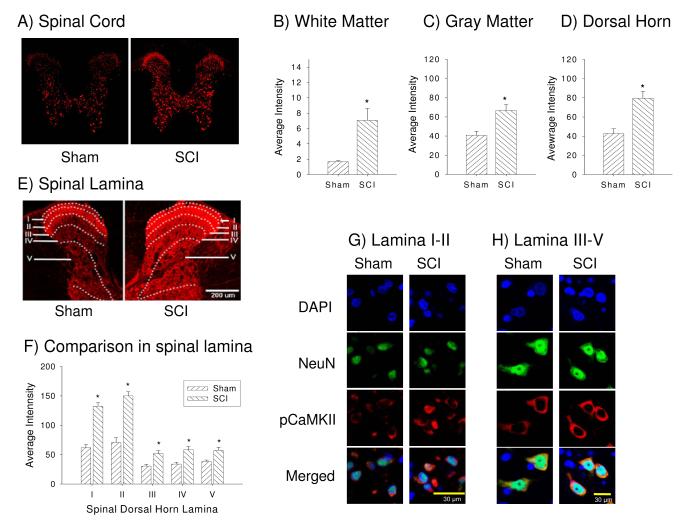
Figure 3.
Spinal cord injury increases pCaMKII expression within the whole spinal cord. (A) Example of phosphorylated CaMKII (pCaMKII) expression in sham (left panel) and SCI (right panel) rats with low laser intensity. Quantifications analysis show the significant increase in pCaMKII expression in white matter (B), gray matter (C) and spinal dorsal horn (D) following SCI (p < 0.05). (E) Example of the laminar distribution of pCaMKII expression in sham (left panel) and SCI (right panel) rats with high laser intensity. (F) Quantification of the significant increase in pCaMKII following SCI in lamina I-V of the dorsal horn (p < 0.05). Example of neuronal pCaMKII expression in both lamina I-II (G) and lamina III-V (H), respectively.