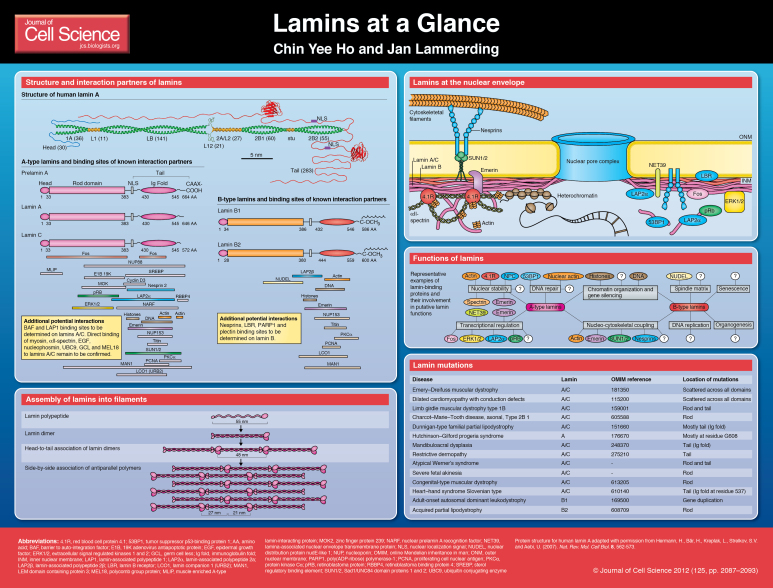
Lamins, the major components of the nuclear lamina, have gained rapidly increasing interest over the past decade as lamin mutations were found to cause numerous devastating diseases. These laminopathies include Emery–Dreifuss muscular dystrophy (EDMD), dilated cardiomyopathy type 1A, limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 1B, familial partial lipodystrophy (FPLD), Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease type 2, mandibuloacral dysplasia and the segmental premature ageing diseases Hutchinson–Gilford progeria syndrome (HGPS) and atypical Werner's progeria. Altered lamin expression has also been reported in various cancers. The molecular mechanism underlying these diverse diseases remains unclear. As such, much effort has been devoted to characterizing the physical and biochemical properties of lamins and their role in cellular function. Here, we provide an overview of the diverse functions of nuclear lamins and how defects in these functions – caused by mutations or altered expression – can contribute to human disease.
Lamin structure and assembly
Lamins are grouped into A-type and B-type lamins. A-type lamins are encoded by a single gene (LMNA); in mammals, alternative splicing gives rise to lamin A and lamin C and the less abundant isoforms lamin AΔ10 and lamin C2 (Fisher et al., 1986; Furukawa et al., 1994; Machiels et al., 1996). A-type lamins are absent in early embryonic cells, but are present in nearly all differentiated cells (Machiels et al., 1996; Röber et al., 1989). B-type lamins are encoded by the LMNB1 (lamin B1) and LMNB2 (lamin B2 and lamin B3) genes, with at least one B-type lamin expressed in all somatic cells (Biamonti et al., 1992; Furukawa and Hotta, 1993; Pollard et al., 1990).
As type V intermediate filaments, lamins are comprised of three major domains, a short N-terminal head domain, a central rod domain and a long C-terminal tail that includes an immunoglobulin-like domain (Dhe-Paganon et al., 2002; Krimm et al., 2002; McKeon et al., 1986; Stuurman et al., 1998). Most lamins
undergo several post-translational modifications that include C-terminal farnesylation, and in the case of prelamin A, enzymatic cleavage to yield mature lamin A (reviewed by Broers et al., 2006; Davies et al., 2011). Although lamins can form heterodimers in vitro, A-type and B-type lamins form distinct, albeit overlapping, lattices at the nuclear envelope (NE) (Goldberg et al., 2008; Shimi et al., 2008), and lamins A and C segregate in living cells (Kolb et al., 2011), suggesting that lamins form distinct homodimers in vivo.
Dimerization of lamins is driven by coiled-coil formation of their central rod domains (Stuurman et al., 1998) (see Poster). Lamin dimers then assemble head to tail into polar polymers, which requires an overlapping interaction between the head and tail domains (Heitlinger et al., 1992; Sasse et al., 1998). These polymers then laterally assemble in an anti-parallel fashion into non-polar filaments (Ben-Harush et al., 2009). Although Caenorhabditis elegans lamins can form protein networks with approximately 10-nm-diameter fibers in vitro (Ben-Harush et al., 2009; Parry and Steinert, 1999), and similar sized filaments have been observed in Xenopus oocytes (Aebi et al., 1986), the structural organization of lamins in somatic cells remains elusive.
Functions of lamins
Lamins were first recognized as components of the nuclear matrix; it is now apparent that they convey a multitude of functions, ranging from structural support of the nucleus to facilitating chromatin organization, gene regulation and DNA repair (reviewed by Dechat et al., 2010a; Dittmer and Misteli, 2011).
Nuclear structure and mechanics
Lamins are important for the incorporation and spacing of nuclear pores (Al-Haboubi et al., 2011; Goldberg et al., 1995; Osouda et al., 2005; Smythe et al., 2000), regulation of nuclear size (Levy and Heald, 2010), and the shape and mechanical properties of the nucleus (reviewed by Zwerger et al., 2011). Cells lacking lamins A and C have fragile nuclei that are more deformable under mechanical strain and which display altered mechanotransduction signaling (Broers et al., 2004; Lammerding et al., 2004). By contrast, the absence of lamin B has only minor effects on nuclear stiffness (Lammerding et al., 2006; Osouda et al., 2005). The reasons for this distinct difference are still not fully understood. Clues come from experiments with ectopic expression of lamin A in Xenopus oocytes, which results in the formation of a thicker nuclear lamin network compared with that of B-type lamins (Schäpe et al., 2009). In mammalian somatic cells, intranuclear (A-type) lamin structures and modulation of chromatin organization by lamins (see below) could further affect nuclear stiffness. A-type lamins also bind to numerous structural proteins, including B-type lamins, emerin, NUP153, lamina-associated polypeptide 2 isoform alpha (LAP2α), nesprins, SUN-domain-containing proteins, nuclear actin and protein 4.1R (see Poster) (Al-Haboubi et al., 2011; Lattanzi et al., 2003; Markiewicz et al., 2002a; Meyer et al., 2011; Sakaki et al., 2001; Sasseville and Langelier, 1998; Simon and Wilson, 2010). Intriguingly, A-type lamins, together with emerin, 4.1R, spectrin and actin, might form a structural network at the nuclear envelope (Meyer et al., 2011), further enhancing nuclear stability.
Lamins also play an important role in physically connecting the nucleus to the cytoskeleton, most likely through their interaction with SUN proteins and nesprins (reviewed by Méjat and Misteli, 2010). The protein complex formed by nesprins and SUN proteins is often referred to as the linker of nucleoskeleton and cytoskeleton (LINC) complex (Crisp et al., 2006) and is essential for intracellular force transmission, cell migration and cell polarization (Méjat and Misteli, 2010). Loss of either type of lamin impairs nucleo-cytoskeletal coupling: cells that lack A-type lamins have defects in nuclear positioning and disturbed cytoskeletal organization, with reduced stiffness (Broers et al., 2004; Folker et al., 2011; Hale et al., 2008; Lammerding et al., 2004; Lee et al., 2007; Luxton et al., 2011); B-type lamins are required for nuclear movement in neuronal migration (Coffinier et al., 2010; Kim et al., 2011) and lamin-B1-deficient cells display sustained spontaneous nuclear rotation (Ji et al., 2007).
During mitosis, the lamina disassembles in vertebrate cells, which is regulated by the cyclin B1-(CCNB1)–CDC2 complex (Heald and McKeon, 1990). After mitosis, reassembly coincides with nuclear envelope formation, where lamins, particularly lamins B1 and B2, could contribute to envelope assembly and chromosome organization (Burke and Gerace, 1986; Liu et al., 2000; Newport et al., 1990).
Gene regulation
Recent studies indicate that the nuclear envelope and the nucleoskeleton can serve as an important filter or modulator in cell signaling and transcriptional regulation (Simon and Wilson, 2011). Lamins interact with numerous transcription factors that affect cellular proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis (reviewed by Prokocimer et al., 2009; Wilson and Foisner, 2010). A-type lamins can modulate cell signaling through several mechanisms, for example, by sequestering transcription factors in inactive complexes, modulating post-translational modifications and degradation, and regulating transcriptional complexes (Andrés and González, 2009; Dechat et al., 2010b; Wilson and Berk, 2010; Wilson and Foisner, 2010). One illustrative example is the interaction between lamin A and the retinoblastoma protein pRb (RB1). Loss of lamins A and C results in reduced levels of pRb as a result of proteolytic degradation, leading to altered cell cycle dynamics (Johnson et al., 2004; Markiewicz et al., 2002a; Moiseeva et al., 2011; Nitta et al., 2007). Furthermore, complex formation between lamin A, LAP2α and pRb controls nucleoplasmic anchoring of pRb and modulates E2F-dependent transcription (Dorner et al., 2006; Markiewicz et al., 2002a; Naetar et al., 2008; Pekovic et al., 2007). Finally, lamin A also serves as a mutually exclusive binding partner for extracellular-signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 (ERK1/2; MAPK3 and MAPK1, repectively) and pRb; activated ERK1/2 disrupt nuclear complexes of lamin A and pRb, and thereby promote E2F activation (Rodríguez et al., 2010).
In addition to pRb and LAP2α, A-type lamins also interact with the transcription factors Fos (González et al., 2008), adipocyte transcription sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBP1) (Lloyd et al., 2002) and ERK1/2 (González et al., 2008), and possibly with melanoma nuclear protein 18 (MEL18) (Zhong et al., 2005) and germ-cell-less (GCL), a repressor protein that forms stable complexes with emerin and lamin A (Holaska et al., 2003). The recent identification of a direct interaction between A-type lamins and muscle enriched A-type-lamin-interacting protein (MLIP) further indicates that many of the tissue-specific functions of lamins might arise from the interaction of lamins with other muscle-specific proteins (Ahmady et al., 2011). A more complete review of the multiple binding partners of A-type lamins has been published (Wilson and Foisner, 2010).
Less is known about the interaction partners of B-type lamins. B-type lamins are important in the regulation of OCT1-dependent genes and can modulate reactive oxygen species (Malhas et al., 2009). Furthermore, lamins might also control transcriptional activity by modulating chromatin structure and organization at the nuclear periphery, for example, in lamina-associated domains (LADs), which are transcriptionally repressed regions at the nuclear envelope, as discussed below (reviewed by Mekhail and Moazed, 2010).
Chromatin organization and DNA transcription
Lamins can interact with chromatin either directly or through histones and other lamin-associated proteins, such as lamin B receptor (LBR), heterochromatin protein 1 (HP1), BAF, emerin, inner nuclear membrane protein MAN1, and several LAP2 isoforms (reviewed by Maraldi et al., 2010; Wilson and Foisner, 2010). These interactions can occur at the nuclear periphery and in the nuclear interior. Tethering of peripheral chromatin to the nuclear lamina is visible in mammalian cells by electron microscopy (Belmont et al., 1993) and can be demonstrated biochemically (Guelen et al., 2008). The resulting changes in chromatin organization can modulate gene expression, for example, by altering their accessibility to transcription factors (Bank and Gruenbaum, 2011; Shevelyov and Nurminsky, 2012; Verstraeten et al., 2007). Consequently, LADs represent repressive chromatin environments with low gene-expression levels (Guelen et al., 2008). Recently, lamins, together with emerin, nuclear actin and myosin have been proposed to form intranuclear complexes that are responsible for moving chromosome segments or genes to transcription sites (Chuang et al., 2006; Dundr et al., 2007; Mehta et al., 2008). Loss-of-function experiments in Caenorhabditis elegans and Drosophila melanogaster reveal perturbations in chromatin organization that correlate with developmental abnormalities (Bao et al., 2007; Liu et al., 2000; Margalit et al., 2005; Mattout et al., 2011; Parnaik, 2008). Expression of B-type lamin coincides with early development programming in Xenopus (Chmielewska et al., 2011; Ralle et al., 1999) and is crucial for organogenesis, but, surprisingly, is dispensable for embryonic stem cell differentiation (Kim et al., 2011). A-type lamins, which are usually absent during embryonic development, are upregulated during the differentiation program (Constantinescu et al., 2006; Röber et al., 1989).
DNA replication and repair
Lamins in the nuclear interior could also provide docking platforms for replications factors. Disruption of the nuclear lamina causes mislocalization of elongation factors, such as proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) (Shumaker et al., 2008) and the replication factor complex (RFC) (Spann et al., 1997). In addition to affecting chromosomal organization and expression, lamin mutations can result in genomic instability by compromising DNA repair through long-range non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) and homologous recombination (HR), and by affecting telomere structure and function (di Masi et al., 2008; Gonzalez-Suarez et al., 2009a; Gonzalez-Suarez et al., 2009b; Redwood et al., 2011). For example, lamin depletion prevents accumulation of p53-binding protein 1 (53BP1) at double-stranded DNA breaks (Redwood et al., 2011). DNA repair proteins such as breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein (BRCA1) and RAD51 are transcriptionally downregulated by pRb- and E2F4-mediated pathways (Liu et al., 2005; Manju et al., 2006; Musich and Zou, 2009; Redwood et al., 2011). Detailed reviews of lamins and DNA repair have been published (Gonzalez-Suarez et al., 2009a; Warren and Shanahan, 2011).
Lamins and disease
Over 400 distinct mutations have been identified in the LMNA gene so far, causing a wide range of human diseases and making LMNA the most mutated gene known to date (Worman et al., 2009). Different hypotheses have been proposed to explain the often tissue-specific aspects of the laminopathies.
The structural hypothesis
The ‘structural hypothesis’ suggests that LMNA mutations render the nucleus more fragile, causing cell death and progressive disease in mechanically stressed tissues such as muscle (Zwerger et al., 2011). This idea is supported by findings that skeletal muscle from patients with Emery–Dreifuss muscular dystrophy (EDMD) and mouse models of the disease contain fragmented nuclei (Arimura et al., 2005; Fidziańska and Hausmanowa-Petrusewicz, 2003; Fidziańska et al., 1998; Markiewicz et al., 2002b; Mounkes et al., 2005; Nikolova et al., 2004); cells lacking lamins A and C have decreased nuclear stiffness and increased nuclear fragility (Broers et al., 2004; Lammerding et al., 2004), and Lmna−/− mice develop severe muscular dystrophy and dilated cardiomyopathy (Sullivan et al., 1999). Nonetheless, a clear correlation between structural defects and associated phenotype in LMNA mutations has not been established yet. In contrast to lamin-deficient cells, cells from patients with Hutchinson–Gilford progeria syndrome (HGPS) develop increasingly stiffer nuclei (Dahl et al., 2006; Verstraeten et al., 2008), possibly as a result of accumulation of progerin at the nuclear envelope. Interestingly, HGPS cells and cells lacking A-type lamins are more susceptible to mechanically induced cell death (Lammerding et al., 2004; Verstraeten et al., 2008), providing a possible mechanism for the progressive loss of vascular smooth muscle cells in blood vessels and the arteriosclerotic disease in HGPS (Capell et al., 2007; Dahl et al., 2010; Gerhard-Herman et al., 2012 Merideth et al., 2008; Stehbens et al., 2001) and muscle loss in EDMD. In addition to affecting nuclear stability, loss of A-type lamins and mutations linked to EDMD can also disrupt nucleo-cytoskeletal coupling, resulting in the loss of synaptic nuclei from neuromuscular junctions (Méjat et al., 2009), impaired nuclear movement and positioning (Folker et al., 2011) and disturbed cytoskeletal organization (reviewed by Méjat and Misteli, 2010).
The gene regulation hypothesis
Nuclear damage alone is insufficient to explain the diverse phenotypes found in many of the laminopathies, such as redistribution of adipose tissue in FPLD. The ‘gene-regulation hypothesis’ postulates that perturbed interaction with tissue-specific transcription factors underlies the development of different disease phenotypes (reviewed by Simon and Wilson, 2011; Worman et al., 2009). In accordance with the gene regulation hypothesis, laminopathies often exhibit misregulation of common signaling pathways, such as mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK), transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β), Wnt–β-catenin and Notch pathways, which are central in directing proliferation, apoptosis and differentiation of the organism (reviewed by Andrés and González, 2009; Hampoelz and Lecuit, 2011; Simon and Wilson, 2011; Wilson and Berk, 2010). Cells harboring LMNA mutations associated with EDMD or having reduced levels of lamins, have upregulated MAPK signaling (Muchir et al., 2007; Muchir et al., 2010); similarly increased activation of ERK1/2, and Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) signaling has been observed in hearts of two mouse models for EDMD (Muchir et al., 2007a; Muchir et al., 2007b). Of note, cells and mice lacking A-type lamins have impaired activation of mechanosensitive genes such as Egr1 and Iex1 (Cupesi et al., 2010; Lammerding et al., 2004), potentially linking the structural and gene regulation hypotheses. Furthermore, many laminopathies are also associated with striking loss of heterochromatin, as seen in HGPS, X-linked EDMD (caused by mutations in the gene encoding emerin), autosomal dominant EDMD, familial partial lipodystrophy (FPLD) and mandibuloacral dysplasia patients, and in cells lacking A-type lamins (Dechat et al., 2007; Parnaik, 2008). Changes in chromatin organization could further modulate (tissue-specific) gene expression (Mattout et al., 2011) and increase susceptibility to DNA damage or impair DNA repair as discussed above.
Stem cell dysfunction in laminopathies
A third, related hypothesis proposes that LMNA mutations can cause depletion and impaired differentiation of adult stem cells (Pekovic and Hutchison, 2008). Whereas neither A-type nor B-type lamins are essential for embryonic stem cell differentiation (Kim et al., 2011; Sullivan et al., 1999), LMNA mutations might impact self-renewal and/or multipotency of adult mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) (Gotzmann and Foisner, 2006; Scaffidi and Misteli, 2008). This idea is supported by findings of epidermal stem cell depletion in an HGPS mouse model (Rosengardten et al., 2011) and reports of altered Notch and Wnt signaling in human and mouse MSCs expressing progerin, and mouse models of HGPS (Espada et al., 2008; Hernandez et al., 2010; Meshorer and Gruenbaum, 2008; Scaffidi and Misteli, 2008). Thus, increased turnover and abnormal differentiation of adult stem cells, coupled with possibly increased mechanical sensitivity, could result in MSC death and inefficient repair of damaged tissue in HGPS and other laminopathies (reviewed by Halaschek-Wiener and Brooks-Wilson, 2007; Meshorer and Gruenbaum, 2008; Prokocimer et al., 2009).
Lamins in cancer
Cancer cells are often characterized by abnormally shaped nuclei, resembling those of lamin-deficient cells (Dey, 2009; Friedl et al., 2011). Recently, changes in lamin expression have been reported in a variety of cancers, frequently correlating with tumorigenic potential and malignant transformation (reviewed by Foster et al., 2010; Chow et al., 2012). For example, expression of A-type lamins is upregulated in skin and ovarian cancers, whereas lamin A or lamin C expression is downregulated in leukemias, lymphomas, breast cancer, colon cancer, gastric carcinoma and ovarian carcinoma (Alaiya et al., 1997; Belt et al., 2011; Capo-chichi et al., 2011; Stadelmann et al., 1990; Wang et al., 2003; Wang et al., 2009; Willis et al., 2008a; Willis et al., 2008b; Wu et al., 2009). For B-type lamins, upregulation has been linked to tumor differentiation in prostate cancer and hepatocarcinoma (Leman and Getzenberg, 2002; Sun et al., 2010). The variable results between different cancers indicate that specific cancers or cancer stages might rely on different functions of lamins. For example, reduced levels of A-type lamins are predicted to result in more malleable nuclei, which could facilitate extravasation and invasion of malignant cells through narrow constrictions (Friedl et al., 2011). At the same time, higher lamin levels could support the increased mechanical stress within solid tumors. In addition to these mechanical considerations, changes in lamin expression could modulate cell proliferation, differentiation, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and migration, each of which constitutes an important step in cancer progression (Foster et al., 2010; Chow et al., 2012).
Conclusions and Perspectives
The broad spectrum of diseases caused by mutations or altered expression of lamins indicate that these nuclear envelope proteins are involved in numerous fundamental cellular functions. In addition to providing structural support to the nucleus and contributing to the physical coupling between the nuclear interior and the cytoskeleton, lamins are important modulators of transcriptional regulation. They can fulfil this role by modulating chromatin structure and organization, for example, by repressing gene expression in lamina-associated domains. In addition, they can directly interact with various transcription factors such as Fos and pRb, controlling their intranuclear localization, stability and binding to other proteins or promoter elements. Consequently, mutations that interfere with some or all of these functions can result in devastating human diseases. Although many new insights into the diverse functions of lamins have emerged over the past two decades, more research is necessary to uncover the molecular mechanism(s) by which lamins act as crucial regulators in diverse cellular processes. Insights gained from these studies will provide new clues into new therapeutic approaches for these laminopathies and will also yield a more complete picture of the many physiological functions of lamins.
Acknowledgements
We apologize to all authors whose work could not be cited due to space constraints.
Footnotes
Funding
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health awards [grant numbers R01 NS059348 and R01 HL082792]; the Department of Defense Breast Cancer Idea Award [grant number BC102152]; and an award from the Progeria Research Foundation.
A high-resolution version of the poster is available for downloading in the online version of this article at jcs.biologists.org. Individual poster panels are available as JPEG files at http://jcs.biologists.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.1242/jcs.087288/-/DC1.
References
- Aebi U., Cohn J., Buhle L., Gerace L. (1986). The nuclear lamina is a meshwork of intermediate-type filaments. Nature 323, 560-564 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmady E., Deeke S. A., Rabaa S., Kouri L., Kenney L., Stewart A. F., Burgon P. G. (2011). Identification of a novel muscle A-type lamin-interacting protein (MLIP). J. Biol. Chem. 286, 19702-19713 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Al-Haboubi T., Shumaker D. K., Köser J., Wehnert M., Fahrenkrog B. (2011). Distinct association of the nuclear pore protein Nup153 with A- and B-type lamins. Nucleus 2, 500-509 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alaiya A. A., Franzén B., Fujioka K., Moberger B., Schedvins K., Silfversvärd C., Linder S., Auer G. (1997). Phenotypic analysis of ovarian carcinoma: polypeptide expression in benign, borderline and malignant tumors. Int. J. Cancer 73, 678-682 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrés V., González J. M. (2009). Role of A-type lamins in signaling, transcription, and chromatin organization. J. Cell Biol. 187, 945-957 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arimura T., Helbling-Leclerc A., Massart C., Varnous S., Niel F., Lacène E., Fromes Y., Toussaint M., Mura A. M., Keller D. I., et al. (2005). Mouse model carrying H222P-Lmna mutation develops muscular dystrophy and dilated cardiomyopathy similar to human striated muscle laminopathies. Hum. Mol. Genet. 14, 155-169 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bank E. M., Gruenbaum Y. (2011). The nuclear lamina and heterochromatin: a complex relationship. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 39, 1705-1709 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bao X., Girton J., Johansen J., Johansen K. M. (2007). The lamin Dm0 allele Ari3 acts as an enhancer of position effect variegation of the wm4 allele in Drosophila. Genetica 129, 339-342 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belmont A. S., Zhai Y., Thilenius A. (1993). Lamin B distribution and association with peripheral chromatin revealed by optical sectioning and electron microscopy tomography. J. Cell Biol. 123, 1671-1685 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belt E. J., Fijneman R. J., van den Berg E. G., Bril H., Delis-van Diemen P. M., Tijssen M., van Essen H. F., de Lange-de Klerk E. S., Beliën J. A., Stockmann H. B., et al. (2011). Loss of lamin A/C expression in stage II and III colon cancer is associated with disease recurrence. Eur. J. Cancer 47, 1837-1845 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Harush K., Wiesel N., Frenkiel-Krispin D., Moeller D., Soreq E., Aebi U., Herrmann H., Gruenbaum Y., Medalia O. (2009). The supramolecular organization of the C. elegans nuclear lamin filament. J. Mol. Biol. 386, 1392-1402 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biamonti G., Giacca M., Perini G., Contreas G., Zentilin L., Weighardt F., Guerra M., Della Valle G., Saccone S., Riva S., et al. (1992). The gene for a novel human lamin maps at a highly transcribed locus of chromosome 19 which replicates at the onset of S-phase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 12, 3499-3506 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broers J. L., Peeters E. A., Kuijpers H. J., Endert J., Bouten C. V., Oomens C. W., Baaijens F. P., Ramaekers F. C. (2004). Decreased mechanical stiffness in LMNA-/- cells is caused by defective nucleo-cytoskeletal integrity: implications for the development of laminopathies. Hum. Mol. Genet. 13, 2567-2580 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broers J. L., Ramaekers F. C., Bonne G., Yaou R. B., Hutchison C. J. (2006). Nuclear lamins: laminopathies and their role in premature ageing. Physiol. Rev. 86, 967-1008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke B., Gerace L. (1986). A cell free system to study reassembly of the nuclear envelope at the end of mitosis. Cell 44, 639-652 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capell B. C., Collins F. S., Nabel E. G. (2007). Mechanisms of cardiovascular disease in accelerated aging syndromes. Circ. Res. 101, 13-26 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capo-chichi C. D., Cai K. Q., Smedberg J., Ganjei-Azar P., Godwin A. K., Xu X. X. (2011). Loss of A-type lamin expression compromises nuclear envelope integrity in breast cancer. Chin. J. Cancer 30, 415-425 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chmielewska M., Dubiñska-Magiera M., Sopel M., Rzepecka D., Hutchison C. J., Goldberg M. W., Rzepecki R. (2011). Embryonic and adult isoforms of XLAP2 form microdomains associated with chromatin and the nuclear envelope. Cell Tissue Res. 344, 97-110 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow K.-H., Factor R. E., Ullman K. S. (2012). The nuclear envelope environment and its cancer connections. Nature Rev. Cancer [Epub ahead of print] doi: 10.1038/nrc3219 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuang C. H., Carpenter A. E., Fuchsova B., Johnson T., de Lanerolle P., Belmont A. S. (2006). Long-range directional movement of an interphase chromosome site. Curr. Biol. 16, 825-831 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffinier C., Fong L. G., Young S. G. (2010). LINCing lamin B2 to neuronal migration: growing evidence for cell-specific roles of B-type lamins. Nucleus 1, 407-411 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constantinescu D., Gray H. L., Sammak P. J., Schatten G. P., Csoka A. B. (2006). Lamin A/C expression is a marker of mouse and human embryonic stem cell differentiation. Stem Cells 24, 177-185 a [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crisp M., Liu Q., Roux K., Rattner J. B., Shanahan C., Burke B., Stahl P. D., Hodzic D. (2006). Coupling of the nucleus and cytoplasm: role of the LINC complex. J. Cell Biol. 172, 41-53 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cupesi M., Yoshioka J., Gannon J., Kudinova A., Stewart C. L., Lammerding J. (2010). Attenuated hypertrophic response to pressure overload in a lamin A/C haploinsufficiency mouse. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 48, 1290-1297 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl K. N., Scaffidi P., Islam M. F., Yodh A. G., Wilson K. L., Misteli T. (2006). Distinct structural and mechanical properties of the nuclear lamina in Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 10271-10276 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl K. N., Kalinowski A., Pekkan K. (2010). Mechanobiology and the microcirculation: cellular, nuclear and fluid mechanics. Microcirculation 17, 179-191 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies B. S., Coffinier C., Yang S. H., Barnes R. H., 2nd, Jung H. J., Young S. G., Fong L. G. (2011). Investigating the purpose of prelamin A processing. Nucleus 2, 4-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dechat T., Shimi T., Adam S. A., Rusinol A. E., Andres D. A., Spielmann H. P., Sinensky M. S., Goldman R. D. (2007). Alterations in mitosis and cell cycle progression caused by a mutant lamin A known to accelerate human aging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 4955-4960 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dechat T., Adam S. A., Taimen P., Shimi T., Goldman R. D. (2010a). Nuclear lamins. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2, a000547 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dechat T., Gesson K., Foisner R. (2010b). Lamina-independent lamins in the nuclear interior serve important functions. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 75, 533-543 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dey P. (2009). Nuclear margin irregularity and cancer: a review. Anal. Quant. Cytol. Histol. 31, 345-352 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhe-Paganon S., Werner E. D., Chi Y. I., Shoelson S. E. (2002). Structure of the globular tail of nuclear lamin. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 17381-17384 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- di Masi A., D'Apice M. R., Ricordy R., Tanzarella C., Novelli G. (2008). The R527H mutation in LMNA gene causes an increased sensitivity to ionizing radiation. Cell Cycle 7, 2030-2037 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dittmer T. A., Misteli T. (2011). The lamin protein family. Genome Biol. 12, 222 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorner D., Vlcek S., Foeger N., Gajewski A., Makolm C., Gotzmann J., Hutchison C. J., Foisner R. (2006). Lamina-associated polypeptide 2 alpha regulates cell cycle progression and differentiation via the retinoblastoma-E2F pathway. J. Cell Biol. 173, 83-93 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dundr M., Ospina J. K., Sung M. H., John S., Upender M., Ried T., Hager G. L., Matera A. G. (2007). Actin-dependent intranuclear repositioning of an active gene locus in vivo. J. Cell Biol. 179, 1095-1103 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espada J., Varela I., Flores I., Ugalde A. P., Cadiñanos J., Pendás A. M., Stewart C. L., Tryggvason K., Blasco M. A., Freije J. M., et al. (2008). Nuclear envelope defects cause stem cell dysfunction in premature-aging mice. J. Cell Biol. 181, 27-35 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidziańska A., Hausmanowa-Petrusewicz I. (2003). Architectural abnormalities in muscle nuclei. Ultrastructural differences between X-linked and autosomal dominant forms of EDMD. J. Neurol. Sci. 210, 47-51 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidziańska A., Toniolo D., Hausmanowa-Petrusewicz I. (1998). Ultrastructural abnormality of sarcolemmal nuclei in Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy (EDMD). J. Neurol. Sci. 159, 88-93 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. Z., Chaudhary N., Blobel G. (1986). cDNA sequencing of nuclear lamins A and C reveals primary and secondary structural homology to intermediate filament proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83, 6450-6454 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folker E. S., Ostlund C., Luxton G. W., Worman H. J., Gundersen G. G. (2011). Lamin A variants that cause striated muscle disease are defective in anchoring transmembrane actin-associated nuclear lines for nuclear movement. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 108, 131-136 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster C. R., Przyborski S. A., Wilson R. G., Hutchison C. J. (2010). Lamins as cancer biomarkers. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 38, 297-300 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedl P., Wolf K., Lammerding J. (2011). Nuclear mechanics during cell migration. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 23, 55-64 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa K., Hotta Y. (1993). cDNA cloning of a germ cell specific lamin B3 from mouse spermatocytes and analysis of its function by ectopic expression in somatic cells. EMBO J. 12, 97-106 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa K., Inagaki H., Hotta Y. (1994). Identification and cloning of an mRNA coding for a germ cell-specific A-type lamin in mice. Exp. Cell Res. 212, 426-430 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhard-Herman M., Smoot L. B., Wake N., Kieran M. W., Kleinman M. E., Miller D. T., Schwartzman A., Giobbie-Hurder A., Neuberg D., Gordon L. B. (2012). Mechanisms of premature vascular aging in children with Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome. Hypertension 59, 92-97 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M., Jenkins H., Allen T., Whitfield W. G., Hutchison C. J. (1995). Xenopus lamin B3 has a direct role in the assembly of a replication competent nucleus: evidence from cell-free egg extracts. J. Cell Sci. 108, 3451-3461 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M. W., Huttenlauch I., Hutchison C. J., Stick R. (2008). Filaments made from A- and B-type lamins differ in structure and organization. J. Cell Sci. 121, 215-225 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González J. M., Navarro-Puche A., Casar B., Crespo P., Andrés V. (2008). Fast regulation of AP-1 activity through interaction of lamin A/C, ERK1/2, and c-Fos at the nuclear envelope. J. Cell Biol. 183, 653-666 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Suarez I., Redwood A. B., Gonzalo S. (2009a). Loss of A-type lamins and genomic instability. Cell Cycle 8, 3860-3865 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Suarez I., Redwood A. B., Perkins S. M., Vermolen B., Lichtensztejin D., Grotsky D. A., Morgado-Palacin L., Gapud E. J., Sleckman B. P., Sullivan T., et al. (2009b). Novel roles for A-type lamins in telomere biology and the DNA damage response pathway. EMBO J. 28, 2414-2427 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotzmann J., Foisner R. (2006). A-type lamin complexes and regenerative potential: a step towards understanding laminopathic diseases? Histochem. Cell Biol. 125, 33-41 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guelen L., Pagie L., Brasset E., Meuleman W., Faza M. B., Talhout W., Eussen B. H., de Klein A., Wessels L., de Laat W., et al. (2008). Domain organization of human chromosomes revealed by mapping of nuclear lamina interactions. Nature 453, 948-951 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halaschek-Wiener J., Brooks-Wilson A. (2007). Progeria of stem cells: stem cell exhaustion in Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 62, 3-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale C. M., Shrestha A. L., Khatau S. B., Stewart-Hutchinson P. J., Hernandez L., Stewart C. L., Hodzic D., Wirtz D. (2008). Dysfunctional connections between the nucleus and the actin and microtubule networks in laminopathic models. Biophys. J. 95, 5462-5475 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampoelz B., Lecuit T. (2011). Nuclear mechanics in differentiation and development. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 23, 668-675 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heald R., McKeon F. (1990). Mutations of phosphorylation sites in lamin A that prevent nuclear lamina disassembly in mitosis. Cell 61, 579-589 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heitlinger E., Peter M., Lustig A., Villiger W., Nigg E. A., Aebi U. (1992). The role of the head and tail domain in lamin structure and assembly: analysis of bacterially expressed chicken lamin A and truncated B2 lamins. J. Struct. Biol. 108, 74-91 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez L., Roux K. J., Wong E. S., Mounkes L. C., Mutalif R., Navasankari R., Rai B., Cool S., Jeong J. W., Wang H., et al. (2010). Functional coupling between the extracellular matrix and nuclear lamina by Wnt signaling in progeria. Dev. Cell 19, 413-425 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holaska J. M., Lee K. K., Kowalski A. K., Wilson K. L. (2003). Transcriptional repressor germ cell-less (GCL) and barrier to autointegration factor (BAF) compete for binding to emerin in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 6969-6975 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ji J. Y., Lee R. T., Vergnes L., Fong L. G., Stewart C. L., Reue K., Young S. G., Zhang Q., Shanahan C. M., Lammerding J. (2007). Cell nuclei spin in the absence of lamin b1. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 20015-20026 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson B. R., Nitta R. T., Frock R. L., Mounkes L., Barbie D. A., Stewart C. L., Harlow E., Kennedy B. K. (2004). A-type lamins regulate retinoblastoma protein function by promoting subnuclear localization and preventing proteasomal degradation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 9677-9682 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y., Sharov A. A., McDole K., Cheng M., Hao H., Fan C. M., Gaiano N., Ko M. S., Zheng Y. (2011). Mouse B-type lamins are required for proper organogenesis but not by embryonic stem cells. Science 334, 1706-1710 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb T., Maass K., Hergt M., Aebi U., Herrmann H. (2011). Lamin A and lamin C form homodimers and coexist in higher complex forms both in the nucleoplasmic fraction and in the lamina of cultured human cells. Nucleus 2, 425-433 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krimm I., Ostlund C., Gilquin B., Couprie J., Hossenlopp P., Mornon J. P., Bonne G., Courvalin J. C., Worman H. J., Zinn-Justin S. (2002). The Ig-like structure of the C-terminal domain of lamin A/C, mutated in muscular dystrophies, cardiomyopathy, and partial lipodystrophy. Structure 10, 811-823 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammerding J., Schulze P. C., Takahashi T., Kozlov S., Sullivan T., Kamm R. D., Stewart C. L., Lee R. T. (2004). Lamin A/C deficiency causes defective nuclear mechanics and mechanotransduction. J. Clin. Invest. 113, 370-378 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammerding J., Fong L. G., Ji J. Y., Reue K., Stewart C. L., Young S. G., Lee R. T. (2006). Lamins A and C but not lamin B1 regulate nuclear mechanics. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 25768-25780 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lattanzi G., Cenni V., Marmiroli S., Capanni C., Mattioli E., Merlini L., Squarzoni S., Maraldi N. M. (2003). Association of emerin with nuclear and cytoplasmic actin is regulated in differentiating myoblasts. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 303, 764-770 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. S., Hale C. M., Panorchan P., Khatau S. B., George J. P., Tseng Y., Stewart C. L., Hodzic D., Wirtz D. (2007). Nuclear lamin A/C deficiency induces defects in cell mechanics, polarization, and migration. Biophys. J. 93, 2542-2552 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leman E. S., Getzenberg R. H. (2002). Nuclear matrix proteins as biomarkers in prostate cancer. J. Cell. Biochem. 86, 213-223 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D. L., Heald R. (2010). Nuclear size is regulated by importin α and Ntf2 in Xenopus. Cell 143, 288-298 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu B., Wang J., Chan K. M., Tjia W. M., Deng W., Guan X., Huang J. D., Li K. M., Chau P. Y., Chen D. J., et al. (2005). Genomic instability in laminopathy-based premature aging. Nat. Med. 11, 780-785 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J., Rolef Ben-Shahar T., Riemer D., Treinin M., Spann P., Weber K., Fire A., Gruenbaum Y. (2000). Essential roles for Caenorhabditis elegans lamin gene in nuclear organization, cell cycle progression, and spatial organization of nuclear pore complexes. Mol. Biol. Cell 11, 3937-3947 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd D. J., Trembath R. C., Shackleton S. (2002). A novel interaction between lamin A and SREBP1: implications for partial lipodystrophy and other laminopathies. Hum. Mol. Genet. 11, 769-777 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luxton G. G., Gomes E. R., Folker E. S., Worman H. J., Gundersen G. G. (2011). TAN lines: a novel nuclear envelope structure involved in nuclear positioning. Nucleus 2, 173-181 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machiels B. M., Zorenc A. H., Endert J. M., Kuijpers H. J., van Eys G. J., Ramaekers F. C., Broers J. L. (1996). An alternative splicing product of the lamin A/C gene lacks exon 10. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 9249-9253 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malhas A. N., Lee C. F., Vaux D. J. (2009). Lamin B1 controls oxidative stress responses via Oct-1. J. Cell Biol. 184, 45-55 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manju K., Muralikrishna B., Parnaik V. K. (2006). Expression of disease-causing lamin A mutants impairs the formation of DNA repair foci. J. Cell Sci. 119, 2704-2714 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maraldi N. M., Capanni C., Cenni V., Fini M., Lattanzi G. (2010). Laminopathies and lamin-associated signaling pathways. J. Cell. Biochem. (in press) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margalit A., Liu J., Fridkin A., Wilson K. L., Gruenbaum Y. (2005). A lamin-dependent pathway that regulates nuclear organization, cell cycle progression and germ cell development. Novartis Found. Symp. 264, 231-240 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markiewicz E., Dechat T., Foisner R., Quinlan R. A., Hutchison C. J. (2002a). Lamin A/C binding protein LAP2alpha is required for nuclear anchorage of retinoblastoma protein. Mol. Biol. Cell 13, 4401-4413 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markiewicz E., Venables R., Mauricio-Alvarez-Reyes, Quinlan R, Dorobek M, Hausmanowa-Petrucewicz I, Hutchison C. (2002b). Increased solubility of lamins and redistribution of lamin C in X-linked Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy fibroblasts. J. Struct. Biol. 140, 241-253 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattout A., Pike B. L., Towbin B. D., Bank E. M., Gonzalez-Sandoval A., Stadler M. B., Meister P., Gruenbaum Y., Gasser S. M. (2011). An EDMD mutation in C. elegans lamin blocks muscle-specific gene relocation and compromises muscle integrity. Curr. Biol. 21, 1603-1614 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeon F. D., Kirschner M. W., Caput D. (1986). Homologies in both primary and secondary structure between nuclear envelope and intermediate filament proteins. Nature 319, 463-468 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehta I. S., Elcock L. S., Amira M., Kill I. R., Bridger J. M. (2008). Nuclear motors and nuclear structures containing A-type lamins and emerin: is there a functional link? Biochem. Soc. Trans. 36, 1384-1388 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Méjat A., Misteli T. (2010). LINC complexes in health and disease. Nucleus 1, 40-52 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Méjat A., Decostre V., Li J., Renou L., Kesari A., Hantaï D., Stewart C. L., Xiao X., Hoffman E., Bonne G., et al. (2009). Lamin A/C-mediated neuromuscular junction defects in Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. J. Cell Biol. 184, 31-44 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekhail K., Moazed D. (2010). The nuclear envelope in genome organization, expression and stability. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 11, 317-328 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merideth M. A., Gordon L. B., Clauss S., Sachdev V., Smith A. C., Perry M. B., Brewer C. C., Zalewski C., Kim H. J., Solomon B., et al. (2008). Phenotype and course of Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 358, 592-604 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meshorer E., Gruenbaum Y. (2008). Gone with the Wnt/Notch: stem cells in laminopathies, progeria, and aging. J. Cell Biol. 181, 9-13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer A. J., Almendrala D. K., Go M. M., Krauss S. W. (2011). Structural protein 4.1R is integrally involved in nuclear envelope protein localization, centrosome-nucleus association and transcriptional signaling. J. Cell Sci. 124, 1433-1444 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moiseeva O., Bourdeau V., Vernier M., Dabauvalle M. C., Ferbeyre G. (2011). Retinoblastoma-independent regulation of cell proliferation and senescence by the p53-p21 axis in lamin A /C-depleted cells. Aging Cell 10, 789-797 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mounkes L. C., Kozlov S. V., Rottman J. N., Stewart C. L. (2005). Expression of an LMNA-N195K variant of A-type lamins results in cardiac conduction defects and death in mice. Hum. Mol. Genet. 14, 2167-2180 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muchir A., Pavlidis P., Bonne G., Hayashi Y. K., Worman H. J. (2007a). Activation of MAPK in hearts of EMD null mice: similarities between mouse models of X-linked and autosomal dominant Emery Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 16, 1884-1895 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muchir A., Pavlidis P., Decostre V., Herron A. J., Arimura T., Bonne G., Worman H. J. (2007b). Activation of MAPK pathways links LMNA mutations to cardiomyopathy in Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. J. Clin. Invest. 117, 1282-1293 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musich P. R., Zou Y. (2009). Genomic instability and DNA damage responses in progeria arising from defective maturation of prelamin A. Aging 1, 28-37 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naetar N., Korbei B., Kozlov S., Kerenyi M. A., Dorner D., Kral R., Gotic I., Fuchs P., Cohen T. V., Bittner R., et al. (2008). Loss of nucleoplasmic LAP2alpha-lamin A complexes causes erythroid and epidermal progenitor hyperproliferation. Nat. Cell Biol. 10, 1341-1348 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newport J. W., Wilson K. L., Dunphy W. G. (1990). A lamin-independent pathway for nuclear envelope assembly. J. Cell Biol. 111, 2247-2259 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikolova V., Leimena C., McMahon A. C., Tan J. C., Chandar S., Jogia D., Kesteven S. H., Michalicek J., Otway R., Verheyen F., et al. (2004). Defects in nuclear structure and function promote dilated cardiomyopathy in lamin A/C-deficient mice. J. Clin. Invest. 113, 357-369 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitta R. T., Smith C. L., Kennedy B. K. (2007). Evidence that proteasome-dependent degradation of the retinoblastoma protein in cells lacking A-type lamins occurs independently of gankyrin and MDM2. PLoS ONE 2, e963 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osouda S., Nakamura Y., de Saint Phalle B., McConnell M., Horigome T., Sugiyama S., Fisher P. A., Furukawa K. (2005). Null mutants of Drosophila B-type lamin Dm(0) show aberrant tissue differentiation rather than obvious nuclear shape distortion or specific defects during cell proliferation. Dev. Biol. 284, 219-232 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnaik V. K. (2008). Role of nuclear lamins in nuclear organization, cellular signaling, and inherited diseases. Int. Rev. Cell. Mol. Biol. 266, 157-206 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry D. A., Steinert P. M. (1999). Intermediate filaments: molecular architecture, assembly, dynamics and polymorphism. Q. Rev. Biophys. 32, 99-187 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pekovic V., Hutchison C. J. (2008). Adult stem cell maintenance and tissue regeneration in the ageing context: the role for A-type lamins as intrinsic modulators of ageing in adult stem cells and their niches. J. Anat. 213, 5-25 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pekovic V., Harborth J., Broers J. L., Ramaekers F. C., van Engelen B., Lammens M., von Zglinicki T., Foisner R., Hutchison C., Markiewicz E. (2007). Nucleoplasmic LAP2alpha-lamin A complexes are required to maintain a proliferative state in human fibroblasts. J. Cell Biol. 176, 163-172 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard K. M., Chan E. K., Grant B. J., Sullivan K. F., Tan E. M., Glass C. A. (1990). In vitro posttranslational modification of lamin B cloned from a human T-cell line. Mol. Cell. Biol. 10, 2164-2175 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prokocimer M., Davidovich M., Nissim-Rafinia M., Wiesel-Motiuk N., Bar D. Z., Barkan R., Meshorer E., Gruenbaum Y. (2009). Nuclear lamins: key regulators of nuclear structure and activities. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 13, 1059-1085 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralle T., Gremmels D., Stick R. (1999). Translational control of nuclear lamin B1 mRNA during oogenesis and early development of Xenopus. Mech. Dev. 84, 89-101 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redwood A. B., Perkins S. M., Vanderwaal R. P., Feng Z., Biehl K. J., Gonzalez-Suarez I., Morgado-Palacin L., Shi W., Sage J., Roti-Roti J. L., et al. (2011). A dual role for A-type lamins in DNA double-strand break repair. Cell Cycle 10, 2549-2560 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Röber R. A., Weber K., Osborn M. (1989). Differential timing of nuclear lamin A/C expression in the various organs of the mouse embryo and the young animal: a developmental study. Development 105, 365-378 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez J., Calvo F., González J. M., Casar B., Andrés V., Crespo P. (2010). ERK1/2 MAP kinases promote cell cycle entry by rapid, kinase-independent disruption of retinoblastoma-lamin A complexes. J. Cell Biol. 191, 967-979 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosengardten Y., McKenna T., Grochová D., Eriksson M. (2011). Stem cell depletion in Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome. Aging Cell 10, 1011-1020 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakaki M., Koike H., Takahashi N., Sasagawa N., Tomioka S., Arahata K., Ishiura S. (2001). Interaction between emerin and nuclear lamins. J. Biochem. 129, 321-327 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasse B., Aebi U., Stuurman N. (1998). A tailless Drosophila lamin Dm0 fragment reveals lateral associations of dimers. J. Struct. Biol. 123, 56-66 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasseville A. M., Langelier Y. (1998). In vitro interaction of the carboxy-terminal domain of lamin A with actin. FEBS Lett. 425, 485-489 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scaffidi P., Misteli T. (2008). Lamin A-dependent misregulation of adult stem cells associated with accelerated ageing. Nat. Cell Biol. 10, 452-459 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäpe J., Prausse S., Radmacher M., Stick R. (2009). Influence of lamin A on the mechanical properties of amphibian oocyte nuclei measured by atomic force microscopy. Biophys. J. 96, 4319-4325 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shevelyov Y. Y., Nurminsky D. I. (2012). The nuclear lamina as a gene-silencing hub. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 14, 27-38 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimi T., Pfleghaar K., Kojima S., Pack C. G., Solovei I., Goldman A. E., Adam S. A., Shumaker D. K., Kinjo M., Cremer T., et al. (2008). The A- and B-type nuclear lamin networks: microdomains involved in chromatin organization and transcription. Genes Dev. 22, 3409-3421 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shumaker D. K., Solimando L., Sengupta K., Shimi T., Adam S. A., Grunwald A., Strelkov S. V., Aebi U., Cardoso M. C., Goldman R. D. (2008). The highly conserved nuclear lamin Ig-fold binds to PCNA: its role in DNA replication. J. Cell Biol. 181, 269-280 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon D. N., Wilson K. L. (2010). Direct actin binding to A- and B-type lamin tails and actin filament bundling by the lamin A tail. Nucleus 1, 264-272 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon D. N., Wilson K. L. (2011). The nucleoskeleton as a genome-associated dynamic ‘network of networks’. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 12, 695-708 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smythe C., Jenkins H. E., Hutchison C. J. (2000). Incorporation of the nuclear pore basket protein nup153 into nuclear pore structures is dependent upon lamina assembly: evidence from cell-free extracts of Xenopus eggs. EMBO J. 19, 3918-3931 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spann T. P., Moir R. D., Goldman A. E., Stick R., Goldman R. D. (1997). Disruption of nuclear lamin organization alters the distribution of replication factors and inhibits DNA synthesis. J. Cell Biol. 136, 1201-1212 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadelmann B., Khandjian E., Hirt A., Lüthy A., Weil R., Wagner H. P. (1990). Repression of nuclear lamin A and C gene expression in human acute lymphoblastic leukemia and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma cells. Leuk. Res. 14, 815-821 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stehbens W. E., Delahunt B., Shozawa T., Gilbert-Barness E. (2001). Smooth muscle cell depletion and collagen types in progeric arteries. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 10, 133-136 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuurman N., Heins S., Aebi U. (1998). Nuclear lamins: their structure, assembly, and interactions. J. Struct. Biol. 122, 42-66 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan T., Escalante-Alcalde D., Bhatt H., Anver M., Bhat N., Nagashima K., Stewart C. L., Burke B. (1999). Loss of A-type lamin expression compromises nuclear envelope integrity leading to muscular dystrophy. J. Cell Biol. 147, 913-920 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun S., Xu M. Z., Poon R. T., Day P. J., Luk J. M. (2010). Circulating Lamin B1 (LMNB1) biomarker detects early stages of liver cancer in patients. J. Proteome Res. 9, 70-78 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verstraeten V. L., Broers J. L., Ramaekers F. C., van Steensel M. A. (2007). The nuclear envelope, a key structure in cellular integrity and gene expression. Curr. Med. Chem. 14, 1231-1248 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verstraeten V. L., Ji J. Y., Cummings K. S., Lee R. T., Lammerding J. (2008). Increased mechanosensitivity and nuclear stiffness in Hutchinson-Gilford progeria cells: effects of farnesyltransferase inhibitors. Aging Cell 7, 383-393 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang G., Wang M., Wu B., You W. (2003). A lamin-like protein gene is down-regulated in human gastric cancer. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi 20, 119-122 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Wu R., Cho K. R., Thomas D. G., Gossner G., Liu J. R., Giordano T. J., Shedden K. A., Misek D. E., Lubman D. M. (2009). Differential protein mapping of ovarian serous adenocarcinomas: identification of potential markers for distinct tumor stage. J. Proteome Res. 8, 1452-1463 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren D. T., Shanahan C. M. (2011). Defective DNA-damage repair induced by nuclear lamina dysfunction is a key mediator of smooth muscle cell aging. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 39, 1780-1785 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willis N. D., Cox T. R., Rahman-Casañs S. F., Smits K., Przyborski S. A., van den Brandt P., van Engeland M., Weijenberg M., Wilson R. G., de Bruïne A., et al. (2008a). Lamin A/C is a risk biomarker in colorectal cancer. PLoS ONE 3, e2988 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willis N. D., Wilson R. G., Hutchison C. J. (2008b). Lamin A: a putative colonic epithelial stem cell biomarker which identifies colorectal tumours with a more aggressive phenotype. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 36, 1350-1353 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson K. L., Berk J. M. (2010). The nuclear envelope at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 123, 1973-1978 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson K. L., Foisner R. (2010). Lamin-binding Proteins. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2, a000554 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worman H. J. (2012). Nuclear lamins and laminopathies. J. Pathol. 226, 316-325 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worman H. J., Fong L. G., Muchir A., Young S. G. (2009). Laminopathies and the long strange trip from basic cell biology to therapy. J. Clin. Invest. 119, 1825-1836 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Z., Wu L., Weng D., Xu D., Geng J., Zhao F. (2009). Reduced expression of lamin A/C correlates with poor histological differentiation and prognosis in primary gastric carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 28, 8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong N., Radu G., Ju W., Brown W. T. (2005). Novel progerin-interactive partner proteins hnRNP E1, EGF, Mel 18, and UBC9 interact with lamin A/C. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 338, 855-861 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwerger M., Ho C. Y., Lammerding J. (2011). Nuclear mechanics in disease. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 13, 397-428 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]