Abstract
Rationale: Despite advances in clinical management, there are currently no reliable diagnostic and therapeutic targets for acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). The inflammasome/caspase-1 pathway regulates the maturation and secretion of proinflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-18). IL-18 is associated with injury in animal models of systemic inflammation.
Objectives: We sought to determine the contribution of the inflammasome pathway in experimental acute lung injury and human ARDS.
Methods: We performed comprehensive gene expression profiling on peripheral blood from patients with critical illness. Gene expression changes were assessed using real-time polymerase chain reaction, and IL-18 levels were measured in the plasma of the critically ill patients. Wild-type mice or mice genetically deficient in IL-18 or caspase-1 were mechanically ventilated using moderate tidal volume (12 ml/kg). Lung injury parameters were assessed in lung tissue, serum, and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid.
Measurements and Main Results: In mice, mechanical ventilation enhanced IL-18 levels in the lung, serum, and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. IL-18–neutralizing antibody treatment, or genetic deletion of IL-18 or caspase-1, reduced lung injury in response to mechanical ventilation. In human patients with ARDS, inflammasome-related mRNA transcripts (CASP1, IL1B, and IL18) were increased in peripheral blood. In samples from four clinical centers, IL-18 was elevated in the plasma of patients with ARDS (sepsis or trauma-induced ARDS) and served as a novel biomarker of intensive care unit morbidity and mortality.
Conclusions: The inflammasome pathway and its downstream cytokines play critical roles in ARDS development.
Keywords: acute respiratory distress syndrome, inflammasome, interleukin-18, mechanical ventilation
At a Glance Commentary
Scientific Knowledge on the Subject
Currently there are no effective predictors or therapies for acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Although inflammatory processes are known to play a role in acute lung injury (ALI)/ARDS pathology, currently the specific role of inflammasome-dependent inflammatory responses remains unknown.
What This Study Adds to the Field
This study suggests that caspase-1–dependent inflammatory responses involving the production and activation of IL-18 may play a role in the propagation of ALI/ARDS.
Acute lung injury (ALI), a common and severe pulmonary complication of critical illness, affects approximately 10 to 15% of patients hospitalized in the intensive care unit (ICU) (1). Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), the most severe form of ALI, has a mortality rate of approximately 40%, despite modern ICU care (2). Since the first description of this syndrome, ARDS mortality has decreased through the implementation of improved supportive measures and a cytoprotective low tidal volume strategy (3). Nevertheless, we still cannot reliably predict ARDS susceptibility (4), nor do we possess effective targeted therapies for afflicted patients (5).
“Inflammasomes” are intracellular macromolecular complexes that serve as platforms for the activation of the proinflammatory caspase-1, which in turn cleaves IL-1β and IL-18 from their respective proforms (6). These inflammasome-activated cytokines belong to the IL-1 cytokine family (7) and play central roles in the propagation of the acute inflammatory response. At least four inflammasome complexes are now recognized (designated NLRP1, NLRP3, IPAF, and AIM2) (6). The NALP3 inflammasome has a basic structure consisting of nucleotide-binding-domain, leucine-rich repeat domain containing protein (NLRP) and the adaptor protein ASC (apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing caspase-1 activator domain [CARD]), which recruit and activate procaspase-1 (8, 9).
In macrophages, the NLRP3 inflammasome can be activated by combined exposure to Toll-like receptor-4 (TLR4) ligand and increased K+ ion efflux via purinergic P2X7 receptors (P2X7R) (10–12). Additionally, the NALP3 inflammasome responds to activation by bacterial and viral pathogens (13) or lysosomal disruption caused by particle irritants such as silica (14), asbestos, monosodium urate crystals (15), and excess production of reactive oxygen species (i.e., neutrophil or mitochondria-derived) (16, 17). In contrast, the IPAF and AIM2 inflammasomes represent specialized responses to activation by gram-negative bacteria and DNA (18, 19).
Recent studies show that inflammasome-dependent responses can be triggered by cell death (17, 20), suggesting intriguing roles for inflammasomes in the development of ARDS. In the current study, we demonstrate that IL-18, whose secretion is increased in ARDS, can serve as a novel biomarker associated with the severity of illness and mortality in the critically ill. Using a mouse model of ventilator-induced lung injury (VILI) in rodents, we have assessed the role of the inflammasome pathway in lung injury. Some of the results of these studies have been previously reported in the form of abstracts (21–23).
Methods
Patients
We established a Registry of Critical Illness (RoCI) in the Brigham and Women’s Hospital (BWH) medical ICU (MICU). RoCI is approved by the Partners Human Research Committee. Informed consent was obtained for blood collection. Patients were classified as nonseptic ICU control subjects, systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS), sepsis, no sepsis ARDS, and sepsis with ARDS (sepsis/ARDS) (see Table E1 in the online supplement). Clinical data were validated using samples from three independent cohorts (Vanderbilt University, Massachusetts General Hospital/Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center [MGH/BIDMC], and University of Pennsylvania) (see online supplement).
Human Plasma Analysis
Human plasma was prepared from blood drawn from RoCI patients and independent patient cohorts. IL-18 and caspase-1 protein levels were measured in plasma using ELISA (Invitrogen [Carlsbad, CA] and R&D Systems [Minneapolis, MN]) (see online supplement).
Human Microarray Analysis
Total RNA was collected from 88 RoCI patients (Table E1). Gene expression profiles were generated using Human HT-12 v4 BeadChip arrays (Illumina, San Diego, CA) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. The microarray data are available through the Gene Expression Omnibus of the National Center for Biotechnology Information (GEO, accession number GSE32707). Gene expression changes were validated using TaqMan Real Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) (see online supplement).
Mouse Experiments
All animal protocols were approved by the BWH Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee. Mice genetically deficient in IL-18 (Il18−/−) (C57Bl/6) or caspase-1 (Casp1−/−) (NOD/shi) (Jackson Laboratories, Bar Harbor, ME; n = 40/group) were allowed to spontaneously breathe or were mechanically ventilated (12 ml/kg tidal volume, 8 h) using a rodent ventilator (Voltek Enterprises, Toronto, ON, Canada). Mouse serum was analyzed for IL-18 using ELISA (Invitrogen). Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) was analyzed for total, differential cell counts, and IL-18 ELISA. Left lung tissue was analyzed by hematoxylin and eosin, immunohistochemical, and immunofluorescence staining, and homogenates were prepared for IL-1β, IL-18 (Invitrogen), and IL-33 (R&D Systems) quantitative ELISA. Right lungs were used to measure wet-to-dry lung weight ratio (see online supplement).
Mouse Microarray Analysis
Total RNA was extracted from lung tissues of ventilated and control NOD/shi mice. Microarray expression profiles were generated using Ref-8 mouse arrays (Illumina) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. The microarray data are available through the GEO accession number GSE29920. Gene expression was confirmed using quantitative TaqMan Real Time PCR (see online supplement).
Mouse IL-18–Neutralizing Antibody Treatment
C57Bl/6 mice (n = 12/group) inhaled 10 μg of mouse IgG (Abcam, Cambridge, MA) or polyclonal rat IL-18 antibody in 10 μl of normal saline 1 hour before experiments. Mice (n = 6) were randomly selected for mechanical ventilation (MV) or control as described above (see online supplement).
Statistics
For human plasma analysis, IL-18 and caspase-1 level were represented as mean ± SEM. Means were compared using Student t test. To compare differences in mortality based on IL-18 level, we used Wilcoxon two-sample test for continuous IL-18 level and Fisher exact test for categorical levels. Analyses were performed using SAS software (SAS Institute, Cary, NC) and significance levels were set at P < 0.05. For mouse experiments, the results are presented as mean ± SEM. Kruskal-Wallis test was performed for multiple group comparison, and intergroup differences were analyzed with the Wilcoxon rank sum test using SPSS software (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL). Significance level was P < 0.05 (see online supplement).
Results
VILI Increases Inflammasome Gene Expression
Using microarray analysis of lungs harvested from rodents subjected to MV in established models of VILI, we have discovered novel target molecules potentially modulating VILI (24, 25). We first performed gene expression profiling analysis of 10,000 mouse genes in an ex vivo model of experimental VILI using isolated, blood-free, perfused BALB/c mouse lungs subjected to high negative-pressure ventilation (−25 cm H2O) versus low-pressure ventilation (−10 cm H2O) (24). In a retrospective analysis of this study, we found significant changes in inflammasome-related gene expression, including interleukin-1α (Il1a), caspase-activator domain-10 (Card10), and IL-1 receptor-1 and -2 (Il1r1 and 2) (Table 1). Furthermore, members of the inflammasome complex family were significantly regulated in a microarray study of an in vivo model of VILI, using C57Bl/6 mice subjected to MV (10 ml/kg tidal volume for 8 h) (25). We identified caspase-activator domain-10, and -15, (Card10 and 15), IL-18 receptor-1 (Il18r1), Il1r2, and IL-1β (Il1b) as genes with significant expression change after MV (Table 2). In a current global gene expression analysis of mice subjected to MV (12 ml/kg tidal volume for 8 h), the expression of the Asc gene, a component of the inflammasome complex, was up-regulated 1.49-fold after MV. TaqMan Real Time PCR analysis confirmed this finding (fold-change = 1.46, P = 0.0075).
TABLE 1.
GENE EXPRESSION ANALYSIS OF INFLAMMASOME-RELATED GENES IN EX VIVO MOUSE VENTILATOR-INDUCED LUNG INJURY
| ENTREZ ID | Functional Description | Fold Change | P Value |
| 16175 | Interleukin 1 alpha (Il1a) | 3.4 | 1.70 × 10−3 |
| 1677 | Interleukin 1 receptor 1 (Il1r1) | 2.6 | 2.60 × 10−2 |
| 16178 | Interleukin 1 receptor 2 (Il1r2) | 2.1 | 5.00 × 10−2 |
| 105844 | Caspase recruitment domain 10 (Card10) | 0.5 | 3.30 × 10−2 |
Isolated, perfused mouse lungs were ventilated with −25 cm H2O pressure (overventilation) or −10 cm H2O pressure (control) for 3 h and their lung gene expression profiles were compared. Microarray was performed on total RNA extracted from whole lung tissue using Codelink Uniset I 10K Bioarrays. Average gene expression fold changes represent overventilation/control, and their respective P values are listed for statistical significance. Technical details and microarray analysis is explained in Reference 24.
TABLE 2.
GENE EXPRESSION ANALYSIS OF INFLAMMASOME-RELATED GENES IN IN VIVO MOUSE VENTILATOR-INDUCED LUNG INJURY
| ENTREZ ID | Functional Description | Fold Change | P Value |
| 16178 | Interleukin 1 receptor 2 (Il1r2) | 6.17 | 3.20 × 10−4 |
| 16176 | Interleukin 1 beta (Il1b) | 1.62 | 3.70 × 10−3 |
| 16177 | Interleukin 1 receptor 1 (Il1r1) | 0.53 | 2.50 × 10−3 |
| 257632 | Caspase recruitment domain 15 (Card 15) | 0.52 | 7.70 × 10−3 |
| 16182 | Interleukin 18 receptor 1 (Il18r1) | 0.45 | 3.70 × 10−2 |
| 105844 | Caspase recruitment domain 10 (Card 10) | 0.08 | 1.19 × 10−5 |
Sedated mice were ventilated with 10 ml/kg tidal volume for 8 h with 2 cm H2O positive end-expiratory pressure (ventilation) or allowed to breathe spontaneously (control), and their gene expression profiles were compared. Microarray was performed on total RNA extracted from whole lung tissue using Codelink Uniset I 20K Bioarrays. Average gene expression fold changes represent ventilation/control, and their respective P values are listed for statistical significance. Technical details and microarray analysis is explained in Reference 25.
Gene Expression Profiling of Critically Ill Patients
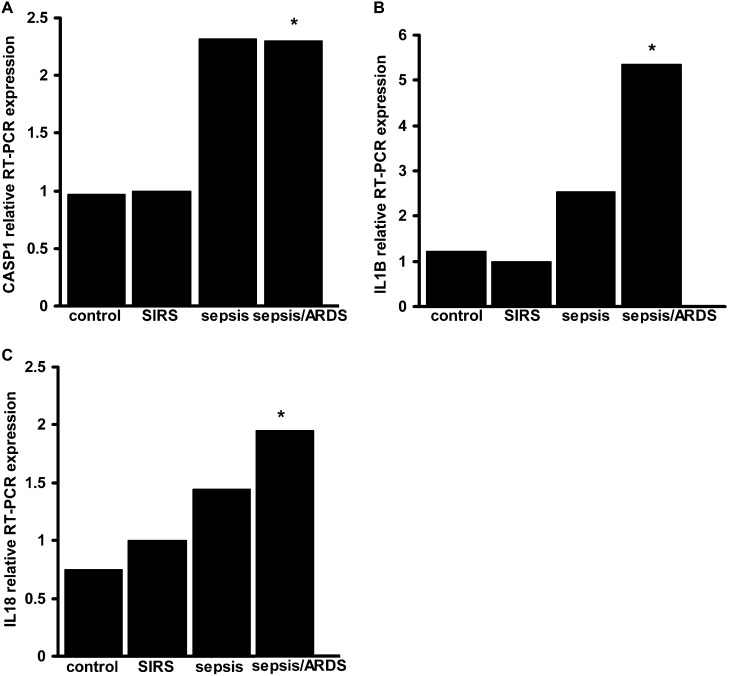
As described above, we observed that genes representing inflammasome complex molecules and downstream cytokines were significantly regulated in ex vivo and in vivo animal models of VILI. We then sought to evaluate whether inflammasome family genes are also regulated in human critical illness such as sepsis and ARDS. We extracted total blood RNA from 88 patients to determine the global gene expression profile of ICU control subjects and patients with SIRS, sepsis, and sepsis/ARDS. On MICU admission, we observed significant up-regulation of ASC and IL1B genes in patients with sepsis/ARDS when compared with SIRS (1.43-fold and 1.44-fold increase, respectively; P < 0.05). To confirm the relevance of these gene expression changes, we performed TaqMan Real Time PCR for selected downstream effectors of the inflammasome pathway. The expression of CASP1, IL-18, and IL1B mRNA transcripts was significantly higher in patients with sepsis/ARDS when compared with SIRS (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Critical illness modulates caspase-1, IL-1β, and IL-18 expression in peripheral blood cells. TaqMan polymerase chain reaction (PCR) results are shown for CASP1 (A), IL1B (B), and IL18 (C). RNA was obtained from medical intensive care unit admission day blood samples. Data are expressed as relative fold-change compared with systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) = 1. For statistical analysis, the Kruskal-Wallis test was performed for multiple group comparison, and intergroup differences were analyzed with Wilcoxon rank sum test, P < 0.05, n = 6 random samples/group. *Represents significant differences between sepsis/acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and SIRS samples.
Protein Profiling of Critically Ill Patients
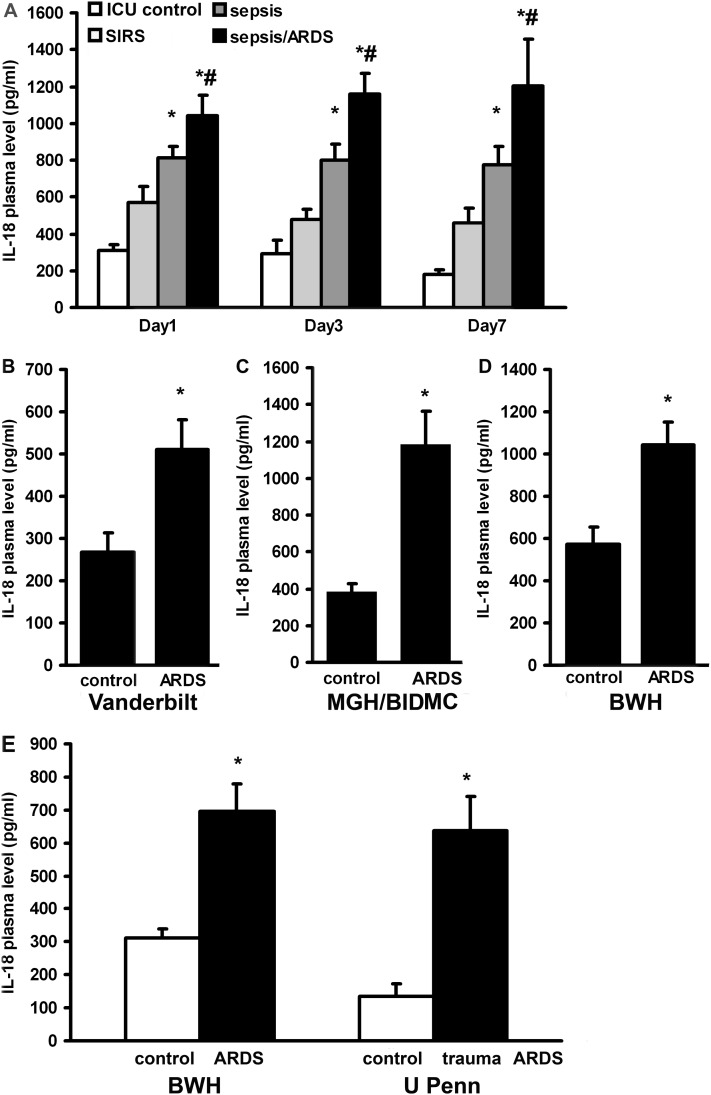
We measured caspase-1 and IL-18 plasma protein levels in 225 critically ill MICU patients in the BWH RoCI. The clinical characteristics of patients in the RoCI are listed in Table 3 and Table E1. IL-18 levels were increased in subjects with SIRS, sepsis, and sepsis/ARDS, with the greatest increase observed in the subjects with sepsis/ARDS (Figure 2A). The kinetics of IL-18 expression in the plasma was also measured as a function of time after MICU admission. Samples were drawn within 48 hours after MICU admission (Day 1), at 72 to 96 hours (Day 3), and at 168 to 192 hours (Day 7). Persistently elevated levels of IL-18 were observed at all time points for patients with sepsis/ARDS from the RoCI (Figure 2A). Caspase-1 plasma levels were also significantly elevated in patients with sepsis/ARDS at Day 1 when compared with control subjects and patients with SIRS (ICU control = 113.19 pg/ml ± 35.58, SIRS = 153.06 pg/ml ± 30.04, sepsis = 157.16 pg/ml ± 21.22, sepsis/ARDS = 258.35 pg/ml ± 47.09).
TABLE 3.
DEMOGRAPHICS OF BRIGHAM AND WOMEN’S HOSPITAL REGISTRY OF CRITICAL ILLNESS PATIENTS
| RoCI | SIRS | ICU Control | P Value | Sepsis | P Value | Sepsis/ARDS | P Value | No Sepsis/ARDS | P Value |
| N | 61 | 35 | 94 | 28 | 7 | ||||
| Age, mean (SD) | 54.9 (15.9) | 63.9 (14.5) | <0.01* | 58.3 (14.7) | 0.16 | 54.0 (14.5) | 0.82 | 56.3 (6.9) | 0.2 |
| Gender, male % (N) | 57.4 (35) | 57.1 (20) | 0.79 | 56.4 (53) | 0.81 | 46.4 (13) | 0.3 | 71.4 (5) | 0.51 |
| Race, % (N) | |||||||||
| Asian/Pacific Islander | 3 (2) | 0 (0) | 2 (2) | 4 (1) | 0 (0) | ||||
| Black | 22 (13) | 17 (6) | 11 (10) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | ||||
| Hispanic | 6 (4) | 3 (1) | 7 (7) | 14 (4) | 0 (0) | ||||
| White | 69 (42) | 80 (28) | 80 (75) | 82 (23) | 100 (7) | ||||
| Length of stay, d, median (min–max) | 10 (0–46) | 4 (1–21) | <0.01* | 12 (1–64) | 0.15 | 19 (1–70) | 0.01* | 14 (5–41) | 0.24 |
| In-hospital mortality, % (N) | 31.1 (19) | 2.8 (1) | <0.01* | 21.3 (20) | 0.15 | 60.7 (17) | 0.01* | 71.4 (5) | 0.04* |
| APACHE II score, mean (SD) | 22.15 (9.5) | 19.63 (6.4) | 0.09 | 25.7 (8.0) | 0.02* | 30.46 (9.0) | <0.01* | 28.86 (5.7) | 0.09 |
| Source of infection, % (N) | |||||||||
| Gastrointestinal | N/A | N/A | 14 (13) | 13 (13) | N/A | ||||
| Genitourinary | N/A | N/A | 11 (10) | 4 (1) | N/A | ||||
| Central nervous system | N/A | N/A | 5 (5) | 0 (0) | N/A | ||||
| Lung | N/A | N/A | 43 (40) | 61 (14) | N/A |
Definition of abbreviations: APACHE = Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation; ARDS = acute respiratory distress syndrome; ICU = intensive care unit; max = maximum; min = minimum; N/A = not applicable; RoCI = Registry of Critical Illness; SIRS = systemic inflammatory response syndrome.
Represents significant differences SIRS vs. other patient groups (P value < 0.05, Student t test).
Figure 2.
Plasma IL-18 levels are elevated in critical illness. (A) IL-18 plasma levels were measured in the Brigham and Women’s Hospital (BWH) Registry of Critical Illness (BWH RoCI). Samples were drawn after admission (Day 1) and at Day 3 and Day 7. Patients with sepsis/acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) have higher levels of IL-18 in their plasma than intensive care unit (ICU) control subjects, patients with systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS), or patients with sepsis only. (B) Patients with severe sepsis-induced ARDS (Vanderbilt cohort) display higher levels of IL-18 than SIRS (control). IL-18 levels in severe sepsis: 603.68 pg/ml ± 71.7, n = 30, coefficient of variance (CV) = 0.65; ARDS with severe sepsis: 509.48 pg/ml ± 72.82, n = 31, CV = 0.8; and SIRS: 266.59 pg/ml ± 46.49, n = 28, CV = 0.92. (C) Levels of IL-18 in patients with sepsis-induced ARDS are also elevated in the Massachusetts General Hospital and Beth Israel Deaconess Hospital (MGH/BIDMC) cohort when compared with patients without ARDS (control). IL18 level in sepsis/ARDS: 1,184.8 pg/ml ± 178.29, n = 23, CV = 0.72 and in control patients without ARDS who had either SIRS or sepsis: 386.1 pg/ml ± 43.36, n = 29, CV = 0.6. (D) Patients with sepsis/ARDS (ARDS) displayed higher levels of IL-18 when compared with patients with SIRS only (control) in the BWH cohort at Day 1. IL-18 level in sepsis/ARDS: 1,043.06 pg/ml ± 108.09, n = 21, CV = 0.47 and in SIRS: 571.73 pg/ml ± 83.38, n = 57, CV = 1.1. (E) IL-18 levels are increased in nonsepsis/ARDS BWH patients (ARDS), when compared with ICU control subjects (control). IL-18 levels in ARDS: 696.68 pg/ml ± 81.0, n = 7, CV = 0.32 and in ICU control subjects: 311.46 pg/ml ± 28.47, n = 35, CV = 0.7. By comparison, IL-18 levels of patients with trauma-induced ARDS (trauma ARDS, University of Pennsylvania cohort [U Penn]) are similar to patients with ARDS in BWH, and elevated relative to their ICU control subjects (control). IL-18 levels in trauma ARDS: 636.05 pg/ml ± 104.89, n = 20, CV = 0.74 and in their control subjects: 134.75 pg/ml ± 37.51, n = 18, CV = 1.18. *Significant differences any condition vs. control. #Significant difference sepsis vs. sepsis/ARDS. Student t test was performed on log10 transformed data, P < 0.05. Sample numbers/condition are listed in the extended Methods section in the online supplement.
To validate our findings in the RoCI patients, we measured IL-18 levels in plasma samples in independent cohorts of critical illness. Samples from the VALID study at Vanderbilt University showed increased IL-18 levels in patients with severe sepsis and ARDS when compared with SIRS control (Figure 2B). In the Molecular Epidemiology of ARDS Study cohort from MGH/BIDMC, patients with sepsis/ARDS at the time of diagnosis had significantly higher levels of IL-18 than control patients without ARDS who had either SIRS or sepsis (Figure 2C). In the BWH RoCI population, IL-18 was significantly higher in the sepsis/ARDS group at Day1 when compared with patients with SIRS only (Figure 2D). IL-18 levels were also elevated in nonsepsis/ARDS (ARDS) patients from the BWH RoCI at Day 1 compared with ICU control subjects (Figure 2E). However, these levels were lower than those with sepsis/ARDS. Similar findings were demonstrated in major trauma subjects from the University of Pennsylvania. In trauma-induced nonseptic ARDS (trauma ARDS), plasma IL-18 levels were similar to those observed in nonsepsis ARDS and significantly higher than similarly injured ICU control subjects without ARDS taken from the same trauma cohort (Figure 2E).
Human Plasma IL-18 Levels Are Correlated with Disease Severity and Mortality in Critically Ill Patients
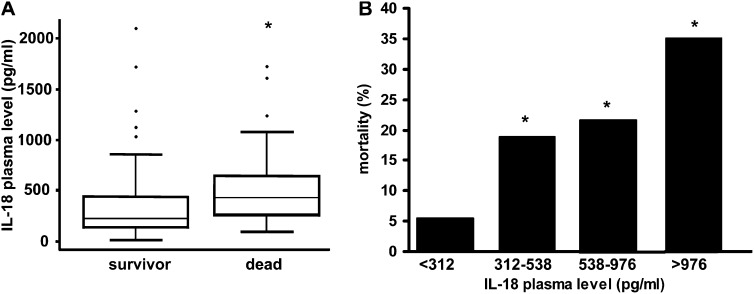
Plasma levels of IL-18 at the time of MICU admission were higher with increasing disease severity categories (control, SIRS, sepsis, and sepsis/ARDS), with the highest levels observed in patients with sepsis/ARDS (Figure 2A). Patients with elevated IL-18 levels at the time of MICU hospitalization had increased mortality (Figure 3A and 3B). For example, after adjusting for important covariates, including Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation (APACHE) II score, for each 500-pg/ml increase in IL-18 level, patients had a 60% increase in their odds of death (odds ratio, 1.60; 95% confidence interval (CI), 1.17–2.20; P = 0.004). To further explore the usefulness of IL-18 as a marker of lung injury, we correlated MICU admission IL-18 levels with plasma lactate levels and APACHE II scores. We found that for each 100-pg/ml increase in IL-18 there is a 0.3-mg/dl increase in lactate level and a 0.1-unit increase in APACHE II score (95% CI, 0.2–0.4; P < 0.0001; and 95% CI, 0.07–0.15; P < 0.0001, for lactate and APACHE II score, respectively).
Figure 3.
IL-18 correlates with mortality in the critically ill. (A) Increased IL-18 levels at medical intensive care unit Day1 were associated with increased in-hospital mortality among critically ill patients. Data were based on 217 patients, of whom 161 were discharged from the hospital and 56 died during hospitalization. Wilcoxon two-sample test, P = 6 × 10−7. (B) Mortality stratification based on plasma IL-18 level quartiles. *Represents significant differences among quartiles, Fisher exact test, P = 5 × 10−5, n/quartile = 54, 53, 55, 55. Changes in quartiles related to death, odds ratio = 2.02; 95% confidence interval, 1.48–2.76; P = 1 × 10−5.
VILI Increases IL-18 and Other Inflammasome-associated Cytokine Levels
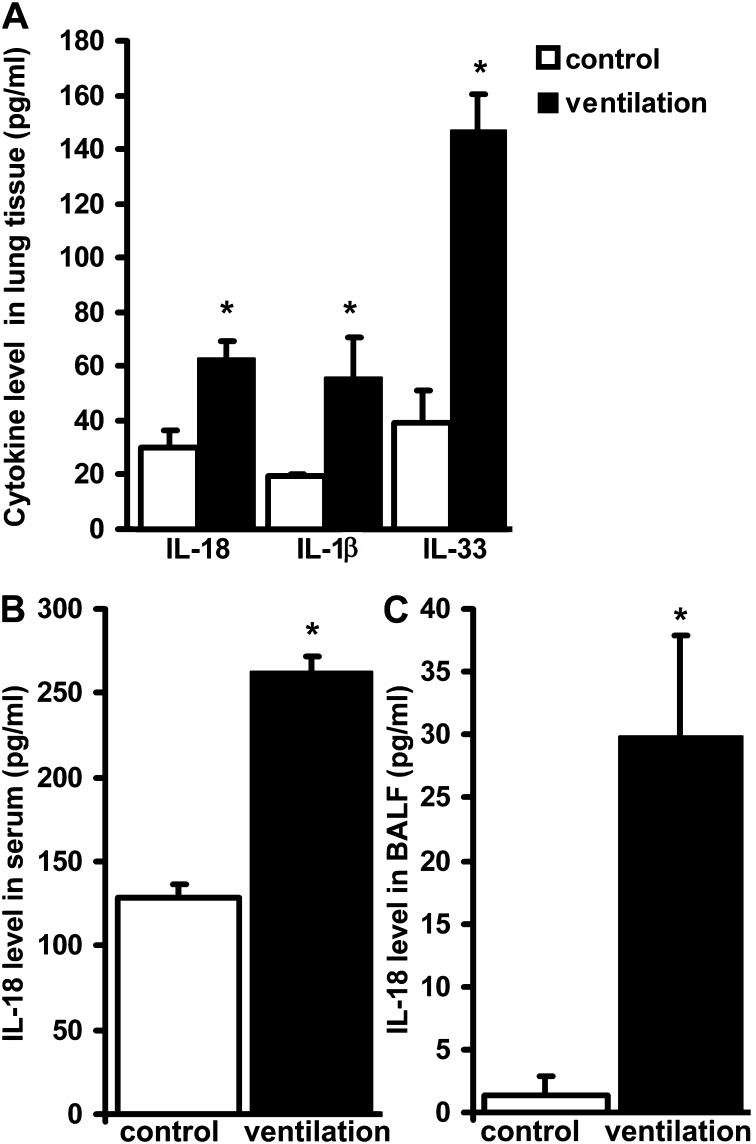
To further study cytokine expression in the lung we used a mouse model of VILI. Mice were subjected to MV (12 ml/kg, 8 h) with a positive end-expiratory pressure of 2 cm H2O without airway recruitment to induce injury. We measured the protein expression of IL-1β, IL-18, and IL-33 in lung tissue (Figure 4A). Increases in IL-18 levels were also detected in the serum (Figure 4B) and the BALF (Figure 4C), suggesting that IL-18 originating and activated in the lung contributes to the systemic cytokine response.
Figure 4.
Inflammatory caspase-activated cytokines are regulated in ventilator-induced lung injury. Mice were mechanically ventilated (ventilation) for 8 hours with 12 ml/kg tidal volume and 2 cm H2O positive end-expiratory pressure (A). IL-18, IL-1β, and IL-33 levels were measured in whole lung homogenates of ventilated wild-type mice and their nonventilated counterparts. Cytokine expression increased in ventilated mice when compared with control animals. IL-18 levels were similarly elevated in serum and in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) (B and C). Kruskal-Wallis test was performed for multiple group comparison and intergroup differences were analyzed with Wilcoxon rank sum test, P < 0.05. For all other animal studies the same statistical tests were performed. *Represents significant differences between ventilation and control, n = 8 animals/group.
Alveolar Macrophages Are Critical Sources of IL-18 in VILI
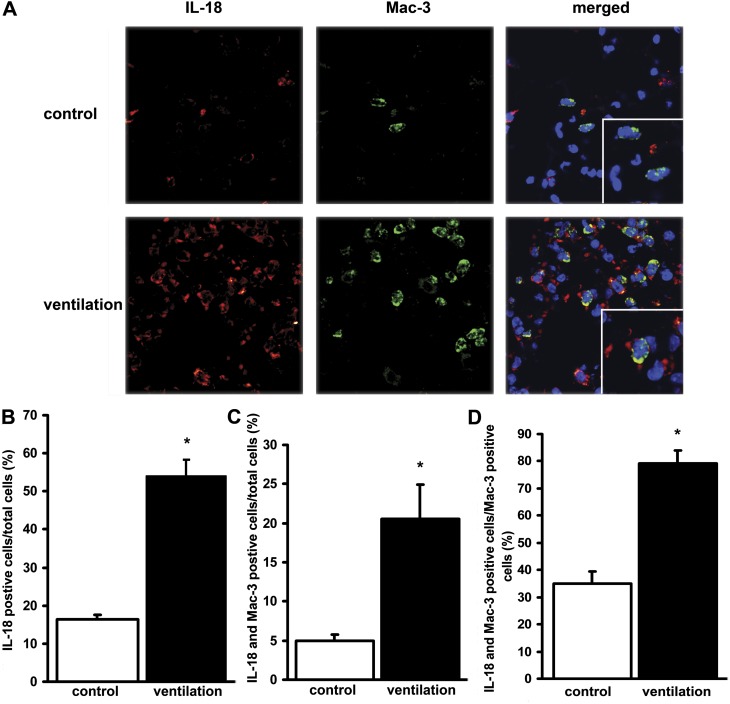
The increased IL-18 expression in the lung tissue of mice after MV was confirmed by immunofluorescence staining using an antibody against cleaved IL-18 (Figure 5A). MV elevated the numbers of Mac-3 positive cells in the lung, which colocalized with IL-18–positive cells (Figure 5B–5D). Of the cells that can infiltrate the alveoli, monocytes and alveolar macrophages express Mac-3, implying that these cells contribute to increased IL-18 production in VILI.
Figure 5.
Mechanical ventilation (MV) increases the expression of the cleaved form of IL-18 in alveolar macrophages. (A) Lung tissue samples obtained from control and ventilated mice were stained with fluorophore-labeled antibodies against IL-18 (cleaved form, Cy3, red), macrophage marker Mac-3 (FITC, green), DAPI (blue nuclear stain) and analyzed by confocal microscopy. Representative images are shown. Magnification ×100, scale 10 μm = 10 mm. Enlarged area magnification ×200, scale 5 μm = 10 mm. Results are quantified by counting positively stained cells in five independent areas. (B) MV increased the number of cleaved IL-18 positive alveolar cells when compared with controls. (C) MV increased the number of cells that stained positive for both cleaved IL-18 and Mac-3. (D) MV increased the relative number of IL-18–positive alveolar macrophages. Numbers are expressed as the percentage of total cells in lung sections. *Represents significant differences between control and ventilation. P < 0.05.
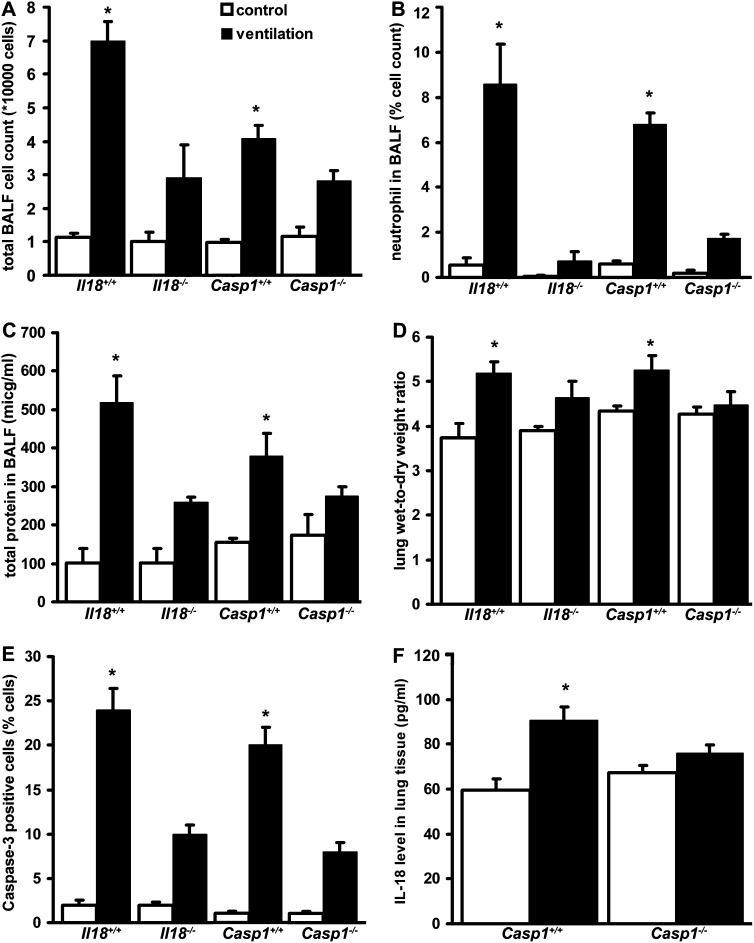
Genetic Deletion of IL-18 and Caspase-1 Confers Resistance to VILI In Vivo
To further investigate the role of IL-18 and caspase-1 in the mechanism of ALI, we exposed mice genetically deficient in IL-18 (Il18−/−) or caspase-1 (Casp1−/−) and their corresponding wild-type mice to MV and evaluated indices of inflammation and lung injury. We measured total and neutrophil cell counts in the BALF as an index of MV-induced inflammation. Both Il18−/− and Casp1−/− mice exhibited fewer cells in the BALF after MV when compared with their wild-type counterparts (C57Bl/6 and NOD/shi, respectively) (Figures 6A and 6B). Histological analysis also showed a lower number of infiltrating neutrophils in the lung after injury in Il18−/− mice (data not shown). Il18−/− mice were protected from MV-induced alveolar-capillary barrier dysfunction as assessed by total protein concentration in the BALF and wet-to-dry lung weight ratio (Figures 6C and 6D). An increased number of apoptotic cells, as assessed by caspase-3 immunohistochemical staining of lung tissue, were detected in wild-type mice after MV, whereas a significant reduction in caspase-3–positive cells was observed in both Il18−/− and Casp1−/− mice (Figure 6E). The Casp1−/− mice displayed no increases in IL-18 production in response to MV (Figure 6F), confirming that caspase-1 is required for the increased IL-18 expression observed in VILI.
Figure 6.
IL-18 and caspase-1 modulate indices of lung injury. IL-18 (Il18−/−) or caspase-1 (casp1−/−) knockout mice and their corresponding C57Bl/6 or NOD/shi wild-type mice, respectively, were mechanically ventilated (ventilation) for 8 hours with 12 ml/kg tidal volume and 2 cm H2O positive end-expiratory pressure. After ventilation or control treatments, mice were analyzed for indices of lung injury. (A) Mechanical ventilation increased bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) total cell count in wild-type (Il18+/+ and casp1+/+) mice. The Il18−/− and casp1−/− mice show minimal increase in total cell count after mechanical ventilation. (B) Il18−/− and casp1−/− mice respond to mechanical ventilation with reduced alveolar neutrophil infiltration. (C) Il18−/− and casp1−/− mice are resistant to ventilator-induced lung injury (VILI)-induced alveolar protein leakage. (D) Lung wet-to-dry ratio measurement confirmed that Il18−/− and casp1−/− mice have increased resistance against alveolar pulmonary edema formation in VILI. (E) Il18−/− and casp1−/− mice were also protected from apoptotic cell death as measured by the number of caspase-3 positive-staining cells in lung tissue. Results were quantified and expressed as the percentage of cells positively stained for caspase-3. (F). IL-18 levels in lung tissue decreased in casp1−/− mice when compared with wild-type mice after mechanical ventilation. *Represents significant differences between ventilation and control; n = 8/group for BALF and lung tissue measurements, n = 12/group for wet-to-dry lung weight ratio measurements, and n = 3/group for immunohistochemical analysis.
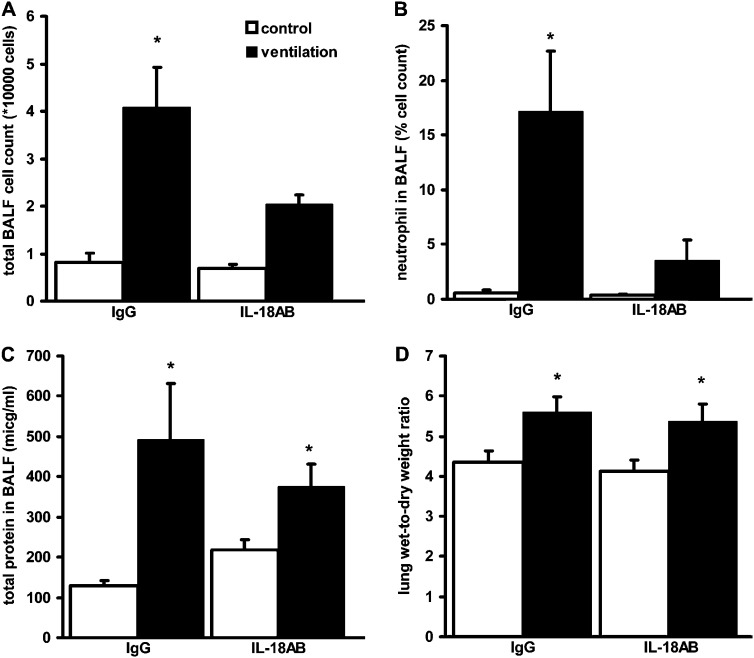
IL-18–Neutralizing Antibody Treatment Reduces VILI
We tested whether exogenous IL-18 inhibition can prevent VILI. Wild-type mice inhaled a single dose of IL-18–neutralizing antibody (10 μg) or an equal dose of control IgG 30 minutes before MV, and lung injury indices were compared. IL-18–neutralizing antibody treatment significantly altered total and neutrophil cell count in the lavage of ventilated mice (Figures 7A and 7B). However, IL-18–neutralizing antibody had no effect on alveolar edema formation (Figures 7C and 7D).
Figure 7.
IL-18–neutralizing antibody blocks ventilator-induced inflammation. Wild-type C57Bl/6 mice were mechanically ventilated (ventilation) for 8 hours with 12 ml/kg tidal volume and 2 cmH2O positive end-expiratory pressure. (A) IL-18 antibody (IL-18AB) inhalation significantly reduced ventilator-induced inflammatory cell count in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) when compared with IgG-treated control mice. (B) BALF neutrophil cell count was also lower in IL-18–neutralizing antibody–treated mice. (C) IL-18AB inhalation only partially reduced protein leakage to the alveoli. (D) No differences were found in wet-to-dry lung weight ratio after ventilation between treatment groups. *Represents significant differences between ventilation and control; (n = 6) animals/group.
Discussion
Our present findings demonstrate that the inflammasome-regulated cytokine IL-18, and its upstream regulator caspase-1, play important roles in the propagation of lung injury in mice, as well as in critically ill patients. Using gene expression analysis, we describe genes corresponding to the inflammasome pathway that are differentially expressed in VILI and in human ARDS. We demonstrate that the plasma level of IL-18 is strongly associated with ARDS risk and indices of morbidity and mortality in four independent cohorts of critically ill patients. Using genetically modified mice, we demonstrate that caspase-1–dependent inflammasome cytokine responses are critical to the propagation of ALI in a rodent model of VILI. This suggests a role for inflammasome pathway activation and its downstream cytokines in ARDS.
The results of our comprehensive gene expression profiling in VILI prompted us to focus on the inflammasome-dependent IL-18 inflammatory pathway (Tables 1 and 2). To evaluate inflammasome-related pathway activation in critical illness, we performed global gene expression profiling using the blood of 88 critically ill patients. ASC and IL1B gene expression was higher in sepsis/ARDS when compared with patients with SIRS. TaqMan analysis confirmed that inflammasome-regulated cytokines IL18, IL1B, and their upstream regulator CASP1 have increased expression in sepsis/ARDS. By comparing SIRS to patients with sepsis/ARDS, we aimed to find pathways that were activated early in illness that influence ARDS development. Our group has previously shown that patients with sepsis/ARDS carry a unique genomic signature different from sepsis alone (26).
To assess the biological relevance of the observed gene expression changes in critical illness, we measured plasma IL-18 and caspase-1 levels in 225 patients (Figure 1, Table 3, and Table E1). IL-18 levels were significantly elevated on admission and remained high in patients with sepsis/ARDS when compared with noninfectious control subjects or patients with sepsis alone. We confirmed our findings by measuring IL-18 levels in independent critical care populations from Vanderbilt University, MGH/BIDMC, and the University of Pennsylvania. Our observations of higher IL-18 plasma levels in patients with sepsis/ARDS, nonseptic ARDS, and trauma-induced ARDS compared with similarly critically ill at-risk control subjects are suggestive of pulmonary contribution to inflammatory cytokine production. Data obtained from patients with severe sepsis with and without ARDS (Vanderbilt University) implies that in severe disease IL-18 production may reach a maximum level beyond which additional organ failure (i.e., lung) will not further contribute to rising cytokine levels.
In the lung, alveolar macrophages produce excessive amounts of IL-1β in patients with ARDS (27). Chemical and biological inhibition of the IL-1 pathway has improved indices of VILI in animal models (28, 29), but most patients with ARDS did not benefit from IL-1 receptor antagonist treatment (30). Inflammasome-mediated IL-1β secretion has been implicated in the pathology of lung inflammation (31), but its relationship to IL-18 is not known. Elevated IL-18 levels have so far been associated with critical illnesses including myocardial ischemia, ALI, acute kidney injury, and sepsis (32–36). Sepsis complicated with ARDS has a high mortality in the ICU (37), yet there are no reliable predictors of mortality (38). In our patient cohort, high levels of IL-18 at admission correlated with increased in-hospital mortality. Although our analysis is limited by not measuring cytokines previously associated with mortality (i.e., IL-6, IL-8) (4, 39, 40), IL-18 level is associated with lactate levels, a clinically established biomarker, and APACHE II scores, a severity indicator, that have both been associated with ICU morbidity and mortality (41–43). Future studies will be needed to compare the predictive power of multiple biomarkers in tandem.
Caspase-1 protein was also detectable in human plasma with a significant increase in sepsis/ARDS patients at MICU admission. However caspase-1 levels rapidly declined to control values by Day 3. The significance of extracellular caspase-1 in the progression of ALI remains unclear, and further studies are warranted to determine its role in inflammation. Recently, Kolliputi and colleagues observed increased inflammasome complex formation and subsequent IL-1β release in alveolar macrophages of mice exposed to hyperoxia (44). Although unable to directly measure inflammasome complex formation in human samples, we provide indirect evidence of increased inflammasome pathway activation in these samples that culminated in observed increases in IL-18 and caspase-1 release.
To further study the role of the inflammasome pathway in ALI, we used a sterile inflammation mouse VILI model. In mice, we observed elevated levels of IL-1β and IL-18 in the lung tissue. MV increased the number of Mac-3–positive cells in the lung, indicating increased numbers of mononuclear cells. Cleaved IL-18 colocalizes with Mac-3–positive alveolar cells. Furthermore, we detected increased IL-18 levels in mouse serum and BALF. From these results we conclude that infiltrating mononuclear cells and alveolar macrophages represent important sources of circulating IL-18 in VILI. Because the inflammasome is critical for IL-18 cleavage in macrophages, we propose that inflammasome activation impacts proinflammatory responses in ALI. Our results also show elevated IL-33 levels in VILI. IL-33 is a proinflammatory cytokine cleaved and subsequently inactivated by caspase-3 and caspase-7 but not caspase-1 during apoptosis (45). These findings suggest that inflammatory caspases not only initiate but also regulate VILI-induced inflammation.
The critical role of caspase-1 was illustrated in Casp1−/− mice, which were protected against VILI. In agreement with our findings, Rowe and colleagues and Fahy and colleagues observed delayed apoptosis in neutrophils isolated from LPS-treated Casp1−/− mice with a transitional inflammatory response (46, 47). The authors concluded that caspase-1 was not required for IL-1β activation but likely modulated lung inflammation via IL-18. Here, we show that Casp1−/− mice produce low levels of IL-18. These results demonstrate that the enhanced production of IL-18 observed in VILI was the product of caspase-1, which was necessary for the propagation of injury. Accordingly, we have also found that the tissue injury was mitigated by the genetic deletion or chemical blockade of IL-18.
The inflammasome plays a central role in host defense against a wide variety of infectious and noninfectious agents (14–16, 19, 20). Our laboratory and others have demonstrated that the NLRP3 inflammasome also regulates IL-18 release in response to proinflammatory stimuli triggered by mitochondrial DNA (17, 48). However, it is unclear to what extent specific inflammasome complexes (i.e., NLRP3) are involved IL-18 activation in ALI and how infection contributes to the propagation of IL-18–mediated injury. Lamkanfi and colleagues have recently suggested that Il18−/− mice have normal susceptibility to bacterial endotoxemia (13). The role of IL-18 in inflammation is further complicated by the fact that neutrophils and alveolar epithelial cells can produce IL-18 via inflammasome-independent neutrophil protease-3 and caspase-4–regulated mechanisms (49, 50). In the future, studies with live bacterial models of pneumonia in mice that are deficient in IL18 and IL1B gene, as well as neutralizing antibody experiments, will be necessary to describe the role of IL-18 in ALI.
Our study includes important limitations. Although findings suggest that IL-18 measurement is correlated with disease severity, lung injury, and mortality in MICU patients, the predictive usefulness of IL-18 measurement as a biomarker remains to be established. We have presented analyses accounting for differences in measurement technique; differences in IL-18 levels between centers (i.e., IL-18 levels in patients at Vanderbilt University compared with BWH) suggest prudence in the interpretation of absolute IL-18 level until measurement methods become standardized. A second potential limitation of this study is the lack of lung tissue and/or BALF samples from our MICU patients to measure local inflammasome-related cytokine expression. Additional limitations include the lack of severity score measured (i.e., APACHE II and Sequential Organ Failure Assessment score) at multiple time points. Future studies will be needed to compare the additive usefulness of IL-18 to commonly measured clinical variables and additional reported (4) and established (41) biomarkers of ICU mortality.
In conclusion, inflammasomes are critical regulators of the innate and adaptive immune system that connect cell death and inflammatory pathways (7, 9, 47). Here, we have found that the inflammasome pathway dependenkt on caspase-1 is activated in critically ill patients and, furthermore, that increases in circulating IL-18 correlate with disease severity and mortality in the MICU. Moreover, we demonstrate that IL-18 and caspase-1 play critical roles in the development of lung injury. Our animal experiments suggest that therapeutics targeting the inflammasome pathway and its downstream mediators may hold promise as novel approaches to therapy.
Supplementary Material
Footnotes
Supported by National Institutes of Health grants PO-HL108801, R01-HL079904, and an FAMRI clinical innovator award (A.M.K.C.); and R01-HL081619 and P01-HL079063 (J.D.C.).
Author Contributions: All authors have seen and approved the manuscript. Conceived and designed the research: T.D., A.M.K.C.; performed animal or biochemical experiments: T.D., Y.S.K., C.H.A., R.L.; performed microarray and data analysis: T.D., J.H., G.M.H., A.R.; provided clinical samples and performed clinical data analysis: T.D., L.F., A.F.M., L.G., K.N., J.A.H., S.E., J.D.C., N.J.M., L.B.W., D.C.C., R.M.B., A.M.K.C.; performed overall data analysis: T.D., S.W.R., A.M.K.C.; wrote the manuscript: T.D., S.W.R., A.M.K.C.; supervised the entire project: A.M.K.C.
This article has an online supplement, which is accessible from this issue’s table of contents at www.atsjournals.org
Originally Published in Press as DOI: 10.1164/rccm.201201-0003OC on March 29, 2012
Author disclosures are available with the text of this article at www.atsjournals.org.
References
- 1.Goss CH, Brower RG, Hudson LD, Rubenfeld GD. Incidence of acute lung injury in the United States. Crit Care Med 2003;31:1607–1611 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Zambon M, Vincent JL. Mortality rates for patients with acute lung injury/ARDS have decreased over time. Chest 2008;133:1120–1127 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.The Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Network Ventilation with lower tidal volumes as compared with traditional tidal volumes for acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med 2000;342:1301–1308 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ware LB, Koyama T, Billheimer DD, Wu W, Bernard GR, Thompson BT, Brower RG, Standiford TJ, Martin TR, Matthay MA, et al. Prognostic and pathogenetic value of combining clinical and biochemical indices in patients with acute lung injury. Chest 2010;137:288–296 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cribbs SK, Martin GS. Biomarkers in acute lung injury: are we making progress? Crit Care Med 2008;36:2457–2459 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Schroder K, Tschopp J. The inflammasomes. Cell 2010;140:821–832 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ichinohe T, Lee HK, Ogura Y, Flavell R, Iwasaki A. Inflammasome recognition of influenza virus is essential for adaptive immune responses. J Exp Med 2009;206:79–87 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Faustin B, Lartigue L, Bruey JM, Luciano F, Sergienko E, Bailly-Maitre B, Volkmann N, Hanein D, Rouiller I, Reed JC. Reconstituted NALP1 inflammasome reveals two-step mechanism of caspase-1 activation. Mol Cell 2007;25:713–724 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sutterwala FS, Ogura Y, Szczepanik M, Lara-Tejero M, Lichtenberger GS, Grant EP, Bertin J, Coyle AJ, Galan JE, Askenase PW, et al. Critical role for NALP3/CIAS1/cryopyrin in innate and adaptive immunity through its regulation of caspase-1. Immunity 2006;24:317–327 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Andrei C, Margiocco P, Poggi A, Lotti LV, Torrisi MR, Rubartelli A. Phospholipases C and A2 control lysosome-mediated IL-1 beta secretion: Implications for inflammatory processes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004;101:9745–9750 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Mariathasan S, Weiss DS, Newton K, McBride J, O'Rourke K, Roose-Girma M, Lee WP, Weinrauch Y, Monack DM, Dixit VM. Cryopyrin activates the inflammasome in response to toxins and ATP. Nature 2006;440:228–232 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Franchi L, Eigenbrod T, Munoz-Planillo R, Nunez G. The inflammasome: a caspase-1-activation platform that regulates immune responses and disease pathogenesis. Nat Immunol 2009;10:241–247 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lamkanfi M, Dixit VM. Modulation of inflammasome pathways by bacterial and viral pathogens. J Immunol 2010;187:597–602 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hornung V, Bauernfeind F, Halle A, Samstad EO, Kono H, Rock KL, Fitzgerald KA, Latz E. Silica crystals and aluminum salts activate the nalp3 inflammasome through phagosomal destabilization. Nat Immunol 2008;9:847–856 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Martinon F, Petrilli V, Mayor A, Tardivel A, Tschopp J. Gout-associated uric acid crystals activate the NALP3 inflammasome. Nature 2006;440:237–241 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Zhou R, Tardivel A, Thorens B, Choi I, Tschopp J. Thioredoxin-interacting protein links oxidative stress to inflammasome activation. Nat Immunol 2010;11:136–140 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Nakahira K, Haspel JA, Rathinam VA, Lee SJ, Dolinay T, Lam HC, Englert JA, Rabinovitch M, Cernadas M, Kim HP, et al. Autophagy proteins regulate innate immune responses by inhibiting the release of mitochondrial DNA mediated by the NALP3 inflammasome. Nat Immunol 2011;12:212–220 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Rathinam VA, Jiang Z, Waggoner SN, Sharma S, Cole LE, Waggoner L, Vanaja SK, Monks BG, Ganesan S, Latz E, et al. The AIM2 inflammasome is essential for host defense against cytosolic bacteria and DNA viruses. Nat Immunol 2010;11:395–402 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Mariathasan S, Newton K, Monack DM, Vucic D, French DM, Lee WP, Roose-Girma M, Erickson S, Dixit VM. Differential activation of the inflammasome by caspase-1 adaptors ASC and Ipaf. Nature 2004;430:213–218 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Iyer SS, Pulskens WP, Sadler JJ, Butter LM, Teske GJ, Ulland TK, Eisenbarth SC, Florquin S, Flavell RA, Leemans JC, et al. Necrotic cells trigger a sterile inflammatory response through the NLRP3 inflammasome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009;106:20388–20393 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Dolinay T, Baron RM, Fredenburgh LE, Massaro AF, Landazury R, Nakahira K, Choi AM. Inflammasome mediators predict disease severity and mortality in patients with sepsis and acute respiratory distress syndrome [abstract]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2009;179:A4646 [Google Scholar]
- 22.Dolinay T, Baron RM, Fredenburgh LE, Massaro AF, Kim YS, Gazourian L, Landazury R, Perrella MA, Choi AM. Inflammasome-activated pro-inflammatory mediators are markers of acute respiratory distress syndrome [abstract]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2010;181:A1698 [Google Scholar]
- 23.Dolinay T, Howrylak JA, Fredenburgh LE, Massaro AF, Gazourian L, Landazury R, Baron RM, Choi AM. Gene expression profiling of sepsis patients reveals inflammasome-mediated susceptibility to acute respiratory distress syndrome development [abstract]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2011;183:A2896 [Google Scholar]
- 24.Dolinay T, Kaminski N, Felgendreher M, Kim HP, Reynolds P, Watkins SC, Karp D, Uhlig S, Choi AM. Gene expression profiling of target genes in ventilator-induced lung injury. Physiol Genomics 2006;26:68–75 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Dolinay T, Wu W, Kaminski N, Ifedigbo E, Kaynar AM, Szilasi M, Watkins SC, Ryter SW, Hoetzel A, Choi AM. Mitogen-activated protein kinases regulate susceptibility to ventilator-induced lung injury. PLoS ONE 2008;3:e1601 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Howrylak JA, Dolinay T, Lucht L, Wang Z, Christiani DC, Sethi JM, Xing EP, Donahoe MP, Choi AM. Discovery of the gene signature for acute lung injury in patients with sepsis. Physiol Genomics 2009;37:133–139 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Jacobs RF, Tabor DR, Burks AW, Campbell GD. Elevated interleukin-1 release by human alveolar macrophages during the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis 1989;140:1686–1692 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Narimanbekov IO, Rozycki HJ. Effect of IL-1 blockade on inflammatory manifestations of acute ventilator-induced lung injury in a rabbit model. Exp Lung Res 1995;21:239–254 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Frank JA, Pittet JF, Wray C, Matthay MA. Protection from experimental ventilator-induced acute lung injury by IL-1 receptor blockade. Thorax 2008;63:147–153 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Opal SM, Fisher CJ, Jr, Dhainaut JF, Vincent JL, Brase R, Lowry SF, Sadoff JC, Slotman GJ, Levy H, Balk RA, et al. Confirmatory interleukin-1 receptor antagonist trial in severe sepsis: a phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial. The interleukin-1 receptor antagonist sepsis investigator group. Crit Care Med 1997;25:1115–1124 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Gasse P, Mary C, Guenon I, Noulin N, Charron S, Schnyder-Candrian S, Schnyder B, Akira S, Quesniaux VF, Lagente V, et al. IL-1R1/MyD88 signaling and the inflammasome are essential in pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis in mice. J Clin Invest 2007;117:3786–3799 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Blankenberg S, Luc G, Ducimetiere P, Arveiler D, Ferrieres J, Amouyel P, Evans A, Cambien F, Tiret L. Interleukin-18 and the risk of coronary heart disease in European men: the Prospective Epidemiological Study of Myocardial Infarction (PRIME). Circulation 2003;108:2453–2459 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Parikh CR, Abraham E, Ancukiewicz M, Edelstein CL. Urine IL-18 is an early diagnostic marker for acute kidney injury and predicts mortality in the intensive care unit. J Am Soc Nephrol 2005;16:3046–3052 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Harada M, Obara K, Hirota T, Yoshimoto T, Hitomi Y, Sakashita M, Doi S, Miyatake A, Fujita K, Enomoto T, et al. A functional polymorphism in IL-18 is associated with severity of bronchial asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2009;180:1048–1055 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Hoshino T, Okamoto M, Sakazaki Y, Kato S, Young HA, Aizawa H. Role of proinflammatory cytokines IL-18 and IL-1beta in bleomycin-induced lung injury in humans and mice. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2009;41:661–670 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Grobmyer SR, Lin E, Lowry SF, Rivadeneira DE, Potter S, Barie PS, Nathan CF. Elevation of IL-18 in human sepsis. J Clin Immunol 2000;20:212–215 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Sheu CC, Gong MN, Zhai R, Chen F, Bajwa EK, Clardy PF, Gallagher DC, Thompson BT, Christiani DC. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of sepsis-related vs non-sepsis-related ARDS. Chest 2010;138:559–567 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kropski JA, Fremont RD, Calfee CS, Ware LB. Clara cell protein (CC16), a marker of lung epithelial injury, is decreased in plasma and pulmonary edema fluid from patients with acute lung injury. Chest 2009;135:1440–1447 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Harbarth S, Holeckova K, Froidevaux C, Pittet D, Ricou B, Grau GE, Vadas L, Pugin J, Geneva Sepsis N. Diagnostic value of procalcitonin, interleukin-6, and interleukin-8 in critically ill patients admitted with suspected sepsis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2001;164:396–402 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Ware LB, Eisner MD, Thompson BT, Parsons PE, Matthay MA. Significance of von Willebrand factor in septic and nonseptic patients with acute lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2004;170:766–772 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Weil MH, Afifi AA. Experimental and clinical studies on lactate and pyruvate as indicators of the severity of acute circulatory failure (shock). Circulation 1970;41:989–1001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.De Backer D, Creteur J, Zhang H, Norrenberg M, Vincent JL. Lactate production by the lungs in acute lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1997;156:1099–1104 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Kruse JA, Thill-Baharozian MC, Carlson RW. Comparison of clinical assessment with APACHE II for predicting mortality risk in patients admitted to a medical intensive care unit. JAMA 1988;260:1739–1742 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Kolliputi N, Shaik RS, Waxman AB. The inflammasome mediates hyperoxia-induced alveolar cell permeability. J Immunol 2010;184:5819–5826 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Luthi AU, Cullen SP, McNeela EA, Duriez PJ, Afonina IS, Sheridan C, Brumatti G, Taylor RC, Kersse K, Vandenabeele P, et al. Suppression of interleukin-33 bioactivity through proteolysis by apoptotic caspases. Immunity 2009;31:84–98 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Rowe SJ, Allen L, Ridger VC, Hellewell PG, Whyte MK. Caspase-1-deficient mice have delayed neutrophil apoptosis and a prolonged inflammatory response to lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. J Immunol 2002;169:6401–6407 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Fahy RJ, Exline MC, Gavrilin MA, Bhatt NY, Besecker BY, Sarkar A, Hollyfield JL, Duncan MD, Nagaraja HN, Knatz NL, et al. Inflammasome mRNA expression in human monocytes during early septic shock. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2008;177:983–988 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Zhou R, Yazdi AS, Menu P, Tschopp J. A role for mitochondria in NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Nature 2011;469:221–225 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Sugawara S, Uehara A, Nochi T, Yamaguchi T, Ueda H, Sugiyama A, Hanzawa K, Kumagai K, Okamura H, Takada H. Neutrophil proteinase 3-mediated induction of bioactive IL-18 secretion by human oral epithelial cells. J Immunol 2001;167:6568–6575 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Tsutsui H, Kayagaki N, Kuida K, Nakano H, Hayashi N, Takeda K, Matsui K, Kashiwamura S, Hada T, Akira S, et al. Caspase-1-independent, Fas/Fas ligand-mediated IL-18 secretion from macrophages causes acute liver injury in mice. Immunity 1999;11:359–367 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.