Abstract
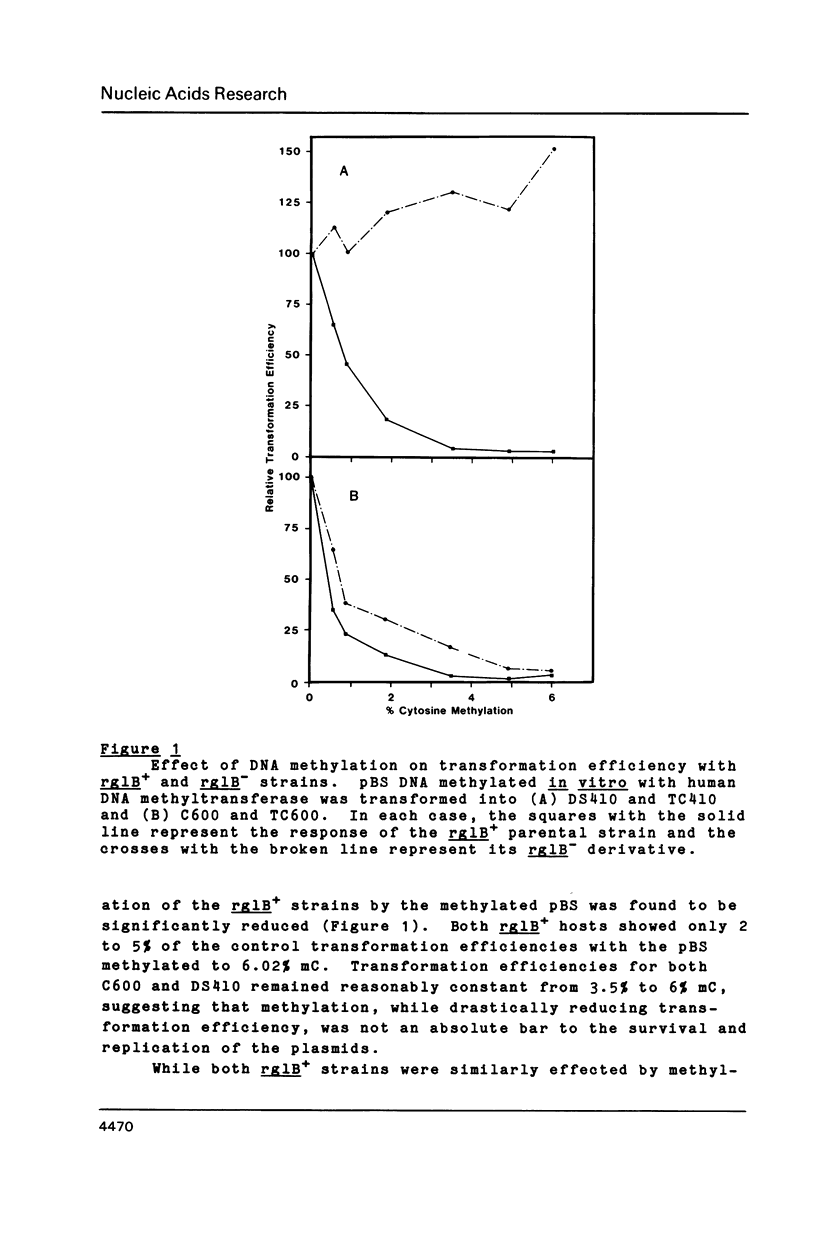
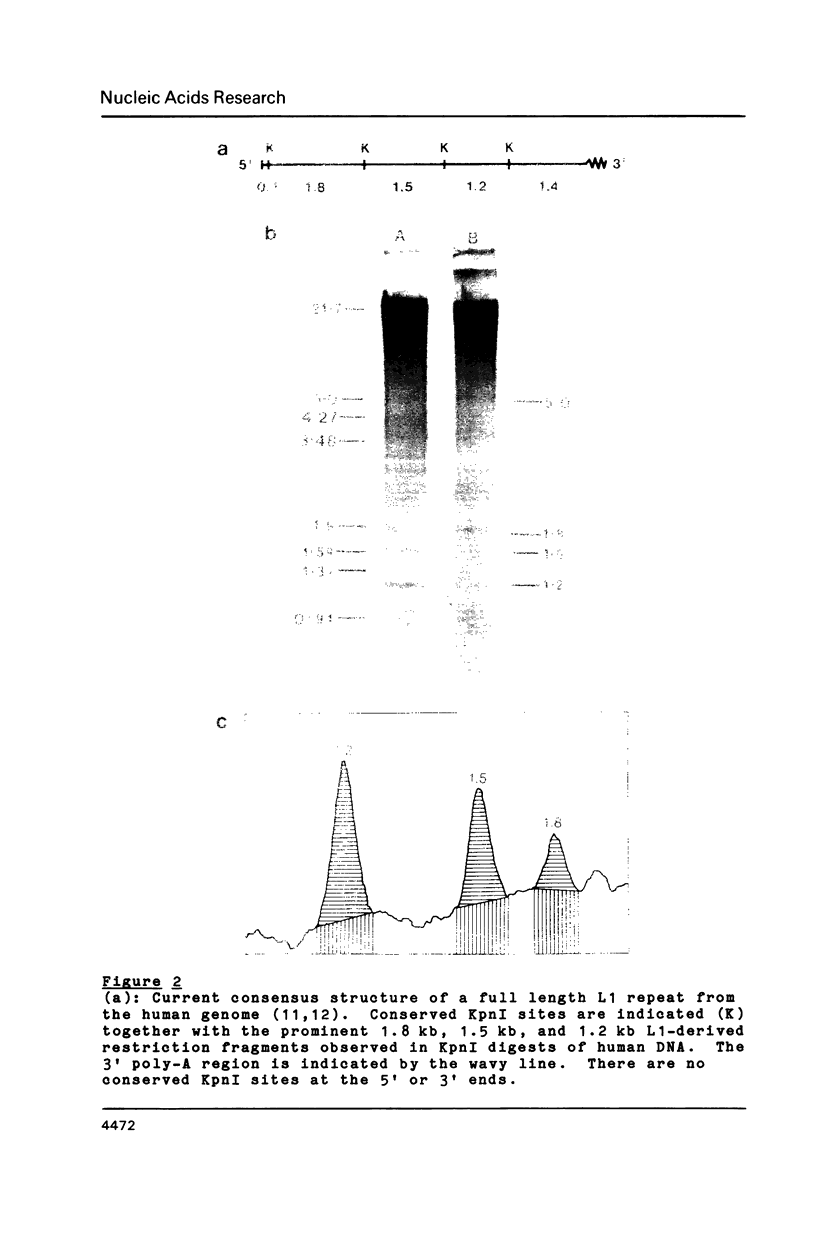
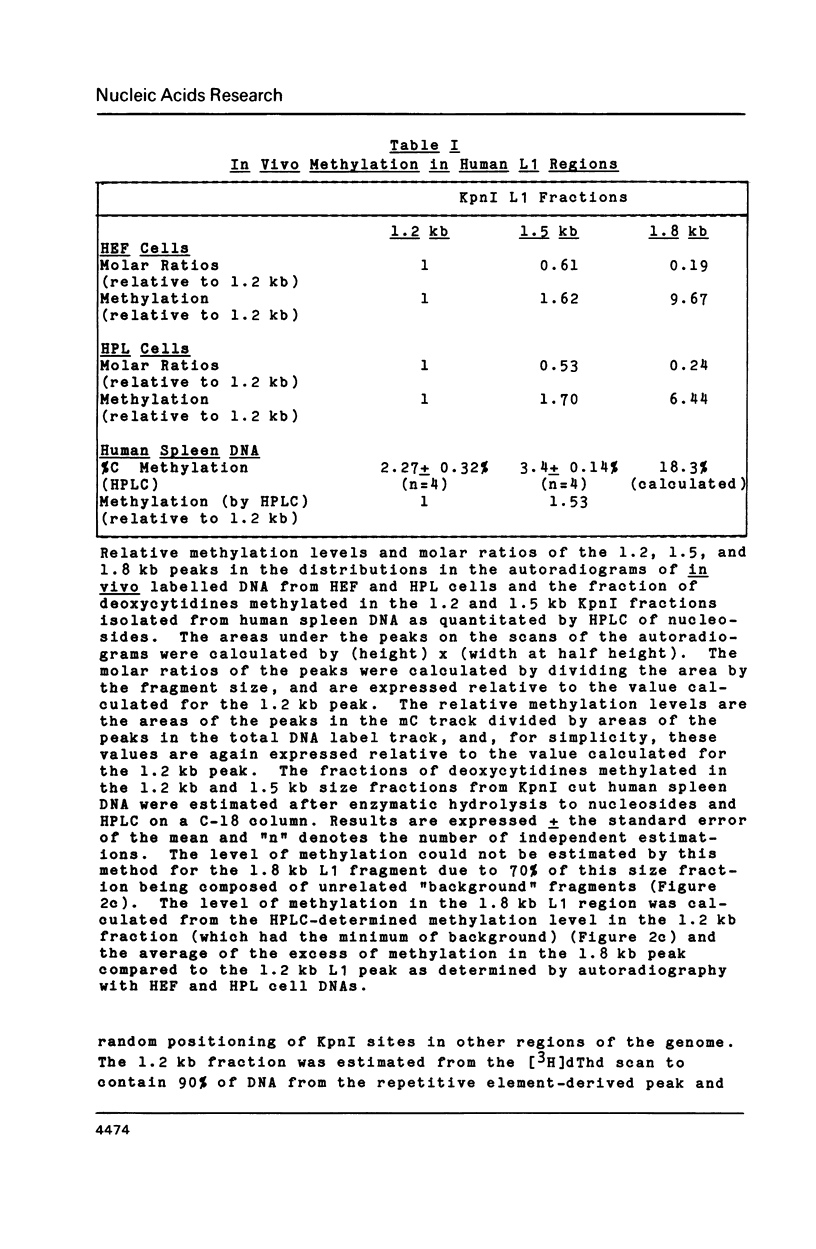
In vitro methylation of Bluescribe plasmid DNA (pBS) with human placental DNA methyltransferase to 6% 5-methylcytosine (mC) reduced transformation efficiencies in rglB+ host strains C600 and DS410 by almost 2 orders of magnitude. By contrast, the rglB- derivative of DS410 showed no reduction in transformation efficiency with methylation while the rglB- derivative of C600 was partially tolerant to methylation. Further, we show that the 1.8 kilobase (kb) and 1.2 kb KpnI fragments derived from the human L1 repeat have respectively 18.3% and 2.3% mC in vivo. Using these hyper- and hypo-methylated genomic segments ligated into the pBS plasmid, transformants with the highly methylated 1.8 kb L1 insert were recovered at 17 to 40 fold higher frequency with the rglB- host strains than with the rglB+ hosts. In addition, recombinant phage (lambda 2001) containing inserts of plant genomic DNA with 26.7% mC (from Petunia hybrida) when plated on rglB- hosts gave titres up to 222 times higher than on the rglB+ strains.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burton F. H., Loeb D. D., Voliva C. F., Martin S. L., Edgell M. H., Hutchison C. A., 3rd Conservation throughout mammalia and extensive protein-encoding capacity of the highly repeated DNA long interspersed sequence one. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jan 20;187(2):291–304. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90235-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougan G., Sherratt D. The transposon Tn1 as a probe for studying ColE1 structure and function. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Mar 7;151(2):151–160. doi: 10.1007/BF00338689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning T., Singer M. The LINE-1 DNA sequences in four mammalian orders predict proteins that conserve homologies to retrovirus proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 11;15(5):2251–2260. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.5.2251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg R. B., Hoschek G., Vodkin L. O. An insertion sequence blocks the expression of a soybean lectin gene. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):465–475. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90428-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi G., Skowronski J., Singer M. F. Defining the beginning and end of KpnI family segments. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1753–1759. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02042.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Kuhara S., Takenaka O., Sakaki Y. L1 family of repetitive DNA sequences in primates may be derived from a sequence encoding a reverse transcriptase-related protein. Nature. 1986 Jun 5;321(6070):625–628. doi: 10.1038/321625a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwu H. R., Roberts J. W., Davidson E. H., Britten R. J. Insertion and/or deletion of many repeated DNA sequences in human and higher ape evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3875–3879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb D. D., Padgett R. W., Hardies S. C., Shehee W. R., Comer M. B., Edgell M. H., Hutchison C. A., 3rd The sequence of a large L1Md element reveals a tandemly repeated 5' end and several features found in retrotransposons. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):168–182. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morley A. A., Trainor K. J., Seshadri R., Ryall R. G. Measurement of in vivo mutations in human lymphocytes. Nature. 1983 Mar 10;302(5904):155–156. doi: 10.1038/302155a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls R. D., Hill A. V., Clegg J. B., Higgs D. R. Direct cloning of specific genomic DNA sequences in plasmid libraries following fragment enrichment. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 11;13(21):7569–7578. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.21.7569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noyer-Weidner M., Diaz R., Reiners L. Cytosine-specific DNA modification interferes with plasmid establishment in Escherichia coli K12: involvement of rglB. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Dec;205(3):469–475. doi: 10.1007/BF00338084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noyer-Weidner M., Jentsch S., Kupsch J., Bergbauer M., Trautner T. A. DNA methyltransferase genes of Bacillus subtilis phages: structural relatedness and gene expression. Gene. 1985;35(1-2):143–150. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90166-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raleigh E. A., Wilson G. Escherichia coli K-12 restricts DNA containing 5-methylcytosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9070–9074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafit-Zagardo B., Brown F. L., Maio J. J., Adams J. W. KpnI families of long, interspersed repetitive DNAs associated with the human beta-globin gene cluster. Gene. 1982 Dec;20(3):397–407. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90208-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shurvinton C. E., Stahl M. M., Stahl F. W. Large palindromes in the lambda phage genome are preserved in a rec+ host by inhibiting lambda DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1624–1628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. S., Hardy T. A., Baker D. J. Human DNA (cytosine-5)methyltransferase selectively methylates duplex DNA containing mispairs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):6899–6916. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.6899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soares M. B., Schon E., Efstratiadis A. Rat LINE1: the origin and evolution of a family of long interspersed middle repetitive DNA elements. J Mol Evol. 1985;22(2):117–133. doi: 10.1007/BF02101690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tewari K. K., Wildman S. G. Chloroplast DNA from tobacco leaves. Science. 1966 Sep 9;153(3741):1269–1271. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3741.1269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vizard D. L., Yarsa J. Comparison of genomic fragment and clone sequences within a long interspersed repeated sequence of the mouse genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jan 25;13(2):473–484. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.2.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voliva C. F., Jahn C. L., Comer M. B., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Edgell M. H. The L1Md long interspersed repeat family in the mouse: almost all examples are truncated at one end. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 20;11(24):8847–8859. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.24.8847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward C., Bolden A., Nalin C. M., Weissbach A. In vitro methylation of the 5'-flanking regions of the mouse beta-globin gene. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 15;262(23):11057–11063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. M., Deininger P. L., Efstratiadis A. Nonviral retroposons: genes, pseudogenes, and transposable elements generated by the reverse flow of genetic information. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:631–661. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodcock D. M., Crowther P. J., Diver W. P. The majority of methylated deoxycytidines in human DNA are not in the CpG dinucleotide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jun 15;145(2):888–894. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyman A. R., Wolfe L. B., Botstein D. Propagation of some human DNA sequences in bacteriophage lambda vectors requires mutant Escherichia coli hosts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2880–2884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker K. E., Riggs A. D., Smith S. S. Purification of human DNA (cytosine-5-)-methyltransferase. J Cell Biochem. 1985;29(4):337–349. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240290407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]