Abstract
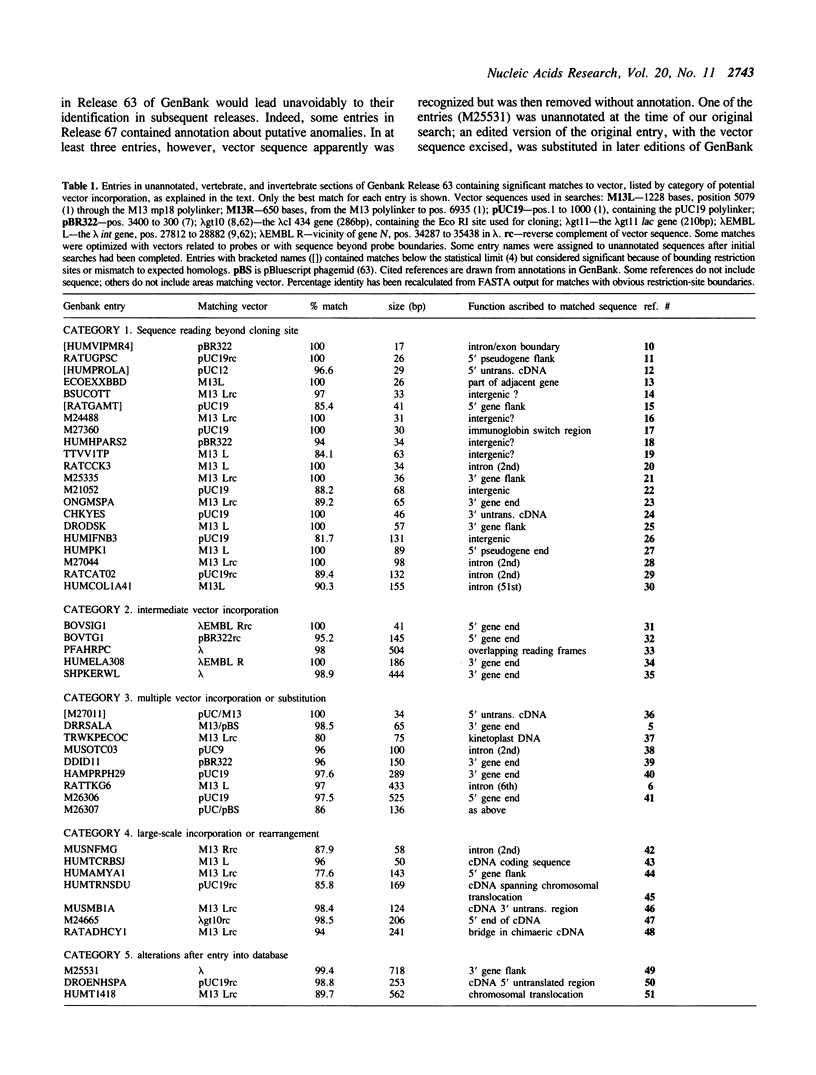
We describe evidence that DNA sequences from vectors used for cloning and sequencing have been incorporated accidentally into eukaryotic entries in the GenBank database. These incorporations were not restricted to one type of vector or to a single mechanism. Many minor instances may have been the result of simple editing errors, but some entries contained large blocks of vector sequence that had been incorporated by contamination or other accidents during cloning. Some cases involved unusual rearrangements and areas of vector distant from the normal insertion sites. Matches to vector were found in 0.23% of 20,000 sequences analyzed in GenBank Release 63. Although the possibility of anomalous sequence incorporation has been recognized since the inception of GenBank and should be easy to avoid, recent evidence suggests that this problem is increasing more quickly than the database itself. The presence of anomalous sequence may have serious consequences for the interpretation and use of database entries, and will have an impact on issues of database management. The incorporated vector fragments described here may also be useful for a crude estimate of the fidelity of sequence information in the database. In alignments with well-defined ends, the matching sequences showed 96.8% identity to vector; when poorer matches with arbitrary limits were included, the aggregate identity to vector sequence was 94.8%.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson K. P., Croyle M. L., Lingrel J. B. Primary structure of a gene encoding rat T-kininogen. Gene. 1989 Sep 1;81(1):119–128. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90342-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ann D. K., Gadbois D., Carlson D. M. Structure, organization, and regulation of a hamster proline-rich protein gene. A multigene family. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):3958–3963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronson A. I., Song H. Y., Bourne N. Gene structure and precursor processing of a novel Bacillus subtilis spore coat protein. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Mar;3(3):437–444. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00189.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barklis E., Pontius B., Lodish H. F. Structure of the Dictyostelium discoideum prestalk D11 gene and protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1473–1479. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Begley C. G., Aplan P. D., Davey M. P., Nakahara K., Tchorz K., Kurtzberg J., Hershfield M. S., Haynes B. F., Cohen D. I., Waldmann T. A. Chromosomal translocation in a human leukemic stem-cell line disrupts the T-cell antigen receptor delta-chain diversity region and results in a previously unreported fusion transcript. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):2031–2035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.2031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodner M., Fridkin M., Gozes I. Coding sequences for vasoactive intestinal peptide and PHM-27 peptide are located on two adjacent exons in the human genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3548–3551. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunak S., Engelbrecht J., Knudsen S. Cleaning up gene databases. Nature. 1990 Jan 11;343(6254):123–123. doi: 10.1038/343123a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cinkosky M. J., Fickett J. W., Gilna P., Burks C. Electronic data publishing and GenBank. Science. 1991 May 31;252(5010):1273–1277. doi: 10.1126/science.1925538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corral M., Baffet G., Defer N. Structure of a cDNA clone specific to hepatoma cells with rearranged mitochondrial sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 25;16(22):10935–10935. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.22.10935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creighton T. E., Charles I. G. Sequences of the genes and polypeptide precursors for two bovine protease inhibitors. J Mol Biol. 1987 Mar 5;194(1):11–22. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90711-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschenes R. J., Haun R. S., Funckes C. L., Dixon J. E. A gene encoding rat cholecystokinin. Isolation, nucleotide sequence, and promoter activity. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):1280–1286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eick-Helmerich K., Braun V. Import of biopolymers into Escherichia coli: nucleotide sequences of the exbB and exbD genes are homologous to those of the tolQ and tolR genes, respectively. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):5117–5126. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.5117-5126.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emi M., Horii A., Tomita N., Nishide T., Ogawa M., Mori T., Matsubara K. Overlapping two genes in human DNA: a salivary amylase gene overlaps with a gamma-actin pseudogene that carries an integrated human endogenous retroviral DNA. Gene. 1988;62(2):229–235. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90561-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freimark B., Pickering L., Concannon P., Fox R. Nucleotide sequence of a uniquely expressed human T cell receptor beta chain variable region gene (V beta) in Sjogren's syndrome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 11;17(1):455–455. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.1.455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H., Poustka A., Murray N. Lambda replacement vectors carrying polylinker sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):827–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadaleta G., Pepe G., De Candia G., Quagliariello C., Sbisà E., Saccone C. The complete nucleotide sequence of the Rattus norvegicus mitochondrial genome: cryptic signals revealed by comparative analysis between vertebrates. J Mol Evol. 1989 Jun;28(6):497–516. doi: 10.1007/BF02602930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner R. C., Howarth A. J., Messing J., Shepherd R. J. Cloning and sequencing of restriction fragments generated by Eco RI*. DNA. 1982;1(2):109–115. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1982.1.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gharib S. D., Roy A., Wierman M. E., Chin W. W. Isolation and characterization of the gene encoding the beta-subunit of rat follicle-stimulating hormone. DNA. 1989 Jun;8(5):339–349. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1989.8.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greslin A. F., Prescott D. M., Oka Y., Loukin S. H., Chappell J. C. Reordering of nine exons is necessary to form a functional actin gene in Oxytricha nova. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6264–6268. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handy D. E., Larsen S. H., Karn R. C., Hodes M. E. Identification of a human salivary amylase gene. Partial sequence of genomic DNA suggests a mode of regulation different from that of mouse, Amy1. Mol Biol Med. 1987 Jun;4(3):145–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley D. A., Preiss A., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. A deduced gene product from the Drosophila neurogenic locus, enhancer of split, shows homology to mammalian G-protein beta subunit. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):785–795. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90134-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson C. P. Cloning vector artifacts in the DNA database. Biotechniques. 1990 Jul;9(1):54–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph L. J., Chang L. C., Stamenkovich D., Sukhatme V. P. Complete nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of human and murine preprocathepsin L. An abundant transcript induced by transformation of fibroblasts. J Clin Invest. 1988 May;81(5):1621–1629. doi: 10.1172/JCI113497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin S., Ghandour G. Comparative statistics for DNA and protein sequences: single sequence analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5800–5804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamperti E. D., Rosen K. M., Villa-Komaroff L. Characterization of the gene and messages for vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) in rat and mouse. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1991 Feb;9(3):217–231. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(91)90005-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenstra R., d'Auriol L., Andrieu B., Le Bras J., Galibert F. Cloning and sequencing of Plasmodium falciparum DNA fragments containing repetitive regions potentially coding for histidine-rich proteins: identification of two overlapping reading frames. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jul 15;146(1):368–377. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90734-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy E., Liem R. K., D'Eustachio P., Cowan N. J. Structure and evolutionary origin of the gene encoding mouse NF-M, the middle-molecular-mass neurofilament protein. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Jul 1;166(1):71–77. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13485.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. M., Russell C. S., Cosloy S. D. The structure of the Escherichia coli hemB gene. Gene. 1989 Jan 30;75(1):177–184. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90394-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez R., Kristensen T., Prydz H. Database contamination. Nature. 1992 Jan 16;355(6357):211–211. doi: 10.1038/355211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda N. Nucleotide sequence of the haptoglobin and haptoglobin-related gene pair. The haptoglobin-related gene contains a retrovirus-like element. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):6698–6709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May L. T., Landsberger F. R., Inouye M., Sehgal P. B. Significance of similarities in patterns: an application to beta interferon-related DNA on human chromosome 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4090–4094. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima H., Yamamoto M., Goto K., Osumi T., Hashimoto T., Endo H. Isolation and characterization of the rat catalase-encoding gene. Gene. 1989 Jul 15;79(2):279–288. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90210-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann H., Schwass V., Eckerskorn C., Zillig W. Identification and characterization of the genes encoding three structural proteins of the Thermoproteus tenax virus TTV1. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 May;217(1):105–110. doi: 10.1007/BF00330948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols R., Schneuwly S. A., Dixon J. E. Identification and characterization of a Drosophila homologue to the vertebrate neuropeptide cholecystokinin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12167–12170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa H., Fujioka M. Nucleotide sequence of the rat guanidinoacetate methyltransferase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 12;16(17):8715–8716. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.17.8715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson M., Hood L., Cantor C., Botstein D. A common language for physical mapping of the human genome. Science. 1989 Sep 29;245(4925):1434–1435. doi: 10.1126/science.2781285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponzi M., Birago C., Battaglia P. A. Two identical symmetrical regions in the minicircle structure of Trypanosoma lewisi kinetoplast DNA. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1984 Sep;13(1):111–119. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(84)90105-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rentier-Delrue F., Swennen D., Prunet P., Lion M., Martial J. A. Tilapia prolactin: molecular cloning of two cDNAs and expression in Escherichia coli. DNA. 1989 May;8(4):261–270. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1989.8.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter D., Schuh R., Jäckle H. The homeotic gene spalt (sal) evolved during Drosophila speciation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5483–5486. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts L. Finding DNA sequencing errors. Science. 1991 May 31;252(5010):1255–1256. doi: 10.1126/science.1925537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts L. New game plan for genome mapping. Science. 1989 Sep 29;245(4925):1438–1440. doi: 10.1126/science.2781288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saba J. A., Busch H., Reddy R. U4 small nuclear RNA pseudogenes from rat genome have common truncated 3'-ends. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jul 31;130(2):828–834. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90491-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakaguchi N., Kashiwamura S., Kimoto M., Thalmann P., Melchers F. B lymphocyte lineage-restricted expression of mb-1, a gene with CD3-like structural properties. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3457–3464. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03220.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer S. E., Veres G., Caskey C. T. The genetic structure of mouse ornithine transcarbamylase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 25;16(4):1593–1601. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.4.1593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott A. L., Dinman J., Sussman D. J., Yenbutr P., Ward S. Major sperm protein genes from Onchocerca volvulus. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Sep;36(2):119–126. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90184-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short J. M., Fernandez J. M., Sorge J. A., Huse W. D. Lambda ZAP: a bacteriophage lambda expression vector with in vivo excision properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7583–7600. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. F., Waterman M. S., Burks C. The statistical distribution of nucleic acid similarities. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jan 25;13(2):645–656. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.2.645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soininen R., Huotari M., Ganguly A., Prockop D. J., Tryggvason K. Structural organization of the gene for the alpha 1 chain of human type IV collagen. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13565–13571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Son H. J., Cook G. A., Hall T., Donelson J. E. Expression site associated genes of Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Feb;33(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90042-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- States D. J., Botstein D. Molecular sequence accuracy and the analysis of protein coding regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5518–5522. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockinger H., Schmidtke J., Bostock C., Epplen J. T. Human DNA sequences isolated with an immunoglobulin switch region probe: sequence, chromosomal localization, and restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Hum Genet. 1986 Jun;73(2):104–109. doi: 10.1007/BF00291596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudol M., Kieswetter C., Zhao Y. H., Dorai T., Wang L. H., Hanafusa H. Nucleotide sequence of a cDNA for the chick yes proto-oncogene: comparison with the viral yes gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9876–9876. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli plasmid pBR322. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):77–90. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tani T., Ohsumi J., Mita K., Takiguchi Y. Identification of a novel class of elastase isozyme, human pancreatic elastase III, by cDNA and genomic gene cloning. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1231–1239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tepler I., Shimizu A., Leder P. The gene for the rat mast cell high affinity IgE receptor alpha chain. Structure and alternative mRNA splicing patterns. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5912–5915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Ouweland A. M., Van Duijnhoven H. L., Deichmann K. A., Van Groningen J. J., de Leij L., Van de Ven W. J. Characteristics of a multicopy gene family predominantly consisting of processed pseudogenes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 25;17(10):3829–3843. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.10.3829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderslice P., Craik C. S., Nadel J. A., Caughey G. H. Molecular cloning of dog mast cell tryptase and a related protease: structural evidence of a unique mode of serine protease activation. Biochemistry. 1989 May 16;28(10):4148–4155. doi: 10.1021/bi00436a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson B. W., Edwards K. J., Sleigh M. J., Byrne C. R., Ward K. A. Complete sequence of a type-I microfibrillar wool keratin gene. Gene. 1988 Dec 15;73(1):21–31. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90309-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Y. X., Pitcovski J., Peterson L., Auffray C., Bourlet Y., Gerndt B. M., Nordskog A. W., Lamont S. J., Warner C. M. Isolation and characterization of three class II MHC genomic clones from the chicken. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 15;142(6):2122–2132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagami T., Ohsawa K., Nishizawa M., Inoue C., Gotoh E., Yanaihara N., Yamamoto H., Okamoto H. Complete nucleotide sequence of human vasoactive intestinal peptide/PHM-27 gene and its inducible promoter. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;527:87–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb26975.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Martynoff G., Pohl V., Mercken L., van Ommen G. J., Vassart G. Structural organization of the bovine thyroglobulin gene and of its 5'-flanking region. Eur J Biochem. 1987 May 4;164(3):591–599. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb11168.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



