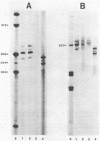
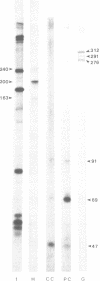
Abstract
The mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) control regions for common chimpanzee, pygmy chimpanzee and gorilla were sequenced and the lengths and termini of their D-loop DNA's characterized. In these and all other species for which there are data, 5' termini map to sequences that contain the trinucleotide YAY. 3' termini are 25-51 nucleotides downstream from a sequence that is moderately conserved among vertebrates. Substitutions were greater than 1.5 times more frequent in the control region than in regions encoding structural genes. Additions and deletions were also frequent, especially in gorilla. Sequences of promoters and of two of four transcription factor binding sites were highly conserved. Comparisons of sequence similarity and transition/transversion ratios suggest that human and chimpanzees may be more closely related to each other than either is to gorilla, if substitution rates are approximately equal among these species.
Full text
PDF





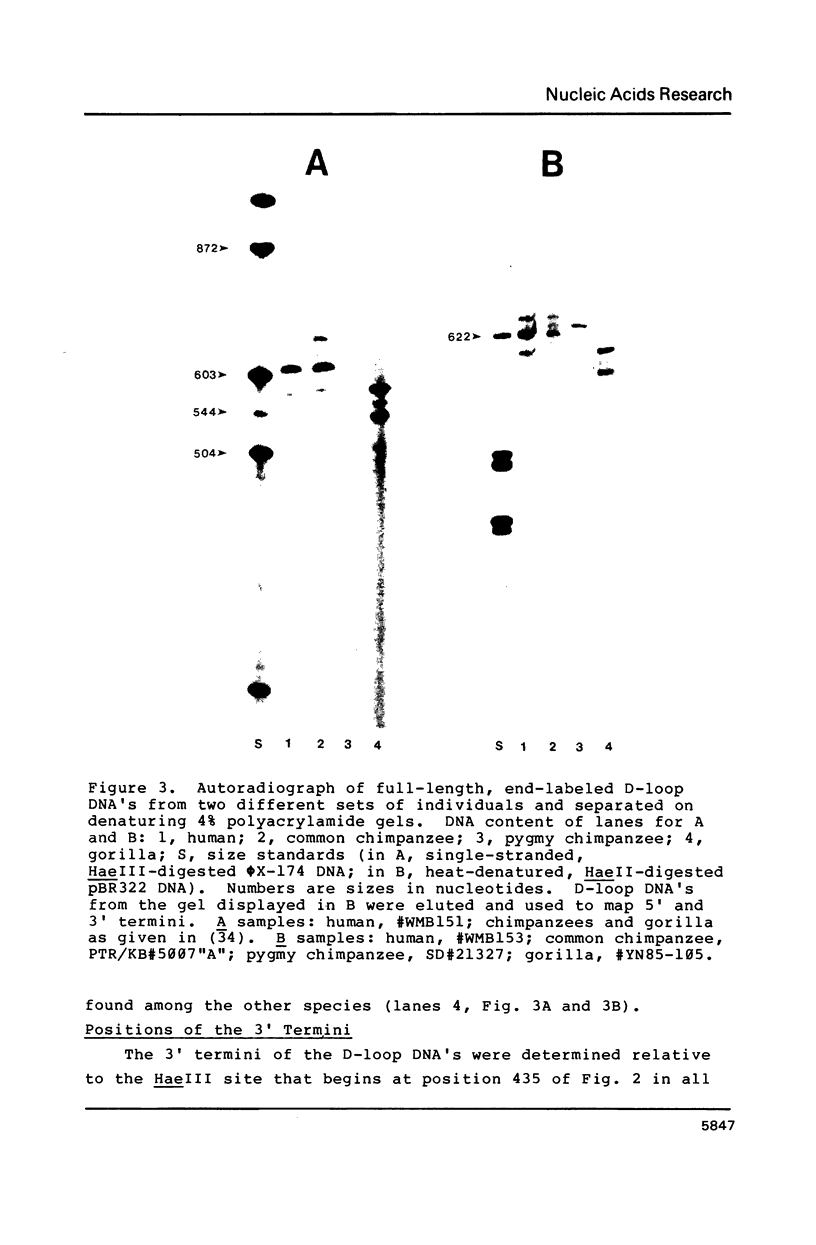














Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albertini A. M., Hofer M., Calos M. P., Miller J. H. On the formation of spontaneous deletions: the importance of short sequence homologies in the generation of large deletions. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):319–328. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90148-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson S., Bankier A. T., Barrell B. G., de Bruijn M. H., Coulson A. R., Drouin J., Eperon I. C., Nierlich D. P., Roe B. A., Sanger F. Sequence and organization of the human mitochondrial genome. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):457–465. doi: 10.1038/290457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson S., de Bruijn M. H., Coulson A. R., Eperon I. C., Sanger F., Young I. G. Complete sequence of bovine mitochondrial DNA. Conserved features of the mammalian mitochondrial genome. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 25;156(4):683–717. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90137-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aquadro C. F., Greenberg B. D. Human mitochondrial DNA variation and evolution: analysis of nucleotide sequences from seven individuals. Genetics. 1983 Feb;103(2):287–312. doi: 10.1093/genetics/103.2.287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldacci G., Chérif-Zahar B., Bernardi G. The initiation of DNA replication in the mitochondrial genome of yeast. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2115–2120. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02099.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Yoza B. K., Cairns S. S. Identification of initiation sites for transcription of Xenopus laevis mitochondrial DNA. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8488–8494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown G. G., Gadaleta G., Pepe G., Saccone C., Sbisà E. Structural conservation and variation in the D-loop-containing region of vertebrate mitochondrial DNA. J Mol Biol. 1986 Dec 5;192(3):503–511. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90272-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. M., George M., Jr, Wilson A. C. Rapid evolution of animal mitochondrial DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1967–1971. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. M., Prager E. M., Wang A., Wilson A. C. Mitochondrial DNA sequences of primates: tempo and mode of evolution. J Mol Evol. 1982;18(4):225–239. doi: 10.1007/BF01734101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. M., Shine J., Goodman H. M. Human mitochondrial DNA: analysis of 7S DNA from the origin of replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):735–739. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. M., Vinograd J. Restriction endonuclease cleavage maps of animal mitochondrial DNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4617–4621. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cairns S. S., Bogenhagen D. F. Mapping of the displacement loop within the nucleotide sequence of Xenopus laevis mitochondrial DNA. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8481–8487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D. D., Clayton D. A. A novel endoribonuclease cleaves at a priming site of mouse mitochondrial DNA replication. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):409–417. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04770.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D. D., Clayton D. A. Precise identification of individual promoters for transcription of each strand of human mitochondrial DNA. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):635–643. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90343-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D. D., Clayton D. A. Priming of human mitochondrial DNA replication occurs at the light-strand promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):351–355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D. D., Hauswirth W. W., Clayton D. A. Replication priming and transcription initiate from precisely the same site in mouse mitochondrial DNA. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1559–1567. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03817.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton D. A. Replication of animal mitochondrial DNA. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):693–705. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90049-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton D. A. Transcription of the mammalian mitochondrial genome. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:573–594. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.003041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Densmore L. D., Wright J. W., Brown W. M. Length variation and heteroplasmy are frequent in mitochondrial DNA from parthenogenetic and bisexual lizards (genus Cnemidophorus). Genetics. 1985 Aug;110(4):689–707. doi: 10.1093/genetics/110.4.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doda J. N., Wright C. T., Clayton D. A. Elongation of displacement-loop strands in human and mouse mitochondrial DNA is arrested near specific template sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6116–6120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunon-Bluteau D. C., Brun G. M. Mapping at the nucleotide level of Xenopus laevis mitochondrial D-loop H strand: structural features of the 3' region. Biochem Int. 1987 Apr;14(4):643–657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferris S. D., Wilson A. C., Brown W. M. Evolutionary tree for apes and humans based on cleavage maps of mitochondrial DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2432–2436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. P., Topper J. N., Clayton D. A. Promoter selection in human mitochondria involves binding of a transcription factor to orientation-independent upstream regulatory elements. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):247–258. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90220-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillum A. M., Clayton D. A. Displacement-loop replication initiation sequence in animal mitochondrial DNA exists as a family of discrete lengths. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):677–681. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg B. D., Newbold J. E., Sugino A. Intraspecific nucleotide sequence variability surrounding the origin of replication in human mitochondrial DNA. Gene. 1983 Jan-Feb;21(1-2):33–49. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90145-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauswirth W. W., Van de Walle M. J., Laipis P. J., Olivo P. D. Heterogeneous mitochondrial DNA D-loop sequences in bovine tissue. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1001–1007. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90434-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hixson J. E., Brown W. M. A comparison of the small ribosomal RNA genes from the mitochondrial DNA of the great apes and humans: sequence, structure, evolution, and phylogenetic implications. Mol Biol Evol. 1986 Jan;3(1):1–18. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hixson J. E., Clayton D. A. Initiation of transcription from each of the two human mitochondrial promoters requires unique nucleotides at the transcriptional start sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2660–2664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong G. F. A systemic DNA sequencing strategy. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jul 5;158(3):539–549. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90213-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karawya E. M., Martin R. G. Monkey (CV-1) mitochondrial DNA contains a unique triplication of 108 bp in the origin region. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jun 6;909(1):30–34. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(87)90043-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King T. C., Low R. L. Mapping of control elements in the displacement loop region of bovine mitochondrial DNA. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 5;262(13):6204–6213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King T. C., Low R. L. Mitochondrial DNA displacement loop structure depends on growth state in bovine cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 5;262(13):6214–6220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKay S. L., Olivo P. D., Laipis P. J., Hauswirth W. W. Template-directed arrest of mammalian mitochondrial DNA synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1261–1267. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montoya J., Christianson T., Levens D., Rabinowitz M., Attardi G. Identification of initiation sites for heavy-strand and light-strand transcription in human mitochondrial DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7195–7199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Air G. M., Barrell B. G., Brown N. L., Coulson A. R., Fiddes C. A., Hutchison C. A., Slocombe P. M., Smith M. Nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage phi X174 DNA. Nature. 1977 Feb 24;265(5596):687–695. doi: 10.1038/265687a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekiya T., Kobayashi M., Seki T., Koike K. Nucleotide sequence of a cloned fragment of rat mitochondrial DNA containing the replication origin. Gene. 1980 Oct;11(1-2):53–62. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90086-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streisinger G., Okada Y., Emrich J., Newton J., Tsugita A., Terzaghi E., Inouye M. Frameshift mutations and the genetic code. This paper is dedicated to Professor Theodosius Dobzhansky on the occasion of his 66th birthday. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1966;31:77–84. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1966.031.01.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapper D. P., Clayton D. A. Mechanism of replication of human mitochondrial DNA. Localization of the 5' ends of nascent daughter strands. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):5109–5115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upholt W. B., Dawid I. B. Mapping of mitochondrial DNA of individual sheep and goats: rapid evolution in the D loop region. Cell. 1977 Jul;11(3):571–583. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90075-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walberg M. W., Clayton D. A. Sequence and properties of the human KB cell and mouse L cell D-loop regions of mitochondrial DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5411–5421. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong J. F., Ma D. P., Wilson R. K., Roe B. A. DNA sequence of the Xenopus laevis mitochondrial heavy and light strand replication origins and flanking tRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jul 25;11(14):4977–4995. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.14.4977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yousaf S. I., Carroll A. R., Clarke B. E. A new and improved method for 3'-end labelling DNA using [alpha-32P]ddATP. Gene. 1984 Mar;27(3):309–313. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90075-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zyskind J. W., Smith D. W. The bacterial origin of replication, oriC. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):489–490. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90873-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]