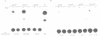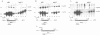Abstract
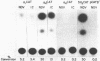
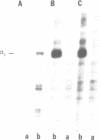
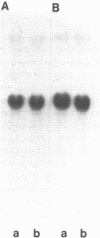
In mouse cells induced with virus infection or dsRNA, the relative levels of alpha-4 interferon mRNA were higher than the levels of alpha-1 and alpha-6 mRNAs; the ratio between relative levels of alpha-4 and alpha-1 or alpha-6 mRNA was, however, dependent on the cell type. Recombinant plasmids, in which the expression of chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) gene was directed by the promoter regions of alpha-1, alpha-4 or alpha-6 interferon genes were constructed and their inducible expression was studied either in transient assay or in permanently transfected mouse cells. The highest levels of CAT activity and CAT mRNA were observed with alpha-4 CAT plasmid, while the expression of alpha-1 CAT was consistently higher than that coded by alpha-6 CAT plasmid; the ratio between CAT activities coded by alpha-4 CAT and alpha-1 CAT was dependent on cell type. However, in heterologous Vero cells, the transfected alpha-1 and alpha-4 genes were expressed constitutively, and the levels of mRNAs were comparable. These results show that the difference in the relative levels of individual alpha-1 and alpha-4 mRNAs reflects the transcriptional inducibility of the respective promoter regions.
Full text
PDF















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Weber F., Jahn G., Dorsch-Häsler K., Fleckenstein B., Schaffner W. A very strong enhancer is located upstream of an immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):521–530. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canaani D., Berg P. Regulated expression of human interferon beta 1 gene after transduction into cultured mouse and rabbit cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5166–5170. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R., Content J., DeClercq E., Volckaert G., Tavernier J., Devos R., Fiers W. Isolation and structure of a human fibroblast interferon gene. Nature. 1980 Jun 19;285(5766):542–547. doi: 10.1038/285542a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dion M., Vodjdani G., Doly J. Sequence and expression of a novel murine interferon alpha gene--homology with enhancer elements in the regulatory region of the gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jul 31;138(2):826–834. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80571-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D., Baty D., Chambon P. The repeated GC-rich motifs upstream from the TATA box are important elements of the SV40 early promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2447–2464. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Ohno S., Yasumitsu H., Taniguchi T. Delimitation and properties of DNA sequences required for the regulated expression of human interferon-beta gene. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):489–496. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Shibuya H., Hotta H., Yamanishi K., Taniguchi T. Interferon-beta gene regulation: tandemly repeated sequences of a synthetic 6 bp oligomer function as a virus-inducible enhancer. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):357–367. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90288-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goeddel D. V., Leung D. W., Dull T. J., Gross M., Lawn R. M., McCandliss R., Seeburg P. H., Ullrich A., Yelverton E., Gray P. W. The structure of eight distinct cloned human leukocyte interferon cDNAs. Nature. 1981 Mar 5;290(5801):20–26. doi: 10.1038/290020a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodbourn S., Zinn K., Maniatis T. Human beta-interferon gene expression is regulated by an inducible enhancer element. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):509–520. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80024-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiscott J., Cantell K., Weissmann C. Differential expression of human interferon genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 11;12(9):3727–3746. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.9.3727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghton M., Jackson I. J., Porter A. G., Doel S. M., Catlin G. H., Barber C., Carey N. H. The absence of introns within a human fibroblast interferon gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):247–266. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley K. A., Kozak C. A., Dandoy F., Sor F., Skup D., Windass J. D., DeMaeyer-Guignard J., Pitha P. M., DeMaeyer E. Mapping of murine interferon-alpha genes to chromosome 4. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(2-3):181–188. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90188-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley K. A., Kozak C. A., Pitha P. M. Localization of the mouse interferon-beta 1 gene to chromosome 4. J Interferon Res. 1985 Summer;5(3):409–413. doi: 10.1089/jir.1985.5.409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley K. A., Pitha P. M. Characterization of a mouse interferon gene locus I. Isolation of a cluster of four alpha interferon genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 11;13(3):805–823. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.3.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley K. A., Pitha P. M. Characterization of a mouse interferon gene locus II. Differential expression of alpha-interferon genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 11;13(3):825–839. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.3.825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley K. A., Pitha P. M. Differential effect of poly rI.rC and Newcastle disease virus on the expression of interferon and cellular genes in mouse cells. Virology. 1985 Dec;147(2):382–393. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90140-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Khoury G., Gorman C., Howard B., Gruss P. Host-specific activation of transcription by tandem repeats from simian virus 40 and Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6453–6457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantei N., Weissmann C. Controlled transcription of a human alpha-interferon gene introduced into mouse L cells. Nature. 1982 May 13;297(5862):128–132. doi: 10.1038/297128a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosca J. D., Pitha P. M. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of exogenous human beta interferon gene in simian cells defective in interferon synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2279–2283. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosca J. D., Reyes G. R., Pitha P. M., Hayward G. S. Differential activation of hybrid genes containing herpes simplex virus immediate-early or delayed-early promoters after superinfection of stable DNA-transfected cell lines. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):867–878. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.867-878.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno S., Taniguchi T. Inducer-responsive expression of the cloned human interferon beta 1 gene introduced into cultured mouse cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Feb 11;10(3):967–977. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.3.967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raj N. B., Kellum M., Kelley K. A., Antrobus S., Pitha P. M. Differential regulation of interferon synthesis in lymphoblastoid cells. J Interferon Res. 1985 Summer;5(3):493–510. doi: 10.1089/jir.1985.5.493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raj N. B., Pitha P. M. Two levels of regulation of beta-interferon gene expression in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3923–3927. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryals J., Dierks P., Ragg H., Weissmann C. A 46-nucleotide promoter segment from an IFN-alpha gene renders an unrelated promoter inducible by virus. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):497–507. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80023-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal P. B., Tamm I. Two mechanisms contribute to the superinduction of poly(I).poly(C)-induced human fibroblast interferon production. Virology. 1979 Jan 15;92(1):240–244. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90230-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G. D., Boll W., Taira H., Mantei N., Lengyel P., Weissmann C. Structure and expression of cloned murine IFN-alpha genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Feb 11;11(3):555–573. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.3.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuttleworth J., Morser J., Burke D. C. Expression of interferon-alpha and interferon-beta genes in human lymphoblastoid (Namalwa) cells. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 15;133(2):399–404. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07476.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompayrac L. M., Danna K. J. Efficient infection of monkey cells with DNA of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7575–7578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T., Ohno S., Fujii-Kuriyama Y., Muramatsu M. The nucleotide sequence of human fibroblast interferon cDNA. Gene. 1980 Jun;10(1):11–15. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90138-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trent J. M., Olson S., Lawn R. M. Chromosomal localization of human leukocyte, fibroblast, and immune interferon genes by means of in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7809–7813. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Weissmann C. Mapping of RNA by a modification of the Berk-Sharp procedure: the 5' termini of 15 S beta-globin mRNA precursor and mature 10 s beta-globin mRNA have identical map coordinates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1175–1193. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., DiMaio D., Maniatis T. Identification of two distinct regulatory regions adjacent to the human beta-interferon gene. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):865–879. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90544-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., Maniatis T. Detection of factors that interact with the human beta-interferon regulatory region in vivo by DNAase I footprinting. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):611–618. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90293-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., Mellon P., Ptashne M., Maniatis T. Regulated expression of an extrachromosomal human beta-interferon gene in mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4897–4901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwarthoff E. C., Mooren A. T., Trapman J. Organization, structure and expression of murine interferon alpha genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 11;13(3):791–804. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.3.791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Korput J. A., Hilkens J., Kroezen V., Zwarthoff E. C., Trapman J. Mouse interferon alpha and beta genes are linked at the centromere proximal region of chromosome 4. J Gen Virol. 1985 Mar;66(Pt 3):493–502. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-3-493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]