Abstract
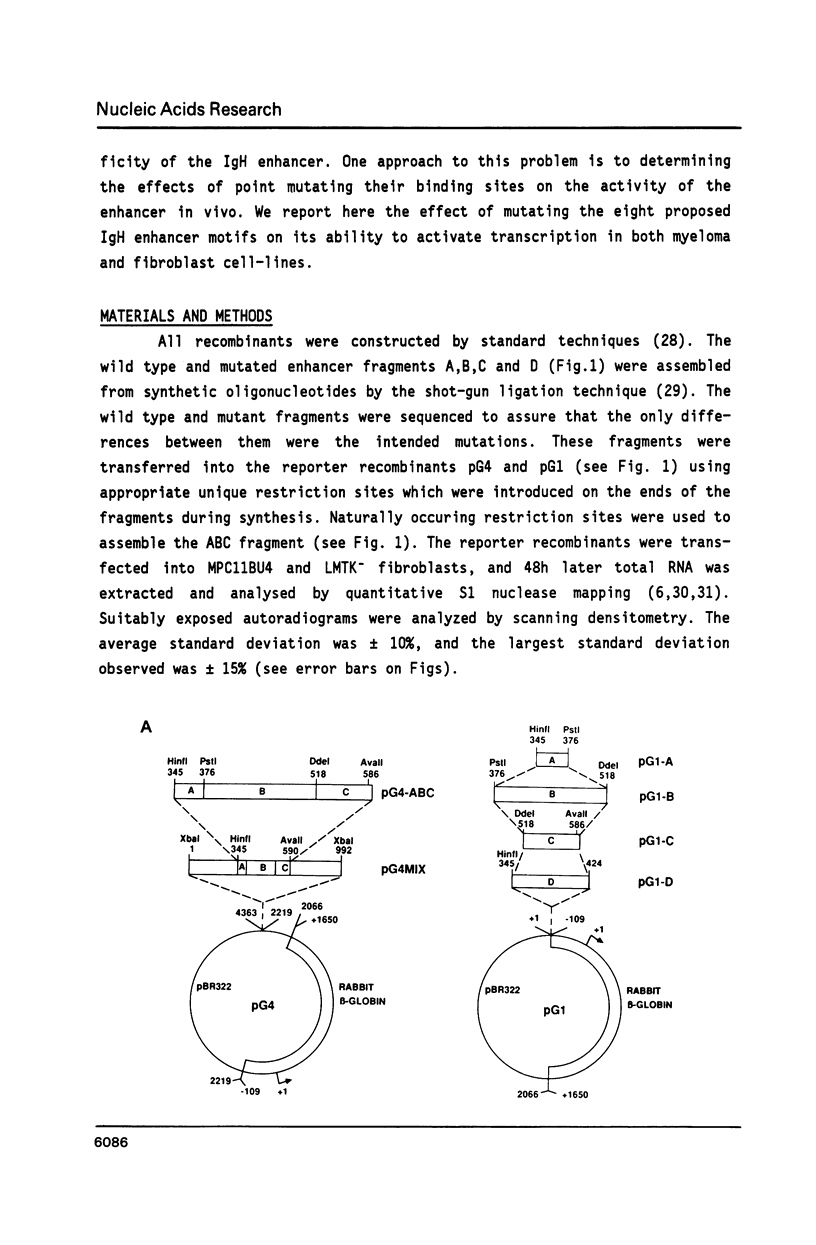
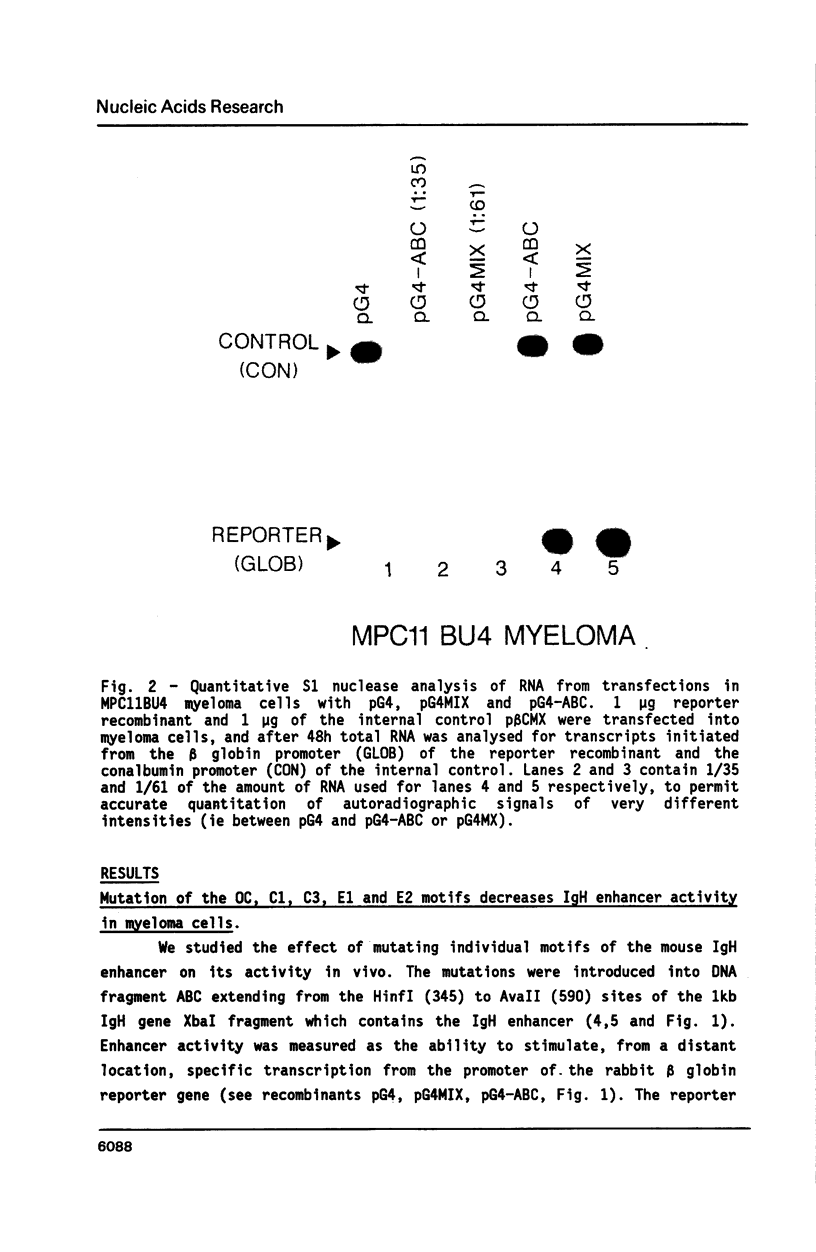
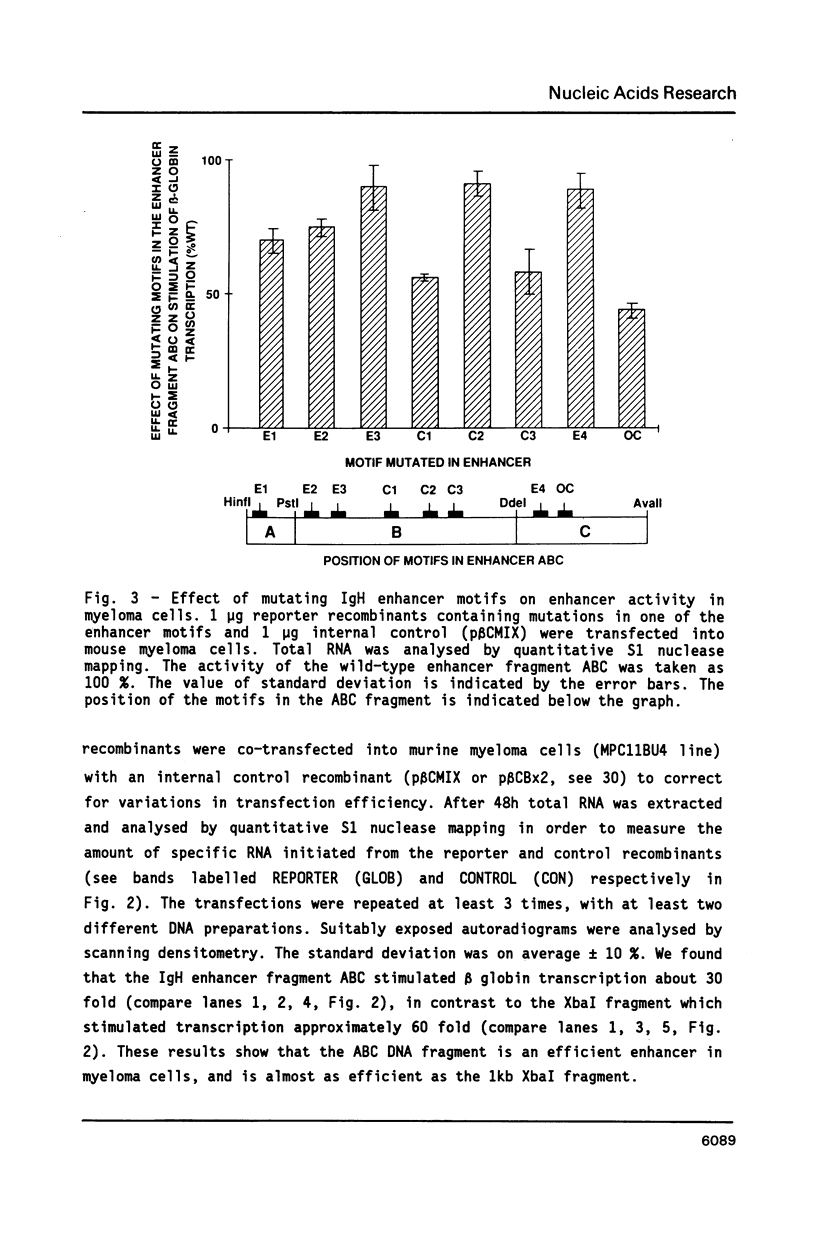
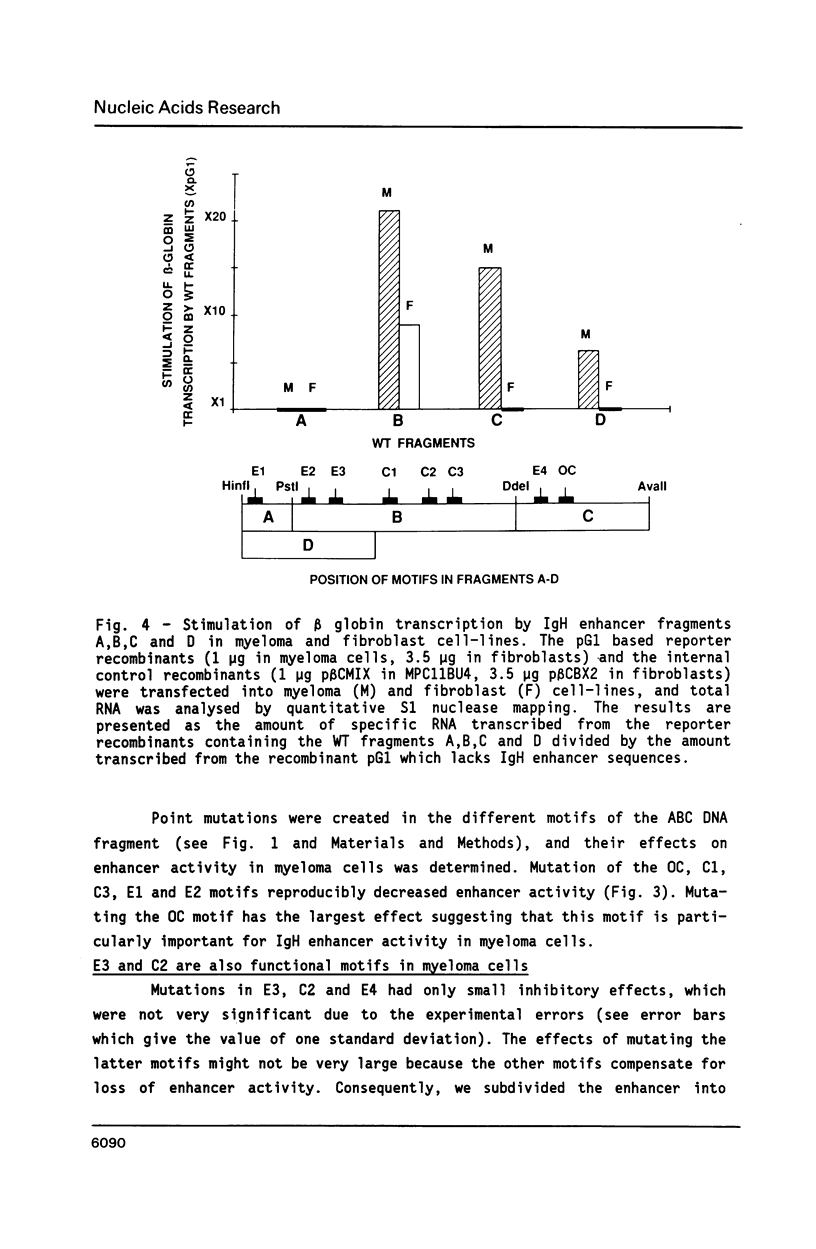
We have investigated the role of sequence motifs in the immunoglobulin heavy chain (IgH) enhancer on its activity in myeloma and fibroblast cell-lines. In transient transfection assays the transcription stimulatory activity of the enhancer is decreased in myeloma cells by mutating the E motifs 1, 2 and 3, the core motifs C1, C2, C3 and the octamer motif (OC) and in fibroblasts by mutating E2, E3, and C2. Our results suggest that transcription factors binding to E1, C1, C3 and OC contribute in a positive manner to the tissue specificity of the IgH enhancer.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Augereau P., Chambon P. The mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer: effect on transcription in vitro and binding of proteins present in HeLa and lymphoid B cell extracts. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1791–1797. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04428.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerji J., Olson L., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific cellular enhancer is located downstream of the joining region in immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):729–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohmann D., Keller W., Dale T., Schöler H. R., Tebb G., Mattaj I. W. A transcription factor which binds to the enhancers of SV40, immunoglobulin heavy chain and U2 snRNA genes. Nature. 1987 Jan 15;325(6101):268–272. doi: 10.1038/325268a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Ephrussi A., Gilbert W., Tonegawa S. Cell-type-specific contacts to immunoglobulin enhancers in nuclei. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):798–801. doi: 10.1038/313798a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson I., Fromental C., Augereau P., Wildeman A., Zenke M., Chambon P. Cell-type specific protein binding to the enhancer of simian virus 40 in nuclear extracts. Nature. 1986 Oct 9;323(6088):544–548. doi: 10.1038/323544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ephrussi A., Church G. M., Tonegawa S., Gilbert W. B lineage--specific interactions of an immunoglobulin enhancer with cellular factors in vivo. Science. 1985 Jan 11;227(4683):134–140. doi: 10.1126/science.3917574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkner F. G., Zachau H. G. Correct transcription of an immunoglobulin kappa gene requires an upstream fragment containing conserved sequence elements. Nature. 1984 Jul 5;310(5972):71–74. doi: 10.1038/310071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia J. V., Bich-Thuy L. T., Stafford J., Queen C. Synergism between immunoglobulin enhancers and promoters. Nature. 1986 Jul 24;322(6077):383–385. doi: 10.1038/322383a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerster T., Matthias P., Thali M., Jiricny J., Schaffner W. Cell type-specificity elements of the immunoglobulin heavy chain gene enhancer. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1323–1330. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02371.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies S. D., Morrison S. L., Oi V. T., Tonegawa S. A tissue-specific transcription enhancer element is located in the major intron of a rearranged immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundström T., Zenke W. M., Wintzerith M., Matthes H. W., Staub A., Chambon P. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis by microscale 'shot-gun' gene synthesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 10;13(9):3305–3316. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.9.3305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imler J. L., Lemaire C., Wasylyk C., Wasylyk B. Negative regulation contributes to tissue specificity of the immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2558–2567. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadesch T., Zervos P., Ruezinsky D. Functional analysis of the murine IgH enhancer: evidence for negative control of cell-type specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 24;14(20):8209–8221. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.20.8209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiledjian M., Su L. K., Kadesch T. Identification and characterization of two functional domains within the murine heavy-chain enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):145–152. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura D., Maeda H., Araki K., Kudo A., Watanabe T. Regulation of immunoglobulin gene transcription by labile repressor factor(s). Eur J Immunol. 1987 Sep;17(9):1249–1256. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M., Pierce J. W., Baltimore D. Protein-binding sites in Ig gene enhancers determine transcriptional activity and inducibility. Science. 1987 Jun 19;236(4808):1573–1577. doi: 10.1126/science.3109035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda H., Araki K., Kitamura D., Wang J., Watanabe T. Nuclear factors binding to the human immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 10;15(7):2851–2869. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.7.2851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocikat R., Falkner F. G., Mertz R., Zachau H. G. Upstream regulatory sequences of immunoglobulin genes are recognized by nuclear proteins which also bind to other gene regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 25;14(22):8829–8844. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.22.8829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomiyama H., Fromental C., Xiao J. H., Chambon P. Cell-specific activity of the constituent elements of the simian virus 40 enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7881–7885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parslow T. G., Blair D. L., Murphy W. J., Granner D. K. Structure of the 5' ends of immunoglobulin genes: a novel conserved sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2650–2654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C. L., Calame K. L. Complex protein binding within the mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4194–4203. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C. L., Orth K., Calame K. L. Binding in vitro of multiple cellular proteins to immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4168–4178. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosales R., Vigneron M., Macchi M., Davidson I., Xiao J. H., Chambon P. In vitro binding of cell-specific and ubiquitous nuclear proteins to the octamer motif of the SV40 enhancer and related motifs present in other promoters and enhancers. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3015–3025. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02607.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidereit C., Heguy A., Roeder R. G. Identification and purification of a human lymphoid-specific octamer-binding protein (OTF-2) that activates transcription of an immunoglobulin promoter in vitro. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):783–793. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90101-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlokat U., Bohmann D., Schöler H., Gruss P. Nuclear factors binding specific sequences within the immunoglobulin enhancer interact differentially with other enhancer elements. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3251–3258. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04636.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staudt L. M., Singh H., Sen R., Wirth T., Sharp P. A., Baltimore D. A lymphoid-specific protein binding to the octamer motif of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):640–643. doi: 10.1038/323640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Vigneron M., Matthes H., Wildeman A., Zenke M., Chambon P. Requirement of stereospecific alignments for initiation from the simian virus 40 early promoter. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):121–126. doi: 10.1038/319121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. Y., Nishiyama K., Araki K., Kitamura D., Watanabe T. Purification of an octamer sequence (ATGCAAAT)-binding protein from human B cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10105–10116. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Wasylyk C., Chambon P. Short and long range activation by the SV40 enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5589–5608. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk C., Imler J. L., Perez-Mutul J., Wasylyk B. The c-Ha-ras oncogene and a tumor promoter activate the polyoma virus enhancer. Cell. 1987 Feb 13;48(3):525–534. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90203-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk C., Wasylyk B. The immunoglobulin heavy-chain B-lymphocyte enhancer efficiently stimulates transcription in non-lymphoid cells. EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):553–560. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04246.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger J., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. Distinct factors bind to apparently homologous sequences in the immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer. 1986 Aug 28-Sep 3Nature. 322(6082):846–848. doi: 10.1038/322846a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger J., Jat P. S., Sharp P. A. Localization of a repressive sequence contributing to B-cell specificity in the immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):988–992. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao J. H., Davidson I., Ferrandon D., Rosales R., Vigneron M., Macchi M., Ruffenach F., Chambon P. One cell-specific and three ubiquitous nuclear proteins bind in vitro to overlapping motifs in the domain B1 of the SV40 enhancer. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3005–3013. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02606.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao J. H., Davidson I., Macchi M., Rosales R., Vigneron M., Staub A., Chambon P. In vitro binding of several cell-specific and ubiquitous nuclear proteins to the GT-I motif of the SV40 enhancer. Genes Dev. 1987 Oct;1(8):794–807. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.8.794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



