptide elongation factors of the developing chick brain. J Neurochem. 1982 May;38(5):1315–1322. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb07907.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata S., Motoyoshi K., Iwasaki K. Interaction of subunits of polypeptide chain elongation factor I from pig liver. Formation of EF-1alpha.EF-1betagamma and EF-1beta complexes. J Biochem. 1978 Feb;83(2):423–429. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata S., Nagashima K., Tsunetsugu-Yokota Y., Fujimura K., Miyazaki M., Kaziro Y. Polypeptide chain elongation factor 1 alpha (EF-1 alpha) from yeast: nucleotide sequence of one of the two genes for EF-1 alpha from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1825–1830. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02053.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connell P. O., Rosbash M. Sequence, structure, and codon preference of the Drosophila ribosomal protein 49 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5495–5513. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao T. R., Slobin L. I. Structure of the amino-terminal end of mammalian elongation factor Tu. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 11;14(5):2409–2409. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.5.2409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth W. W., Bragg P. W., Corrias M. V., Reddy N. S., Dholakia J. N., Wahba A. J. Expression of a gene for mouse eucaryotic elongation factor Tu during murine erythroleukemic cell differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):3929–3936. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.3929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schirmaier F., Philippsen P. Identification of two genes coding for the translation elongation factor EF-1 alpha of S. cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3311–3315. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02295.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. M., Tuohy T. M., Mosurski K. R. Codon usage in yeast: cluster analysis clearly differentiates highly and lowly expressed genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 11;14(13):5125–5143. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.13.5125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slobin L. I., Möller W. Purification and properties of an elongation factor functionally analogous to bacterial elongation factor Ts from embryos of Artemia salina. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Mar;84(1):69–77. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12142.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiele D., Cottrelle P., Iborra F., Buhler J. M., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. Elongation factor 1 alpha from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Rapid large-scale purification and molecular characterization. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):3084–3089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viel A., Djé M. K., Mazabraud A., Denis H., le Maire M. Thesaurin a, the major protein of Xenopus laevis previtellogenic oocytes, present in the 42 S particles, is homologous to elongation factor EF-1 alpha. FEBS Lett. 1987 Nov 2;223(2):232–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80295-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walldorf U., Hovemann B., Bautz E. K. F1 and F2: Two similar genes regulated differently during development of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5795–5799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]