Abstract
Polynucleobacter necessarius subsp. asymbioticus strain QLW-P1DMWA-1T is a planktonic freshwater bacterium affiliated with the family Burkholderiaceae (class Betaproteobacteria). This strain is of interest because it represents a subspecies with cosmopolitan and ubiquitous distribution in standing freshwater systems. The 16S-23S ITS genotype represented by the sequenced strain comprised on average more than 10% of bacterioplankton in its home habitat. While all strains of the subspecies P. necessarius asymbioticus are free-living freshwater bacteria, strains belonging to the only other subspecies, P. necessarius subsp. necessarius are obligate endosymbionts of the ciliate Euplotes aediculatus. The two subspecies of P. necessarius are the instances of two closely related subspecies that differ in their lifestyle (free-living vs. obligate endosymbiont), and they are the only members of the genus Polynucleobacter with completely sequenced genomes. Here we describe the features of P. necessarius subsp. asymbioticus, together with the complete genome sequence and annotation. The 2,159,490 bp long chromosome with a total of 2,088 protein-coding and 48 RNA genes is the first completed genome sequence of the genus Polynucleobacter to be published and was sequenced as part of the DOE Joint Genome Institute Community Sequencing Program 2006.
Keywords: aerobic, chemoorganotrophic, Gram-negative, non-motile, free-living, planktonic, freshwater habitats, Burkholderiaceae, Betaproteobacteria, CSP2006
Introduction
Strain QLW-P1DMWA-1T (= DSM 18221 = CIP 10981) is the type strain of Polynucleobacter necessarius subsp. asymbioticus [1], which is one of two subspecies in the species P. necessarius [1]. The genus was first named by Heckmann and Schmidt in 1987 [2] in which ‘omicron from stock 15 of Euplotes aediculatus’ was designated as the type species [2]. The genus name was derived from the Greek words polys, numerous, bactrum, rod, and the Latin word nucleus, nut. The species epithet originated from the Latin adjective necessarius, indispensible [2]. ‘Omicron’-like symbionts were known for some time since their isolation from several freshwater Euplotes spp. [3], and are also known to be essential for the host cells [2]. Only 22 years later, Hahn et al. described a closely related free-living strain, QLW-P1DMWA-1T, which they considered to be another member of the species P. necessarius [1]. The description of P. necessarius subsp. asymbioticus followed several years after the observation that these free-living planktonic bacteria are closely related to P. necessarius and are cosmopolitan in freshwater habitats, occurring in different climatic zones in Europe, Asia and Africa [4]. This observation was confirmed by several cultivation-independent investigations of freshwater bacterioplankton diversity (for review see Newton et al., 2011 [5]). Furthermore, a systematic survey of almost all stagnant freshwater habitats of a 2000 km2 area located in Central Europe by specific fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) probes revealed ubiquity (i.e. presence in all investigated habitats) of free-living P. necessarius [6]. Meanwhile, three more members of the genus were described; P. cosmopolitanus from freshwater lakes and rivers [7], P. rarus from an acidic lake located in Wisconsin, USA [8], and P. acidiphobus from a freshwater rock pool located on the Mediterranean island Corsica (France) [9]. Furthermore, the establishment of a fifth Polynucleobacter species, P. difficilis, was recently proposed [10]. Strain QLW-P1DMWA-1T was isolated from a small acidic pond located at an altitude of 1,300 meters in the Austrian Alps near the city of Salzburg [11]. The strain represents a group of closely related strains sharing identical 16S rRNA, 16S-23S ITS and glutamine synthetase (glnA) genes. The group is persistent in the pond and comprises approximately 11% to total bacterioplankton [12]. Here we present a summary classification and a set of features for P. necessarius subsp. asymbioticus QLW-P1DMWA-1T, together with the description of the complete genomic sequencing and annotation.
Classification and features
The single genomic 16S rRNA sequence of P. necessarius subsp. asymbioticus QLW-P1DMWA-1T was compared using NCBI BLAST [13] under default settings (e.g., considering only the high-scoring segment pairs (HSPs) from the best 250 hits) with the most recent release of the Greengenes database [14] and the relative frequencies of taxa and keywords (reduced to their stem [15]) were determined, weighted by BLAST scores. The most frequently occurring genera were Polynucleobacter (99.1%) and Polaromonas (0.9%) (103 hits in total). Regarding the 19 hits to sequences from members of the species, the average identity within HSPs was 99.7%, whereas the average coverage by HSPs was 97.8%. No hits to sequences associated with other species names were found. (Note that the Greengenes database uses the INSDC (= EMBL/NCBI/DDBJ) annotation, which is not an authoritative source for nomenclature or classification.) The highest-scoring environmental sequence was DQ234242 ('determined library mangrove clone DS160'), which showed an identity of 99.9% and an HSP coverage of 99.3%. The most frequently occurring keywords within the labels of environmental samples which yielded hits were 'aquat, bai, rank' (9.9%), 'chesapeak' (5.3%), 'delawar' (4.6%), 'river' (4.4%) and 'freshwat' (3.1%) (147 hits in total). The most frequently occurring keywords within the labels of environmental samples which yielded hits of a higher score than the highest scoring species were 'freshwat' (9.7%), 'belong, climat, cosmopolitan, habitat, isol, locat, necessariu, polynucleobact, three, zone' (8.1%), 'determin, librari, mangrov' (1.6%) and 'cultur, lake, watercolumn' (1.6%) (7 hits in total). Those keywords that refer to habitats fit well with the ecological properties reported for strain QLW-P1DMWA-1T in the original description [1], whereas others reflect technical information of the studies from which the sequences were generated.
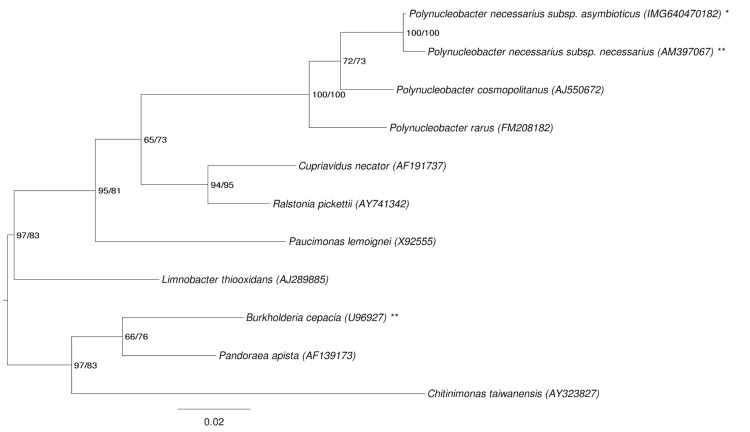
Figure 1 shows the phylogenetic neighborhood of P. necessarius subsp. asymbioticus in a 16S rRNA based tree. The sequence of the single 16S rRNA gene copy in the genome does not differ from the previously published 16S rRNA sequence (AJ879783).
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic tree highlighting the position of P. necessarius subsp. asymbioticus relative to the type strains of the genus and the type species of the other closely related genera within the family Burkholderiaceae. The tree was inferred from 1,483 aligned characters [16,17] of the 16S rRNA gene sequence under the maximum likelihood (ML) criterion [18]. Rooting was done initially using the midpoint method [19] and then checked for its agreement with the current classification (Table 1). The branches are scaled in terms of the expected number of substitutions per site. Numbers adjacent to the branches are support values from 150 ML bootstrap replicates [20] (left) and from 1,000 maximum-parsimony bootstrap replicates [21] (right) if larger than 60%. Lineages with type strain genome sequencing projects registered in GOLD [22] are labeled with one asterisk, those also listed as 'Complete and Published' (as well as the target genome) with two asterisks (see Burkholderia cepacia, CP000151).
Table 1. Classification and general features of P. necessarius subsp. asymbioticus according to the MIGS recommendations [23] and the NamesforLife database [24].
| MIGS ID | Property | Term | Evidence code |
|---|---|---|---|
| Current classification | Domain Bacteria | TAS [25] | |
| Phylum Proteobacteria | TAS [26] | ||
| Class Betaproteobacteria | TAS [27,28] | ||
| Order Burkholderiales | TAS [28,29] | ||
| Family Burkholderiaceae | TAS [28,30] | ||
| Genus Polynucleobacter | TAS [1,2] | ||
| Species Polynucleobacter necessarius | TAS [1] | ||
| Subspecies asymbioticus | TAS [1] | ||
| Type strain QLW-P1DMWA-1 | TAS [1] | ||
| Gram stain | negative | TAS [1] | |
| Cell shape | rod-shaped | TAS [1] | |
| Motility | non-motile | TAS [1] | |
| Sporulation | none | TAS [1] | |
| Temperature range | mesophile, 5–34°C | TAS [1] | |
| Optimum temperature | not reported | ||
| Salinity | 0-0.5% (w/v) NaCl | TAS [1] | |
| MIGS-22 | Oxygen requirement | aerobic, facultatively anaerobic | TAS [1] |
| Carbon source | various organic acids, sugars and amino acids | TAS [1] | |
| Energy metabolism | chemoorganotroph | TAS [1] | |
| MIGS-6 | Habitat | fresh water | TAS [4] |
| MIGS-15 | Biotic relationship | obligately free living | TAS [1] |
| MIGS-14 | Pathogenicity | none | NAS |
| Biosafety level | 1 | TAS [31] | |
| Isolation | acidic freshwater pond | TAS [1] | |
| MIGS-4 | Geographic location | Austrian Alps | TAS [1] |
| MIGS-5 | Sample collection time | October 15, 2003 | NAS |
| MIGS-4.1 | Latitude | 47.7398 | TAS [11,12] |
| MIGS-4.2 | Longitude | 13.3017 | TAS [11,12] |
| MIGS-4.3 | Depth | 0.3 m | NAS |
| MIGS-4.4 | Altitude | 1300 m | TAS [1] |
Evidence codes - NAS: Non-traceable Author Statement (i.e., not directly observed for the living, isolated sample, but based on a generally accepted property for the species, or anecdotal evidence). These evidence codes are from the Gene Ontology project [32].
Cells of P. necessarius subsp. asymbioticus strain QLW-P1DMWA-1T are straight rods, 0.7–1.2 by 0.4–0.5 µm in size [1]. The multiple nucleoid-like structures, which were originally considered to be typical for the cells of members of the genus, are absent in this strain but were observed rarely in some elongated cells of other strains of this subspecies [1]. QLW-P1DMWA-1T cells stain Gram-negative, are catalase- and oxidase-positive, chemoorganotrophic, non-motile, facultatively anaerobic, and non-spore-forming [1]. Cells grow at salt concentrations of up to 0.5% (w/v) NaCl [1]. The pH range for growth was not reported, neither an optimal growth temperature, only a growth range of 5-34°C [1]. The substrate spectrum and biochemistry are reported in detail by Hahn et al. [1], however, weak growth in complex media and poor growth in media containing a single carbon source hampered more extensive physiological analysis [1].
Chemotaxonomy
Data on the structure of the cell wall, quinones and polar lipids are not available for strain QLW-P1DMWA-1T. Major cellular fatty acids are C16:1 ω7c (41.3%), C16:0 (22.2%), C18:1 ω7c (12.9%), summed feature 2 including C14:0 3-OH (9.6%), C12:0 (3.4%), and 11-methyl C18:1 ω7c (3.1%) [1]. All members of P. necessarius lack 2-hydroxylated fatty acids other than C12:0, which can be used for differentiation from members of the genera Ralstonia and Cupriavidus.
Genome sequencing and annotation
Genome project history
This organism was selected for sequencing on the basis of the DOE Joint Genome Institute Community Sequencing Program 2006. The genome project is deposited in the Genomes On Line Database [22] and the complete genome sequence is deposited in GenBank. Sequencing, finishing and annotation were performed by the DOE Joint Genome Institute (JGI). A summary of the project information is shown in Table 2.
Table 2. Genome sequencing project information.
| MIGS ID | Property | Term |
|---|---|---|
| MIGS-31 | Finishing quality | Finished |
| MIGS-28 | Libraries used | Three genomic Sanger libraries: 4 kb pUC, 8 kb pMCL200 and fosmid pcc1Fos libraries. |
| MIGS-29 | Sequencing platforms | ABI3730 |
| MIGS-31.2 | Sequencing coverage | 12.0 × Sanger |
| MIGS-30 | Assemblers | phrap |
| MIGS-32 | Gene calling method | Critica complemented with the output of Glimmer |
| INSDC ID | CP000655 | |
| GenBank Date of Release | April 23, 2007 | |
| GOLD ID | Gc00537 | |
| NCBI project ID | 16679 | |
| Database: IMG-GEBA | 640427129 | |
| MIGS-13 | Source material identifier | DSM 18221 |
| Project relevance | Ecology, Biotechnology |
Growth conditions and DNA isolation
A culture of DSM 18221 grown aerobically in NSY medium [1] at room temperature was used to prepare genomic DNA (gDNA) for sequencing. Genomic DNA was extracted by following the CTAB protocol recommended by JGI [33]. The purity, quality and size of the bulk gDNA preparation were assessed by JGI according to DOE-JGI guidelines.
Genome sequencing and assembly
The genome was sequenced using a combination of 4 kb, 8 kb and fosmid DNA libraries. All general aspects of library construction and sequencing can be found at the JGI website [33]. Draft assemblies were based on 28,841 total reads and contained 14 contigs in one scaffold. The Phred/Phrap-/Consed software package was used for sequence assembly and quality assessment [34]. Possible mis-assemblies were corrected with Dupfinisher [35]. Gaps between contigs were closed by editing in Consed, custom priming, or PCR amplification. A total of 1,238 additional reactions were needed to close gaps and to raise the quality of the finished sequence. The error rate of the completed genome sequence is less than 1 in 100,000. Together all libraries provided 12.0 × coverage of the genome.
Genome annotation
Genes were identified using two gene modeling programs, Glimmer [36] and Critica [37] as part of the Oak Ridge National Laboratory genome annotation pipeline. The two sets of gene calls were combined using Critica as the preferred start call for genes with the same stop codon. Genes with less than 80 amino acids, which were predicted by only one of the gene callers and had no Blast hit in the KEGG database at 1e-05, were deleted. This was followed by a round of manual curation to eliminate obvious overlaps. The predicted CDSs were translated and used to search the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) nonredundant database, UniProt, TIGRFam, Pfam, PRIAM, KEGG, COG, and InterPro databases. These data sources were combined to assert a product description for each predicted protein. Non-coding genes and miscellaneous features were predicted using tRNAscan-SE [38], TMHMM [39], and signalP [40].
Genome properties
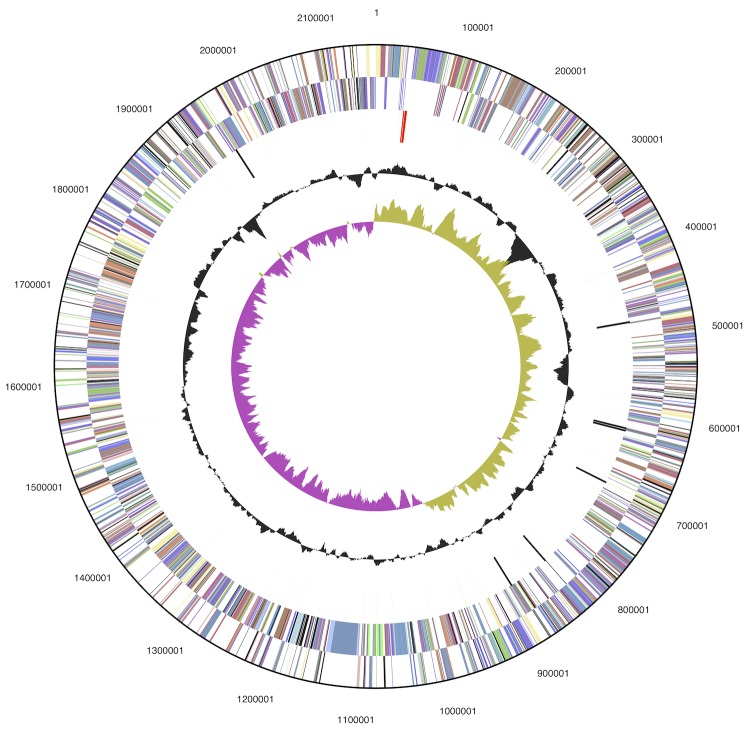
The genome consists of a 2,159,490 bp long chromosome with a 44.8% G+C content (Table 3 and Figure 2). Of the 2,136 genes predicted, 2,088 were protein-coding genes, and 48 RNAs; 11 pseudogenes were also identified. The majority of the protein-coding genes (76.7%) were assigned a putative function while the remaining ones were annotated as hypothetical proteins. The distribution of genes into COGs functional categories is presented in Table 4.
Table 3. Genome Statistics.
| Attribute | Value | % of Total |
|---|---|---|
| Genome size (bp) | 2,159,490 | 100.00% |
| DNA coding region (bp) | 2,011,351 | 93.14% |
| DNA G+C content (bp) | 968,188 | 44.83% |
| Number of replicons | 1 | |
| Extrachromosomal elements | 0 | |
| Total genes | 2,136 | 100.00% |
| RNA genes | 48 | 2.25% |
| rRNA operons | 1 | |
| Protein-coding genes | 2,088 | 97.75% |
| Pseudo genes | 11 | 0.51% |
| Genes with function prediction | 1,639 | 76.73% |
| Genes in paralog clusters | 183 | 8.57% |
| Genes assigned to COGs | 1,719 | 80.48% |
| Genes assigned Pfam domains | 1,772 | 82.96% |
| Genes with signal peptides | 480 | 22.47% |
| Genes with transmembrane helices | 535 | 25.05% |
| CRISPR repeats | 0 |
Figure 2.
Graphical circular map of the chromosome. From outside to the center: Genes on forward strand (color by COG categories), Genes on reverse strand (color by COG categories), RNA genes (tRNAs green, rRNAs red, other RNAs black), GC content, GC skew.
Table 4. Number of genes associated with the general COG functional categories.
| Code | value | %age | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| J | 155 | 8.3 | Translation, ribosomal structure and biogenesis |
| A | 1 | 0.1 | RNA processing and modification |
| K | 68 | 3.6 | Transcription |
| L | 101 | 5.4 | Replication, recombination and repair |
| B | 2 | 0.1 | Chromatin structure and dynamics |
| D | 19 | 1.0 | Cell cycle control, cell division, chromosome partitioning |
| Y | 0 | 0.0 | Nuclear structure |
| V | 18 | 1.0 | Defense mechanisms |
| T | 54 | 2.9 | Signal transduction mechanisms |
| M | 153 | 8.2 | Cell wall/membrane biogenesis |
| N | 9 | 0.5 | Cell motility |
| Z | 0 | 0.0 | Cytoskeleton |
| W | 0 | 0.0 | Extracellular structures |
| U | 44 | 2.3 | Intracellular trafficking and secretion, and vesicular transport |
| O | 99 | 5.3 | Posttranslational modification, protein turnover, chaperones |
| C | 156 | 8.3 | Energy production and conversion |
| G | 77 | 4.1 | Carbohydrate transport and metabolism |
| E | 161 | 8.6 | Amino acid transport and metabolism |
| F | 47 | 2.5 | Nucleotide transport and metabolism |
| H | 111 | 5.9 | Coenzyme transport and metabolism |
| I | 88 | 4.7 | Lipid transport and metabolism |
| P | 86 | 4.6 | Inorganic ion transport and metabolism |
| Q | 46 | 2.5 | Secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport and catabolism |
| R | 208 | 11.1 | General function prediction only |
| S | 174 | 9.3 | Function unknown |
| - | 417 | 19.5 | Not in COGs |
Insights into the genome
P. necessarius, initially described as a taxon exclusively harboring obligate endosymbionts of E. aediculatus [2], is one of a small number of bacterial species with a validly published name for which an axenic culture of a type strain does not exist in a public strain collections [1], all of which predate the introduction of the Candidatus concept [41]. Interestingly, the genome of P. necessarius subsp. necessarius STIR1, the endosymbiont of the ciliate E. aediculatus STIR1 [42,43] has been sequenced under the same JGI Community Sequencing Program 2006 as the genome of the free-living strain QLW-P1DMWA-1T, and was deposited in the INSDC databases as CP001010. As for taxonomic purposes, however, it is important to note that the endosymbiotic strain STIR1 has not been proposed as the type strain of P. necessarius [2]. Today, P. necessaries would have been designated as Candidatus.
At the time P. necessarius subsp. asymbioticus was described [1], it was not possible to perform a DNA-DNA hybridization to evaluate the degree of relatedness between the two subspecies, because it was not possible to obtain enough DNA of endosymbionts contained in the ciliate culture used for description of P. necessarius. There was insufficient pure genomic DNA obtainable from the type strain of P. necessarius. However, it is now possible to perform a digital DNA-DNA hybridization of the two completed genome sequences of representatives of the two subspecies by means of genome-to-genome sequence comparison [44-46].
The 2,159,490 bp long genome sequence of P. necessarius subsp. asymbioticus QLW-P1DMWA-1T (CP000655, NC_009379) and the 1,560,469 bp long genome sequence of P. necessarius subsp. necessarius STIR1 (CP001010, NC_010531) were used for digital DNA-DNA hybridization via the gbdb-Server [44]. Just like in the conventional wet lab DNA-DNA hybridizations [47] digital DDH values ≤70% are considered as an indication that the tested organisms belong to a different species [47]. When analyzed with NCBI-BLAST using the three formulas described in [45,46] for the estimation of digital DDH values, the resulting DDH values for strains QLW-P1DMWA-1T and STIR1 were: 40.8% (formula 1), 11.4% (formula 2) and 43.3% (formula 3).
Given the low degree of DNA-DNA similarity between the two strains it appears justified to assume that these strains represent different species. However, additional investigations comparing the phylogenetic relationship between the type strain of P. necessarius subsp. necessarius (i.e. the symbionts contained in the E. aediculatus ‘stock 15’ culture [2]) and the genome-sequenced strain STIR1 are required before a separation of the two subspecies into two different species can be proposed.
Acknowledgements
The work conducted by the U.S. Department of Energy Joint Genome Institute was supported by the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy under Contract No. DE-AC02-05CH11231, and was also supported by grant FWF-P19853 to M.W.H.
References
- 1.Hahn MW, Lang E, Brandt U, Wu QL, Scheuerl T. Emended description of the genus Polynucleobacter and the species Polynucleobacter necessarius and proposal of two subspecies, P. necessarius subsp. necessarius subsp. nov. and P. necessarius subsp. asymbioticus subsp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2009; 59:2002-2009 10.1099/ijs.0.005801-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Heckmann K, Schmidt HJ. Polynucleobacter necessarius gen. nov., sp. nov., an obligately endosymbiotic bacterium living in the cytoplasm of Euplotes aediculatus. Int J Syst Bacteriol 1987; 37:456-457 10.1099/00207713-37-4-456 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Fauré-Fremiet E. Symbiontes bactérienes des ciliés du genre Euplotes. [In French]. CR Acad Sci 1952; 235:402-403 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hahn MW. Isolation of strains belonging to the cosmopolitan Polynucleobacter necessarius cluster from freshwater habitats in three climatic zones. Appl Environ Microbiol 2003; 69:5248-5254 10.1128/AEM.69.9.5248-5254.2003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Newton RJ, Jones SE, Eiler A, McMahon KD, Bertilsson S. A guide to the natural history of freshwater lake bacteria. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 2011; 75:14-49 10.1128/MMBR.00028-10 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Jezberová J, Jezbera J, Brandt U, Lindström ES, Langenheder S, Hahn MW. Ubiquity of Polynucleobacter necessarius ssp. asymbioticus in lentic freshwater habitats of a heterogeneous 2000 km2 area. Environ Microbiol 2010; 12:658-669 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2009.02106.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hahn MW, Lang E, Brandt U, Lünsdorf H, Wu QL, Stackebrandt E. Polynucleobacter cosmopolitanus sp. nov., free-living planktonic bacteria inhabiting freshwater lakes and rivers. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2010; 60:166-173 10.1099/ijs.0.010595-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hahn MW, Lang E, Tarao M, Brandt U. Polynucleobacter rarus sp. nov., a free-living planktonic bacterium isolated from an acidic lake. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2011; 61:781-787 10.1099/ijs.0.017350-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hahn MW, Lang E, Brandt U, Spröer C. Polynucleobacter acidiphobus sp. nov., a representative of an abundant group of planktonic freshwater bacteria. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2011; 61:788-794 10.1099/ijs.0.023929-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hahn MW, Minasyan A, Lang E, Koll U, Spröer C. Polynucleobacter difficilis sp. nov., a planktonic freshwater bacterium affiliated with subcluster B1 of the genus Polynucleobacter. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol (In press). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hahn MW, Pöckl M, Wu Q. L. Low intraspecific diversity in a Polynucleobacter subcluster population numerically dominating bacterioplankton of a freshwater pond. Appl Environ Microbiol 2005; 71:4539-4547 10.1128/AEM.71.8.4539-4547.2005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hahn MW, Scheuerl T, Jezberova J, Koll U, Jezbera J, Simek K, Vannini C, Petroni G, Wu QL. The passive yet successful way of planktonic life: genomic and experimental analysis of the ecology of a planctonic Polynucleobacter population. PLoS ONE (In press). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Bascic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 1990; 215:403-410 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.DeSantis TZ, Hugenholtz P, Larsen N, Rojas M, Brodie EL, Keller K, Huber T, Dalevi D, Hu P, Andersen GL. Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. Appl Environ Microbiol 2006; 72:5069-5072 10.1128/AEM.03006-05 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Porter MF. An algorithm for suffix stripping. Program: electronic library and information systems 1980; 14:130-137.
- 16.Lee C, Grasso C, Sharlow MF. Multiple sequence alignment using partial order graphs. Bioinformatics 2002; 18:452-464 10.1093/bioinformatics/18.3.452 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Castresana J. Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Mol Biol Evol 2000; 17:540-552 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Stamatakis A, Hoover P, Rougemont J. A rapid bootstrap algorithm for the RAxML web servers. Syst Biol 2008; 57:758-771 10.1080/10635150802429642 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hess PN, De Moraes Russo CA. An empirical test of the midpoint rooting method. Biol J Linn Soc Lond 2007; 92:669-674 10.1111/j.1095-8312.2007.00864.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Pattengale ND, Alipour M, Bininda-Emonds ORP, Moret BME, Stamatakis A. How many bootstrap replicates are necessary? Lect Notes Comput Sci 2009; 5541:184-200 10.1007/978-3-642-02008-7_13 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Swofford DL. PAUP*: Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (*and Other Methods), Version 4.0 b10. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Liolios K, Chen IM, Mavromatis K, Tavernarakis N, Kyrpides NC. The genomes On line database (GOLD) in 2009: Status of genomic and metagenomic projects and their associated metadata. Nucleic Acids Res 2010; 38:D346-D354 10.1093/nar/gkp848 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Field D, Garrity G, Gray T, Morrison N, Selengut J, Sterk P, Tatusova T, Thomson N, Allen MJ, Angiuoli SV, et al. The minimum information about a genome sequence (MIGS) specification. Nat Biotechnol 2008; 26:541-547 10.1038/nbt1360 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Garrity G. NamesforLife. BrowserTool takes expertise out of the database and puts it right in the browser. Microbiol Today 2010; 37:9 [Google Scholar]
- 25.Woese CR, Kandler O, Wheelis ML. Towards a natural system of organisms. Proposal for the domains Archaea and Bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1990; 87:4576-4579 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4576 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Garrity GM, Bell JA, Lilburn T. Phylum XIV. Proteobacteria phyl. nov. In: Brenner DJ, Krieg NR, Staley JT, Garrity GM (eds), Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, second edition, vol. 2 (The Proteobacteria), part B (The Gammaproteobacteria), Springer, New York, 2005, p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Garrity GM, Bell JA, Lilburn T. Class II. Betaproteobacteria class. nov. In: Garrity GM, Brenner DJ, Krieg NR, Staley JT (eds), Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, Second Edition, Volume 2, Part C, Springer, New York, 2005, p. 575. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Editor L. Validation List No. 107. List of new names and new combinations previously effectively, but not validly, published. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2006; 56:1-6 10.1099/ijs.0.64188-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Garrity GM, Bell JA, Lilburn T. Order I. Burkholderiales ord. nov. In: Garrity GM, Brenner DJ, Krieg NR, Staley JT (eds), Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, Second Edition, Volume 2, Part C, Springer, New York, 2005, p. 575. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Garrity GM, Bell JA, Lilburn T. Family I. Burkholderiaceae fam. nov. In: Garrity GM, Brenner DJ, Krieg NR, Staley JT (eds), Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, Second Edition, Volume 2, Part C, Springer, New York, 2005, p. 575. [Google Scholar]
- 31.BAuA. Classification of bacteria and archaea in risk groups. http://www.baua.de TRBA 2010; 466:172.
- 32.Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT, et al. Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat Genet 2000; 25:25-29 10.1038/75556 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.The DOE Joint Genome Institute www.jgi.doe.gov
- 34.Phrap and Phred for Windows. MacOS, Linux, and Unix. www.phrap.com
- 35.Cliff S. Han, Patrick Chain. 2006. Finishing repeat regions automatically with Dupfinisher. Proceeding of the 2006 international conference on bioinformatics & computational biology. Edited by Hamid R. Arabnia & Homayoun Valafar, CSREA Press. June 26-29, 2006: 141-146. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Delcher AL, Bratke K, Powers E, Salzberg S. Identifying bacterial genes and endosymbiont DNA with Glimmer. Bioinformatics 2007; 23:673-679 10.1093/bioinformatics/btm009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Badger JH, Olsen GJ. CRITICA: Coding region identification tool invoking comparative analysis. Mol Biol Evol 1999; 16:512-524 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Lowe TM, Eddy SR. tRNAscan-SE: a program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucleic Acids Res 1997; 25:955-964 10.1093/nar/25.5.955 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Krogh A, Larsson B, von Heijne G, Sonnhammer ELL. Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: Application to complete genomes. J Mol Biol 2001; 305:567-580 10.1006/jmbi.2000.4315 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Bendtsen JD, Nielsen H, von Heijne G, Brunak S. Improved prediction of signal peptides: SignalP 3.0. J Mol Biol 2004; 340:783-795 10.1016/j.jmb.2004.05.028 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Murray RGE, Stackebrandt E. Taxonomic note: implementation of the provisional status Candidatus for incompletely described procaryotes. Int J Syst Bacteriol 1995; 45:186-187 10.1099/00207713-45-1-186 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Petroni G, Dini F, Verni F, Rosati G. A molecular approach to the tangled intrageneric relationships underlying phylogeny in Euplotes (Ciliophora, Spirotrichea). Mol Phylogenet Evol 2002; 22:118-130 10.1006/mpev.2001.1030 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Vannini C, Pöckl M, Petroni G, Wu QL, Lang E, Stackebrandt E, Schrallhammer M, Richardson PM, Hahn MW. Endosymbiosis in statu nascendi: close phylogenetic relationship between obligately endosymbiotic and obligately free-living Polynucleobacter strains (Betaproteobacteria). Environ Microbiol 2007; 9:347-359 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2006.01144.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.genome-to-genome distance calculator. http://ggdc.gbdp.org/
- 45.Auch AF, Klenk HP, Göker M. Standard operating procedure for calculating genome-to-genome distances based on high-scoring segment pairs. Stand Genomic Sci 2010; 2:142-148 10.4056/sigs.541628 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Auch AF, von Jan M, Klenk HP, Göker M. Digital DNA-DNA hybridization for microbial species delineation by means of genome-to-genome sequence comparison. Stand Genomic Sci 2010; 2:117-134 10.4056/sigs.531120 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Wayne LG, Brenner DJ, Colwell RR, Grimont PAD, Kandler O, Krichevsky MI, Moore LH, Moore WEC, Murray RGE, Stackebrandt E, et al. Report of the Ad Hoc Committee on Reconciliation of Approaches to Bacterial Systematics. Int J Syst Bacteriol 1987; 37:463-464 10.1099/00207713-37-4-463 [DOI] [Google Scholar]