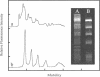
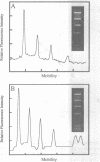
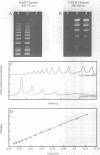
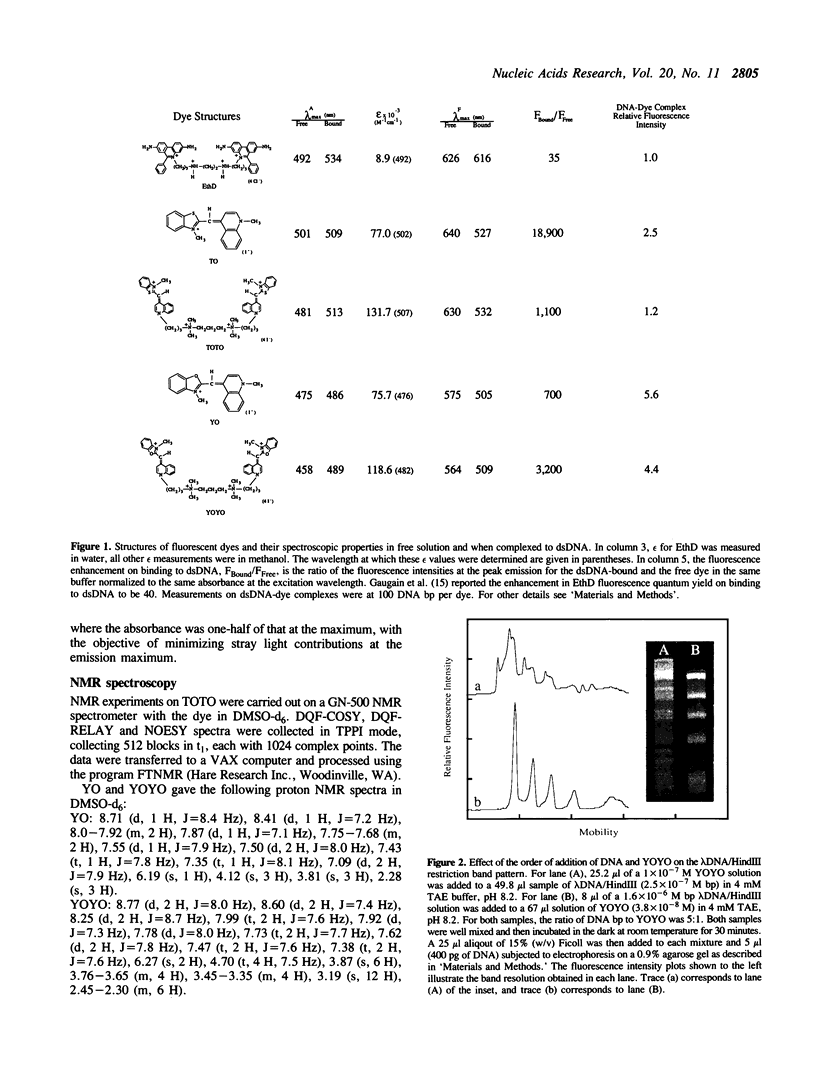
Abstract
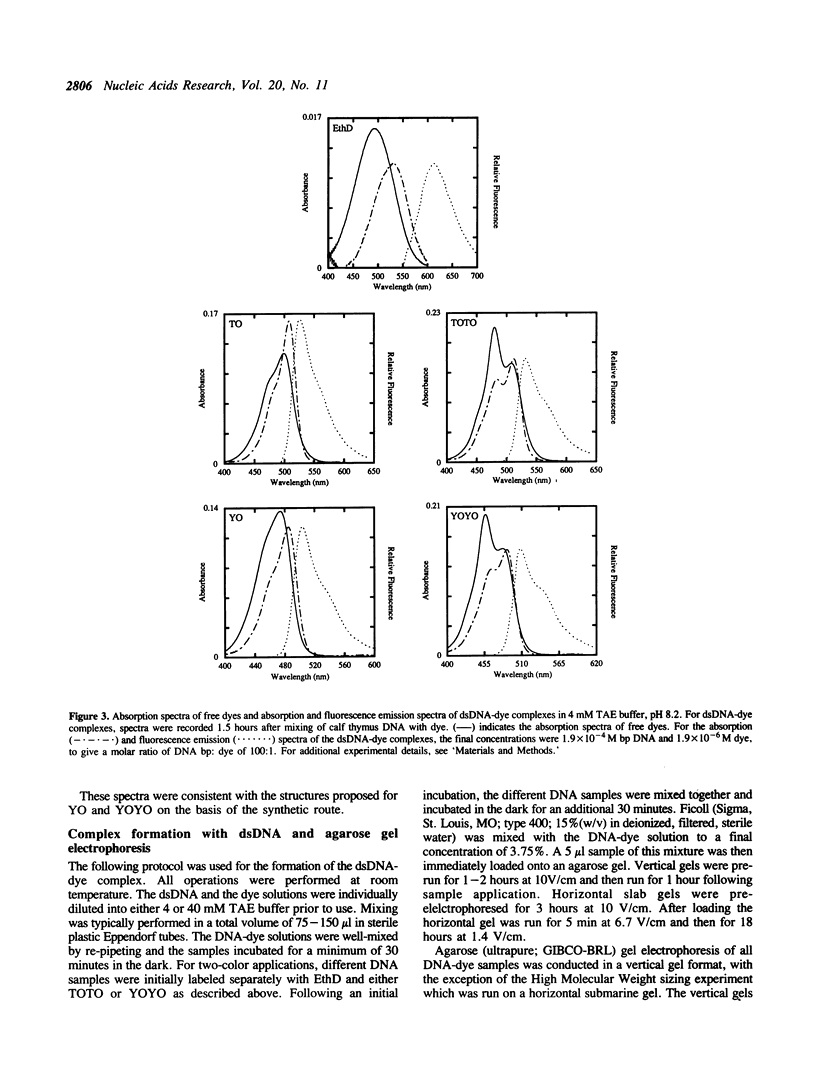
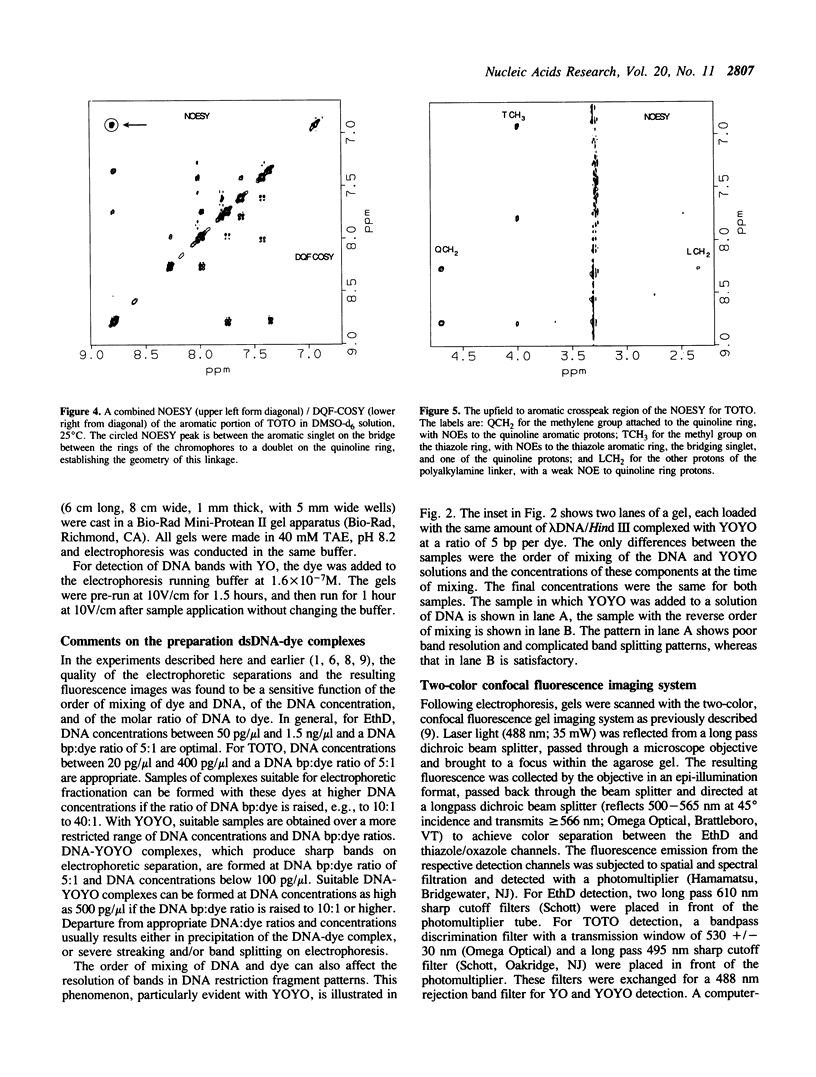
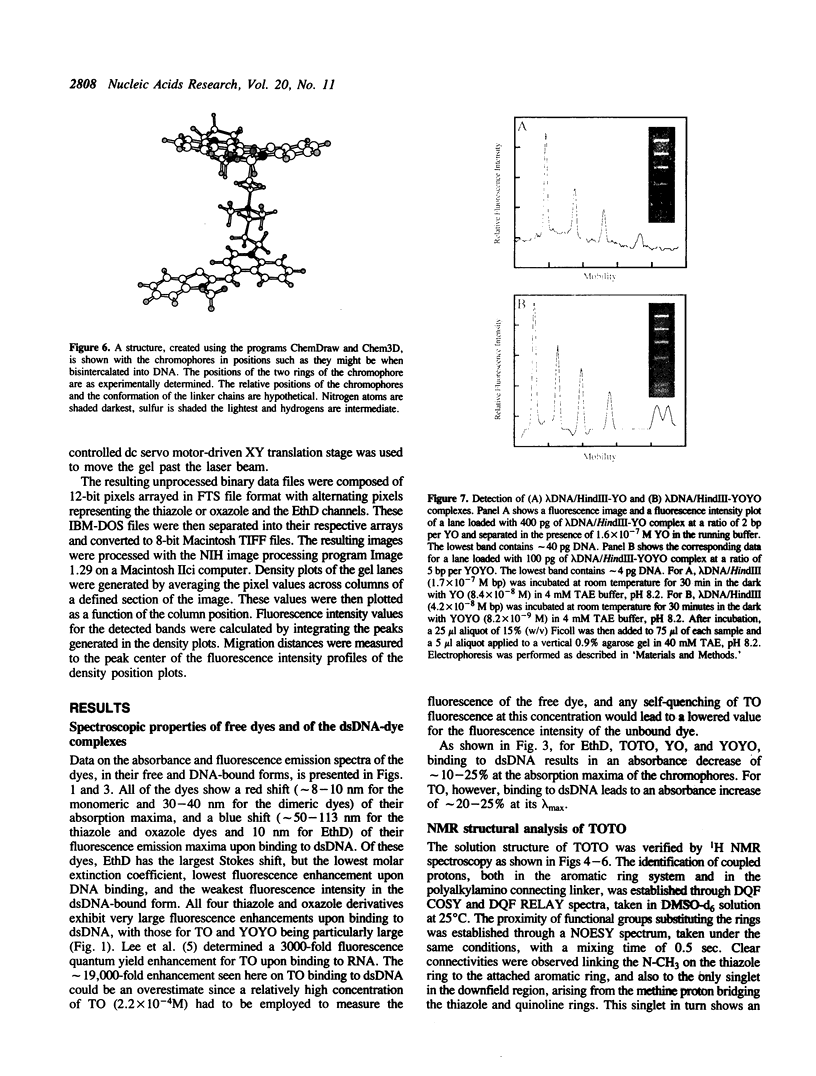
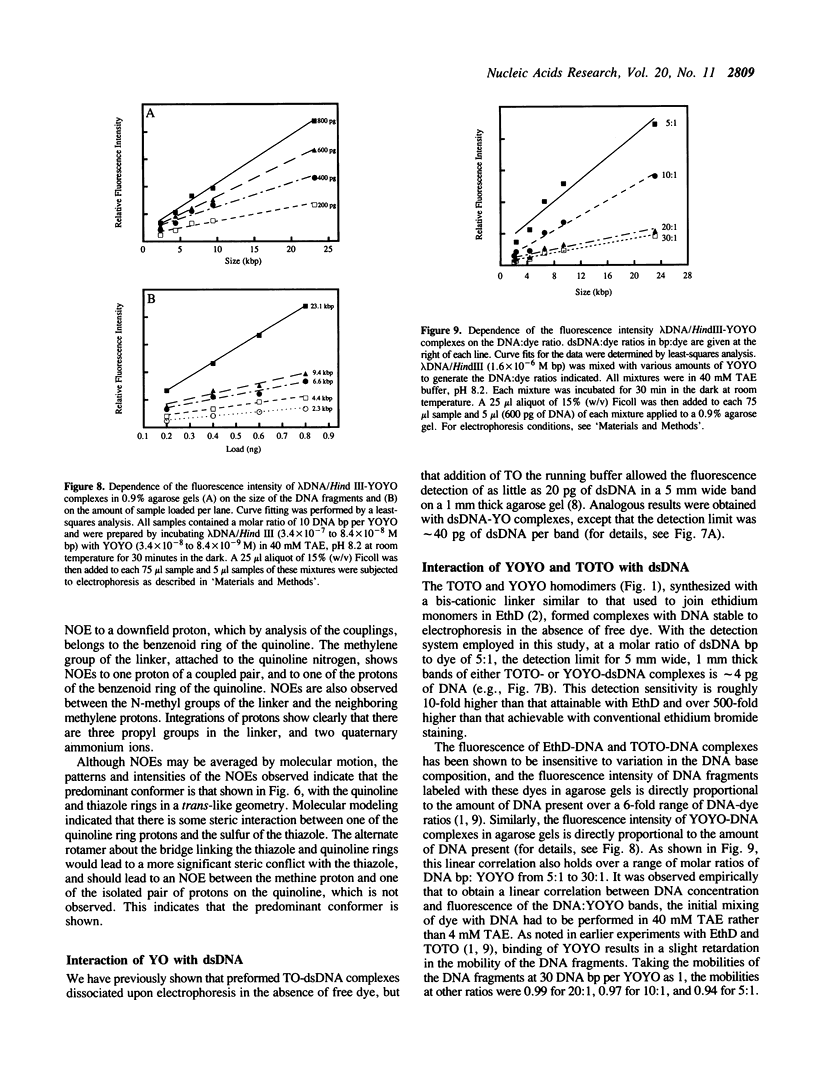
The synthesis, proof of structure, and the absorption and fluorescence properties of two new unsymmetrical cyanine dyes, thiazole orange dimer (TOTO; 1,1'-(4,4,7,7-tetramethyl-4,7- diazaundecamethylene)-bis-4-[3-methyl-2,3-dihydro-(benzo-1,3-thiaz ole)-2- methylidene]-quinolinium tetraiodide) and oxazole yellow dimer (YOYO; an analogue of TOTO with a benzo-1,3-oxazole in place of the benzo-1,3-thiazole) are reported. TOTO and YOYO are virtually non-fluorescent in solution, but form highly fluorescent complexes with double-stranded DNA (dsDNA), up to a maximum dye to DNA bp ratio of 1:4, with greater than 1000-fold fluorescence enhancement. The dsDNA-TOTO (lambda max 513 nm; lambda maxF 532 nm) and dsDNA-YOYO (lambda max 489 nm; lambda maxF 509 nm) complexes are completely stable to electrophoresis on agarose and acrylamide gels. Mixtures of restriction fragments pre-labeled with ethidium dimer (EthD; lambda maxF 616 nm) and those pre-labeled with either TOTO or YOYO were separated by electrophoresis. Laser excitation at 488 nm and simultaneous confocal fluorescence detection at 620-750 nm (dsDNA-EthD emission) and 500-565 nm (dsDNA-TOTO or dsDNA-YOYO emission) allowed sensitive detection, quantitation, and accurate sizing of restriction fragments ranging from 600 to 24,000 bp. The limit of detection of dsDNA-TOTO and YOYO complexes with a laser-excited confocal fluorescence gel scanner for a band 5-mm wide on a 1-mm thick agarose gel was 4 picograms, about 500-fold lower than attainable by conventional staining with ethidium bromide.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Assa-Munt N., Denny W. A., Leupin W., Kearns D. R. 1H NMR study of the binding of Bis(acridines) to d(AT)5.d(AT)5. 1. Mode of binding. Biochemistry. 1985 Mar 12;24(6):1441–1449. doi: 10.1021/bi00327a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assa-Munt N., Leupin W., Denny W. A., Kearns D. R. 1H NMR study of the binding of bis(acridines) to d(AT)5.d(AT)5. 2. Dynamic aspects. Biochemistry. 1985 Mar 12;24(6):1449–1460. doi: 10.1021/bi00327a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst L. A., Gupta R. K., Mujumdar R. B., Waggoner A. S. Cyanine dye labeling reagents for sulfhydryl groups. Cytometry. 1989 Jan;10(1):3–10. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990100103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaugain B., Barbet J., Capelle N., Roques B. P., Le Pecq J. B. DNA Bifunctional intercalators. 2. Fluorescence properties and DNA binding interaction of an ethidium homodimer and an acridine ethidium heterodimer. Biochemistry. 1978 Nov 28;17(24):5078–5088. doi: 10.1021/bi00617a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaugain B., Barbet J., Oberlin R., Roques B. P., Le Pecq J. B. DNA bifunctional intercalators. I. Synthesis and conformational properties of an ethidium homodimer and of an acridine ethidium heterodimer. Biochemistry. 1978 Nov 28;17(24):5071–5078. doi: 10.1021/bi00617a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glazer A. N., Peck K., Mathies R. A. A stable double-stranded DNA-ethidium homodimer complex: application to picogram fluorescence detection of DNA in agarose gels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3851–3855. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laugâa P., Markovits J., Delbarre A., Le Pecq J. B., Roques B. P. DNA tris-intercalation: first acridine trimer with DNA affinity in the range of DNA regulatory proteins. Kinetic studies. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 24;24(20):5567–5575. doi: 10.1021/bi00341a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. G., Chen C. H., Chiu L. A. Thiazole orange: a new dye for reticulocyte analysis. Cytometry. 1986 Nov;7(6):508–517. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990070603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mujumdar R. B., Ernst L. A., Mujumdar S. R., Waggoner A. S. Cyanine dye labeling reagents containing isothiocyanate groups. Cytometry. 1989 Jan;10(1):11–19. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990100104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen P. E., Zhen W. P., Henriksen U., Buchardt O. Sequence-influenced interactions of oligoacridines with DNA detected by retarded gel electrophoretic migrations. Biochemistry. 1988 Jan 12;27(1):67–73. doi: 10.1021/bi00401a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelaprat D., Delbarre A., Le Guen I., Roques B. P., Le Pecq J. B. DNA intercalating compounds as potential antitumor agents. 2. Preparation and properties of 7H-pyridocarbazole dimers. J Med Chem. 1980 Dec;23(12):1336–1343. doi: 10.1021/jm00186a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quesada M. A., Rye H. S., Gingrich J. C., Glazer A. N., Mathies R. A. High-sensitivity DNA detection with a laser-excited confocal fluorescence gel scanner. Biotechniques. 1991 May;10(5):616–625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rye H. S., Quesada M. A., Peck K., Mathies R. A., Glazer A. N. High-sensitivity two-color detection of double-stranded DNA with a confocal fluorescence gel scanner using ethidium homodimer and thiazole orange. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 25;19(2):327–333. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southwick P. L., Ernst L. A., Tauriello E. W., Parker S. R., Mujumdar R. B., Mujumdar S. R., Clever H. A., Waggoner A. S. Cyanine dye labeling reagents--carboxymethylindocyanine succinimidyl esters. Cytometry. 1990;11(3):418–430. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990110313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakelin L. P. Polyfunctional DNA intercalating agents. Med Res Rev. 1986 Jul-Sep;6(3):275–340. doi: 10.1002/med.2610060303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright R. G., Wakelin L. P., Fieldes A., Acheson R. M., Waring M. J. Effects of ring substituents and linker chains on the bifunctional intercalation of diacridines into deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1980 Dec 9;19(25):5825–5836. doi: 10.1021/bi00566a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]