Abstract
The family Hyphomonadaceae within the Alphaproteobacteria is largely comprised of bacteria isolated from marine environments with striking morphologies and an unusual mode of cell growth. Here, we report the complete genome sequence Hirschia baltica, which is only the second a member of the Hyphomonadaceae with a published genome sequence. H. baltica is of special interest because it has a dimorphic life cycle and is a stalked, budding bacterium. The 3,455,622 bp long chromosome and 84,492 bp plasmid with a total of 3,222 protein-coding and 44 RNA genes were sequenced as part of the DOE Joint Genome Institute Program CSP 2008.
Keywords: aerobic, chemoheterotrophic, mesophile, Gram-negative, motile, budding, stalk-forming, Hyphomonadaceae, Alphaproteobacteria, CSP 2008
Introduction
Strain IFAM 1418T (= ATCC 49814 = DSM 5838 = KCTC 12471) is the type strain of the species Hirschia baltica, which is the type species of the genus Hirschia. The genus name Hirschia Baker 1896 has been applied to a member of the Asteraceae, although the type and only species, Hirschia anthemidifolia has also been placed in the genus Iphiona [1]. The genus Hirschia was named in honor of Peter Hirsch, a German microbiologist and expert on budding and hyphal bacteria. The species epithet refers to the Neo-Latin baltica, pertaining to the Baltic Sea [2]. IFAM 1418T was isolated in 1982 along with two additional stalk-forming isolates belonging to the same species, IFAM 1408 and IFAM 1415, from a sample of surface water taken from a boat landing in the Kiel Fjord [2].
H. baltica reproduces by budding from the tip of a stalk and has a dimorphic life-cycle similar to that described in bacteria belonging to the closely related genus Hyphomonas [2]. Newborn swarmer cells are motile by means of a polar flagellum. Swarmer cells differentiate into stalked sessile cells by ejecting the flagellum and synthesizing a stalk at the same pole. The sessile cells reproduce by budding such that motile daughter cells are formed at and released from the tip of the stalk. Here we present a summary classification and a set of features for H. baltica IFAM 1418T, together with the description of the complete genomic sequencing and annotation.
Classification and features
A representative genomic 16S rRNA sequence of H. baltica was compared using NCBI BLAST [3] under default settings (e.g., considering only the high-scoring segment pairs (HSPs) from the best 250 hits) with the most recent release of the Greengenes database [4] and the relative frequencies of taxa and keywords (reduced to their stem [5]) were determined, weighted by BLAST scores. The most frequently occurring genera were Hyphomonas (37.8%), Maricaulis (29.5%), Hirschia (14.3%), Caulobacter (7.4%) and Woodsholea (3.6%) (74 hits in total). Regarding the four hits to sequences from members of the Hirschia species, the average identity within HSPs was 99.3%, whereas the average coverage by HSPs was 98.8%. Among all other species, the one yielding the highest score was Hyphomonas johnsonii (NR_024938), which corresponded to an identity of 93.1% and an HSP coverage of 59.6%. (Note that the Greengenes database uses the INSDC (= EMBL/NCBI/DDBJ) annotation, which is not an authoritative source for nomenclature or classification.) The highest-scoring environmental sequence was FR684125 ('effect ocean acidification upon microbial prokaryotes marine biome fjord coastal water clone 16 07 04A09'), which showed an identity of 89.4% and an HSP coverage of 99.0%. The most frequently occurring keywords within the labels of environmental samples which yielded hits were 'marin' (2.2%), 'microbi' (2.1%), 'water' (2.0%), 'biofilm' (1.9%) and 'sea' (1.6%) (176 hits in total). Environmental samples which yielded hits of a higher score than the highest scoring species were not found. These keywords reflect very well some the ecological and physiological properties reported for strain IFAM 1418T in the original description [2].
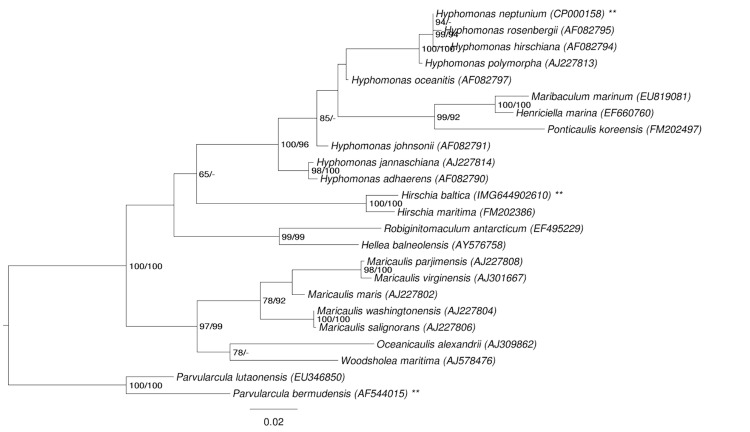
Figure 1 shows the phylogenetic neighborhood of H. baltica in a 16S rRNA based tree. The sequences of the two identical 16S rRNA gene copies in the genome differ by one nucleotide from the previously published 16S rRNA sequence (AJ421782), which contains one ambiguous base call.
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic tree highlighting the position of H. baltica relative to the type strains of the other species within the family Hyphomonadaceae. The tree was inferred from 1,332 aligned characters [6,7] of the 16S rRNA gene sequence under the maximum likelihood (ML) criterion [8] and rooted with the neighboring family Parvularculaceae. The branches are scaled in terms of the expected number of substitutions per site. Numbers adjacent to the branches are support values from 450 ML bootstrap replicates [9] (left) and from 1,000 maximum parsimony (MP) bootstrap replicates [10] (right) if larger than 60%. Lineages with type strain genome sequencing projects registered in GOLD [11] are labeled with one asterisk, those also listed as 'Complete and Published' (as well as the target genome) with two asterisks [12,13].
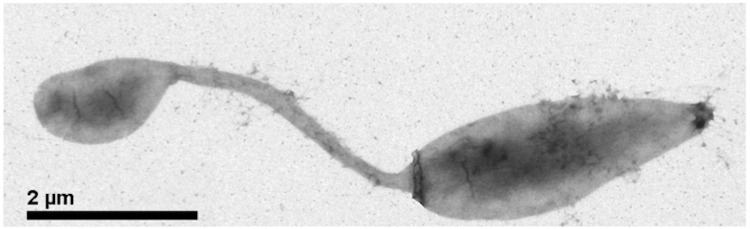
Cells of H. baltica strain IFAM 1418T are rod-shaped, elliptical or ovoid with 0.5 – 1.0 by 0.5 – 6.0 µm in size (without hyphae which have a diameter of about 0.2 µm) (Figure 2) [2]. IFAM 1418T cells stain Gram-negative, are motile and strictly aerobic [2]. 1 to 2 hyphae are located polarly and flagellation is monotrichous polar [2]. Cells grow best in artificial sea water with a broad range of NaCl concentrations (Table 1). The strain grows on a broad spectrum of organic compounds as carbon source such as amino acids, organic acids and sugars (Table 1), but not on C1 compounds [2]. In contrast to its phylogenetic neighbors H. baltica strains do not store PHB [2]. Colonies of strain IFAM 1418T show a yellow pigmentation whereas strain IFAM 1408 colonies are white [2].
Figure 2.
Scanning Electron micrograph of H. baltica IFAM 1418T
Table 1. Classification and general features of H. baltica according to the MIGS recommendations [14].
| MIGS ID | Property | Term | Evidence code |
|---|---|---|---|
| Current classification | Domain Bacteria | TAS [15] | |
| Phylum Proteobacteria | TAS [16] | ||
| Class Alphaproteobacteria | TAS [17,18] | ||
| Order Caulobacterales | TAS [19,20] | ||
| Family Hyphomonadaceae | TAS [21] | ||
| Genus Hirschia | TAS [2] | ||
| Species Hirschia baltica | TAS [2] | ||
| Type strain IFAM 1418 | TAS [2] | ||
| Gram stain | negative | TAS [2] | |
| Cell shape | rod-shaped | TAS [2] | |
| Motility | motile | TAS [2] | |
| Sporulation | none | TAS [2] | |
| Temperature range | mesophile | TAS [2] | |
| Optimum temperature | 22-28°C | TAS [2] | |
| Salinity | artificial sea water, 0.5 – 8.6% NaCl | TAS [2] | |
| MIGS-22 | Oxygen requirement | aerobe | TAS [2] |
| Carbon source | various amino acids, organic acids and sugars | TAS [2] | |
| Energy metabolism | chemoheterotroph | TAS [2] | |
| MIGS-6 | Habitat | brackish water | TAS [2] |
| MIGS-15 | Biotic relationship | free living | TAS [2] |
| MIGS-14 | Pathogenicity | none | NAS |
| Biosafety level | 1 | TAS [22] | |
| Isolation | surface water samples | TAS [2] | |
| MIGS-4 | Geographic location | Baltic Sea, Kiel Fjord | TAS [2] |
| MIGS-5 | Sample collection time | October 1982 | NAS |
| MIGS-4.1 | Latitude | approximately 54.5 | NAS |
| MIGS-4.2 | Longitude | approximately 10.2 | NAS |
| MIGS-4.3 | Depth | 5 cm | TAS [2] |
| MIGS-4.4 | Altitude | sea level | NAS |
Evidence codes - TAS: Traceable Author Statement (i.e., a direct report exists in the literature); NAS: Non-traceable Author Statement (i.e., not directly observed for the living, isolated sample, but based on a generally accepted property for the species, or anecdotal evidence). These evidence codes are from of the Gene Ontology project [23].
Chemotaxonomy
Cell walls of H. baltica contain meso-diamonopimelic acid [2]. The main quinone component is Q10 [2,24]. In the original publications by Schlesner et al. [2] and Sittig and Hirsch [24] the fatty acids were separated into non-hydroxy fatty acids and hydroxy-fatty acids. Main cellular non-hydroxy fatty acids are C18:1 Δ11 (48.8%), C16:0 (22.1%), C18:2 Δ5,11 (9.5%), C16:1 Δ5 (4.6%), and C14:1 Δ7 (3.2%). Among the hydroxylated fatty acids IFAM 1418T 3-OH fatty acids with C14:1 3-OH (79%) and C12:0 3-OH (15.8%) predominate, which are useful for the discrimination for H. baltica from strains of Hyphomicrobium and Hyphomonas (Figure 1). Kang and Lee [25] were unable to confirm the presence of these hydoxylated fatty acids in H. baltica. There are two reports [2,24] on the lipid composition of H. baltica and one on the lipids of H. maritima [25]. While all confirm the presence of a single phospholipid, phosphatidylglycerol in members of this genus, it is unclear whether these studies were limited to the detection of only phospholipids. There is evidence that H. baltica contains five major lipids, of which one is phosphatidlyglycerol (BJ Tindall, unpublished). The remaining four lipids are not phosphate positive, but their Rf values and staining behavior indicate similarities to a number of the unusual lipids reported from Hyphomonas jannaschiana [26,27].
Genome sequencing and annotation
Genome project history
This organism was selected for sequencing as a part of the DOE Joint Genome Institute Program CSP 2008. The genome project is deposited in the Genomes OnLine Database [11] and the complete genome sequence is deposited in GenBank. Sequencing, finishing and annotation were performed by the DOE Joint Genome Institute (JGI). A summary of the project information is shown in Table 2.
Table 2. Genome sequencing project information.
| MIGS ID | Property | Term |
|---|---|---|
| MIGS-31 | Finishing quality | Finished |
| MIGS-28 | Libraries used | Three genomic libraries: one 454 pyrosequence standard library, one 454 PE library (24 kb insert size), one Illumina library |
| MIGS-29 | Sequencing platforms | 454 GS FLX Titanium, Illumina GAii |
| MIGS-31.2 | Sequencing coverage | 116.6 × Illumina; 34.0 x pyrosequence |
| MIGS-30 | Assemblers | Newbler version 2.0.00.20, Velvet, phrap |
| MIGS-32 | Gene calling method | Critica complemented with the output of Glimmer |
| INSDC ID | CP001678 (chromosome) CP001679 (plasmid pHbal01) |
|
| GenBank Date of Release | July 19, 2009 | |
| GOLD ID | Gc01064 | |
| NCBI project ID | 33191 | |
| Database: IMG | 644736375 | |
| MIGS-13 | Source material identifier | ATCC 49814 |
| Project relevance | Bioremediation, Biotechnology |
Strain history
The history of strain IFAM 1418T starts with H. Schlesner who independently deposited the strain in two culture collections, ATCC and DSMZ (in 1989).
Growth conditions and DNA isolation
The culture of strain IFAM 1418T used to prepare genomic DNA (gDNA) for sequencing was obtained directly from the ATCC. ATCC 49814 was grown in Hirschia medium (ATCC medium 1883) at 30°C with shaking.
Genome sequencing and assembly
The genome was sequenced using a combination of Illumina and 454 sequencing platforms. All general aspects of library construction and sequencing can be found at the JGI website [28]. Pyrosequencing reads were assembled using the Newbler assembler (Roche). The initial Newbler assembly consisting of nine contigs in two scaffolds was converted into a phrap [29] assembly by making fake reads from the consensus, to collect the read pairs in the 454 paired end library. Illumina GAii sequencing data (50 Mb) were assembled with Velvet [30] and the consensus sequences were shredded into 1.5 kb overlapped fake reads and assembled together with the 454 data. The 454 draft assembly was based on 128.0 Mb 454 draft data and all of the 454 paired end data. Newbler parameters were -consed -a 50 - l350 -g -m -ml 20. The Phred/Phrap/Consed software package [29] was used for sequence assembly and quality assessment in the subsequent finishing process. After the shotgun stage, reads were assembled with parallel phrap (High Performance Software, LLC). Possible mis-assemblies were corrected with gapResolution [28], Dupfinisher [31], or sequencing cloned bridging PCR fragments with subcloning. Gaps between contigs were closed by editing in Consed, by PCR and by Bubble PCR primer walks (J.-F. Chang, unpublished). A total of 55 additional reactions were necessary to close gaps and to raise the quality of the finished sequence. Illumina reads were also used to correct potential base errors and increase consensus quality using a software Polisher developed at JGI [28,32]. The error rate of the completed genome sequence is less than 1 in 100,000. Together, the combination of the Illumina and 454 sequencing platforms provided 150.6 × coverage of the genome. The final assembly contained 333,683 pyrosequence and 12,860,398 Illumina reads.
Genome annotation
Genes were identified using Prodigal [33] as part of the Oak Ridge National Laboratory genome annotation pipeline, followed by a round of manual curation using the JGI GenePRIMP pipeline [34]. The predicted CDSs were translated and used to search the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) non-redundant database, UniProt, TIGRFam, Pfam, PRIAM, KEGG, COG, and InterPro databases. These data sources were combined to assert a product description for each predicted protein. Non-coding genes and miscellaneous features were predicted using tRNAscan-SE [35], RNAMMer [36], Rfam [37], TMHMM [38], and signalP [39].
Genome properties
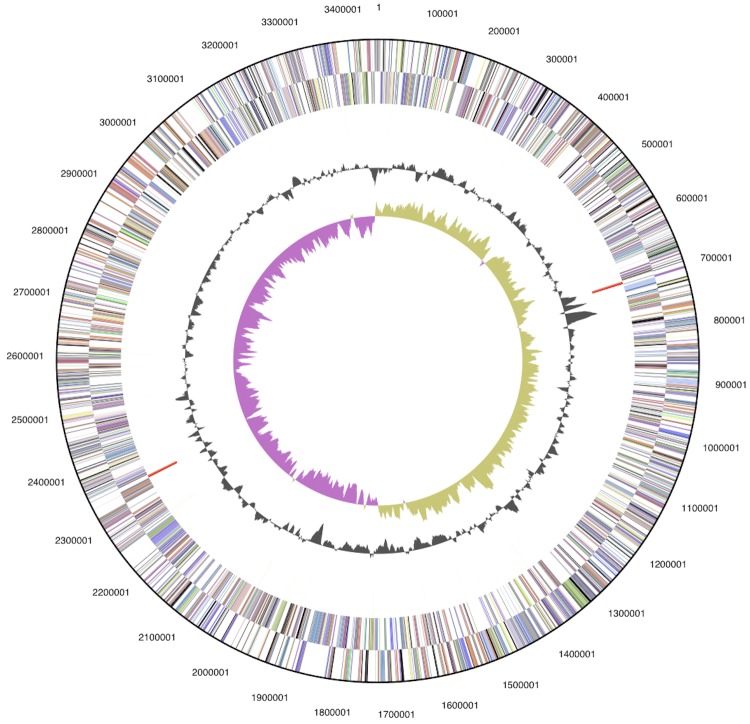
The genome consists of a 3,455,622 bp long chromosome with a 45% G+C content and a 84,492 bp long plasmid with a 44% G+C content (Table 3 and Figure 3). Of the 3,266 genes predicted, 3,222 were protein-coding genes, and 44 RNAs; 35 pseudogenes were also identified. The majority of the protein-coding genes (71.6%) were assigned a putative function while the remaining ones were annotated as hypothetical proteins. The distribution of genes into COGs functional categories is presented in Table 4.
Table 3. Genome Statistics.
| Attribute | Value | % of Total |
|---|---|---|
| Genome size (bp) | 3,540,114 | 100.00% |
| DNA coding region (bp) | 3,172,944 | 89.63% |
| DNA G+C content (bp) | 1,599,770 | 45.19% |
| Number of replicons | 2 | |
| Extrachromosomal elements | 1 | |
| Total genes | 3,266 | 100.00% |
| RNA genes | 44 | 1.35% |
| rRNA operons | 2 | |
| Protein-coding genes | 3,222 | 98.65% |
| Pseudo genes | 35 | 1.07% |
| Genes with function prediction | 2,337 | 71.65% |
| Genes in paralog clusters | 223 | 6.83% |
| Genes assigned to COGs | 2,443 | 74.80% |
| Genes assigned Pfam domains | 2,551 | 78.11% |
| Genes with signal peptides | 797 | 24.40% |
| Genes with transmembrane helices | 759 | 23.24% |
| CRISPR repeats | not reported |
Figure 3.
Graphical circular map of the chromosome (plasmid not shown). From outside to the center: Genes on forward strand (color by COG categories), Genes on reverse strand (color by COG categories), RNA genes (tRNAs green, rRNAs red, other RNAs black), GC content, GC skew.
Table 4. Number of genes associated with the general COG functional categories.
| Code | value | %age | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| J | 158 | 5.9 | Translation, ribosomal structure and biogenesis |
| A | 0 | 0.0 | RNA processing and modification |
| K | 167 | 6.2 | Transcription |
| L | 106 | 3.9 | Replication, recombination and repair |
| B | 1 | 0.0 | Chromatin structure and dynamics |
| D | 28 | 1.0 | Cell cycle control, cell division, chromosome partitioning |
| Y | 0 | 0.0 | Nuclear structure |
| V | 34 | 1.3 | Defense mechanisms |
| T | 140 | 5.2 | Signal transduction mechanisms |
| M | 196 | 7.3 | Cell wall/membrane biogenesis |
| N | 70 | 2.6 | Cell motility |
| Z | 0 | 0.0 | Cytoskeleton |
| W | 0 | 0.0 | Extracellular structures |
| U | 92 | 3.4 | Intracellular trafficking and secretion, and vesicular transport |
| O | 129 | 4.8 | Posttranslational modification, protein turnover, chaperones |
| C | 152 | 5.7 | Energy production and conversion |
| G | 141 | 5.2 | Carbohydrate transport and metabolism |
| E | 204 | 7.6 | Amino acid transport and metabolism |
| F | 55 | 2.1 | Nucleotide transport and metabolism |
| H | 119 | 4.4 | Coenzyme transport and metabolism |
| I | 133 | 5.0 | Lipid transport and metabolism |
| P | 152 | 5.7 | Inorganic ion transport and metabolism |
| Q | 82 | 3.1 | Secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport and catabolism |
| R | 287 | 10.7 | General function prediction only |
| S | 243 | 9.0 | Function unknown |
| - | 823 | 25.2 | Not in COGs |
Notable features of the H. baltica genome sequence
H. baltica genome is enriched in TonB-dependent receptors
TonB-dependent receptors are outer membrane proteins that function in the energy-dependent uptake of macromolecules, including siderophores and vitamins, that are too large to be taken up by passive diffusion. The genome sequences of C. crescentus and H. neptunium contain large numbers (63 and 43, respectively) of TonB dependent receptors [40,41]. One possibility is that the presence of many TonB-dependent receptors is a common feature among bacteria belonging to the order Caulobacterales. Indeed, the annotation of the H. baltica genome sequence suggests that there are 46 TonB-dependent receptors. The presence of many TonB-dependent receptors may be part of the adaptations that have allowed the Caulobacterales to not only inhabit, but also thrive in low-nutrient environments.
H. baltica genome contains known regulators of the cell cycle
A recent bioinformatic analysis of genes controlling the dimorphic cell cycle within the Alphaproteobacteria suggests the circuitry for cell-cycle control is largely conserved [42]. The conservation of 14 key proteins that function in the regulation of the cell cycle in C. crescentus was addressed among the Alphaproteobacteria with sequenced genomes, including three bacteria belonging to the Caulobacterales. All of the regulatory proteins were conserved among the genomes of the Caulobacterales with one notable exception: DivJ, a histidine kinase, is absent in the H. neptunium genome.
Expanding the analysis to include 8 additional bacteria belonging to the Caulobacterales, including H. baltica, we find that all 14 regulatory proteins are conserved with the exception of DivJ, which is absent only from the H. neptunium and H. baltica genomes. The fact that most developmental regulators are conserved in the budding bacteria H. neptunium and H. baltica as well as the non-budding bacteria belonging to the Caulobacterales suggests that regulation of the cell cycle is evolved prior to the separation of the budding and non-budding bacteria in the Caulobacterales. The finding that DivJ is absent from H. neptunium and H. baltica but present in the closely related non-budding Maricaulis maris and Oceanicaulis alexandrii (Figure 1) is an intriguing observation, although the significance of this finding remains unknown.
H. baltica genome contains genes for holdfast synthesis and attachment
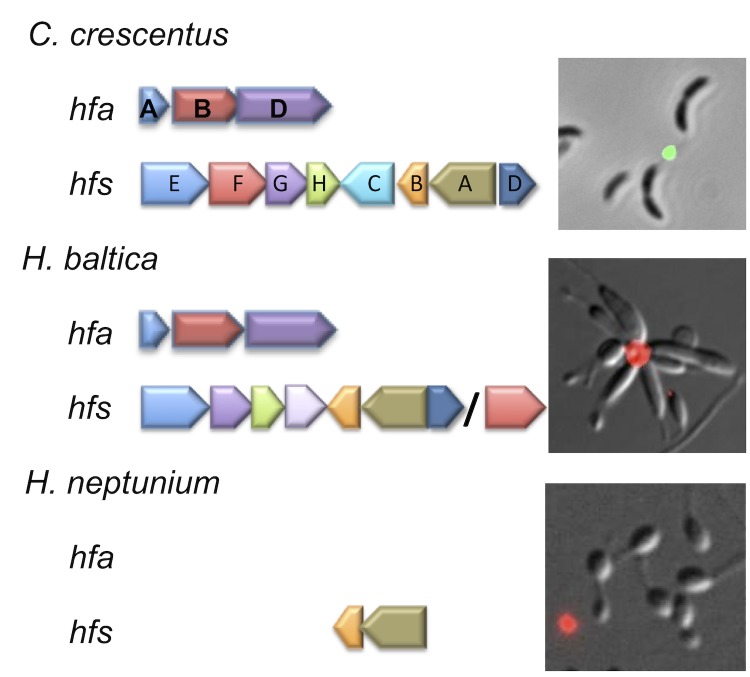
Bacteria belonging to the order Caulobacterales are known for the ability to produce a polar polysaccharide, termed holdfast, which mediates strong adhesion to surfaces (For review see [43]). Notably, extracellular polysaccharides from some of the stalked bacteria sequester metals [44,45], a feature that could be used to remediate environments affected by metal toxicity. The genes required for the synthesis [46,47] and anchoring [48] of the holdfast have been identified and characterized in C. crescentus. The holdfast synthesis and anchor genes are largely absent from the genome of H. neptunium, which does not produce a polar holdfast (Figure 4 and [41]). The genome sequence of H. baltica revealed that the genes predicted to be involved in polar holdfast synthesis are present (Figure 4). Furthermore, a holdfast on H. baltica cells was readily detected using a fluorescent wheat germ agglutinin lectin using the procedure detailed in [44] (Figure 4). The holdfast of H. baltica is found at the cell pole opposite the stalk of the mother cell and is responsible for the formation of star-shaped cell aggregates known as rosettes in cell culture (Figure 4). This finding, coupled with the observation that other species of Hyphomonas produce detectable holdfasts [49], suggests the ability to synthesize holdfast is a conserved feature among the Hyphomonadaceae family and the loss of the holdfast synthesis and anchoring genes in H. neptunium was a recent evolutionary event.
Figure 4.
Holdfast anchor (hfa) and synthesis (hfs) gene cluster conservation is depicted among C. crescentus, H. baltica and H. neptunium. Presence of holdfast genes is correlated to the ability to detect polar holdfast polysaccharide using fluorescent wheat germ agglutinin lectin. The H. neptunium genome contains only hfsAB and fails to make a polar polysaccharide. In contrast, the H. baltica genome contains all essential hfs and hfa genes and produces a holdfast.
Concluding Remarks
The completion of the H. baltica genome sequence is expected to provide a valuable resource for understanding the biology of stalked budding bacteria with a dimorphic life cycle. Further comparative genomic analyses (especially as more bacteria belonging to the Caulobacterales are sequenced) are likely to provide insights regarding the evolution, mechanism, and advantages underlying processes such as budding, and stalk synthesis. Understanding stalk biosynthesis is of particular interest as the ability of these structures to transport nutrients [50,51] could likely be exploited to facilitate the uptake of toxic compounds from contaminated water sources.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a Department of Energy Joint Genome Institute (DOE-JGI) 2008 Community Sequencing Project (787681) award to Y.V.B. The work conducted by the U.S. DOE-JGI was supported by the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy under Contract No. DE-AC02-05CH11231. This work was also supported by National Institutes of Health (GM051986 and GM077648) and National Science Foundation (MCB0731950) awards to Y.V.B. P.J.B.B. and D.T.K. were supported by National Institutes of Health National Research Service Awards AI072992 and GM083581, respectively. M.A.P. was supported by Ministry of Education and Science, Spain (MEC, BFU2006-04574) and Fundación Ramón Areces. Part of this work was also supported by a grant from the Indiana University META-Cyt program funded in part by a major endowment from the Lilly Foundation.
References
- 1.Anderberg A. The genus Iphiona (Compositae-Inuleae). Nord J Bot 1985; 5:169-194 10.1111/j.1756-1051.1985.tb02086.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Schlesner H, Bartels C, Sittig M, Dorsch M, Stackebrandt E. Taxonomic and phylogenetic studies on a new taxon of budding, hyphal Proteobacteria, Hirschia baltica gen. nov., sp. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 1990; 40:443-451 10.1099/00207713-40-4-443 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Bascic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 1990; 215:403-410 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.DeSantis TZ, Hugenholtz P, Larsen N, Rojas M, Brodie EL, Keller K, Huber T, Dalevi D, Hu P, Andersen GL. Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. Appl Environ Microbiol 2006; 72:5069-5072 10.1128/AEM.03006-05 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Porter MF. An algorithm for suffix stripping. Program: electronic library and information systems 1980; 14:130-137.
- 6.Lee C, Grasso C, Sharlow MF. Multiple sequence alignment using partial order graphs. Bioinformatics 2002; 18:452-464 10.1093/bioinformatics/18.3.452 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Castresana J. Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Mol Biol Evol 2000; 17:540-552 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Stamatakis A, Hoover P, Rougemont J. A rapid bootstrap algorithm for the RAxML web servers. Syst Biol 2008; 57:758-771 10.1080/10635150802429642 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Pattengale ND, Alipour M, Bininda-Emonds ORP, Moret BME, Stamatakis A. How many bootstrap replicates are necessary? Lect Notes Comput Sci 2009; 5541:184-200 10.1007/978-3-642-02008-7_13 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Swofford DL. PAUP*: Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (*and Other Methods), Version 4.0 b10. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Liolios K, Chen IM, Mavromatis K, Tavernarakis N, Kyrpides NC. The genomes on line database (GOLD) in 2009: Status of genomic and metagenomic projects and their associated metadata. Nucleic Acids Res 2010; 38:D346-D354 10.1093/nar/gkp848 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Badger JH, Hoover TR, Brun YV, Weiner RM, Laub MT, Alexandre G, Mrázek J, Ren Q, Paulsen IT, Nelson KE, et al. Comparative genomic evidence for a close relationship between the dimorphic prosthecate bacteria Hyphomonas neptunium and Caulobacter crescentus. J Bacteriol 2006; 188:6841-6850 10.1128/JB.00111-06 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Oh HM, Kang I, Vergin KL, Kang D, Rhee KH, Giovannoni SJ, Cho JC. Complete Genome Sequence of Strain HTCC2503T of Parvularcula bermudensis, the Type Species of the Order 'Parvularculales' in the Class Alphaproteobacteria. J Bacteriol 2011; 193:305-306 10.1128/JB.01205-10 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Field D, Garrity G, Gray T, Morrison N, Selengut J, Sterk P, Tatusova T, Thomson N, Allen MJ, Angiuoli SV, et al. The minimum information about a genome sequence (MIGS) specification. Nat Biotechnol 2008; 26:541-547 10.1038/nbt1360 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Woese CR, Kandler O, Wheelis ML. Towards a natural system of organisms. Proposal for the domains Archaea and Bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1990; 87:4576-4579 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4576 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Garrity GM, Bell JA, Lilburn T. Phylum XIV. Proteobacteria phyl. nov. In: DJ Brenner, NR Krieg, JT Staley, GM Garrity (eds), Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, second edition, vol. 2 (The Proteobacteria), part B (The Gammaproteobacteria), Springer, New York, 2005, p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Validation List No. 107. List of new names and new combinations previously effectively, but not validly, published. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2006; 56:1-6 10.1099/ijs.0.64188-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Garrity GM, Bell JA, Lilburn T. Class I. Alphaproteobacteria class. nov. In: Garrity GM, Brenner DJ, Krieg NR, Staley JT (eds), Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, Second Edition, Volume 2, Part C, Springer, New York, 2005, p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Henrici AT, Johnson DE. Studies of Freshwater Bacteria: II. Stalked bacteria, a New Order of Schizomycetes J Bacteriol 1935; 30:61-93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Skerman VDB, Gowan V, Sneath PHA, eds. Approved Lists of Bacterial Names. Int J Syst Bacteriol 1980; 30:225-420 10.1099/00207713-30-1-225 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Lee KB, Liu CT, Anzai Y, Kim H, Aono T, Oyaizu H. The hierarchical system of the 'Alphaproteobacteria': description of Hyphomonadaceae fam. nov., Xanthobacteraceae fam. nov. and Erythrobacteraceae fam. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2005; 55:1907-1919 10.1099/ijs.0.63663-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.BAuA Classification of bacteria and archaea in risk groups. TRBA 2005; 466:205 [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT, et al. Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat Genet 2000; 25:25-29 10.1038/75556 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Sittig M, Hirsch P. Chemotaxonomic investigations of budding and/or hyphal bacteria. Syst Appl Microbiol 1992; 15:209-222 [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kang HS, Lee SD. Hirschia maritima sp. nov., isolated from seawater. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2009; 59:2264-2268 10.1099/ijs.0.008326-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Batrakov SG, Nikitin DI, Pitryuk IA. Lipid composition of the gram-negative, budding, seawater bacterium Hyphomonas jannaschiana lacking in phospholipids. Biochim Biophys Acta 1996; 1303:39-46 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Batrakov SG, Nikitin DI, Pitryuk IA. A novel glycolipid, 1,2-diacyl-3-α-D-glucuronopyranosyl-sn-glycerol taurineamide, from the budding seawater bacterium Hyphomonas jannaschiana. Biochim Biophys Acta 1996; 1302:167-176 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.JGI website. http://ww.jgi.doe.gov
- 29.The Phred/Phrap/Consed software package. www.phrap.com
- 30.Zerbino DR, Birney E. Velvet: algorithms for de novo short read assembly using de Bruijn graphs. Genome Res 2008; 18:821-829 10.1101/gr.074492.107 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Han C, Chain P. Finishing repeat regions automatically with Dupfinisher. In: Proceeding of the 2006 international conference on bioinformatics & computational biology. Arabnia HR, Valafar H (eds), CSREA Press. June 26-29, 2006: 141-146. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Lapidus A, LaButti K, Foster B, Lowry S, Trong S, Goltsman E. POLISHER: An effective tool for using ultra short reads in microbial genome assembly and finishing. AGBT, Marco Island, FL, 2008 [Google Scholar]
- 33.Hyatt D, Chen GL, Locascio PF, Land ML, Larimer FW, Hauser LJ. Prodigal Prokaryotic Dynamic Programming Genefinding Algorithm. BMC Bioinformatics 2010; 11:119 10.1186/1471-2105-11-119 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Pati A, Ivanova N, Mikhailova N, Ovchinikova G, Hooper SD, Lykidis A, Kyrpides NC. GenePRIMP: A Gene Prediction Improvement Pipeline for microbial genomes. Nat Methods 2010; 7:455-457 10.1038/nmeth.1457 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lowe TM, Eddy SR. tRNAscan-SE: a program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucleic Acids Res 1997; 25:955-964 10.1093/nar/25.5.955 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Lagesen K, Hallin PF, Rødland E, Stærfeldt HH, Rognes T, Ussery DW. RNammer: consistent annotation of rRNA genes in genomic sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 2007; 35:3100-3108 10.1093/nar/gkm160 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Griffiths-Jones S, Bateman A, Marshall M, Khanna A, Eddy SR. Rfam: an RNA family database. Nucleic Acids Res 2003; 31:439-441 10.1093/nar/gkg006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Krogh A, Larsson B, von Heijne G, Sonnhammer ELL. Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: Application to complete genomes. J Mol Biol 2001; 305:567-580 10.1006/jmbi.2000.4315 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Bendtsen JD, Nielsen H, von Heijne G, Brunak S. Improved prediction of signal peptides: SignalP 3.0. J Mol Biol 2004; 340:783-795 10.1016/j.jmb.2004.05.028 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Nierman WC, Feldblyum TV, Laub MT, Paulsen IT, Nelson KE, Eisen JA, Heidelberg JF, Alley MR, Ohta N, Maddock JR, et al. Complete genome sequence of Caulobacter crescentus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98:4136-4141 10.1073/pnas.061029298 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Badger JH, Hoover TR, Brun YV, Weiner RM, Laub MT, Alexandre G, Mrazek J, Ren Q, Paulsen IT, Nelson KE, et al. Comparative genomic evidence for a close relationship between the dimorphic prosthecate bacteria Hyphomonas neptunium and Caulobacter crescentus. J Bacteriol 2006; 188:6841-6850 10.1128/JB.00111-06 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Brilli M, Fondi M, Fani R, Mengoni A, Ferri L, Bazzicalupo M, Biondi EG. The diversity and evolution of cell cycle regulation in alpha-proteobacteria: a comparative genomic analysis. BMC Syst Biol 2010; 4:52 10.1186/1752-0509-4-52 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Brown PJ, Hardy GG, Trimble MG, Brun YV. Complex regulatory pathways coordinate cell-cycle progression and development in Caulobacter crescentus. Adv Microb Physiol 2008; 54:1-101 10.1016/S0065-2911(08)00001-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Merker RI, Smit J. Characterization of the adhesive holdfast of marine and freshwater Caulobacters. Appl Environ Microbiol 1988; 54:2078-2085 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Quintero EJ, Langille SE, Weiner RM. The polar polysaccharide capsule of Hyphomonas adhaerens MHS-3 has a strong affinity for gold. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 2001; 27:1-4 10.1038/sj.jim.7000143 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Smith CS, Hinz A, Bodenmiller D, Larson DE, Brun YV. Identification of genes required for synthesis of the adhesive holdfast in Caulobacter crescentus. J Bacteriol 2003; 185:1432-1442 10.1128/JB.185.4.1432-1442.2003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Toh E, Kurtz HD, Jr, Brun YV. Characterization of the Caulobacter crescentus holdfast polysaccharide biosynthesis pathway reveals significant redundancy in the initiating glycosyltransferase and polymerase steps. J Bacteriol 2008; 190:7219-7231 10.1128/JB.01003-08 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Hardy GGR, Allen C, Toh E, Long M, Brown PJ, Cole-Tobian JL. Brun YV. A localized multimeric anchor attaches the Caulobacter holdfast to the cell pole. Mol Microbiol 2010; 76:409-427 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07106.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Langille SE, Weiner RM. Spatial and temporal deposition of Hyphomonas strain VP-6 capsules involved in biofilm formation. Appl Environ Microbiol 1998; 64:2906-2913 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Larson RJ, Pate JL. Glucose transport in isolated prosthecae of Asticcacaulis biprosthecum. J Bacteriol 1976; 126:282-293 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Wagner JK, Setayeshgar S, Sharon LA, Reilly JP, Brun YV. A nutrient uptake role for bacterial cell envelope extensions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103:11772-11777 10.1073/pnas.0602047103 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]