Abstract
Aim and Background:
A botanical study is conducted to provide a standard diagnostic tool. In order to improve the quality assurance of the secondary tuberized roots of Harpagophytum procumbens, derived extract and phytomedicine, a simple, rapid, and accurate high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method was developed to assess the harpagoside.
Material and Mehods:
This HPLC assay was performed on a reversedphase C18 column with methanol and water (50/50–V/V) as the mobile phase with a flow rate of 1.5 mL/min and using a monitoring wavelength at 278 nm.
Results and Conclusion:
This method was successfully applied to quantify these bioactive iridoid in an aqueous extract of H. procumbens and in its related phytomedicine “harpagophyton”. The result demonstrated that the quantification of harpagoside, indicating that the quality control of the bioactive ingredient in H. procumbens, derived extract and phytomedicine, is critical to ensure its clinical benefits.
Keywords: Anatomical study, harpagophytum, harpagoside, high-performance liquid chromatography quantification
INTRODUCTION
Indigenous plants, of Kalahari Desert of Africa, Harpagophytum procumbens DC (De Candolle—Pedaliaceae), is rare and only found in Southern Africa. It comes only from South Africa, Namibia, Botswana, and South-Eastern Africa, where it was harvested in the wild form.[1] The plant named “Devil's claw” is also cultivated. In Europe, it was introduced for the first time by O. H. Volk in 1953. It was in 1989 that H. procumbens was included in the French pharmacopoeia. Traditionally in southern Africa, the H. procumbens, also called Devil's claw, is used among indigenous diseases of the liver, stomach, gallbladder, kidney, and pancreas. In fever, it is used as tonic, in disorders of pregnancy and bleeding. In Europe, H. procumbens is also used in self and without evidence experimental in metabolic disorders, diabetes, and disorders of the elderly.
Secondary tuberized roots are the therapeutic parts of the plant; they contain between 0.5 and 3% of iridoid glycosides assumed to be the active compounds.[2]
Harpagoside (8-cinnamoyl harpagide) is the main iridoid. Some other compounds are also present in Harpagophytum, gluco-iridoid like Harpagide, procumbide, and its 60-para-coumaroyl ester from the iridoid family, some flavonoids, phenolic acids, quinones, phytosterols, and sugars. They are present in too small amounts or they are not specific for Harpagophytum.[3–5] Chemical structures of harpagoside [Figure 1] and harpagide have previously been underscored.[6,7]
Figure 1.
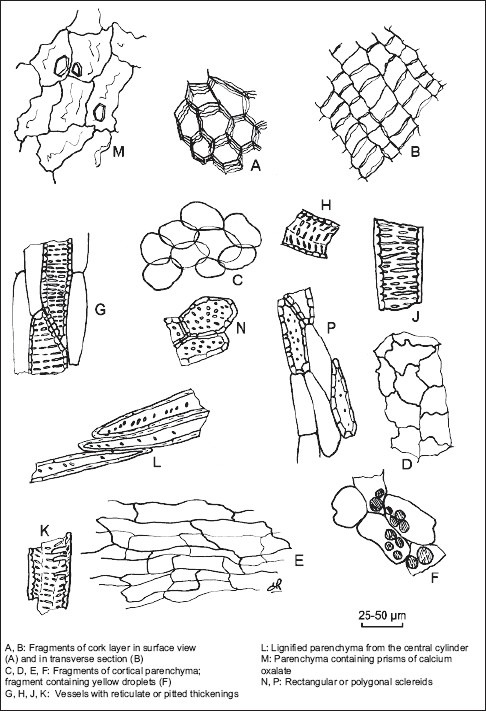
Illustration of powdered herbal drug of devil's claw root (see identification B)
The European Scientific Cooperative on Phytotherapy (ESCOP) monograph summarizes the pharmacological and clinical evidence behind the therapeutic indications for the individual plant materials. ESCOP recommends the use of Devil's claw for symptomatic treatment of painful osteoarthritis, relief of low back pain, loss of appetite, and dyspepsia.[5] The effectiveness of Harpagophytum in the treatment of exacerbation of low back pain has been extensively studied.[8–11] As a result of a number of recent studies, Harpagophytum is proposed as a complementary treatment for chronic rheumatism, tendonitis, osteoarthritis, and arthritis.[12–16]
The aim of our work is to propose a quantification method of the harpagoside by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) in Devil's claw and its related phytomedicine “harpagophyton” speciality developed by RandD Pharma laboratory. Therefore, a reliable quality control method[17,18] is needed for the qualitative and quantitative determination[19,20] of this gluco-iridoid in the secondary tuberized roots of H. procumbens.[21] A simple HPLC-UV assay using an external standard method has been developed, for the first time. The developed method has been subsequently applied to analyze various extract.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Plant material
Secondary tuberized roots of H. procumbens samples were collected in November 2000 from Namibie. Voucher specimens of roots were identified by Professor Isabelle Fouraste and deposited at the herbarium of the Pharmacognosy Laboratory, Faculty of Pharmacy in Toulouse.
Preparing slides
Observations were based on microscopic study of sectioned and stained tissue materials. Transverse sections were prepared with a sliding microtome (MSE), stained in alun carmine-green combination or Mirande reagent[22] for 2–3 minutes, and then washed with water. Following staining, the transverse sections were mounted on glass slides using glycerine gel. Some observations were made using Chloral hydrate solution R (European Pharmacopoeia in force). Observations were made with a LEICA Microsystems DMLB microscope (Toulouse, France), and pictures were taken with Digital Camera Power Shot S40 CANON photo-micrographic system (Toulouse, France). For the description purpose, we used some help books.[23,24]
Chemicals and standards
HPLC grade methanol (VWR International, France) was used for the HPLC analysis. All other organic solvents used in this study were of analytical grade from VWR.
Harpagoside reference was furnished by Extrasynthese (® Réf. 02295, Lot 01120515).
The dried roots were crushed into pieces before extraction. The secondary tuberized roots of H. procumbens sample collected from Namibie were used for the assessment of the precision and recovery and limits of detection.
Apparatus
HPLC was performed on Kontron and Merck-Hitachi liquid chromatography systems, equipped with a quaternary solvent delivery system, an auto-sampler, and UV detector. The column configuration consisted of an LICHROSORB, 100 RP-18 reserved-phase column (5 μm, 150 mm × 4.6 mm, i.d.) (Chromoptic Ref: LB613B64—Lot 206 L 849633) with its pre-column Lichrosorb 100 Å RP 18 (5 μm; Ref: LB181505). The colorimetric method was performed on HPLC 430 and 335 Detector spectrometers (UVK-LAB, France).
Quantification of harpagoside by high-performance liquid chromatography
Calibration curves
To prepare the standard solutions, accurately weighed amounts of the harpagoside standard (0.02, 0.04, 0.06, 0.08, 0.10, and 0.12 mg, respectively) were dissolved in methanol (10 mL) for analysis. The standard solutions were injected and run for calibration curves. Calibration graphs were plotted subsequently for linear regression analysis of the peak area with amount of analyte injected.
Sample preparation
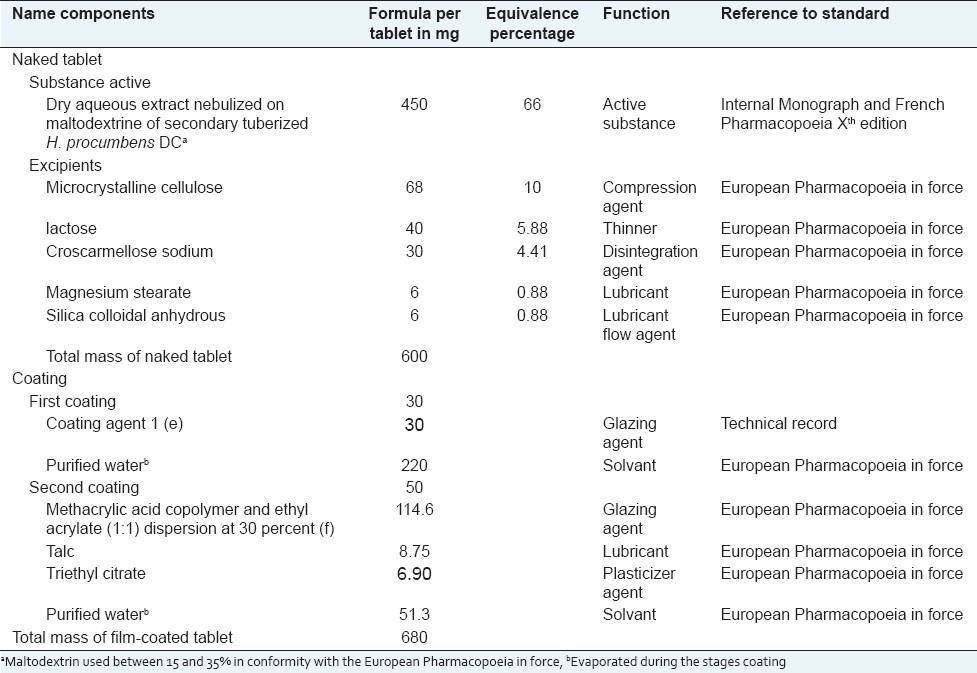
An aliquot of the dried powder of the secondary tuberized roots of H. procumbens (20–40 mesh, 10 g) was extracted, by reflux extraction method, with 8–10 times its weight in purified water for 2 hours at 50°C. The macerate was filtered and then evaporated to dryness under reduced pressure (20 mm Hg) and temperature (under 50°C) to yield an aqueous extract. The dry atomized extract of secondary tuberized roots of H. procumbens obtained was then used to prepare (as described in Table 1) coated tablets of the phytomedicine called “harpagophyton.”
Table 1.
Formulated tablets of “harpagophyton” phytomedicine
The suitable amount of each residue (extracts and phytomedicine) was dissolved in 10 mL of methanol, respectively. The afforded solution was filtered through a 0.45-μm syringe filter before HPLC. All separations were performed at ambient temperature. In addition, assigning peaks were based on their retention times or by spiking the test solution with standard compound.
Linearity study
The linearity shows that test results were directly proportional to the amount of harpagoside in H. procumbens and “harpagophyton”. The linearity of a HPLC assay was established throughout the measurement interval ranging from 70 to 130% of the concentration test. Each solution is injected once randomly.
Precision and recovery studies
The measurements of intra- and interday variability were used to determine repeatability and intermediate precision of the developed assay method. A concentration standard solution containing harpagoside was prepared. Quantity for the analyte was calculated from its corresponding calibration curve.
Each sample was analyzed in six times within the same day to determine the intraday variability. The interday reproducibility was determined by analyzing the sample on two separate days and on two different equipments.
The coefficient of variation was taken as a measure of the repeatability and the test of equal variances (F-test) was taken as a measure of the intermediate precision.
In addition, to further evaluate the recovery of the developed assay, amounts of harpagoside calculated (mcalculated) were calculated from harpagoside standard calibration curve, and amounts of harpagoside measured (mmeasured) were measured directly in the tested plant roots. Each sample was analyzed in six times. The analyte concentration was determined from the corresponding calibration curve, and the recovery of the measurement for the analyte was calculated by the following equation:
Recovery (%) = (m measured / m calculated) × 100
where mmeasured is harpagoside amount measured above and mcalculated is the calculated amount of harpagoside calculated with calibration curve.
Limits of detection
The standard solution containing all authentic compounds was diluted with methanol to provide appropriate concentrations. The limit of detection for each analyte was determined when the ratio of the testing peak signal-to-noise was greater than 5.
Statistical analysis
All data were expressed as means ± standard deviations (SD) of triplicate measurements. The confidence limits were set at P < 0.05. SD did not exceed 5% for the majority of the values obtained.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Botanical analysis
The drug is made by tuberized, cut and dried H. procumbens (N° 206 G146) secondary roots tuberized. The Devil's claw roots are odorless, brown gray to dark brown with bitter taste. These roots consist of thick, fan-shaped or rounded slices or of roughly crushed discs. The outer surface, dark, is crossed by tortuous longitudinal wrinkles. The central cylinder shows fine concentric striations. Seen under a lens, the cut surface presents yellow to brownish-red granules.
Microscopic examination of its paler cut surface shows from the outside to the inside a thin cork consisting of slightly suberized walled cell; a developed phelloderm consisting of cellulosic thin-walled cell, a cortical parenchyma, poorly developed, consisting of polyhedral cells, with thin cellulose walls, separated meatuses. The fibrovascular bundle organized in a continuous ring consists of secondary structure. Secondary phloem completed by narrow cones is separated by cellulosic pluriseriate rays. A dark cambial zone consists of small rectangular attached cells, aligned in radial files. Secondary xylem includes cellulosic parenchyma, reticulately thickened, or pitted vessels often isolated and/or grouped by two or three and divided into concentric zones. The marrow consists of thin-walled cellulosic cells.
The powder [Figure 1], yellow-brown, is examined under a microscope using chloral hydrate solution R and shows the following:
Cork fragments consisting of polyhedral cells brown-yellow, thin-walled regular and which are superimposed.
Fragments consist of cortical parenchyma cells ovoid, thin-walled inclusions sometimes contain granular brown-red (stained orange in the reagent lactic) and yellow droplets isolated.
Fragments of vessels with reticulate thickenings, of tracheids associated with ligneous parenchyma, from the central cylinder, needles and small crystals of calcium oxalate in the parenchyma. The sclereids punctuated, of rectangular or polygonal, containing dark red-brown. Powder H. procumbens DC (206G146 lot) does not contains starch.
High-performance liquid chromatography separation optimization
The selection of the HPLC conditions was guided by the requirement for obtaining chromatograms with better resolution of adjacent peaks within a short time, especially when large amount of samples were analyzed. The solvent system of A–B (A, methanol; B, distillate water) was tested by changing the volume ratio of the components to obtain the optimal composition. After optimizing the separation parameters, the ratio 50:50 (v/v) of the solvent system of A–B at a flow rate of 1.5 mL/min was used so as to ensure that each run of analysis was completed within 25 minutes with better resolution of adjacent peaks and low solvent consumption; 278 nm was chosen as the detection wavelength, as it is close to the maximum absorbency of iridoid.
Linearity, precision, and recovery of the high-performance liquid chromatography method
The areas under the curve peak of harpagoside measured linearly dependent quantities of tracer harpagoside, tested in the area between 0.050 and 0.113 μg/20 μL for the aqueous solution of H. procumbens DC.
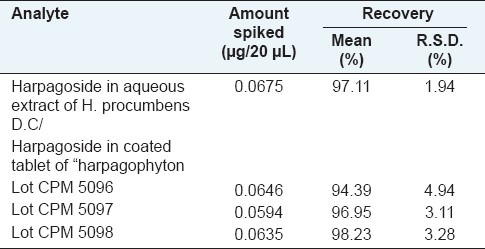
Under the optimal chromatographic conditions used in this study, calibration curve exhibited good linear regression as shown in Table 2, and the limit of detection was in the range of 0.050 and 0.113 μg/20μL for harpagoside. The results in Table 3 demonstrated that the developed analytical method was reproducible with good accuracy and sensitivity for the analyte examined. The overall intra- and interday variations were less than 10% for the analyte. The recovery assays of harpagoside were carried out by adding the standard to the treated material, and the result is as shown in Table 4, from which it is clear that the recovery for harpagoside determined were in the range of 94–99%.
Table 2.
Calibration curve and accuracy of this iridoid in the secondary tuberized roots of H. procumbens and the coated tablet of “harpagophyton” phytomedicine
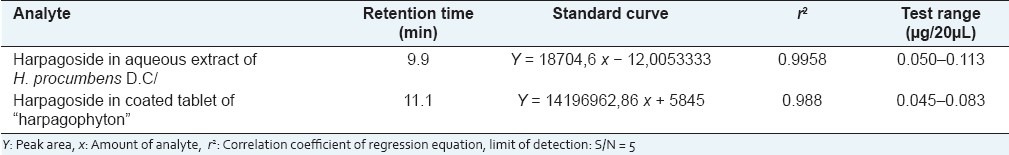
Table 3.
Intra- and interday precision for the determination of harpagoside
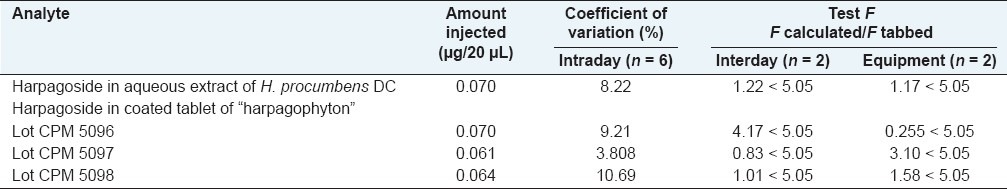
Table 4.
Recovery of harpagoside in the secondary tuberized roots of H. procumbens and the coated tablet of “harpagophyton” phytomedicine
Result analysis
Quantification of bioactive component, harpagoside, and its qualitative assessment in the extract of herb and its phytomedicine correspondent
In order to obtain quantitative extraction, variables involved in the procedure such as the extraction solvent and extraction time were optimized. The optimal experimental conditions were as follows: the powder of secondary tuberized roots of H. procumbens was extracted with 8-10 times its weight in purified water for 2 hours at 50°C. The macerate was filtered and then evaporated to dryness under reduced pressure (20 mm Hg) and temperature (under 50°C) to yield an aqueous extract. A suitable amount of residue was dissolved in 10 mL of methanol. The afforded solution was filtered through a 0.45-μm syringe filter before HPLC. All separations were performed at ambient temperature. This newly developed HPLC assay method was subsequently applied to determination of harpagoside in “harpagophyton”. The yield and purity of harpagoside were determined by HPLC.
Furthermore, to ensure the consistency of therapeutic benefits, the determination of the major bioactive component was more important and meaningful than a measurement of the content of bioactive ingredients only before its use as herbal prescription or as the plant source for the manufacture of natural product-based pharmaceutical preparations.
CONCLUSION
Our botanical study provides a standard diagnostic tool to help for the preliminary identification before the medicinal use of this plant.
Moreover, our work relate on the development of a simple, sensitive, and specific HPLC-UV method to quantify the bioactive ingredient, harpagoside, in H. procumbens DC and in its related phytomedicine. The results demonstrate that the developed method is accurate and reproducible and could be readily used as a suitable quality control method.
Footnotes
Source of Support: Nil,
Conflict of Interest: None declared.
REFERENCES
- 1.Grote K. The Increased Harvest and Trade of Devil's Claw (Harpagophytum procumbens) and Its Impacts on the Peoples and Environment of Namibia, Botswana and South Africa – 2003. [last accessed on 2011 Mar 1]. Available from: http://www.underutilized-species.org/documents/devils claw.pdf .
- 2.Bradley R, editor. British Herbal Compendium. Vol. 1. UK: British Herbal Medicine Association; 1992. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Baghdikian B, Lanhers MC, Fleurentin J, Ollivier E, Maillard C, Balansard G, et al. An analytical study, anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of Harpagophytum procumbens and Harpagophytum zeyheri. Planta Med. 1997;63:171–6. doi: 10.1055/s-2006-957638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Eich J, Schmidt M, Betti G. HPLC Analysis of Iridoid Compounds of Harpagophytum taxa: Quality control of pharmaceutical drug material. Pharm. Phamacol. Lett. 1998;8:98. [Google Scholar]
- 5.ESCOP Monographs. 2nd ed. New York: Thieme; 2003. Harpagophiti radix; p. 233. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Elnaggar LJ, Beal JL. Iridoids - A review. J Nat Prod. 1980;43:649–707. doi: 10.1021/np50012a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Boros CA, Stermitz FR. Iridoids - An updated review.1. J Nat Prod. 1990;53:1055–147. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chrubasik S, Junck H, Breitschwerdt H, Conradt C, Zappe H. Effectiveness of Harpagophytum extract WS 1531 in the treatment of exacerbation of low back pain: A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 1999;16:118–29. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2346.1999.00435.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chrubasik S, Thanner J, Kunzel O, Conradt C, Black A, Pollak S. Comparison of outcome measures during treatment with the proprietary Harpagophytum extract Doloteffin (R) in patients with pain in the lower back, knee or hip. Phytomedicine. 2002;9:181–94. doi: 10.1078/0944-7113-00140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Chrubasik S, Kunzel O, Thanner J, Conradt C, Black A. A 1-year follow-up after a pilot study with Doloteffin ((R)) for low back pain. Phytomedicine. 2005;12:1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2004.01.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Chrubasik S, Conradt C, Black A. The quality of clinical trials with Harpagophytum procumbens. Phytomedicine. 2003;10:613–23. doi: 10.1078/094471103322331647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Chrubasik S, Conradt C, Roufogalis BD. Effectiveness of Harpagophytum extracts and clinical efficacy. Phytother Res. 2004;18:187–9. doi: 10.1002/ptr.1416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Andersen ML, Santos EH, Seabra MD, da Silva AA, Tufik S. Evaluation of acute and chronic treatments with Harpagophytum procumbens on Freund's adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2004;91:325–30. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2004.01.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Chantre P, Cappelaere A, Leblan D, Guedon D, Vandermander J, Fournie B. Efficacy and tolerance of Harpagophytum procumbens versus diacerhein in treatment of osteoarthritis. Phytomedicine. 2000;7:177–83. doi: 10.1016/S0944-7113(00)80001-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gagnier JJ, Chrubasik S, Manheimer E. Harpgophytum procumbens for osteoarthritis and low back pain: A systematic review. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2004;4:13. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-4-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Mahomed IM, Ojewole JA. Analgesic, antiinflammatory and antidiabetic properties of Harpagophytum procumbens DC (Pedaliaceae) secondary root aqueous extract. Phytother Res. 2004;18:982–9. doi: 10.1002/ptr.1593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Arambewela LS, Arawwawala LD. Standardization of Alpinia calcarata Roscoe rhizomes. Pharmacogn Res. 2010;2:285–8. doi: 10.4103/0974-8490.72324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ajazuddin, Saraf S. Evaluation of physicochemical and phytochemical properties of Safoof-E-Sana, a Unani polyherbal. Pharmacogn Res. 2010;2:318–22. doi: 10.4103/0974-8490.72332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hussain K, Ismail Z, Sadikun A, Ibrahim P. Proximate and qualitative analysis of different parts of Piper sarmentosum, and quantification of total amides in various extracts. Pharmacogn Res. 2009;1:113–9. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Taur DJ, Kulkarni VB, Patil RY. Chromatographic evaluation and anthelmintic activity of Eucalyptus globulus oil. Pharmacogn Res. 2010;2:125–7. doi: 10.4103/0974-8490.65504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Grant L, McBean DE, Fyfe L, Warnock AM. A review of the biological and potential therapeutic actions of Harpagophytum procumbens. Phytother Res. 2007;21:199–209. doi: 10.1002/ptr.2029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Mirande R. Sur le carmin aluné et son emploi, combiné avec celui du vert d’iode, en Histologie végétale. CR Acad Sci. 1920;170:197–9. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Maison Neuve SA, Moulins, Metz L, editors. European Pharmacopoeia (in force or 2011) [Google Scholar]
- 24.Speranza A, Calzoni GL. In: Atlas de la structure des plantes. Belin, editor. Berlin, Germany: 2005. pp. 125–203. [Google Scholar]


