Abstract
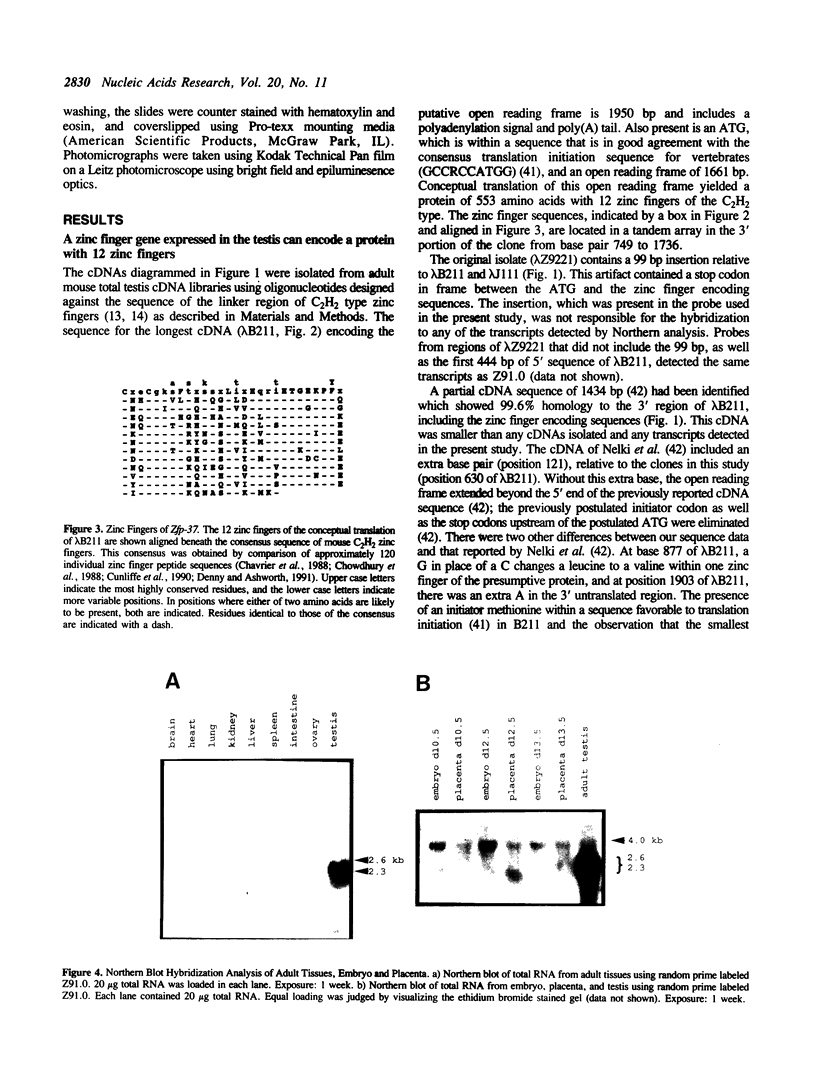
To begin to examine the function in the mouse testis of genes containing the zinc finger motif, we have screened an adult mouse total testis cDNA library with probes to a conserved region of zinc fingers. We have isolated cDNAs for a new murine zinc finger encoding gene that has been designated Zfp-37. Northern blot hybridization analysis revealed Zfp-37 transcripts at high levels in the testis, the only adult tissue in which Zfp-37 expression was observed. Zfp-37 was also expressed at lower levels in the mid-gestation embryo and placenta. The major testicular transcripts are 2.3 and 2.6 kb. A 4.0 kb transcript was detected at lower levels in the testis as well as in embryo and placenta. Northern blot and in situ hybridization analysis revealed that expression of Zfp-37 was most abundant in germ cells which have completed meiosis and are undergoing the complex morphogenetic changes of spermiogenesis. The pattern of expression of Zfp-37 and the presence of the zinc finger domain suggest that Zfp-37 may have a role in regulating spermiogenesis.
Full text
PDF


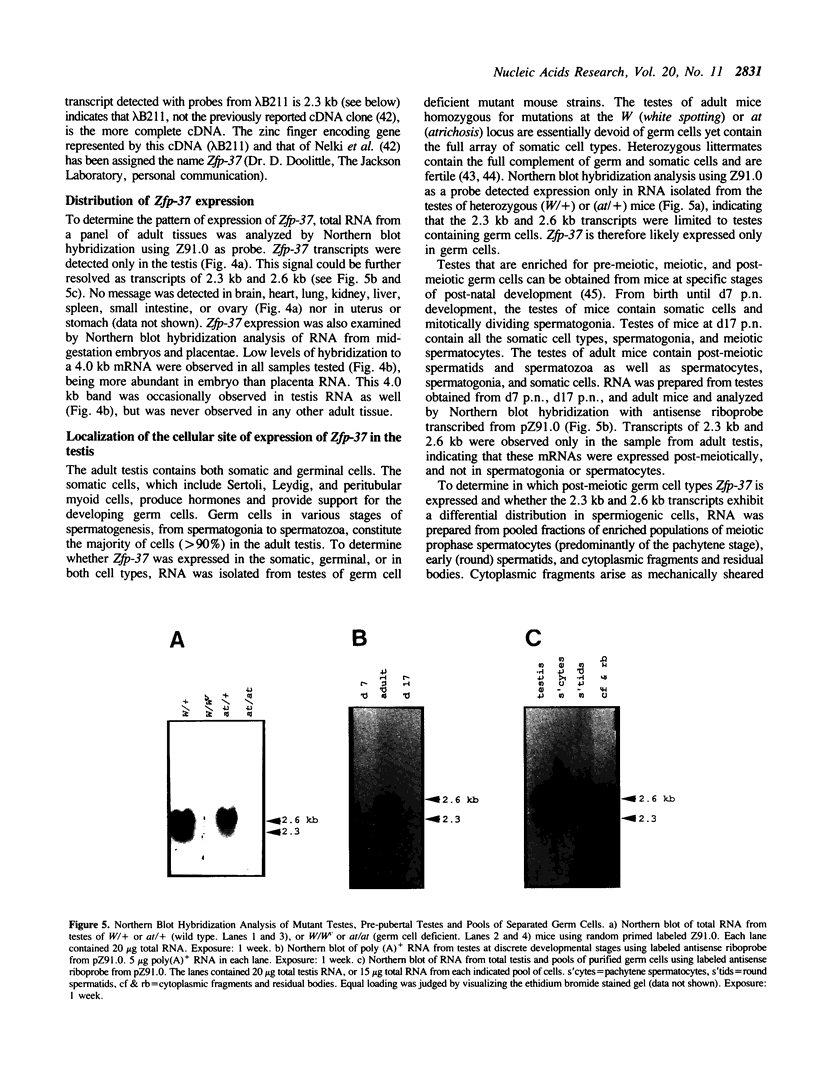
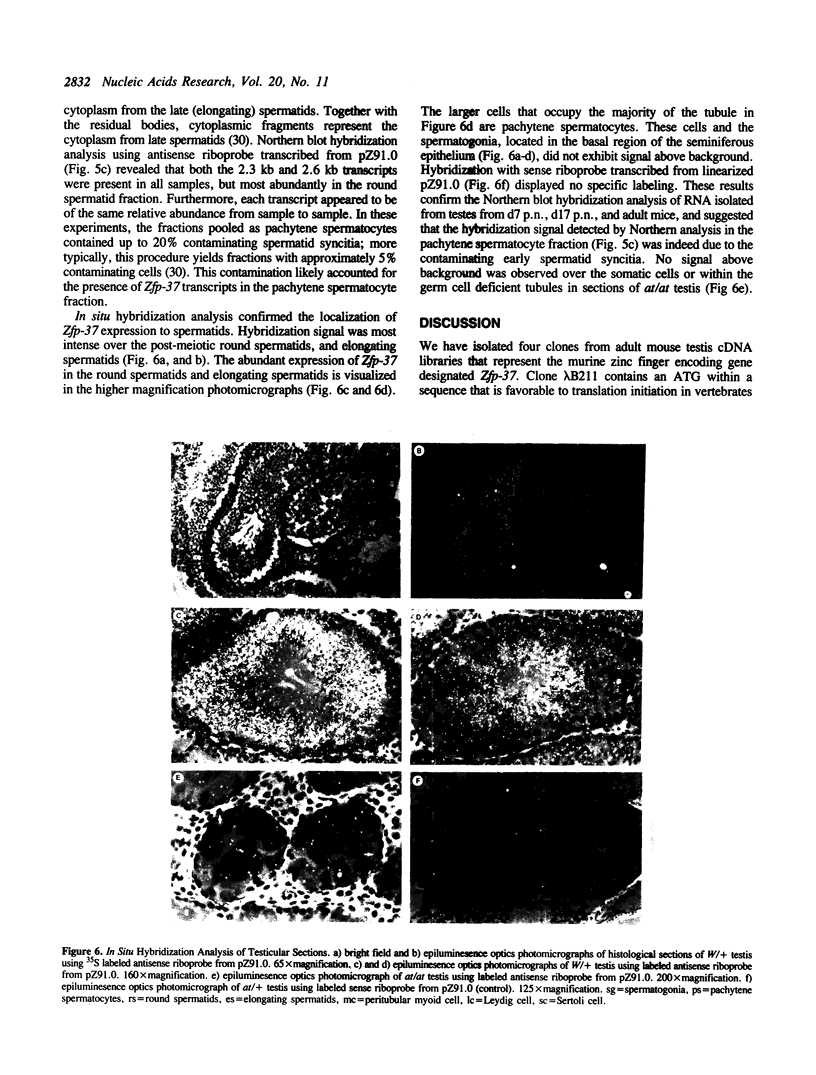


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellvé A. R., Cavicchia J. C., Millette C. F., O'Brien D. A., Bhatnagar Y. M., Dym M. Spermatogenic cells of the prepuberal mouse. Isolation and morphological characterization. J Cell Biol. 1977 Jul;74(1):68–85. doi: 10.1083/jcb.74.1.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. S., Sander C., Argos P. The primary structure of transcription factor TFIIIA has 12 consecutive repeats. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jul 8;186(2):271–274. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80723-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cathala G., Savouret J. F., Mendez B., West B. L., Karin M., Martial J. A., Baxter J. D. A method for isolation of intact, translationally active ribonucleic acid. DNA. 1983;2(4):329–335. doi: 10.1089/dna.1983.2.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavrier P., Lemaire P., Revelant O., Bravo R., Charnay P. Characterization of a mouse multigene family that encodes zinc finger structures. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1319–1326. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavrier P., Vesque C., Galliot B., Vigneron M., Dollé P., Duboule D., Charnay P. The segment-specific gene Krox-20 encodes a transcription factor with binding sites in the promoter region of the Hox-1.4 gene. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1209–1218. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08228.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavrier P., Zerial M., Lemaire P., Almendral J., Bravo R., Charnay P. A gene encoding a protein with zinc fingers is activated during G0/G1 transition in cultured cells. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):29–35. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02780.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury K., Dietrich S., Balling R., Guenet J. L., Gruss P. Structure, expression and chromosomal localization of Zfp-1, a murine zinc finger protein gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 25;17(24):10427–10438. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.24.10427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury K., Rohdewohld H., Gruss P. Specific and ubiquitous expression of different Zn finger protein genes in the mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 11;16(21):9995–10011. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.21.9995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conti M., Geremia R., Monesi V. Adenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate dependent protein kinase activity in differentiating germ cells of the mouse testis. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1979 Feb;13(2):137–148. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(79)90014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox K. H., DeLeon D. V., Angerer L. M., Angerer R. C. Detection of mrnas in sea urchin embryos by in situ hybridization using asymmetric RNA probes. Dev Biol. 1984 Feb;101(2):485–502. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90162-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunliffe V., Koopman P., McLaren A., Trowsdale J. A mouse zinc finger gene which is transiently expressed during spermatogenesis. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):197–205. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08096.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denny P., Ashworth A. A zinc finger protein-encoding gene expressed in the post-meiotic phase of spermatogenesis. Gene. 1991 Oct 15;106(2):221–227. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90202-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M., Hollenberg S. M. Zinc fingers: gilt by association. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90522-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairall L., Rhodes D., Klug A. Mapping of the sites of protection on a 5 S RNA gene by the Xenopus transcription factor IIIA. A model for the interaction. J Mol Biol. 1986 Dec 5;192(3):577–591. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90278-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehring W. J. Homeo boxes in the study of development. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1245–1252. doi: 10.1126/science.2884726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe L., Jeannotte L., Bikoff E. K., Robertson E. J. Analysis of beta 2-microglobulin gene expression in the developing mouse embryo and placenta. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 15;145(10):3474–3482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennelly P. J., Krebs E. G. Consensus sequences as substrate specificity determinants for protein kinases and protein phosphatases. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15555–15558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klevit R. E. Recognition of DNA by Cys2,His2 zinc fingers. Science. 1991 Sep 20;253(5026):1367–1393. doi: 10.1126/science.1896847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koopman P., Gubbay J., Collignon J., Lovell-Badge R. Zfy gene expression patterns are not compatible with a primary role in mouse sex determination. Nature. 1989 Dec 21;342(6252):940–942. doi: 10.1038/342940a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krumlauf R., Holland P. W., McVey J. H., Hogan B. L. Developmental and spatial patterns of expression of the mouse homeobox gene, Hox 2.1. Development. 1987 Apr;99(4):603–617. doi: 10.1242/dev.99.4.603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langan T. A., Gautier J., Lohka M., Hollingsworth R., Moreno S., Nurse P., Maller J., Sclafani R. A. Mammalian growth-associated H1 histone kinase: a homolog of cdc2+/CDC28 protein kinases controlling mitotic entry in yeast and frog cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3860–3868. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. S., Gippert G. P., Soman K. V., Case D. A., Wright P. E. Three-dimensional solution structure of a single zinc finger DNA-binding domain. Science. 1989 Aug 11;245(4918):635–637. doi: 10.1126/science.2503871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann R., Nüsslein-Volhard C. hunchback, a gene required for segmentation of an anterior and posterior region of the Drosophila embryo. Dev Biol. 1987 Feb;119(2):402–417. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90045-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MINTZ B., RUSSELL E. S. Gene-induced embryological modifications of primordial germ cells in the mouse. J Exp Zool. 1957 Mar;134(2):207–237. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401340202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mardon G., Page D. C. The sex-determining region of the mouse Y chromosome encodes a protein with a highly acidic domain and 13 zinc fingers. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):765–770. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90680-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijer D., Hermans A., von Lindern M., van Agthoven T., de Klein A., Mackenbach P., Grootegoed A., Talarico D., Della Valle G., Grosveld G. Molecular characterization of the testis specific c-abl mRNA in mouse. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4041–4048. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02749.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., McLachlan A. D., Klug A. Repetitive zinc-binding domains in the protein transcription factor IIIA from Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1609–1614. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muriel W. J., Cole J., Lehmann A. R. Molecular analysis of ouabain-resistant mutants of the mouse lymphoma cell line L5178Y. Mutagenesis. 1987 Sep;2(5):383–389. doi: 10.1093/mutage/2.5.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mével-Ninio M., Terracol R., Kafatos F. C. The ovo gene of Drosophila encodes a zinc finger protein required for female germ line development. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2259–2266. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07762.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagamine C. M., Chan K., Hake L. E., Lau Y. F. The two candidate testis-determining Y genes (Zfy-1 and Zfy-2) are differentially expressed in fetal and adult mouse tissues. Genes Dev. 1990 Jan;4(1):63–74. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.1.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nardelli J., Gibson T. J., Vesque C., Charnay P. Base sequence discrimination by zinc-finger DNA-binding domains. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):175–178. doi: 10.1038/349175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelki D., Dudley K., Cunningham P., Akhavan M. Cloning and sequencing of a zinc finger cDNA expressed in mouse testis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 25;18(12):3655–3655. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.12.3655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Protein-DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:293–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavletich N. P., Pabo C. O. Zinc finger-DNA recognition: crystal structure of a Zif268-DNA complex at 2.1 A. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):809–817. doi: 10.1126/science.2028256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pustell J. M. Interactive molecular biology computing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 11;16(5):1813–1820. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.1813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers M. B., Hosler B. A., Gudas L. J. Specific expression of a retinoic acid-regulated, zinc-finger gene, Rex-1, in preimplantation embryos, trophoblast and spermatocytes. Development. 1991 Nov;113(3):815–824. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.3.815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz i Altaba A., Perry-O'Keefe H., Melton D. A. Xfin: an embryonic gene encoding a multifingered protein in Xenopus. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3065–3070. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02613.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenoy S., Choi J. K., Bagrodia S., Copeland T. D., Maller J. L., Shalloway D. Purified maturation promoting factor phosphorylates pp60c-src at the sites phosphorylated during fibroblast mitosis. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):763–774. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90791-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigler P. B. Transcriptional activation. Acid blobs and negative noodles. Nature. 1988 May 19;333(6170):210–212. doi: 10.1038/333210a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. R., Jackson I. J., Brown D. D. Domains of the positive transcription factor specific for the Xenopus 5S RNA gene. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):645–652. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90396-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent A., Colot H. V., Rosbash M. Sequence and structure of the serendipity locus of Drosophila melanogaster. A densely transcribed region including a blastoderm-specific gene. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 5;186(1):149–166. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90265-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieschaus E., Nusslein-Volhard C., Kluding H. Krüppel, a gene whose activity is required early in the zygotic genome for normal embryonic segmentation. Dev Biol. 1984 Jul;104(1):172–186. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90046-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson D. G., Bhatt S., Chavrier P., Bravo R., Charnay P. Segment-specific expression of a zinc-finger gene in the developing nervous system of the mouse. Nature. 1989 Feb 2;337(6206):461–464. doi: 10.1038/337461a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolgemuth D. J., Gizang-Ginsberg E., Engelmyer E., Gavin B. J., Ponzetto C. Separation of mouse testis cells on a Celsep (TM) apparatus and their usefulness as a source of high molecular weight DNA or RNA. Gamete Res. 1985;12:1–10. doi: 10.1002/mrd.1120120102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yelick P. C., Kwon Y. H., Flynn J. F., Borzorgzadeh A., Kleene K. C., Hecht N. B. Mouse transition protein 1 is translationally regulated during the postmeiotic stages of spermatogenesis. Mol Reprod Dev. 1989;1(3):193–200. doi: 10.1002/mrd.1080010307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]