Abstract
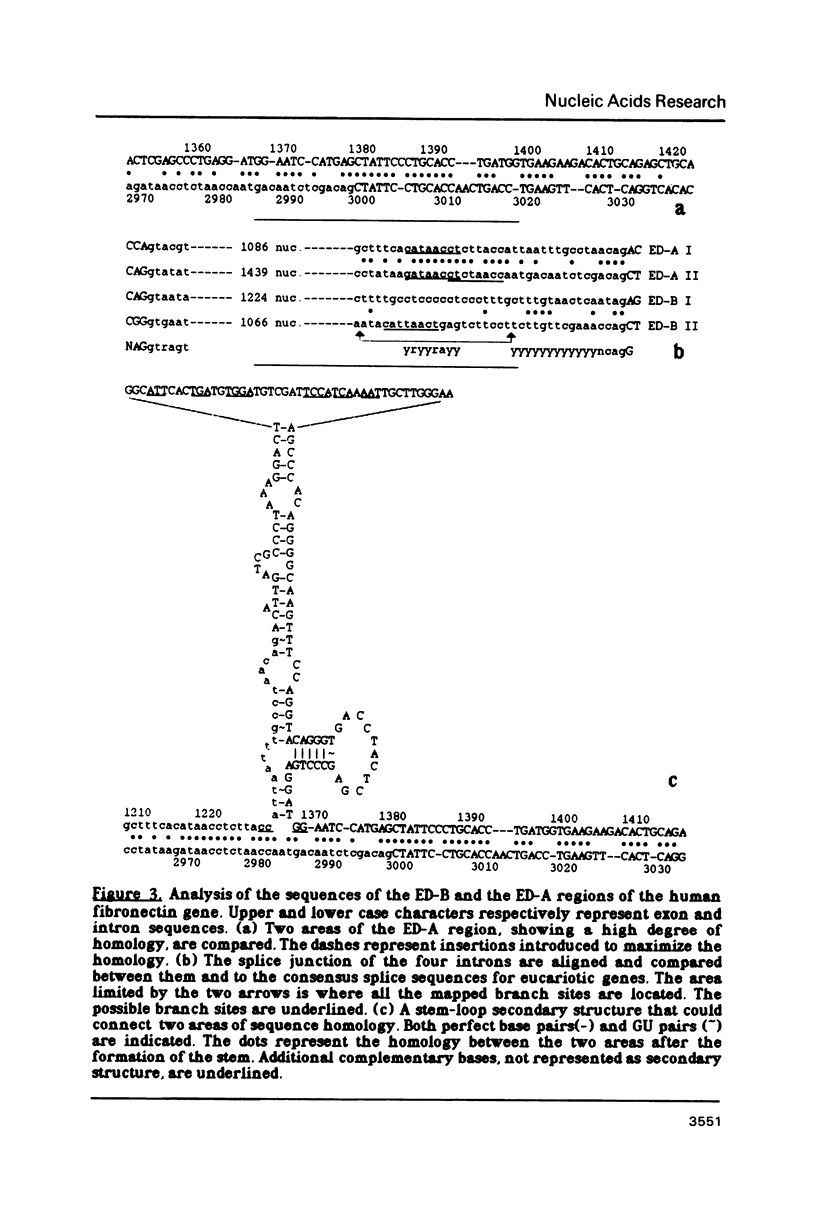
The structure of two alternatively spliced regions. ED-A and ED-B, of human fibronectin gene, was determined, in order to show whether any similarity was present between the two. Although some interesting features are present in each, no obvious common structure or sequence homology was found. Functional analysis of the alternative splicing events was carried out by transient expression in Hela cells. A hybrid gene was constructed by inserting the ED-B region into the third exon of the human alpha 1-globin gene. The transfected hybrid gene is expressed and produces, in Hela cells, two alternatively spliced RNAs, showing a pattern very similar to that observed for the endogenous fibronectin gene in fibroblasts. Cotransfection of this gene with a similar gene containing the ED-A region, shows that no interference is present between the two alternative splicing processes.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alt F. W., Bothwell A. L., Knapp M., Siden E., Mather E., Koshland M., Baltimore D. Synthesis of secreted and membrane-bound immunoglobulin mu heavy chains is directed by mRNAs that differ at their 3' ends. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):293–301. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90615-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amara S. G., Jonas V., Rosenfeld M. G., Ong E. S., Evans R. M. Alternative RNA processing in calcitonin gene expression generates mRNAs encoding different polypeptide products. Nature. 1982 Jul 15;298(5871):240–244. doi: 10.1038/298240a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnemolla B., Borsi L., Zardi L., Owens R. J., Baralle F. E. Localization of the cellular-fibronectin-specific epitope recognized by the monoclonal antibody IST-9 using fusion proteins expressed in E. coli. FEBS Lett. 1987 May 11;215(2):269–273. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80160-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froman B. E., Tait R. C., Kado C. I., Rodriguez R. L. Purification of restriction endonuclease XcyI from Xanthomonas cyanopsidis. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):331–335. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90150-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld G. C., de Boer E., Shewmaker C. K., Flavell R. A. DNA sequences necessary for transcription of the rabbit beta-globin gene in vivo. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):120–126. doi: 10.1038/295120a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornig H., Aebi M., Weissmann C. Effect of mutations at the lariat branch acceptor site on beta-globin pre-mRNA splicing in vitro. Nature. 1986 Dec 11;324(6097):589–591. doi: 10.1038/324589a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. Molecular biology of fibronectin. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:67–90. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.000435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornblihtt A. R., Vibe-Pedersen K., Baralle F. E. Human fibronectin: cell specific alternative mRNA splicing generates polypeptide chains differing in the number of internal repeats. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5853–5868. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornblihtt A. R., Vibe-Pedersen K., Baralle F. E. Human fibronectin: molecular cloning evidence for two mRNA species differing by an internal segment coding for a structural domain. EMBO J. 1984 Jan;3(1):221–226. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01787.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mardon H. J., Sebastio G., Baralle F. E. A role for exon sequences in alternative splicing of the human fibronectin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):7725–7733. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.7725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odermatt E., Tamkun J. W., Hynes R. O. Repeating modular structure of the fibronectin gene: relationship to protein structure and subunit variation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6571–6575. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens R. J., Kornblihtt A. R., Baralle F. E. Fibronectin, the generation of multiple polypeptides from a single gene. Oxf Surv Eukaryot Genes. 1986;3:141–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul J. I., Schwarzbauer J. E., Tamkun J. W., Hynes R. O. Cell-type-specific fibronectin subunits generated by alternative splicing. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12258–12265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Greene J. M., Green M. R. Cryptic branch point activation allows accurate in vitro splicing of human beta-globin intron mutants. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):833–844. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarzbauer J. E., Patel R. S., Fonda D., Hynes R. O. Multiple sites of alternative splicing of the rat fibronectin gene transcript. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2573–2580. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02547.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarzbauer J. E., Tamkun J. W., Lemischka I. R., Hynes R. O. Three different fibronectin mRNAs arise by alternative splicing within the coding region. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):421–431. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90175-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vibe-Pedersen K., Kornblihtt A. R., Baralle F. E. Expression of a human alpha-globin/fibronectin gene hybrid generates two mRNAs by alternative splicing. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2511–2516. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02165.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zardi L., Carnemolla B., Siri A., Petersen T. E., Paolella G., Sebastio G., Baralle F. E. Transformed human cells produce a new fibronectin isoform by preferential alternative splicing of a previously unobserved exon. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2337–2342. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02509.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]