Abstract
The relaxation of long-lived states (LLS) corresponds to the slow return to statistical thermal equilibrium between symmetric and antisymmetric proton spin states. This process is remarkably sensitive to the presence of external spins and can be used to obtain information about partial unfolding of proteins. We detected the appearance of a destabilized conformer of ubiquitin when urea is added to the protein in its native state. This conformer shows increased mobility in the C-terminus, which significantly extends the lifetimes of proton LLS magnetisation in Ser-65. These changes could not be detected by conventional measurements of T1 and T2 relaxation times of protons, and would hardly be sensed by carbon-13 or nitrogen-15 relaxation measurements. Conformers with similar dynamic and structural features, as revealed by LLS relaxation times, could be observed, in the absence of urea, in two ubiquitin mutants, L67S and L69S.
Keywords: NMR, Proteins, Mutation, Ubiquitin, Long-Lived States, Singlet States
Introduction
Protein folding and unfolding are complex phenomena that remain difficult to characterize, despite numerous advancements in bio-analytical techniques. Proteins undergo conformational changes after their biosynthesis by the ribosome, and chaperons are believed to play a significant role in their folding. These changes can be described in terms of a trajectory through an energy landscape comprising partially folded states, leading in fine to the native state.[1] Misfolding or partial unfolding can lead to various diseases.[2] Understanding protein folding is a prerequisite to gain insight into many cellular activities. Methods like MD simulations, NMR, fluorescence spectroscopy, etc., have been employed to shed some light on protein folding pathways, but numerous ambiguities remain.
Ubiquitin (Ub) is a particularly stable protein composed of 76 amino acids, which remains folded even up to 100 °C.[3] It is involved in marking proteins for proteosomal degradation and other cellular signalling pathways. In eukaryotic cells, ubiquitin is found either as a monomer or as polyubiquitin chains.[4] The structure of ubiquitin obtained from X-ray diffraction[5] and multidimensional NMR[6] shows that ca. 85 % of the amino acids constitute its secondary structure, involving one α-helix, one 310-helix and five β-strands. The prevalence of secondary structure elements, its compactness, as well as its large hydrophobic core are likely the reasons behind the unusual stability of ubiquitin.
Ubiquitin has been used as a convenient model for both chemical[7] and thermal[8] unfolding studies. For this purpose, various methods including two-dimensional (2D) NMR, 2D–IR spectroscopy,[9] AFM,[10] and MD simulations have been used. H/D exchange kinetics in ubiquitin was sampled by NMR,[11] some of those studies using SOFAST 2D experiments.[12] It was observed that H/D exchange of amide protons is the slowest for residues in the β1–β2 strands and in the α-helix, and noticeably faster in the less stable C-terminal β-strand of ubiquitin. Interestingly, a replacement of Leu-69 by a serine (L69S) in ubiquitin resulted in a dramatic, up to 650-fold increase in the H/D exchange rates in the β5 strand, indicating weakening of the H-bonding contacts between this strand and its neighbours.[12b] The partially-folded A state of Ub, which appears in a 60/40 % methanol/water mixture at low pH, retains a native-like structure of the N-terminal β1–β2 strands and α-helix, whereas the C-terminal β-strands switch to a structure with a predominantly helical character, as revealed by a study of the backbone dynamics by NMR.[13] Cordier and Grzesiek[14] have shown, by measuring the temperature dependence of 3hJ(15N, 13CO) scalar coupling constants, that the H-bonds between the parallel β1 – β5 strands are the least stable, with Glu-64 → Gln-2 being the weakest H-bond. Molecular dynamics simulations were also used to study the kinetics of thermal unfolding of ubiquitin.[15] It was found that the β-strands are less stable than the α-helix, the weakest being the strand β5 at the C-terminus. Free-energy surface calculations[16] show that at low temperatures the thermal unfolding occurs in steps: the strands β3 – β5 are first disrupted, while the strands β1 – β2 are unfolded later. Many questions remain open, however, especially regarding the early steps of the unfolding process.
The populations of long-lived states (LLS)[17] return to equilibrium with time constants TLLS that can be much longer than spin-lattice relaxation time constants, e.g., TLLS/T1 > 37 in partially deuterated saccharides.[18] Long relaxation time constants TLLS are observed in partially-deuterated molecules dissolved in deuterated solvents. It is known that hydrogen bonds are weakened in D2O, but we expect the effect to be consistent throughout the protein after an equilibrium has been established, and conclusions on the relative stability of different protein segments drawn from relaxation time constants TLLS in D2O are therefore relevant. It is possible to excite LLS in two-spin systems of glycine residues of small peptides as well as in the mobile C-terminus of ubiquitin.[19] LLS have also been observed in some amino acids like serine, cysteine, aspartate, etc., where the isolated Hα and the pair of Hβ protons constitute a scalar-coupled three-spin system.[20]
LLS have long relaxation times because the main relaxation mechanism, i.e., the dipolar interaction between the involved spins, does not significantly affect their lifetimes,[17c] while interactions with other magnetic nuclei do. The time constants TLLS are therefore much more sensitive to the environment of these spins than T1 or T2 relaxation times and can thus provide information about the geometry of molecules.[21] We have measured LLS lifetimes in various amino acid residues of wild-type (WT) ubiquitin partly denatured by the addition of urea and by changing the pH, in order to obtain information about changes in structure and mobility during unfolding. In addition, we compared the values of relaxation time constants TLLS in thermodynamically-destabilized L69S and L67S mutants of ubiquitin[12b] with those of WT ubiquitin.
Results and Discussion
Ubiquitin denaturation using urea
Decay time constants of long-lived states with observed ratios TLLS/T1 > 1 are referred to as significantly enhanced lifetimes. LLS with significant lifetimes have been observed in the loose C-terminus of ubiquitin in its native state while singlet-triplet population differences of amino acids buried in the dense core of ubiquitin tend to have shorter TLLS because of strong dipolar interactions with surrounding protons. We have observed that T1 ≈ 1 s for most protons in ubiquitin. However, as proton T1's cannot be easily determined in proteins due to coupled multi-exponential relaxation, we do not report TLLS/T1 ratios. Changes of TLLS will be used to report on structural changes during unfolding.
Table 1 reports lifetimes TLLS measured in the absence and in the presence of urea, at different pH values. The relaxation time constant TLLS of the aliphatic protons of Gly-76 remains unchanged upon addition of 8 M urea, even upon changing the pH from 7 to 4.5. At 8 M urea and pH 3, the proton chemical shifts seen in TOCSY become similar to those of fully-unfolded ubiquitin.[22] In the absence of any structural or dynamic changes that would induce an increase in TLLS, these time constants are expected to become shorter, due to increased solvent viscosity in presence of urea[19, 23] and to the increased radius of gyration of the partially unfolded protein in solution. In Gly-75, TLLS decreases from 6.3 to 3.8 s upon addition of 8 M urea and further decreases to 2.9 s when the pH is lowered to 4.5. The decrease in TLLS might be partly due to dipolar interactions with external protons arising from structural changes at the C-terminus. The side chain of Arg-74, for instance, may come closer to the protons of Gly-75 upon urea addition.
Table 1.
Lifetimes TLLS protons in Gly-76, Gly-75, and Ser-65 of WT ubiquitin in the absence and in the presence of urea, as a function of pH. The reported standard deviations are derived from 50 fits of the exponential decays I(t) = I0exp(-t/TLLS), adding random noise to the experimental signal intensities in proportion to the noise observed in the spectra.
| Urea / M | pH | TLLS (Gly-76) / s | TLLS (Gly-75) / s | TLLS (Ser-65) / s |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 7 | 6.5 ± 0.4 | 6.3 ± 0.2 | < 1 |
| 8 | 7 | 6.4 ± 0.3 | 3.8 ± 0.6 | 12 ± 1 |
| 8 | 4.5 | 6.4 ± 0.3 | 2.9 ± 0.1 | 11 ± 1 |
| 8 | 3 | * | * | 11 ± 1 |
(*) lifetimes could not be measured due to spectral overlap.
In Ser-65, we have observed a dramatic increase in singlet-triplet equilibration lifetimes, from TLLS < 1 s in the native state to TLLS = 12 s after addition of 8 M urea, while T1 ≈ 1 s remains unchanged. The increase in TLLS could indicate structural changes in the β5 strand which would allow Ser-65 to move out of the proton-rich core of ubiquitin.
Ubiquitin TOCSY[24] spectra at pH 7 do not change significantly after addition of 8 M urea, and information about structural changes induced by urea is difficult to obtain. The spectra remain the same down to pH 4, but the chemical shifts suddenly collapse when the pH drops from 4 to 3, thus indicating extensive denaturation.[22]
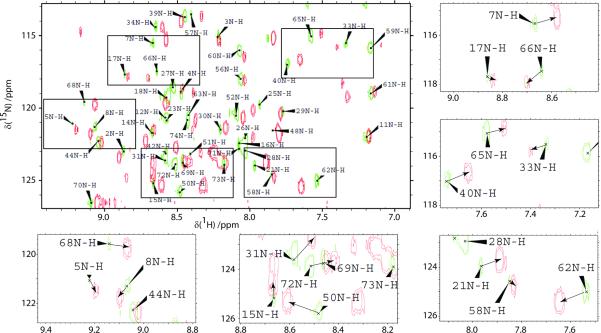
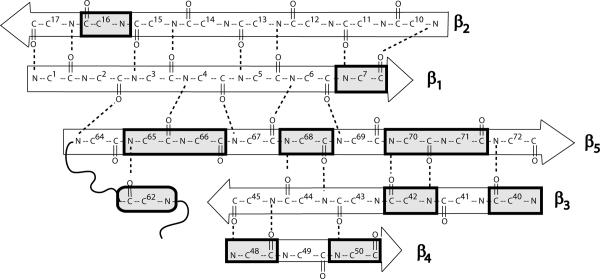
Fig. 1 shows 15N-1H HSQC spectra of WT ubiquitin [25], dissolved in 90/10 % H2O/D2O at pH 7, before and after addition of 8 M urea. Fig. 2 shows residues in the β-strand structure of regions of ubiquitin that feature significant differences in terms of the weighted chemical shifts[26] Δav = [(ΔδHN2 + ΔδN2/25) /2]½. It is interesting to remark that the HSQC signal of Gln-62, the H-bond partner of Ser-65, shifts considerably upon addition of urea.
Figure 1.
15N -1H HSQC spectra of WT ubiquitin (measured at 15N natural abundance) at pH 7 before (green) and after (red) addition of 8 M urea. The experiments were carried out at 18.8 T (800 MHz for protons) and T = 298 K. Shown insets outline signals of residues undergoing significant shifts.
Figure 2.
Residues in the β-strand structure of ubiquitin and selected H-bond partners. The residues that show weighted (see text) chemical shift differences larger than the average value for all the amino acids in the 15N-1H HSQC spectra of Fig. 1 are marked by rectangles.
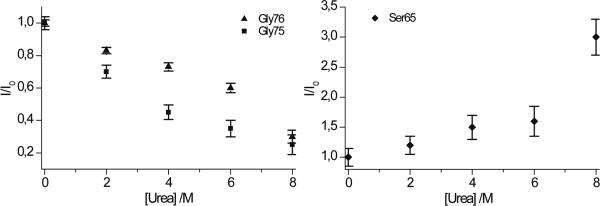
Figure 3 shows signal intensities in LLS experiments using a sustaining interval τLLS = 1 s at pH 7 as a function of urea concentration between 0 and 8 M. The TLLS of various residues change after initial addition of urea but remain constant (see Table 1) when the urea concentration increases from 2 to 8 M. Changes in signal intensities result from changes in TLLS and from sample dilution. Taking into consideration the errors introduced by spectral noise and pulse imperfections at different urea concentrations, the increase in intensity of the signal of Ser-65 can only be conservatively interpreted as indicating that a conformer with a significantly longer lifetime TLLS progressively appears upon urea addition. The decrease in the signal intensities of Gly-75 and Gly-76 mainly reflects sample dilution.
Figure 3.
Intensities of signals of Gly-75, Gly-76 (left) and Ser-65 (right) as a function of the concentration of urea, using a constant sustaining interval τLLS = 1 s. Error bars reflect noise in the spectra. The Ser-65 signal intensity increases, while the Gly-75, Gly-76 signal intensities decrease.
Similarities with ubiquitin mutants L69S and L67S
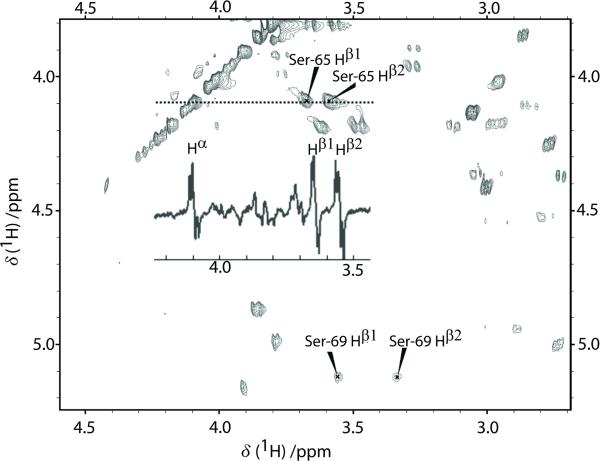
In two mutants of ubiquitin, L69S and L67S, the replacement of hydrophobic leucines by polar serines induces a loss of hydrophobic interactions, resulting in a lower thermodynamic stability of the protein, increased distances between the α-helix and the β3 and β5 strands, as well as in increased rates of H-D exchange in the β5 strand.[12b] Figure 4 shows the assignments of Ser-65 and Ser-69 signals in a TOCSY spectrum of L69S ubiquitin. The spectrum obtained by conversion of LLS into observable magnetisation (inset) shows that an LLS with significant lifetimes (TLLS >> T1) was excited and sustained in Ser-65.
Figure 4.
Region of a 1H - 1H TOCSY spectrum of the L69S mutant of ubiquitin. The chemical shifts of Ser-69 and Ser-65 are shown. The experiments were carried out at 14.1 T (600 MHz for protons) with a mixing interval τm = 80 ms. The inset shows a 1D spectrum of L69S ubiquitin obtained after transfer into observable magnetisation from an LLS comprising the three protons Hα, Hβ1, and Hβ2 of Ser-65. The LLS was sustained during τLLS = 1 s by a train of Sinc pulses.
Transverse relaxation times
Table 2 shows a comparison between the lifetimes TLLS of Gly-75, Gly-76, and Ser-65 in WT ubiquitin and its mutants at pH 7. In the mutants, a remarkably long TLLS ≈ 15 s is observed in Ser-65. Analysis of the TLLS lifetimes of Gly-75 and Gly-76 leads to the conclusion that the C-termini of both mutants have structural and dynamic similarities with WT ubiquitin at pH 7 and in the presence of 8 M urea.
Table 2.
The lifetimes TLLS of Gly-76, Gly-75, and Ser-65 in WT ubiquitin at pH 7 in the absence and in the presence of urea, compared with the corresponding lifetimes in L69S and L67S mutants in the absence of urea.
| Mutant | Urea (M) | TLLS (Gly-76) / s | TLLS (Gly-75) / s | TLLS (Ser-65) / s |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | 0 | 6.5 ± 0.4 | 6.3 ± 0.2 | <1 |
| WT | 8 | 6.4 ± 0.3 | 3.8 ± 0.6 | 12 ± 1 |
| L69S | 0 | 4.2 ± 0.3 | 1.4 ± 0. 1 | 15.0 ± 0.2 |
| L67S | 0 | 2.9 ± 0.3 | * | 16.4 ± 0.2 |
(*) signal intensities too weak to obtain a good fit.
Since the measurement of proton T2's is challenging in systems with homonuclear scalar couplings,[27] we measured instead T1ρ's of the Hα protons[28] in Gly-75, Gly-76, and Ser-65 of WT ubiquitin as a function of the urea concentration. Similar measurements were carried out for the L69S mutant of ubiquitin. For this purpose, a LLS sequence was inserted as a filter prior to the actual T1ρ pulse sequence. Only states that have a sufficiently long TLLS survive this filter. Furthermore, a J-filter consisting of a combination of π-pulses and gradients was inserted, in order to dephase undesired coherences from other residues.[29] Table 3 gives a comparison of the values of T1ρ and TLLS in Gly-76 and Gly-75 of WT ubiquitin at pH 7, before and after addition of 8 M urea. No significant changes in T1ρ's were observed upon addition of urea, while TLLS in Gly-75 changes significantly.
Table 3.
Lifetimes T1ρ and TLLS in various amino acids of WT ubiquitin and its L69S mutant at pH 7 and various urea concentrations.
| Mutant | Residue | T1ρ (ms) [Urea] = 0 M | T1ρ (ms) [Urea] = 8 M | TLLS (s) [Urea] = 0 M | TLLS (s) [Urea] = 8 M |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | Gly-75 | 110 ± 2 | 115 ± 2 | 6.3 ± 0.2 | 3.85 ± 0.6 |
| WT | Gly-76 | 195 ± 2 | 190 ± 2 | 6.5 ± 0.4 | 6.41 ± 0.3 |
| WT | Ser-65 | * | * | * | 12 ± 1 |
| L69S | Gly-75 | ** | * | 1.4 ± 0.1 | * |
| L69S | Gly-76 | 120 ± 1 | * | 4.2 ± 0.3 | * |
| L69S | Ser-65 | 200 ± 1 | * | 15.0 ± 0.2 | * |
(*) not measured;
(**) signal intensities too weak to obtain a good fit.
The T1ρ of Ser-65 is longer than that of Gly-76 in the L69S mutant, indicating that Ser-65 is quite mobile, which explains why a very long TLLS = 15.0 ± 0.2 s is obtained for this amino acid residue.
These observations show how ubiquitin is affected by urea. Under these conditions, the residues in the β1 – β2 hairpin and between the parallel β1 – β5 strands are the first to undergo changes in the chemical environment, as can be appreciated when comparing HSQC spectra at pH = 7 in the presence and absence of urea (Figures 1 and 2). The increase in the TLLS of Ser-65 after addition of urea points to an increased β5 mobility due to the weakening of H-bond interactions in the parallel β1 – β5 strands, an observation which is in agreement with earlier reports about the unfolding pathways of ubiquitin, the β-strand structure of ubiquitin at its C-terminus being the least stable.
Conclusions
The lifetimes of LLS, more sensitive to structural changes than proton relaxation time constants T1, T2, or T1ρ can be used as a probe to study protein unfolding. We could detect a partly unfolded conformer where the H-bonds between the β1 and β5 strands are weakened. We found structural and dynamic similarities between partly-denatured WT ubiquitin and thermodynamically destabilized mutants L69S or L67S in their native state. We were able to excite LLS in the labile C-terminal part of native ubiquitin and in one inner residue of destabilised proteins. We expect to be able to sustain LLS in protein samples using various deuteration techniques[30] or in proteins extracted from bacteria grown in deuterated environments to which protonated Gly are added. Since these proteins contain selectively-protonated Gly, and, due to the cellular metabolism, Ser residues, this practice may extend the scope of protein dynamics studied by LLS.
Experimental Section
The TLLS and 2D-TOCSY experiments on ubiquitin (2 mM in D2O at 298 K) were carried out at 600 and 800 MHz. Gaseous nitrogen was bubbled through the samples for ten minutes prior to all experiments in order to reduce the concentration of dissolved oxygen. Before addition, urea was lyophilized and dissolved in D2O twice to exchange labile protons by deuterons. The pH of the solution was adjusted by adding concentrated HCl. LLS experiments were run using the method described by Sarkar et al.[18] Presaturation pulses of 1 s were applied before the beginning of the sequence. During the sustaining period, the carrier was placed at the water frequency, and Sinc pulses[31] were used to sustain the LLS over a broad bandwidth. For each LLS experiment, 128 transients were acquired using a recovery delay of 10 s and an acquisition time of 2.73 s. Experimental TLLS values were obtained by fitting spectral intensities for 8 increments τLLS = 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15 s for Gly-75, 76 and τLLS = 1, 3, 6, 10, 15, 21, 28, 36 s for Ser-65 to mono-exponentially decaying functions. 2D 1H-15N HSQC experiments were recorded at 800 MHz on a sample of ubiquitin (2 mM dissolved in 90/10 % H2O/D2O).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Martin Blackledge (Institut de Biologie Structurale Jean-Pierre Ebel, Grenoble) for useful suggestions. Martial Rey provided valuable technical assistance. This work was supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation (`Ambizione' grant PZOOP2_121928 to P.V. and FNRS grant 200020_124694 to G. B. and P. V.), the Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), the Swiss Commission for Technology and Innovation (CTI grant 9991.1 PFIW-IW to G. B., Paul Dyson, Jean-Philippe Ansermet, and P. V.), the French CNRS, and the National Institutes of Health (NIH grant GM065334 to D.F.). P.V. thanks the Faculty of Basic Sciences, EPFL, for financial support.
References
- [1].Dobson CM, Karplus M. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1999;9:92–101. doi: 10.1016/s0959-440x(99)80012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [2].Fersht AR, Daggett V. Cell. 2002;108:573–582. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00620-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [3].Ibarra-Molero B, Loladze VV, Makhatadze GI, Sanchez-Ruiz JM. Biochemistry (Mosc) 1999;38:8138–8149. doi: 10.1021/bi9905819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [4].Pickart CM, Fushman D. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2004;8:610–616. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2004.09.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [5].Vijaykumar S, Bugg CE, Cook WJ. J Mol Biol. 1987;194:531–544. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90679-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [6].a Cornilescu G, Marquardt JL, Ottiger M, Bax A. J Am Chem Soc. 1998;120:6836–6837. [Google Scholar]; b Lakomek NA, Lange OF, Walter KFA, Fares C, Egger D, Lunkenheimer P, Meiler J, Grubmuller H, Becker S, de Groot BL, Griesinger C. Biochem Soc T. 2008;36:1433–1437. doi: 10.1042/BST0361433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [7].a Khorasanizadeh S, Peters ID, Butt TR, Roder H. Biochemistry-Us. 1993;32:7054–7063. doi: 10.1021/bi00078a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; b Khorasanizadeh S, Peters ID, Roder H. Nat Struct Biol. 1996;3:193–205. doi: 10.1038/nsb0296-193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; c Krantz BA, Sosnick TR. Biochemistry-Us. 2000;39:11696–11701. doi: 10.1021/bi000792+. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [8].Noronha M, Gerbelova H, Faria TQ, Lund DN, Smith DA, Santos H, Macanita AL. J Phys Chem B. 2010;114:9912–9919. doi: 10.1021/jp104167h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [9].Chung HS, Ganim Z, Jones KC, Tokmakoff A. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:14237–14242. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0700959104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [10].Grater F, Grubmuller H. J Struct Biol. 2007;157:557–569. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2006.11.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [11].Johnson EC, Lazar GA, Desjarlais JR, Handel TM. Struct Fold Des. 1999;7:967–976. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(99)80123-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [12].a Schanda P, Forge V, Brutscher B. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:11257–11262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0702069104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; b Haririnia A, Verma R, Purohit N, Twarog MZ, Deshaies RJ, Bolon D, Fushman D. J Mol Biol. 2008;375:979–996. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.11.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [13].Brutscher B, Brüschweiler R, Ernst RR. Biochemistry. 1997;36:13043–13053. doi: 10.1021/bi971538t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [14].Cordier F, Grzesiek S. J Am Chem Soc. 1999;121:1601–1602. [Google Scholar]
- [15].a Krishnan A, Giuliani A, Zbilut JP, Tomita M. Plos One. 2008;3 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0002149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; b Das A, Mukhopadhyay C. J Chem Phys. 2007;127 doi: 10.1063/1.2796165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [16].Chung HS, Tokmakoff A. Proteins. 2008;72:488–497. doi: 10.1002/prot.22042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [17].a Carravetta M, Johannessen OG, Levitt MH. Phys Rev Lett. 2004;92 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.92.153003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; b Carravetta M, Levitt MH. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126:6228–6229. doi: 10.1021/ja0490931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; c Carravetta M, Levitt MH. J Chem Phys. 2005;122 doi: 10.1063/1.1893983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; d Pileio G, Levitt MH. J Chem Phys. 2009;130 doi: 10.1063/1.3139064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [18].Sarkar R, Vasos PR, Bodenhausen G. J Am Chem Soc. 2007;129:328–334. doi: 10.1021/ja0647396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [19].Ahuja P, Sarkar R, Vasos PR, Bodenhausen G. J Am Chem Soc. 2009;131:7498. doi: 10.1021/ja902030k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [20].Ahuja P, Sarkar R, Vasos PR, Bodenhausen G. Chemphyschem. 2009;10:2217–2220. doi: 10.1002/cphc.200900335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [21].a Tayler MCD, Marie S, Ganesan A, Levitt MH. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010;132:8225. doi: 10.1021/ja1012917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; b Grant AK, Vinogradov E. J. Magn. Reson. 2008;193:177–190. doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2008.04.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [22].Peti W, Smith LJ, Redfield C, Schwalbe H. J. Biomol. NMR. 2001;19:153–165. doi: 10.1023/a:1008307323283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [23].Ahuja P, Sarkar R, Vasos PR, Bodenhausen G. J Chem Phys. 2007;127 doi: 10.1063/1.2778429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [24].Marion D, Bax A. J Magn Reson. 1988;80:528–533. [Google Scholar]
- [25].Bodenhausen G, Ruben DJ. Chem Phys Lett. 1980;69:185–189. [Google Scholar]
- [26].Grzesiek S, Bax A, Clore GM, Gronenborn AM, Hu JS, Kaufman J, Palmer I, Stahl SJ, Wingfield PT. Nat Struct Biol. 1996;3:340–345. doi: 10.1038/nsb0496-340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [27].a Segawa TF, Baishya B, Bodenhausen G. Chemphyschem. 2010;11:3343–3354. doi: 10.1002/cphc.201000350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; b Baishya B, Segawa TF, Bodenhausen G. J Am Chem Soc. 2009;131:17538–17539. doi: 10.1021/ja907391z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [28].Peng JW, Thanabal V, Wagner G. J. Magn. Reson. 1991;94:82–100. [Google Scholar]
- [29].Sarkar R, Ahuja P, Vasos PR, Bornet A, Wagnières O, Bodenhausen G. Prog. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2010 doi: 10.1016/j.pnmrs.2010.10.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [30].a Lichtenecker R, Ludwiczek ML, Schmid W, Konrat R. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126:5348–5349. doi: 10.1021/ja049679n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; b Sibille N, Hanoulle X, Bonachera F, Verdegem D, Landrieu I, Wieruszeski JM, Lippens G. J Biomol Nmr. 2009;43:219–227. doi: 10.1007/s10858-009-9307-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [31].Sarkar R, Ahuia P, Moskau D, Vasos PR, Bodenhausen G. Chemphyschem. 2007;8:2652–2656. doi: 10.1002/cphc.200700545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]