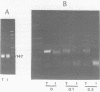
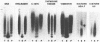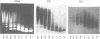Abstract
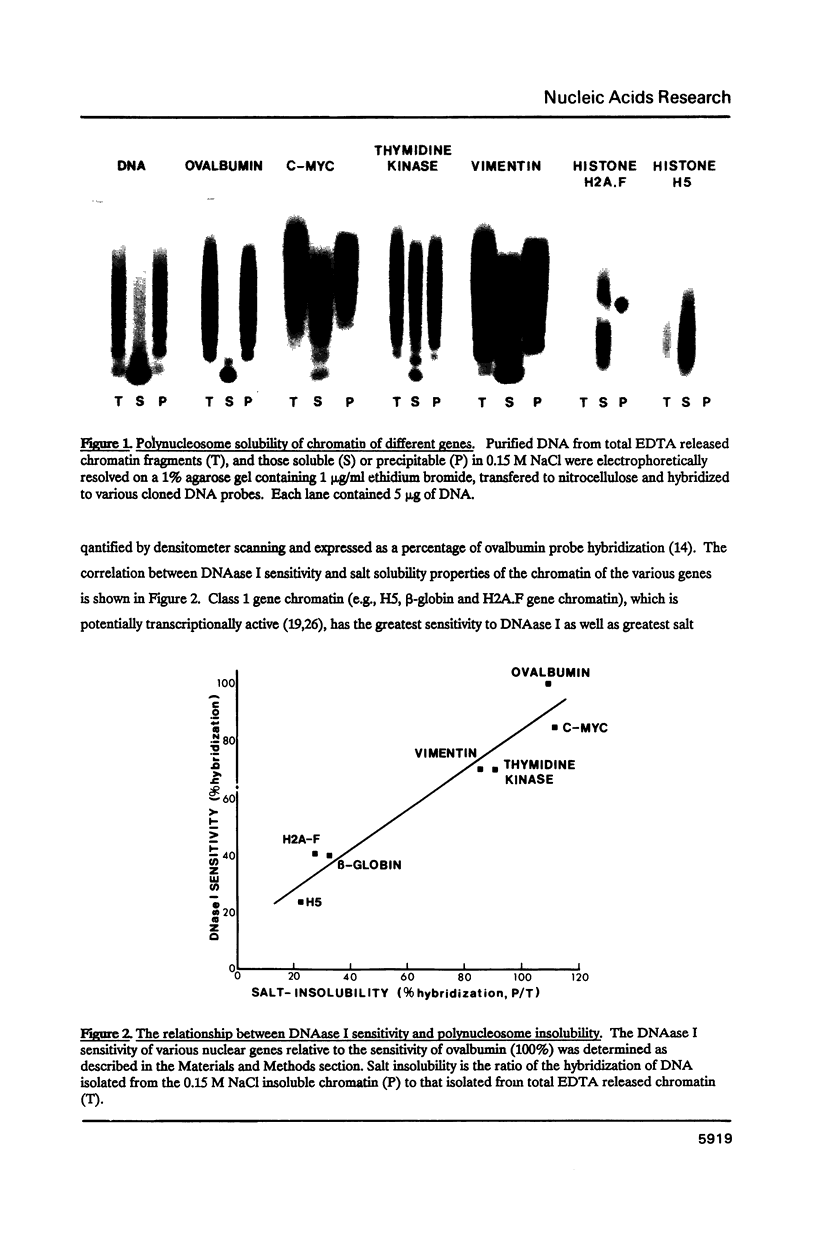
The chromatin of several genes was assayed for sensitivity to DNAase I and for solubility as polynucleosomes in 0.15 M NaCl. The degree of solubility of chromatin fragments as polynucleosomes in 0.15 M NaCl correlates well with the sensitivity to DNAase I for several genes. Chromatin of repressed, housekeeping and erythroid-specific genes can be distinguished as distinct groups by the degree to which they display these properties. NaCl precipitation of chromatin fragments stripped and then reconstituted with varying quantities of H1 and H5 (linker) histones indicate that the polynucleosomes of erythroid-specific genes have altered interaction with these histones. Linker histones interacted with bulk chromatin and in the chromatin of the repressed ovalbumin and vitellogenin genes to form salt precipitable structures. Chromatin of erythroid-specific genes (histone H5 and beta-globin) as well as that of the histone H2A.F gene was resistant to linker histone induced precipitation.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Affolter M., Côté J., Renaud J., Ruiz-Carrillo A. Regulation of histone and beta A-globin gene expression during differentiation of chicken erythroid cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3663–3672. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan J., Harborne N., Rau D. C., Gould H. Participation of core histone "tails" in the stabilization of the chromatin solenoid. J Cell Biol. 1982 May;93(2):285–297. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.2.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alonso W. R., Ferris R. C., Zhang D. E., Nelson D. A. Chicken erythrocyte beta-globin chromatin: enhanced solubility is a direct consequence of induced histone hyperacetylation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 25;15(22):9325–9337. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.22.9325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode J., Gómez-Lira M. M., Schröter H. Nucleosomal particles open as the histone core becomes hyperacetylated. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Feb 15;130(3):437–445. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07170.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. D. The role of stable complexes that repress and activate eucaryotic genes. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):359–365. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90366-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch J. B., Weintraub H. Temporal order of chromatin structural changes associated with activation of the major chicken vitellogenin gene. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):65–76. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90335-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caplan A., Kimura T., Gould H., Allan J. Perturbation of chromatin structure in the region of the adult beta-globin gene in chicken erythrocyte chromatin. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jan 5;193(1):57–70. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90626-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferenz C. R., Nelson D. A. N-Butyrate incubation of immature chicken erythrocytes preferentially enhances the solubility of beta A chromatin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 25;13(6):1977–1995. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.6.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goring D. R., Rossant J., Clapoff S., Breitman M. L., Tsui L. C. In situ detection of beta-galactosidase in lenses of transgenic mice with a gamma-crystallin/lacZ gene. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):456–458. doi: 10.1126/science.3099390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld F., van Assendelft G. B., Greaves D. R., Kollias G. Position-independent, high-level expression of the human beta-globin gene in transgenic mice. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):975–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90584-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey R. P., Whiting J. A., Coles L. S., Krieg P. A., Wells J. R. H2A.F: an extremely variant histone H2A sequence expressed in the chicken embryo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):2819–2823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.2819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchison N., Weintraub H. Localization of DNAase I-sensitive sequences to specific regions of interphase nuclei. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):471–482. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90177-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai B. S., Yau P., Baldwin J. P., Ibel K., May R. P., Bradbury E. M. Hyperacetylation of core histones does not cause unfolding of nucleosomes. Neutron scatter data accords with disc shape of the nucleosome. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8784–8792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libertini L. J., Small E. W. Salt induced transitions of chromatin core particles studied by tyrosine fluorescence anisotropy. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Aug 25;8(16):3517–3534. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.16.3517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Goodbourn S., Fischer J. A. Regulation of inducible and tissue-specific gene expression. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1237–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.3296191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Wood W. I., Dolan M., Engel J. D., Felsenfeld G. A 200 base pair region at the 5' end of the chicken adult beta-globin gene is accessible to nuclease digestion. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):45–55. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90359-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMurray C. T., van Holde K. E. Binding of ethidium bromide causes dissociation of the nucleosome core particle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8472–8476. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. A., Ferris R. C., Zhang D. E., Ferenz C. R. The beta-globin domain in immature chicken erythrocytes: enhanced solubility is coincident with histone hyperacetylation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 25;14(4):1667–1682. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.4.1667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson P. P., Albright S. C., Wiseman J. M., Garrard W. T. Reassociation of histone H1 with nucleosomes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11751–11760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliva R., Bazett-Jones D., Mezquita C., Dixon G. H. Factors affecting nucleosome disassembly by protamines in vitro. Histone hyperacetylation and chromatin structure, time dependence, and the size of the sperm nuclear proteins. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 15;262(35):17016–17025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quaife C. J., Pinkert C. A., Ornitz D. M., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Pancreatic neoplasia induced by ras expression in acinar cells of transgenic mice. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):1023–1034. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90710-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rattner J. B., Hamkalo B. A. Higher order structure in metaphase chromosomes. I. The 250 A fiber. Chromosoma. 1978 Dec 6;69(3):363–372. doi: 10.1007/BF00332139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridsdale J. A., Davie J. R. Chicken erythrocyte polynucleosomes which are soluble at physiological ionic strength and contain linker histones are highly enriched in beta-globin gene sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):1081–1096. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.1081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocha E., Davie J. R., van Holde K. E., Weintraub H. Differential salt fractionation of active and inactive genomic domains in chicken erythrocyte. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8558–8563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Carrillo A., Affolter M., Renaud J. Genomic organization of the genes coding for the six main histones of the chicken: complete sequence of the H5 gene. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):843–859. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80191-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun Y. L., Xu Y. Z., Bellard M., Chambon P. Digestion of the chicken beta-globin gene chromatin with micrococcal nuclease reveals the presence of an altered nucleosomal array characterized by an atypical ladder of DNA fragments. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):293–300. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04212.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villeponteau B., Landes G. M., Pankratz M. J., Martinson H. G. The chicken beta globin gene region. Delineation of transcription units and developmental regulation of interspersed DNA repeats. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):11015–11023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villeponteau B., Lundell M., Martinson H. Torsional stress promotes the DNAase I sensitivity of active genes. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):469–478. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90454-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H. Assembly and propagation of repressed and depressed chromosomal states. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):705–711. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90267-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H. Histone-H1-dependent chromatin superstructures and the suppression of gene activity. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):17–27. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90522-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woo S. L., Dugaiczyk A., Tsai M. J., Lai E. C., Catterall J. F., O'Malley B. W. The ovalbumin gene: cloning of the natural gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3688–3692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaniv M., Cereghini S. Structure of transcriptionally active chromatin. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1986;21(1):1–26. doi: 10.3109/10409238609113607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zehner Z. E., Paterson B. M. Characterization of the chicken vimentin gene: single copy gene producing multiple mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):911–915. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]