Abstract
Experience-dependent plasticity is closely linked with the development of sensory function. Beyond this sensitive period, developmental plasticity is actively limited; however, new studies provide growing evidence for plasticity in the adult visual system. The amblyopic visual system is an excellent model for examining the “brakes” that limit recovery of function beyond the critical period. While amblyopia can often be reversed when treated early, conventional treatment is generally not undertaken in older children and adults. However new clinical and experimental studies in both animals and humans provide evidence for neural plasticity beyond the critical period. The results suggest that perceptual learning and video game play may be effective in improving a range of visual performance measures and importantly the improvements may transfer to better visual acuity and stereopsis. These findings, along with the results of new clinical trials, suggest that it might be time to re-consider our notions about neural plasticity in amblyopia.
Keywords: amblyopia, stereopsis, perceptual learning, plasticity, video-game play
Amblyopia (from the Greek, amblyos – blunt; opia – vision) is a developmental abnormality that results from physiological alterations in the visual cortex and impairs form vision1. Amblyopia is clinically important because, aside from refractive error, it is the most frequent cause of vision loss in infants and young children, occurring naturally in about 2–4 percent of the population; and it is of basic interest because it reflects the neural impairment which can occur when normal visual development is disrupted. The damage produced by amblyopia is generally expressed in the clinical setting as a loss of visual acuity in an apparently healthy eye, despite appropriate optical correction; however, there is a great deal of evidence showing that amblyopia results in a broad range of neural, perceptual, oculomotor and clinical abnormalities (for reviews see Refs. 2 and 3).
Amblyopia can be reversed or eliminated when diagnosed and treated early in life. Thus, there is a premium on early detection of amblyopia and its risk factors. It has been estimated that as many as three quarters of a million preschoolers are at risk for amblyopia in the United States, and roughly half of those may not be detected before school age. Moreover, detection is likely to be more delayed in low socio-economic areas. Improved vision screening and access to treatment could, in principle, eliminate amblyopia as a public health issue4.
There has been a sea-change in our thinking about amblyopia in the last decade based on a new understanding of the underlying patho-physiology (based in part on new brain-imaging methods such as functional MRI), and a massive shift in our thinking about adult plasticity and the treatment of amblyopia fueled by a number of important clinical trials, and by new rodent models of amblyopia5,6.
Critical Periods in Perceptual Development
Critical periods for experience-dependent plasticity are ubiquitous. They occur in virtually every species, from Drosophila to human7 and for a wide range of sensory functions. Hubel & Wiesel’s Nobel prize winning work showing the importance of sensory experience in shaping neural connections during a critical period early in life, was inspired, in large measure by the eighteenth century notion that early visual deprivation (e.g. blindness at birth) resulted in brain changes that led in turn to defective visual perception8. Based in good measure on the work of Hubel & Wiesel and subsequent anatomical and physiological studies, it is now clear that the visual cortex is by no means a Tabula Rasa, and there is a good deal of specification at birth9,10. However, it is also clear that there is an important role for maturation and experience11.
It is now clear that that there are different critical periods for different functions (even within the same sensory system12,13, different critical periods for different parts of the brain, even within different layers of the primary visual cortex14, and different critical periods for recovery than for induction of sensory deprivation7.
It has long been held that there is a close correspondence between sensory development and the critical period (e.g. Ref 15), and the idea that experience-dependent plasticity is closely linked with the development of sensory function is still widely held7. However, as we shall discuss later, there is also growing evidence for plasticity in the adult nervous system.
Critical Periods and Neural Plasticity in Human Vision
Much of the evidence for critical periods stems from work on the effects of altered sensory input in cat and monkey, in particular, monocular visual deprivation, strabismus or unequal refractive error8,16. If the sensory deprivation occurs early, the animal is left with a permanent visual impairment - amblyopia - and with permanent alterations in primary visual cortex.
In humans, amblyopia occurs naturally in about 2–4 percent of the population1 and the presence of amblyopia is almost always associated with an early history of abnormal visual experience: binocular misregistration (strabismus), image degradation (high refractive error, anisometropia), or form deprivation (cataract). The severity of the amblyopia appears to be associated with the degree of imbalance between the two eyes (e.g. dense unilateral cataract results in severe loss), and the age at which the amblyogenic factor occurred. Precisely how these factors interact is as yet unknown, but it is now clear that different early visual experiences result in different functional losses in amblyopia17,18. A significant factor that distinguishes performance among amblyopes is the presence or absence of binocular function17.
Clinicians are well aware that amblyopia does not develop after age 6 to 8 years of age19,20 suggesting that there is a “sensitive period” for the development of amblyopia. Psychophysical studies of interocular transfer in humans with a history of strabismus21,22 provide an indirect estimate of the period of susceptibility of binocular connections. The results of both studies suggest that binocular connections are highly vulnerable during the first 18 months of life, and remain susceptible to the effects of strabismus until at least age 7 years.
Is There a Critical Period for Treatment of Amblyopia?
The notion that there is a critical period (or periods) for the development of amblyopia, has often been taken to indicate that there is also a critical period for the treatment of amblyopia. This concept grew out of the work of Claude Worth19. Worth suggested that the presence of a “sensory obstacle” (e.g., unilateral strabismus) arrested the development of visual acuity (“amblyopia of arrest”), so that the patient’s acuity remained fixed at the level achieved at the time of onset of strabismus. In this view, the depth of amblyopia is a direct function of the age of onset of the “sensory obstacle”. Worth further suggested that if amblyopia of arrest were allowed to persist, that “amblyopia of extinction” could occur as a result of binocular inhibition. In Worth’s view, only this “extra” loss of sensory function (i.e., the amblyopia of extinction) could be recovered by treatment. Although this latter notion is open to question in the light of present knowledge, the ideas of Worth have had a powerful influence upon both clinicians and basic scientists. Thus, many of our currently held concepts of amblyopia, such as plasticity, sensitive periods, and abnormal binocular interaction, were already described more than a century ago, and gained currency with the work of Hubel & Wiesel23 and the many anatomical and physiological studies that followed. Thus, while amblyopia can often be reversed when treated early, treatment is generally not undertaken in older children and adults. This paper will review both experimental and clinical evidence for plasticity in the adult visual system that calls into question the notion of a critical period for treatment.
For centuries, the primary treatment for amblyopia has consisted of patching or penalizing the fellow preferred eye, thus “forcing” the brain to use the weaker amblyopic eye, but it is often assumed that amblyopia cannot be treated beyond a certain age (see Ref. 24 for a discussion). For example, in their review of randomized controlled clinical trials of patching and penalization, Wu & Hunter4 concluded that there is “no compelling evidence that treatment is beneficial for older (over age 10) children with amblyopia.” However a review of the literature suggests otherwise. For example, clinical trials suggest that treatment may be just as effective in older (13 to 17 years) patients who have not been previously treated as in younger (7 to 12 year old) children25. To date there have been no such clinical trials in adults with amblyopia.
Plasticity in adults with amblyopia is also evident in the report of amblyopic patients whose visual acuity spontaneously improved in the wake of visual loss due to macular degeneration or other forms of vision loss in the fellow (non-amblyopic) eye26,27. These studies are consistent with the notion that the connections from the amblyopic eye may be suppressed or inhibited rather than destroyed. Loss of the fellow eye would allow these existing connections to be unmasked, as occurs in adult cats with retinal lesions28.
Removing the “Brakes” on Brain Plasticity in Adults with Amblyopia
The evidence suggests that there is brain plasticity in adults; however, brain plasticity is more restricted in adulthood than during development. At a cellular and molecular level, adult brain plasticity is actively limited. Some of these “brakes” on plasticity are structural, such as peri-neuronal nets or myelin, which inhibit neurite outgrowth. Others are functional, acting directly upon the balance of excitation and inhibition within local neural circuits5. One way to non-invasively induce plasticity late in life is by regulating “functional” excitatory and inhibitory neuromodulators6. For example, manipulations that locally reduce inhibition (e.g. norepinephrine, acetylcholine, serotonin or dopamine) result in a more favorable excitatory-inhibitory (E/I) balance and increased plasticity29,30,31,32. Thus, approaches that alter the E/I balance may provide a way to re-activate plasticity in the mature amblyopic visual system. Indeed, other manipulations, including dark exposure, and enriched environments can alter the E/I balance and restore plasticity in animal models of amblyopia5,6,32. Below we describe two approaches to restoring brain plasticity in human adults with amblyopia: Perceptual Learning (PL) and video game play.
Perceptual Learning
Human adults are capable of improving performance on sensory tasks though repeated practice or perceptual learning (yes you can teach old dogs new tricks! – for a recent review see ref. 33), and this learning also has consequences in the cortex (Buonomano & Merzenich; 1998). Perceptual Learning was defined by Eleanor Gibson34 as “Any relatively permanent and consistent change in the perception of a stimulus array following practice or experience with this array …”. Over the last half-century or so, Perceptual Learning has been studied intensively. It has formed the basis of thousands of articles, chapters and books (a Google search results in over 1.2 million hits), and for several Special Issues of Vision Research. Indeed, an advertisement for the book Perceptual Learning35 states: “A familiar example is the treatment for a ‘lazy’ or crossed eye. Covering the good eye causes gradual improvement in the weaker eye’s cortical representations. If the good eye is patched too long, however, it learns to see less acutely.”
The focus here is on a rather narrower definition of perceptual learning – specifically, the notion that practicing visual tasks can lead to dramatic and long-lasting improvements in performing them, i.e., practice makes perfect! In adults with normal vision, practice can improve performance on a variety of visual tasks, and this learning can be quite specific (to the trained task, orientation, eye, etc.) 33,36.
The strong interest in visual learning stems from the possibility that the learning takes place in early stages of visual processing. Indeed the finding that learning with simple patterns shows non-transfer to different locations, different orientations or the untrained eye, has been taken as evidence that the learning might take place in early stages of processing, such as cortical area V1. However, non-transfer of learning, often thought to be early, can sometimes be explained by later mechanisms (downstream of V1)37, and the massive interconnectedness of cortex makes it difficult to separate early and late stages of processing. Moreover, recent work38–40 shows complete transfer of learning from one location or orientation to another, if the second location or orientation has been sensitized with an irrelevant stimulus and task. The complete transfer of perceptual learning to new retinal locations and orientations calls into question both location specificity as a key property of visual perceptual learning, and the assumption by many researchers that the retinotopic early visual cortex is the locus basis of perceptual learning. Rather it points to a crucial role for non-retinotopic higher brain areas that engage attention and decision making for perceptual learning41. This may have important implications for perceptual learning in amblyopia.
While amblyopia can often be reversed when treated early, conventional treatment (patching) is generally not undertaken in older children and adults. Moreover, patching itself may lead to a reduction in binocular vision and stereopsis, and to psycho-social problems such as a loss of self-esteem42. Thus, it is desirable to minimize the duration and extent of patching.
Perceptual Learning in Amblyopia
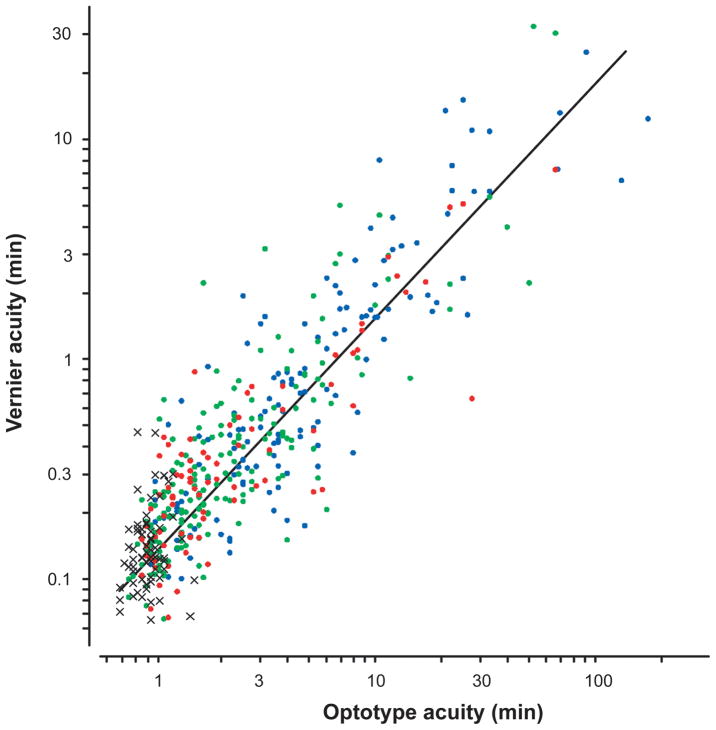
Our approach to improving vision in adult amblyopia is based on perceptual learning (PL). During PL, using only their amblyopic eye, patients are required to practice a challenging visual task. Our lab has mostly focused on training positional acuity because: i) the loss of position acuity in amblyopia is tightly coupled to the loss of Snellen acuity17,43,44 (Figure 1); ii) position acuity is thought to be limited by cortical (rather than retinal) processes; and iii) we have developed sensitive methods for measuring and modeling the deficit in position acuity45–48. In the following sections we ask whether it is possible to repair the amblyopic deficit through PL, and if so, how it occurs.
Figure 1.
Vernier acuity vs. Snellen acuity for the non-preferred eye for the entire sample of McKee, Levi and Movshon.17 The crosses show the normal observers. The dots show the amblyopic eyes of aniometropic (green), strabismic (blue) and mixed (i.e., both stabismic and anisometropic – red) subjects.
As noted above, in adults with normal vision, practice can improve performance on a variety of visual tasks, and this learning can be quite specific. The improvement in performance following practice is considered to be a form of neural plasticity. In our first studies of PL in amblyopia, we asked adults with amblyopia to perform a Vernier acuity task with their amblyopic eye repeatedly, with each observer completing 4000 to 5000 trials in which they judged the position of a “test” line relative to a “reference” line, and received feedback after each trial.
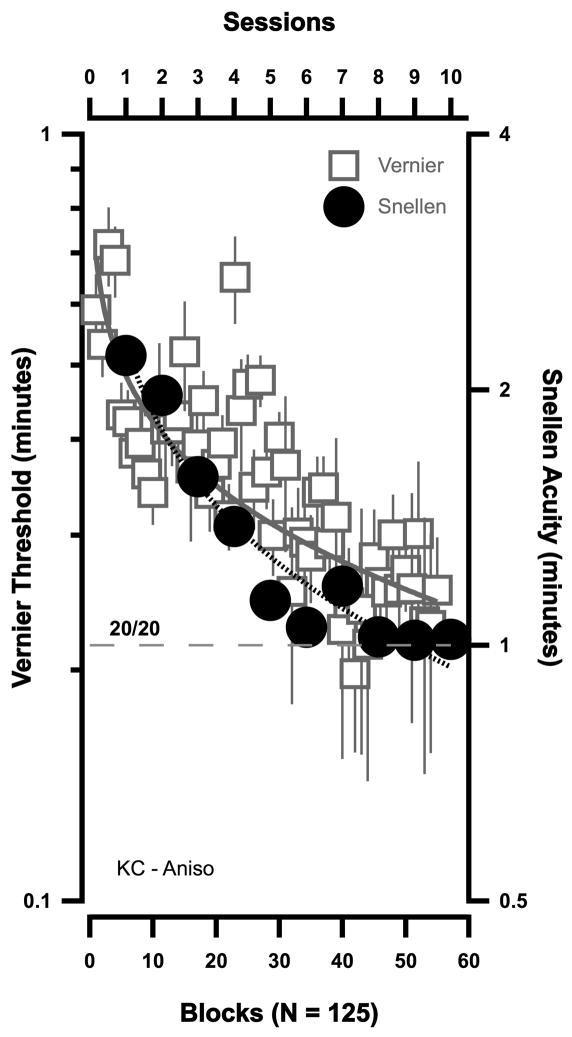
Adults with amblyopia also demonstrate substantial and significant perceptual learning of Vernier acuity49,50. All eleven observers in our original study showed significant improvement after practicing Vernier acuity at one orientation. The improvement was most marked at the trained orientation, with little improvement at the untrained orientation. In some (anisometropic amblyopes) there was substantial transfer to the untrained eye at the trained orientation - and much less transfer at the untrained orientation. In contrast to the marked improvement in the (trained) Vernier task, there was very little improvement in an untrained (line detection) task. Thus, perceptual learning in amblyopia is task specific; however, in that study, several observers also showed improvements in Snellen acuity that were comparable to their Vernier improvement. Both the Vernier (squares) and Snellen acuity (circles) results of one of these amblyopes is shown in Figure 2. For this observer, Snellen acuity reached 20/20 after practicing the Vernier task.
Figure 2.
The improvement in Vernier acuity (squares – left ordinate) and Snellen acuity (circles – right ordinate) in an anisometropic amblyope following PL; after Levi, Polat & Hu.50 Each Vernier threshold represents 125 trials.
Since our initial studies49,50, there have been more than twenty studies of PL in amblyopia published to date, involving more than 300 amblyopic subjects, as well as several recent review articles51,52,53,54. The extant studies cover a range of tasks including Vernier acuity, contrast detection, letter identification (both first and second-order), position discrimination, spatial frequency discrimination, grating acuity, letter acuity and motion coherence (see Table 1). Most of the approximately 300 amblyopic observers showed improvement in the trained task, although the amount of improvement varied substantially both between tasks and between individuals.
Table 1.
Previous Perceptual learning and videogame studies.
| Study | Ref | Task | N amblyopes | Age |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Levi et al. (1996; 1997) | 49, 50 | Vernier acuity | 6 | 19–53 (median 26) |
| 11 (6 from Ref 49) | ||||
| Polat et al. (2004) | 55 | Gabor detection (1.5 – 12 cpd) | 77 | 9–55 (mean 35) |
| Li & Levi (2004) | 45 | Position discrimination in noise | 7 | 20–55 (Mean 37) |
| Fronius et al. (2005; 2006) | 56,57 | Loss of Vision in Fellow eye + PL | 1 | 60 |
| Levi (2005) | 58 | Letter identification in noise | 4 | 19–28 (mean 23) |
| Li et al. (2005) | 46 | Position discrimination in noise | 5 – all previously patched | 7–10 (mean 8.5) |
| Zhou et al. (2006) | 59 | Contrast Detection | 14–27 (mean 19) | |
| Group I – SF near cutoff | 7 (aniso) | |||
| Group II - Full CSF | 10 (aniso) | |||
| Group III - No training | 6 (aniso) | |||
| Chung et al. (2006) | 60 | Identify contrast defined letters | 10 | 21–58 (median 27) |
| Li et al. (2007) | 47 | Position discrimination in noise | 2 | 9 and 12 |
| Huang et al. (2008) | 61 | Contrast detection SF near cutoff | 10 aniso (7 from Ref 59) | 15–22 (mean 18.6) |
| Chen et al. (2008) | 62 | Group 1: Gabor detection | 26 (aniso) | Mean 17.3 |
| Group 2: Patching | 27 (aniso) | Mean 13 | ||
| Chung et al. (2008) | 63 | 1. Identify luminance defined letters. | 11 | 15–58 (median 22) |
| 2. Identify contrast defined letters | 7/11 | |||
| Li et al. (2008) | 48 | Position discrimination in noise | 7 | 18–39 (median 23) |
| Polat et al. (2009) | 64 | Gabor detection (1.5 – 12 cpd) | 5 (patching failed/non-compliant) | 7–8 (mean 7.3) |
| Huang et al. (2009) | 65 | Contrast detection in noise | 10 | 18–25 (mean 21.1) |
| Astle et al. (2010) | 66 | Spatial frequency discrimination | 17 | 17–57 (mean 37) |
| Astle et al. (2011) | 67 | Group I – Letter acuity | 5 | 17–63 (mean 39) |
| Group II – Letter contrast | 10 | |||
| Group III – Grating acuity | 8 | |||
| Group IV – Grating contrast | 6 | |||
| Hess et al. (2010) | 68 | Motion coherence (dichoptic) | 9 | 24–49 (mean 39.7) |
| Hou et al. (2011) | 69 | Contrast detection | 9 | 14–34 (mean 22) |
| Liu et al. (2011) | 70 | Grating acuity | 10 previously patched (PT) | 8–17 (mean 11.6) |
| 13 not patched (NPT) | ||||
| Knox et al. (2012) | 71 | Motion coherence (dichoptic) | 14 | 5–14 (mean 8.5) |
| Li et al. (2011) | 72 | Videogame play | 20 | 15–61 (mean 31.4) |
| Hussain et al. (2011) | 73 | Flanked acuity | 10 | 17–70 (mean 39.5) |
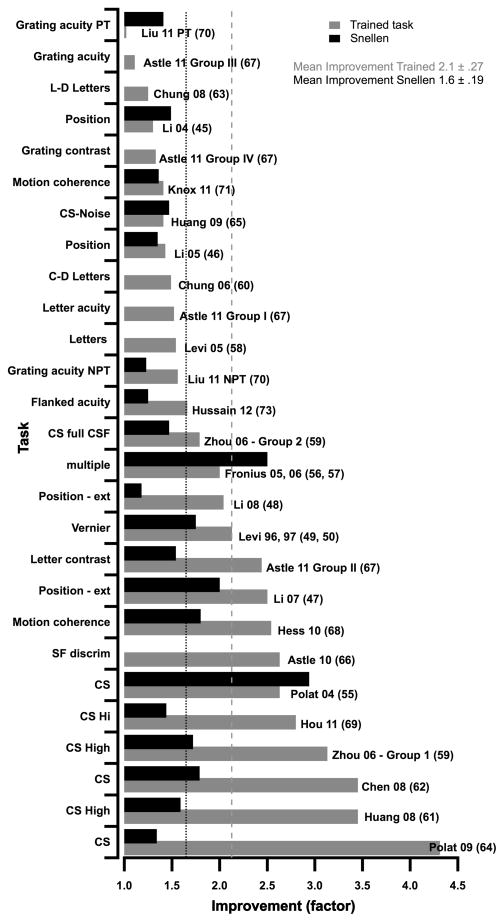
Figure 3 summarizes the main results of each of these studies by showing the improvement, expressed as a factor, on the trained task (gray bars) and in Snellen acuity (black bars). The results are ordered on the improvement on the trained task, from least (top) to most (bottom), and it is interesting to note that the ordering of the improvement in optotype acuity does not follow the ordering of the trained task very closely. The dotted lines show that, on average, the performance on the trained task improved by a factor of ≈2.1, while Snellen acuity improved by a factor of ≈1.6.
Figure 3.
The improvement in performance (expressed as a factor along the abscissa) following PL on different tasks from previous studies (ordinate). Improvement on the trained task is shown by the gray bars and in Snellen acuity by the black bars. The results are ordered on the improvement on the trained task, from least (top) to most (bottom).
Many of the studies summarized in Table 1 and Figure 3 were discussed in the review by Levi & Li51, so here I shall focus on the more recent studies, and new insights from this figure. One fairly obvious point is that contrast sensitivity tasks seem to have resulted in the greatest improvements (on the trained task) as evidenced by the 6 studies at the bottom of the graph (see also Ref 67). Indeed, the largest improvement was in a group of 5 children (mean age 7.3 years) who had undergone patching treatment but either failed to improve, or were non-compliant64. They practiced a contrast sensitivity task for, on average, 33 hours, and played a computer game between training blocks. The improvement, averaged across spatial frequencies was more than a factor of 4; however, there was little improvement at low spatial frequencies (where performance was nearly normal) and very substantial improvement at high spatial frequencies (almost a factor of 15 at 12 cpd).
At the other end of the scale, only one study failed to show any improvement on the trained task – Ref. 70 – Liu 11PT in Figure 3) in a group of juvenile amblyopes (mean age ≈ 12) who had been successfully patched for more than two years, and whose acuity had already improved by, on average more than a factor of three as a result of the patching. Given the success of the patching, one might expect little additional improvement from PL. Indeed, in general grating acuity tasks were less effective than many other tasks67. Surprisingly, despite the absence of improvement on the trained grating acuity task, Liu’s subjects showed a factor of 1.4 improvement in optotype acuity, and several also showed improved stereoacuity (discussed further below). Not evident from the average data in Figure 3 is the wide range of individual differences in PL within a given study, with some amblyopes showing little or no learning, and others showing very substantial improvement.
While most of the PL studies reviewed here involved monocular training (typically, with the non-amblyopic eye patched), two recent studies have used a dichoptic training task (motion coherence) in order to attempt to reduce suppression and enhance binocular interaction in adults68 and children 71. This training led to a substantial improvement (factor of ≈2.5) in adults with a concomitant improvement in acuity (factor of ≈1.8) as well as improvement in stereoacuity (discussed below). The improvement in children was smaller, but statistically significant, suggesting the promise of the PL approach in children. Ultimately, it will be important to determine which type of PL tasks (monocular or dichoptic; contrast sensitivity vs position acuity) are most successful in improving visual performance in adults and children with amblyopia, and to compare the outcome of PL to patching, which is still the gold standard.
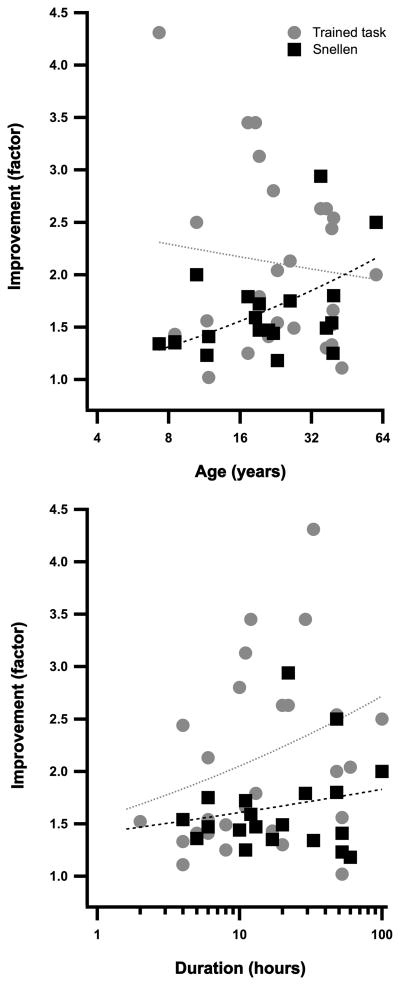
Interestingly, age appears to have little influence on the outcome of PL. For the trained task, there is a small, non-significant decrease in the amount of improvement with age (Fig 4 top panel, gray symbols and line). On the other hand, Snellen acuity appears to improve more with increasing age (Fig 4 top panel, black symbols) in that the slope of the best fitting power function (black line) is shallow but positive (0.25 ± 0.09). However, this may be simply due to the fact that the youngest subjects had the briefest duration of training, and may have the mildest amblyopia. As can be seen in Fig 4 (bottom panel), the effect of PL increases with duration. Not apparent from this figure is the relationship between the depth of amblyopia and the amount and duration of learning. The more severe the visual loss, the longer the time course required to obtain the maximal effect of PL, and the greater the benefit48,67. It should be noted that there have been no systematic studies of PL in amblyopia in very young children (less than 5 years old) when treatment might be expected to be most effective.
Figure 4.
The effect of age (top) and duration (bottom) on the improvement (trained task - gray; Snellen acuity – black) in performance following PL.
What is Learned in Perceptual Learning?
An important question is “what is learned during perceptual learning?” One approach to answering this question is to inject “noise” into the stimulus, and to ask how that influences performance. Our studies, using positional noise, show that practicing position discrimination reduces spatial distortion (internal positional noise) and enhances the ability to extract stimulus information efficiently in amblyopic vision45–48. The improved efficiency is a result of the amblyopic visual system learning to use the most salient stimulus information48. Through practice, observers learn to make better use of the most salient cues for accomplishing the task, and to ignore or down weight the less important stimulus information. In a similar vein, practicing identification of low contrast letters or gratings in noise improves the contrast threshold primarily through internal noise reduction and a more efficient use of the stimulus information58,65.
A Rationale for Perceptual Learning as an Adjunct to Patching
Occlusion (patching) is considered the “gold standard” method for treating childhood amblyopia. To date, there is no accepted treatment for adult amblyopia. In most PL studies, amblyopic subjects are occluded while performing the visual task, so it is reasonable to ask whether “active” PL provides an added benefit over occlusion alone. We have argued that PL does indeed provide an added benefit for the following reasons. First, in one study we found that PL improved both position discrimination and letter acuity in amblyopes who were not responsive to occlusion46, and similar findings have been reported for contrast sensitivity by Polat et al.64 Second, the dose response rate for occlusion (in children aged 6 to 8 years) is slow, with acuity in those 6–8 years old improving, on average, by a factor of ≈1.6 after about 240 hours of occlusion74. Our preliminary results suggest that occlusion plus PL may be more efficient than occlusion alone, by as much as a factor of 8– i.e. PL has a much faster time course than patching alone47. Thus combining occlusion with PL may be a useful method for obtaining the optimal treatment outcome in the shortest possible time. Eliminating or reducing the need to wear an eye patch in public would, at the very least, reduce the emotional stress that often accompanies occlusion75. We note that this approach is quite different from the (discredited) CAM approach, in which amblyopes passively viewed rotating gratings for 7 minutes a day76,77. In contrast, during PL observers are engaged in attending and making fine visual discriminations using their amblyopic eyes, under conditions where their visual system is “challenged”, thus the learning is “intensive” and “active”. Observers receive repeated exposure (up to 50 hours) to the same stimuli, and are given feedback. Thus we speculate that PL in amblyopia reflects the amblyopic brain learning to attend to and use the most salient or reliable information for the task when viewing with the amblyopic eye. This speculation is consistent with the improvement in efficiency45,48. It should be noted that during normal everyday life, an amblyopic patient wearing a patch may engage in fine visual discriminations without undertaking specific PL, and that may at least in part account for the success of patching. However, PL provides intensive, active, supervised visual experience with feedback, requiring attention and action using the amblyopic eye, and thus may be more efficient than simply relying on everyday experiences. However, there are two important limitations of PL: specificity and boredom.
The Curse of Specificity
The specificity of perceptual learning noted above poses some interesting issues. If the improvement following practice was solely limited to the trained stimulus, condition and task, then the type of plasticity documented here would have very limited (if any) therapeutic value for amblyopia, since amblyopia is defined primarily on the basis of reduced Snellen acuity. Importantly, perceptual learning has a broader spatial frequency bandwidth in amblyopia, than in normal vision61,66, and many tasks (Vernier acuity, position discrimination, contrast sensitivity and spatial frequency discrimination) appear to transfer, at least in part, to improvements in Snellen acuity51. In addition to visual acuity improvement, other degraded visual functions such as stereoacuity and visual counting sometimes improve as well45. Nonetheless, PL generally only partially transfers to Snellen acuity, perhaps because it is specific to the orientation of the trained stimulus45,49,50.
Playing Video Games
To date, perceptual learning has had limited impact on clinical practice, because of its limited transfer and the rather dull nature of the training, leading to boredom and compliance issues. Work by Shawn Green and Daphne Bavelier suggests that in normal vision, similar to PL, action video game playing reflects the brain learning to develop the best perceptual template for the task at hand78–81. In contrast to perceptual learning, action game play is extremely varied in its demands and rich in the set of visual experiences it offers. Thus, they suggest that the very act of action game playing seems to train the brain to learn, on the fly, how to make the best use of the available information in the display, independently of the specifics of this display allowing for the broad transfer of learning, and thus possible improvements in quality of life81.
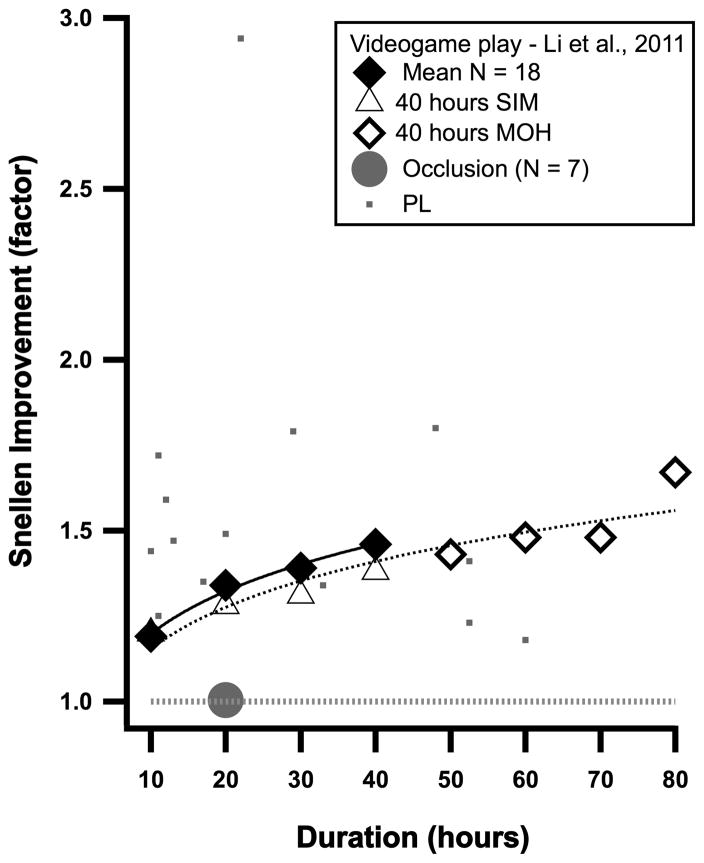
Does playing a video game result in improved performance in amblyopia? Li et al.72 (2011) asked adults (18–58 years old) with amblyopia to play an off-the-shelf action video-game (Medal of Honor: Pacific Assault) with their fellow eye patched. Acuity was measured after every 10 hours of game play for 40 hours. All observers showed improvements in visual acuity, from about 13 to 44%. For two amblyopes who were very mild to begin with, “after” play acuity improved to 20/20! Figure 5 shows the average improvement in Snellen acuity as a function of the duration of game playing in the 18 observers who completed the experiments (solid diamonds). Unlike normal subjects who do not improve after playing a non-action game (Tetris)78, amblyopic observers also improve when playing a non-action game (SIM City – triangles in Figure 5) for 40 hours, and may continue to improve when switched to an action game (Medal of Honor) for another 40 hours (open diamonds in Figure 5). It is interesting that the improvement in visual acuity with video game play seems to parallel that for PL (small squares), although it is lower than the most effective PL results. It is also noteworthy that the improvement may not have reached a plateau even after 80 hours of video game play.
Figure 5.
The improvement in Snellen acuity in the amblyopic eye following videogame play (diamonds and triangles) or patching (gray circle); after Li et al.72 For comparison, the effect of PL over the same time course is shown (small squares from Figure 4).
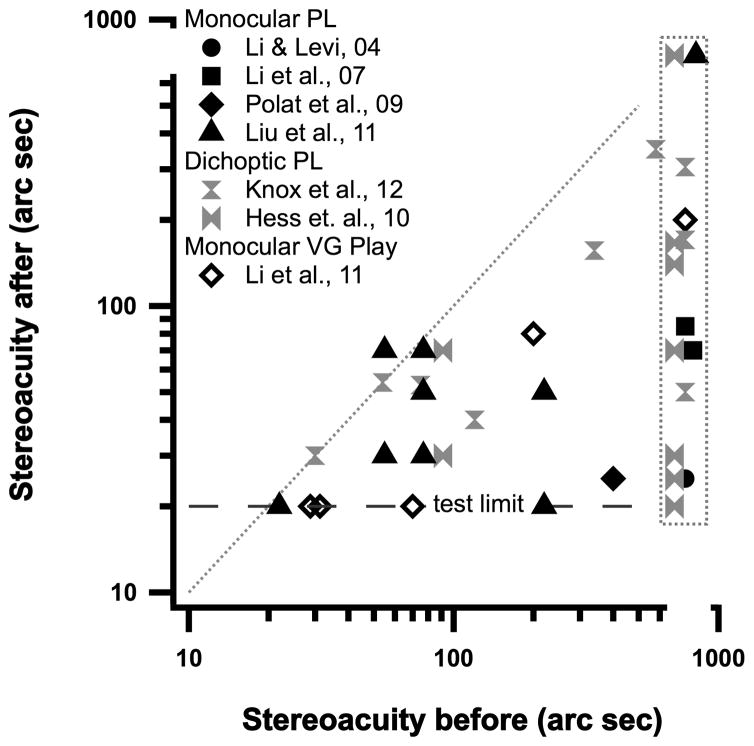
Other visual functions such as counting and Vernier acuity also improve following videogame play72. Importantly, 5 anisometropic amblyopes showed substantial improvement in stereoacuity after 40 hours of action video game play (Figure 6), 3 of them to 20 arc sec – the lower limit of this test. Similar improvements in stereopsis occur following monocular perceptual learning (Figure 6 – discussed further below).
Figure 6.
Stereoacuity before (abscissa) and after PL (monocular PL shown by solid black symbols; dichoptic PL by gray symbols) or Video game play (open diamond).
Because the amblyopes played with their fellow eye patched, one might wonder whether the improvement was simply due to the patching. To test this, Li et al. 72, had 7 adult amblyopes wear a patch over their non-amblyopic eye for 20 hours prior to starting the action videogames, with no improvement in visual acuity after 20 hours of patching (gray circle in Figure 5).
The idea of using a computer game to enhance visual skills in amblyopia is far from new. There are several computer-based programs that are now being offered and branded as “good for vision”. However, there is a paucity of evidence-based research to support the use of one over another. The games that Li et al., 72 used are entertainment videogames. Why use entertainment games that were not developed for clinical applications when computer games specially designed for vision training are readily available? There are two key differences between entertainment video games and games developed for clinical purposes. First, games developed for clinical purposes often mirror the type of psychophysical tasks that are typically used in vision laboratories (reading letters, looking for a geometric shape among other geometric shapes, etc.). In doing so they provide the player with a set of rather specific visual tasks. In contrast, entertainment videogames are designed to give the player a fully integrated experience in a very rich yet learnable environment. Games developers know that successful games are challenging, yet allow the player to progress. Second, a key to a successful video game is a good script which enables players to reach goals, unlock mysteries, discover new lands, etc. This aspect of game play is seldom present in games developed for clinical purposes; yet it is likely to be important in the arousal and reward players seek in the video game experience.
Action game play enhances not only early aspects of normal vision but also visuo-spatial selective attention, aspects of visual short-term memory, and the ability to select a target in an ever-changing stream of stimuli78–81. These enhanced capacities might also benefit amblyopes who not only suffer from low-level vision problems, but also exhibit higher-level vision deficits2,3. By capitalizing on the “fun” factor, action video game play provides the ideal training tool by fostering deliberate practice. Videogame play is popular in part because it is an arousing and extremely rewarding activity (after all people are ready to pay for these games because they like playing – not because they believe it may be good for them). These games may therefore trigger the appropriate milieu that fosters brain plasticity4. Indeed, the literature suggests that neuromodulators associated with arousal and reward (Ach and Dopamine) may foster brain plasticity5,6,32. Although more data are needed on this topic, playing a simple action video game (shooting cartoon tanks) is associated with significant release of dopamine82. This does not mean that amblyopes have to play action games to benefit from playing. Indeed, persons with degraded vision due to amblyopia, can also benefit from non-action video games72. Finally, and probably related to these last points, the issue of compliance with the training regimen, which is so thorny for more standard training methods, is much alleviated with an activity as engrossing as video games83.
Our current studies, in collaboration with Daphne Bavelier, at the University of Rochester and Jessica Bayliss at Rochester Institute of Technology, combine both the highly motivating aspects of playing videogames, with the efficient (but boring) aspects of PL. Specifically, we have developed an action videogame, played under dichoptic conditions to reduce suppression (inhibition) and promote fusion and stereopsis, and have embedded a psychophysical resolution task within the game, enabling a more targeted approach and allowing us to track changes in visual performance during play. A video clip of this can be seen at: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=71RML96XxCI
Recovery of Stereopsis
PL has generally been aimed at improving visual acuity and visual performance of the amblyopic eye. However, as noted above, for some amblyopes (mostly anisometropes) improvement in stereopsis comes for “free”, either as a consequence of the improved acuity and/or contrast sensitivity47,64,72 or because PL (and the attendant improvement in function) alters the excitatory/inhibitory (E/I) balance between the two eyes. Figure 6 (black solid symbols) show stereoacuity before and after monocular PL for individual amblyopes in four different studies. Points below the gray equality line indicate improved stereopsis, in some cases from no measurable stereopsis before training (points inside the gray vertical rectangle). The open diamonds show a similar improvement in stereopsis in 5 anisometropic amblyopes following monocular video game play72. For comparison, the gray symbols show the results of dichoptic PL, aimed at reducing suppression68,71 and altering the excitatory/inhibitory balance between the two eyes. Figure 6 suggests that both monocular and dichoptic training may be effective in improving stereopsis in some amblyopes.
It is possible to improve stereopsis in adults with abnormal binocular visual experience through visual training84 or perceptual learning of stereopsis per se. For example, Nakatsuka et al.85, reported that adult monkeys reared with prisms had mild stereo deficiencies that improved through PL after 10,000 – 20,000 trials. More recently, Ding & Levi86 provided the first evidence for the recovery of stereopsis through perceptual learning in human adults long deprived of normal binocular vision. They used a novel training paradigm that combined monocular cues that were perfectly correlated with the disparity cues. Following PL (thousands of trials) with stereoscopic gratings, adults who were initially stereoblind or stereoanomalous showed substantial recovery of stereopsis. Importantly, these subjects reported that depth “popped out” in real life, and they were able to enjoy 3-D movies for the first time. Their recovered stereopsis is based on perceiving depth by detecting binocular disparity, but has reduced resolution and precision. A recent case report documented similar improvements in two anisometropic adults who had undergone monocular PL followed by stereo training87.
Beyond Perceptual Learning – Resetting the Excitatory-inhibitory (E/I) Balance
Although much of the original work on critical periods was done in cat and monkey, recent work in rodents, where genetic manipulations are possible and the lifespan is brief, have provided a number of new insights into the mechanisms of plasticity and the potential for recovery in adults5,6,32. For example, chronic administration of the antidepressant Fluoxetine (Prozac) reduces intracortical inhibition and increases expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (bdnf) in adult rats that had been monocularly deprived during the critical period88. Most importantly, Fluoxetine also restored visual acuity in these “amblyopic” adult rats. Other rodent studies suggest that reverse suture coupled with environmental enrichment89, or 10 days of dark exposure90 all result in substantial recovery of visual acuity in adult rodents5. All of these manipulations locally reduce inhibition thus resetting the E/I balance and restoring a heightened level of plasticity5,6,32. Our working hypothesis is that PL and video game play may operate to improve the vision in adults with amblyopia through similar mechanisms.
A Caveat
Over the centuries, there have been many attempts to increase the effectiveness of treatment for amblyopia. These attempts include: subcutaneous injection of strychnine, electrical stimulation of the retina and optic nerve, flashing lights and red filters (reviewed in Ref 91), rotating gratings76,77, administration of Levodopa/Carbidopa92,93, and shocks to the brain via Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation94. Few have been subjected to rigorous scrutiny, and those that were often failed to stand up to it. Thus, any “promising” new method should be examined critically and there is a clear need for careful controlled randomized clinical trials.
SUMMARY & CONCLUSIONS
Amblyopia is, aside from refractive error, the most common cause of visual loss in children. Thus amblyopia is a serious public health issue. When diagnosed and treated early, the visual losses may be reversed. With early detection and treatment, amblyopia could conceivably be eliminated. Treatment for amblyopia is generally only undertaken in children, however as discussed above, there is now considerable evidence that PL and video game play may also be effective in improving vision in adults with amblyopia. These findings, along with the results of new clinical trials, suggest that it might be possible to remove the brakes on plasticity in the adult amblyopic visual system.
Acknowledgments
I am so grateful to the American Academy of Optometry, and my friends and colleagues who nominated me, for honoring me with the Charles F. Prentice Medal. This would not have been possible without the support of many friends and colleagues over the years. My mentor and long-time friend Ron Harwerth taught me the joy of research and the thrill of discovery. Roger Li, my partner in this research over the last 12 years or so has made very significant contributions to all aspects of the work, and Stan Klein, my long-time collaborator always showed me another way to look at things. I am fortunate to have collaborated with wonderful colleagues, post docs, students and visiting scholars, both in Berkeley and Houston, who have contributed to the lab.
I thank Roger Li for insightful comments on an earlier version of this paper.
This work was supported by grants from the National Eye Institute, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD (R01EY01728 and R01EY020976).
References
- 1.Ciuffreda KJ, Levi DM, Selenow A. Amblyopia: Basic and Clinical Aspects. Boston: Butterworth-Heinemann; 1991. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kiorpes L. Visual processing in amblyopia: animal studies. Strabismus. 2006;14:3–10. doi: 10.1080/09273970500536193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Levi DM. Visual processing in amblyopia: human studies. Strabismus. 2006;14:11–9. doi: 10.1080/09273970500536243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Wu C, Hunter DG. Amblyopia: diagnostic and therapeutic options. Am J Ophthalmol. 2006;141:175–84. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2005.07.060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Morishita H, Hensch TK. Critical period revisited: impact on vision. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2008;18:101–7. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2008.05.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bavelier D, Levi DM, Li RW, Dan Y, Hensch TK. Removing brakes on adult brain plasticity: from molecular to behavioral interventions. J Neurosci. 2010;30:14964–71. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4812-10.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Berardi N, Pizzorusso T, Maffei L. Critical periods during sensory development. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2000;10:138–45. doi: 10.1016/s0959-4388(99)00047-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Wiesel TN. Postnatal development of the visual cortex and the influence of environment. Nature. 1982;299:583–91. doi: 10.1038/299583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Horton JC, Hocking DR. An adult-like pattern of ocular dominance columns in striate cortex of newborn monkeys prior to visual experience. J Neurosci. 1996;16:1791–807. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-05-01791.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Chino YM, Smith EL, 3rd, Hatta S, Cheng H. Postnatal development of binocular disparity sensitivity in neurons of the primate visual cortex. J Neurosci. 1997;17:296–307. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-01-00296.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Maruko I, Zhang B, Tao X, Tong J, Smith EL, 3rd, Chino YM. Postnatal development of disparity sensitivity in visual area 2 (v2) of macaque monkeys. J Neurophysiol. 2008;100:2486–95. doi: 10.1152/jn.90397.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Harwerth RS, Smith EL, 3rd, Duncan GC, Crawford ML, von Noorden GK. Multiple sensitive periods in the development of the primate visual system. Science. 1986;232:235–8. doi: 10.1126/science.3952507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Harwerth RS, Smith EL, 3rd, Crawford ML, von Noorden GK. Behavioral studies of the sensitive periods of development of visual functions in monkeys. Behav Brain Res. 1990;41:179–98. doi: 10.1016/0166-4328(90)90107-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.LeVay S, Wiesel TN, Hubel DH. The development of ocular dominance columns in normal and visually deprived monkeys. J Comp Neurol. 1980;191:1–51. doi: 10.1002/cne.901910102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Teller DY, Movshon JA. Visual development. Vision Res. 1986;26:1483–506. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(86)90169-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Mitchell DE. The effects of early forms of visual deprivation on perception. In: Chalupa LM, Werner JS, editors. The Visual Neurosciences. Vol. 1. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press; 2004. pp. 189–204. [Google Scholar]
- 17.McKee SP, Levi DM, Movshon JA. The pattern of visual deficits in amblyopia. J Vis. 2003;3:380–405. doi: 10.1167/3.5.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Levi DM, McKee SP, Movshon JA. Visual deficits in anisometropia. Vision Res. 2011;51:48–57. doi: 10.1016/j.visres.2010.09.029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Worth CA. Squint: Its Causes, Pathology and Treatment. Philadelphia: Blakiston; 1903. [Google Scholar]
- 20.von Noorden GK. New clinical aspects of stimulus deprivation amblyopia. Am J Ophthalmol. 1981;92:416–21. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(81)90534-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Banks MS, Aslin RN, Letson RD. Sensitive period for the development of human binocular vision. Science. 1975;190:675–7. doi: 10.1126/science.1188363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hohmann A, Creutzfeldt OD. Squint and the development of binocularity in humans. Nature. 1975;254:613–4. doi: 10.1038/254613a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hubel DH, Wiesel TN. The period of susceptibility to the physiological effects of unilateral eye closure in kittens. J Physiol. 1970;206:419–36. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Mintz-Hittner HA, Fernandez KM. Successful amblyopia therapy initiated after age 7 years: compliance cures. Arch Ophthalmol. 2000;118:1535–41. doi: 10.1001/archopht.118.11.1535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Scheiman MM, Hertle RW, Beck RW, Edwards AR, Birch E, Cotter SA, Crouch ER, Jr, Cruz OA, Davitt BV, Donahue S, Holmes JM, Lyon DW, Repka MX, Sala NA, Silbert DI, Suh DW, Tamkins SM the Pediatric Eye Disease Investigator Group. Randomized trial of treatment of amblyopia in children aged 7 to 17 years. Arch Ophthalmol. 2005;123:437–47. doi: 10.1001/archopht.123.4.437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.El Mallah MK, Chakravarthy U, Hart PM. Amblyopia: is visual loss permanent? Br J Ophthalmol. 2000;84:952–6. doi: 10.1136/bjo.84.9.952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Vereecken EP, Brabant P. Prognosis for vision in amblyopia after the loss of the good eye. Arch Ophthalmol. 1984;102:220–4. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1984.01040030170019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Chino YM, Kaas JH, Smith EL, 3rd, Langston AL, Cheng H. Rapid reorganization of cortical maps in adult cats following restricted deafferentation in retina. Vision Res. 1992;32:789–96. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(92)90021-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Morishita H, Miwa JM, Heintz N, Hensch TK. Lynx1, a cholinergic brake, limits plasticity in adult visual cortex. Science. 2010;330:1238–40. doi: 10.1126/science.1195320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Sugiyama S, Di Nardo AA, Aizawa S, Matsuo I, Volovitch M, Prochiantz A, Hensch TK. Experience-dependent transfer of Otx2 homeoprotein into the visual cortex activates postnatal plasticity. Cell. 2008;134:508–20. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.05.054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kasamatsu T. Adrenergic regulation of visuocortical plasticity: a role of the locus coeruleus system. Prog Brain Res. 1991;88:599–616. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)63837-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Baroncelli L, Maffei L, Sale A. New perspectives in amblyopia therapy on adults: a critical role for the excitatory/inhibitory balance. Front Cell Neurosci. 2011;5:25. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2011.00025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Sagi D. Perceptual learning in Vision Research. Vision Res. 2011;51:1552–66. doi: 10.1016/j.visres.2010.10.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Gibson EJ. Perceptual learning. Annu Rev Psychol. 1963;14:29–56. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ps.14.020163.000333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Fahle M, Poggio T. Perceptual Learning. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press; 2002. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Fahle M. Learning to tell apples from oranges. Trends Cogn Sci. 2005;9:455–7. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2005.07.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Mollon JD, Danilova MV. Three remarks on perceptual learning. Spat Vis. 1996;10:51–8. doi: 10.1163/156856896x00051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Xiao LQ, Zhang JY, Wang R, Klein SA, Levi DM, Yu C. Complete transfer of perceptual learning across retinal locations enabled by double training. Curr Biol. 2008;18:1922–6. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2008.10.030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Zhang JY, Zhang GL, Xiao LQ, Klein SA, Levi DM, Yu C. Rule-based learning explains visual perceptual learning and its specificity and transfer. J Neurosci. 2010;30:12323–8. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0704-10.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Wang R, Zhang JY, Klein SA, Levi DM, Yu C. Task relevancy and demand modulate double-training enabled transfer of perceptual learning. Vision Res. 2012;52 doi: 10.1016/j.visres.2011.07.019. in press. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Law CT, Gold JI. Reinforcement learning can account for associative and perceptual learning on a visual-decision task. Nat Neurosci. 2009;12:655–63. doi: 10.1038/nn.2304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Webber AL, Wood JM, Gole GA, Brown B. Effect of amblyopia on self-esteem in children. Optom Vis Sci. 2008;85:1074–81. doi: 10.1097/OPX.0b013e31818b9911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Levi DM, Klein S. Hyperacuity and amblyopia. Nature. 1982;298:268–70. doi: 10.1038/298268a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Levi DM, Klein SA. Vernier acuity, crowding and amblyopia. Vision Res. 1985;25:979–91. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(85)90208-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Li RW, Levi DM. Characterizing the mechanisms of improvement for position discrimination in adult amblyopia. J Vis. 2004;4:476–87. doi: 10.1167/4.6.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Li RW, Young KG, Hoenig P, Levi DM. Perceptual learning improves visual performance in juvenile amblyopia. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005;46:3161–8. doi: 10.1167/iovs.05-0286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Li RW, Provost A, Levi DM. Extended perceptual learning results in substantial recovery of positional acuity and visual acuity in juvenile amblyopia. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007;48:5046–51. doi: 10.1167/iovs.07-0324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Li RW, Klein SA, Levi DM. Prolonged perceptual learning of positional acuity in adult amblyopia: perceptual template retuning dynamics. J Neurosci. 2008;28:14223–9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4271-08.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Levi DM, Polat U. Neural plasticity in adults with amblyopia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996;93:6830–4. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.13.6830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Levi DM, Polat U, Hu YS. Improvement in Vernier acuity in adults with amblyopia. Practice makes better Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1997;38:1493–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Levi DM, Li RW. Perceptual learning as a potential treatment for amblyopia: a mini-review. Vision Res. 2009;49:2535–49. doi: 10.1016/j.visres.2009.02.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Levi DM, Li RW. Improving the performance of the amblyopic visual system. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2009;364:399–407. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2008.0203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Polat U. Restoration of underdeveloped cortical functions: evidence from treatment of adult amblyopia. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 2008;26:413–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Astle AT, Webb BS, McGraw PV. Can perceptual learning be used to treat amblyopia beyond the critical period of visual development? Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2011;31:564–73. doi: 10.1111/j.1475-1313.2011.00873.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Polat U, Ma-Naim T, Belkin M, Sagi D. Improving vision in adult amblyopia by perceptual learning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101:6692–7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0401200101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Fronius M, Cirina L, Cordey A, Ohrloff C. Visual improvement during psychophysical training in an adult amblyopic eye following visual loss in the contralateral eye. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2005;243:278–80. doi: 10.1007/s00417-004-1014-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Fronius M, Cirina L, Kuhli C, Cordey A, Ohrloff C. Training the adult amblyopic eye with “perceptual learning” after vision loss in the non-amblyopic eye. Strabismus. 2006;14:75–9. doi: 10.1080/09273970600701077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Levi DM. Perceptual learning in adults with amblyopia: a reevaluation of critical periods in human vision. Dev Psychobiol. 2005;46:222–32. doi: 10.1002/dev.20050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Zhou Y, Huang C, Xu P, Tao L, Qiu Z, Li X, Lu ZL. Perceptual learning improves contrast sensitivity and visual acuity in adults with anisometropic amblyopia. Vision Res. 2006;46:739–50. doi: 10.1016/j.visres.2005.07.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Chung STL, Li RW, Levi DM. Identification of contrast-defined letters benefits from perceptual learning in adults with amblyopia. Vision Res. 2006;46:3853–61. doi: 10.1016/j.visres.2006.06.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Huang CB, Zhou Y, Lu ZL. Broad bandwidth of perceptual learning in the visual system of adults with anisometropic amblyopia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105:4068–73. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0800824105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Chen PL, Chen JT, Fu JJ, Chien KH, Lu DW. A pilot study of anisometropic amblyopia improved in adults and children by perceptual learning: an alternative treatment to patching. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2008;28:422–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1475-1313.2008.00588.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Chung STL, Li RW, Levi DM. Learning to identify near-threshold luminance-defined and contrast-defined letters in observers with amblyopia. Vision Res. 2008;48:2739–50. doi: 10.1016/j.visres.2008.09.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Polat U, Ma-Naim T, Spierer A. Treatment of children with amblyopia by perceptual learning. Vision Res. 2009;49:2599–603. doi: 10.1016/j.visres.2009.07.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Huang CB, Lu ZL, Zhou Y. Mechanisms underlying perceptual learning of contrast detection in adults with anisometropic amblyopia. J Vis. 2009;9:24, 1–14. doi: 10.1167/9.11.24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Astle AT, Webb BS, McGraw PV. Spatial frequency discrimination learning in normal and developmentally impaired human vision. Vision Res. 2010;50:2445–54. doi: 10.1016/j.visres.2010.09.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Astle AT, Webb BS, McGraw PV. The pattern of learned visual improvements in adult amblyopia. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011;52:7195–204. doi: 10.1167/iovs.11-7584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Hess RF, Mansouri B, Thompson B. A new binocular approach to the treatment of amblyopia in adults well beyond the critical period of visual development. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 2010;28:793–802. doi: 10.3233/RNN-2010-0550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Hou F, Huang CB, Tao L, Feng L, Zhou Y, Lu ZL. Training in contrast detection improves motion perception of sinewave gratings in amblyopia. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011;52:6501–10. doi: 10.1167/iovs.11-7541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Liu XY, Zhang T, Jia YL, Wang NL, Yu C. The therapeutic impact of perceptual learning on juvenile amblyopia with or without previous patching treatment. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011;52:1531–8. doi: 10.1167/iovs.10-6355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Knox PJ, Simmers AJ, Gray LS, Cleary M. An exploratory study: prolonged periods of binocular stimulation can provide an effective treatment for childhood amblyopia. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012;53:817–24. doi: 10.1167/iovs.11-8219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Li RW, Ngo C, Nguyen J, Levi DM. Video-game play induces plasticity in the visual system of adults with amblyopia. PLoS Biol. 2011;9:e1001135. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Hussain Z, Webb BS, Astle AT, McGraw PV. Perceptual learning reduces crowding in amblyopia and in the normal periphery. J Neurosci. 2012;32:474–80. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3845-11.2012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Stewart CE, Stephens DA, Fielder AR, Moseley MJ. Modeling dose-response in amblyopia: toward a child-specific treatment plan. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007;48:2589–94. doi: 10.1167/iovs.05-1243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Koklanis K, Abel LA, Aroni R. Psychosocial impact of amblyopia and its treatment: a multidisciplinary study. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol. 2006;34:743–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-9071.2006.01317.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Campbell FW, Hess RF, Watson PG, Banks R. Preliminary results of a physiologically based treatment of amblyopia. Br J Ophthalmol. 1978;62:748–55. doi: 10.1136/bjo.62.11.748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Tytla ME, Labow-Daily LS. Evaluation of the CAM treatment for amblyopia: a controlled study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1981;20:400–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Green CS, Bavelier D. Action video game modifies visual selective attention. Nature. 2003;423:534–7. doi: 10.1038/nature01647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Green CS, Li R, Bavelier D. Perceptual learning during action video game playing. TopiCS. 2010;2:206–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1756-8765.2009.01054.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Li R, Polat U, Makous W, Bavelier D. Enhancing the contrast sensitivity function through action video game training. Nat Neurosci. 2009;12:549–51. doi: 10.1038/nn.2296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Green CS, Pouget A, Bavelier D. Improved probabilistic inference as a general learning mechanism with action video games. Curr Biol. 2010;20:1573–9. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2010.07.040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Koepp MJ, Gunn RN, Lawrence AD, Cunningham VJ, Dagher A, Jones T, Brooks DJ, Bench CJ, Grasby PM. Evidence for striatal dopamine release during a video game. Nature. 1998;393:266–8. doi: 10.1038/30498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Cleary M, Moody AD, Buchanan A, Stewart H, Dutton GN. Assessment of a computer-based treatment for older amblyopes: the Glasgow Pilot Study. Eye (Lond) 2009;23:124–31. doi: 10.1038/sj.eye.6702977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Barry SR. Fixing My Gaze: A Scientist’s Journey into Seeing in Three Dimensions. New York: Basic Books; 2009. [Google Scholar]
- 85.Nakatsuka C, Zhang B, Watanabe I, Zheng J, Bi H, Ganz L, Smith EL, Harwerth RS, Chino YM. Effects of perceptual learning on local stereopsis and neuronal responses of V1 and V2 in prism-reared monkeys. J Neurophysiol. 2007;97:2612–26. doi: 10.1152/jn.01001.2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Ding J, Levi DM. Recovery of stereopsis through perceptual learning in human adults with abnormal binocular vision. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108:E733–41. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1105183108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Astle AT, McGraw PV, Webb BS. Recovery of stereo acuity in adults with amblyopia. BMJ Case Reports. 2011 doi: 10.1136/bcr.07.2010.3143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Maya Vetencourt JF, Sale A, Viegi A, Baroncelli L, De Pasquale R, O’Leary OF, Castren E, Maffei L. The antidepressant fluoxetine restores plasticity in the adult visual cortex. Science. 2008;320:385–8. doi: 10.1126/science.1150516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Sale A, Maya Vetencourt JF, Medini P, Cenni MC, Baroncelli L, De Pasquale R, Maffei L. Environmental enrichment in adulthood promotes amblyopia recovery through a reduction of intracortical inhibition. Nat Neurosci. 2007;10:679–81. doi: 10.1038/nn1899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.He HY, Ray B, Dennis K, Quinlan EM. Experience-dependent recovery of vision following chronic deprivation amblyopia. Nat Neurosci. 2007;10:1134–6. doi: 10.1038/nn1965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Revell MJ. Strabismus, A History Orthoptic Techniques. London: Barrie and Jenkins; 1971. [Google Scholar]
- 92.Leguire LE, Rogers GL, Bremer DL, Walson PD, McGregor ML. Levodopa/carbidopa for childhood amblyopia. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1993;34:3090–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Levi DM. Pathophysiology of binocular vision and amblyopia. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 1994;5:3–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Thompson B, Mansouri B, Koski L, Hess RF. Brain plasticity in the adult: modulation of function in amblyopia with rTMS. Curr Biol. 2008;18:1067–71. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2008.06.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]