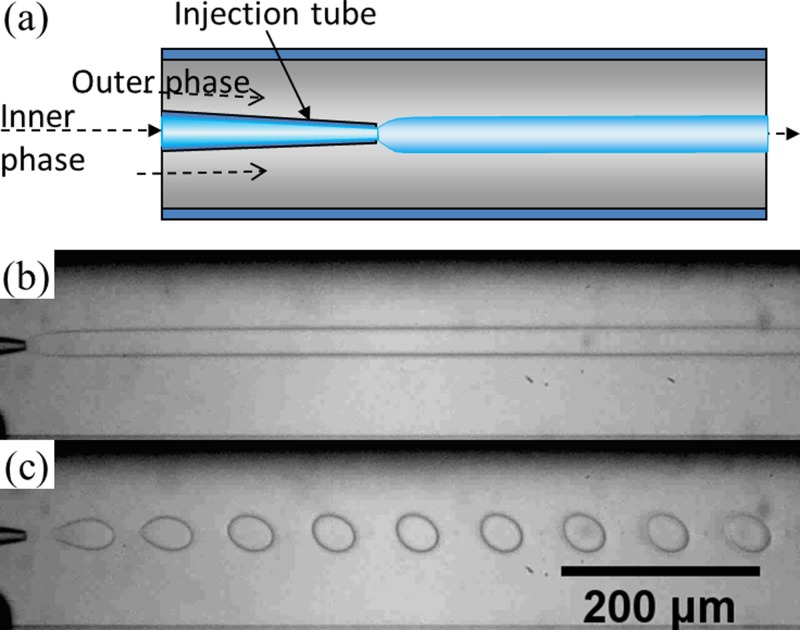
Figure 1.
(a) Schematic of a capillary microfluidic device used in this study; (b) optical microscope image showing a jet of 17 wt. % PEG solution in a continuous phase of 16 wt. % dextran solution in the microfluidic device. Flow rates of the PEG solution and the dextran solution are 40 μl/h and 5000 μl/h, respectively; (c) optical microscope image of monodisperse droplets of 17 wt. % PEG solution in 16 wt. % dextran solution with an agitation of the tubing of the dispersed phase at 6.7 Hz. Flow rates of the two phases are the same as those for (b).