Abstract
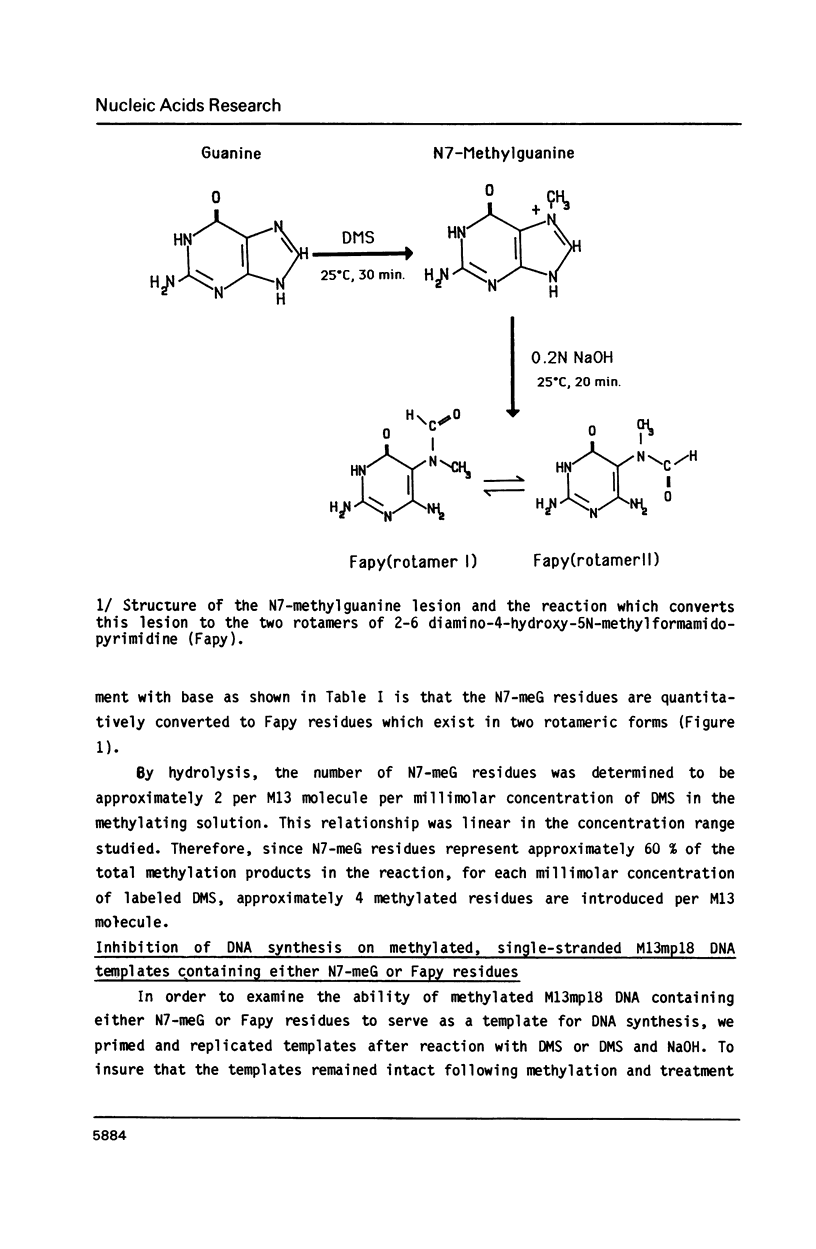
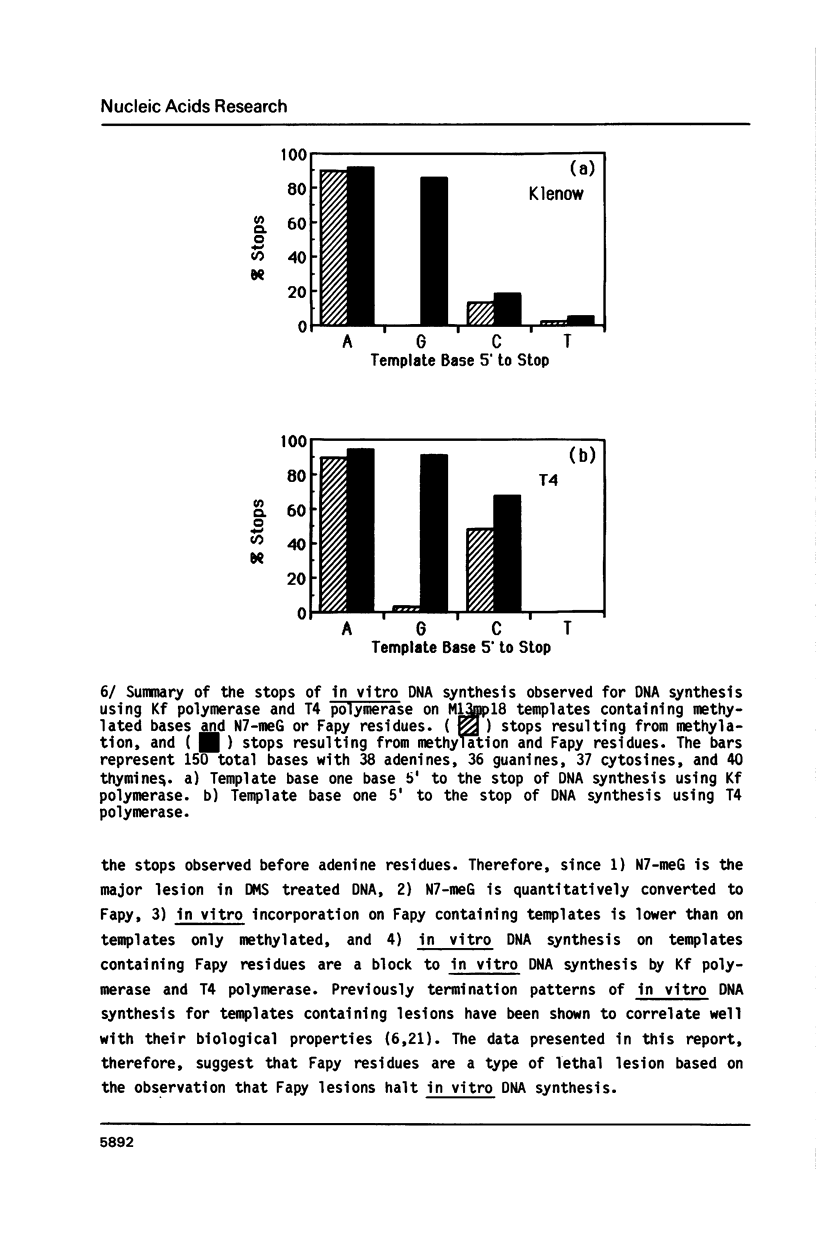
Single-stranded M13mp18 phage DNA was methylated with dimethylsulfate (DMS), and further treated with alkali to ring-open N7-methylguanine residues and yield 2-6-diamino-4-hydroxy-5N-methylformamidopyrimidine (Fapy) residues. Nucleotide incorporation during in vitro DNA synthesis on methylated template using E. coli DNA polymerase Klenow fragment (Kf polymerase) was reduced compared to the unmethylated template. Additional treatment of the methylated template with NaOH to generate Fapy residues, further reduced in vitro DNA synthesis compared to the synthesis on methylated templates, which suggested that Fapy residues were a block to in vitro DNA synthesis. Analysis of the termination products on sequencing gels, assuming that synthesis stops one base before a blocking lesion, indicated that arrest of DNA synthesis upon direct alkylation of single-stranded DNA occurred 1 base 3' to template adenine residues in the case of Kf polymerase and 1 base 3' to adenine and cystosine residues for T4 polymerase. When the alkylated templates were treated with NaOH to produce a template which converted all the N7-methylguanine residues to Fapy residues, the blocks to DNA synthesis were still observed one base before adenine residues. In addition to the stops previously observed for the methylated templates, however, new stops occurred one base 3' to template guanine residues for synthesis using both Kf polymerase and T4 polymerase. Fapy residues, therefore, represent a potential lethal lesion which may also arrest in vivo DNA synthesis if not repaired.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beranek D. T., Weis C. C., Evans F. E., Chetsanga C. J., Kadlubar F. F. Identification of N5-methyl-N5-formyl-2,5,6-triamino-4-hydroxypyrimidine as a major adduct in rat liver DNA after treatment with the carcinogens, N,N-dimethylnitrosamine or 1,2-dimethylhydrazine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jan 27;110(2):625–631. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91195-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boiteux S., Belleney J., Roques B. P., Laval J. Two rotameric forms of open ring 7-methylguanine are present in alkylated polynucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5429–5439. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boiteux S., Laval J. Coding properties of poly(deoxycytidylic acid) templates containing uracil or apyrimidinic sites: in vitro modulation of mutagenesis by deoxyribonucleic acid repair enzymes. Biochemistry. 1982 Dec 21;21(26):6746–6751. doi: 10.1021/bi00269a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boiteux S., Laval J. Imidazole open ring 7-methylguanine: an inhibitor of DNA synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jan 27;110(2):552–558. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91185-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boiteux S., Laval J. Mutagenesis by alkylating agents: coding properties for DNA polymerase of poly (dC) template containing 3-methylcytosine. Biochimie. 1982 Aug-Sep;64(8-9):637–641. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(82)80103-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boiteux S., O'Connor T. R., Laval J. Formamidopyrimidine-DNA glycosylase of Escherichia coli: cloning and sequencing of the fpg structural gene and overproduction of the protein. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3177–3183. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02629.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evensen G., Seeberg E. Adaptation to alkylation resistance involves the induction of a DNA glycosylase. Nature. 1982 Apr 22;296(5859):773–775. doi: 10.1038/296773a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ide H., Kow Y. W., Wallace S. S. Thymine glycols and urea residues in M13 DNA constitute replicative blocks in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 25;13(22):8035–8052. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.22.8035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadlubar F. F., Beranek D. T., Weis C. C., Evans F. E., Cox R., Irving C. C. Characterization of the purine ring-opened 7-methylguanine and its persistence in rat bladder epithelial DNA after treatment with the carcinogen N-methylnitrosourea. Carcinogenesis. 1984 May;5(5):587–592. doi: 10.1093/carcin/5.5.587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAWLEY P. D., BROOKES P. FURTHER STUDIES ON THE ALKYLATION OF NUCLEIC ACIDS AND THEIR CONSTITUENT NUCLEOTIDES. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:127–138. doi: 10.1042/bj0890127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson K., Sahm J., Shenkar R., Strauss B. Methylation-induced blocks to in vitro DNA replication. Mutat Res. 1985 Jun-Jul;150(1-2):77–84. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(85)90103-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laval J., Pierre J., Laval F. Release of 7-methylguanine residues from alkylated DNA by extracts of Micrococcus luteus and Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):852–855. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawley P. D., Orr D. J. Specific excision of methylation products from DNA of Escherichia coli treated with N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine. Chem Biol Interact. 1970 Aug;2(2):154–157. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(70)90047-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb L. A., Kunkel T. A. Fidelity of DNA synthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:429–457. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.002241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loechler E. L., Green C. L., Essigmann J. M. In vivo mutagenesis by O6-methylguanine built into a unique site in a viral genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6271–6275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margison G. P., Pegg A. E. Enzymatic release of 7-methylguanine from methylated DNA by rodent liver extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):861–865. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P., Strauss B. S. Sites of inhibition of in vitro DNA synthesis in carcinogen- and UV-treated phi X174 DNA. Nature. 1979 Apr 12;278(5705):664–666. doi: 10.1038/278664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffhill R. Differences in the promutagenic nature of 3-methylcytosine as revealed by DNA and RNA polymerising enzymes. Carcinogenesis. 1984 May;5(5):691–693. doi: 10.1093/carcin/5.5.691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




