Abstract
We identified Onchocerca jakutensis as the causative agent of an unusual human filariasis in a patient with lupus erythematosus. To our knowledge, this is the first case of human infection with O. jakutensis and the first human case of zoonotic onchocercosis involving >1 worm.
Keywords: Onchocerca jakutensis, zoonosis, filariasis, PCR, paraffin-embedded tissue, lupus erythematosus, dispatch
Zoonotic filarial infestations occur worldwide, and in most reported cases the involved species are members of the genus Dirofilaria. However, zoonotic Onchocerca infections are rare and to date only 13 cases (originating from Europe, Russia, the United States, Canada, and Japan) have been described. In all of these cases only 1 immature worm was found, and the causative species was identified as O. gutturosa, O. cervicalis, O. reticulata, or O. dewittei japonica on the basis of morphologic and in some cases serologic parameters (1–4). O. cervicalis and O. reticulata are found in the ligaments of the neck and extremities of horses, O. gutturosa is typically found in the nuchal ligaments of cattle, and O. dewittei japonica is found in the distal parts of the limbs and adipose tissue of footpads of wild boars.
We identified the causative agent of a zoonotic Onchocerca infection with multiple nodules in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) who had been receiving hemodialysis. The parasite was identified in paraffin-embedded tissue samples by PCR and DNA sequence analysis.
The Study
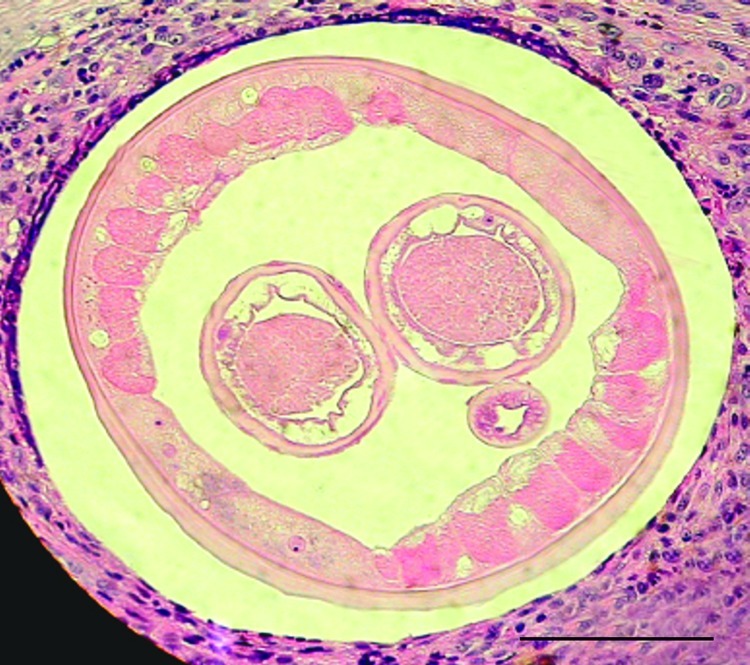
The patient was a 59-year-old woman with SLE who had developed multiple nodules on the neck and face over several years. Because of major renal insufficiency, she also had been receiving hemodialysis 3 times per week (3.5 hours) for >10 years. The first clinical differential diagnoses were cutaneous SLE, nephrogenous dermatopathy, calciphylaxis, and calcinosis. The clinical picture was obscured by secondary inflammations and ulcerations caused by self-inflicted trauma. Multiple sampling attempts by cutaneous core biopsies resulted in histologic diagnosis of unspecific, secondary inflammatory changes. Deep surgical excision of 1 subcutaneous nodule on the scalp indicated subcutaneous helminthosis (Figure). The patient was treated with ivermectin and subjected to 2 plastic surgeries for facial reconstruction, after which she recovered.
Figure.
Transverse section of a female worm and surrounding tissue isolated from the patient (hematoxylin and eosin stained). Scale bar = 100 μm.
At this point, species identification of the causative agent was still pending. A history of travel anamnesis and location of the nodules indicated a possible Dirofilaria infection, but a specific PCR showed negative results. Morphologic features of the few available sections suggested Onchocerca spp. To our knowledge, multiple nodules had never been reported in cases of infection with zoonotic Onchocerca. Because a definitive morphologic identification of the causative nematode was not possible, molecular identification from DNA isolated from the only available material (formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded tissue) was conducted.
To evaluate the causative genus, universal filarial primers were constructed on the basis of filarial sequences available in GenBank (primer FILfw 5′-cggtgatattggttggtctc-3′ for the first internal transcribed spacer region and primer FILrev 5′-ctagctgcgttcttcatcgatc-3′ for the 5.8S rRNA gene). PCR and sequencing were performed and a similarity matrix was calculated after multiple sequence alignment (5).
The DNA fragment obtained was 226 bp and showed greatest similarities to Onchocerca sequences, ranging from 87% to 95%. Similarities to Wuchereria, Brugia, Mansonella, Dirofilaria, and Acanthocheilonema were lower, ranging from 75% to 80%. Assignment to the genus Onchocerca was obvious, but species identification still posed a problem because published O. volvulus sequences showed higher similarities among each other (98.8%–100%) than with our sequence. The only exception was a clinical O. volvulus strain (OvNod1–3) from Bolo, Cameroon, which showed 94.8% sequence similarity. However, the authors of that report indicated that their strain might be a zoonotic Onchocerca sp. (6).
An identical thymine mononucleotide repeat motif in our strain and strain OvNod1–3, which was shorter in all O. volvulus sequences, indicated that both strains were not O. volvulus because repeat motifs have been reported to occur in species-specific patterns. The negative results with an O. volvulus–specific PCR (6) corroborated this assumption. Therefore, 2 additional primer pairs for Onchocerca spp. identification were constructed, 1 for the mitochondrial NADH dehydrogenase subunit 5 gene (OND5fw 5′-ctcctgttagttgtttggttc-3′, OND5rev 5′-gcaaacccctaccaatagc-3′) and 1 for the 16S mitochondrial rRNA gene (O16fw 5′-gcgtgatggcataaaagtagc-3′, O16rev 5′-caaccctgttaactccggag-3′), on the basis of available Onchocerca spp. sequences (7,8). PCR products were sequenced and similarity matrices were calculated (Tables 1, 2). The NADH amplicon was 201 bp and the 16S rRNA amplicon was 225 bp. Both amplicons unambiguously identified our strain as O. jakutensis with 100% and 99.55% sequence similarities, respectively. Sequence data were deposited in GenBank and are available under the following accession nos.: EF202184, EF202185, and EF202186.
Table 1. Sequence similarities in the NADH dehydrogenase subunit 5 gene in the Onchocerca sp. isolated in this study and other Onchocerca spp.*.
| Species | % Sequence similarity |
|||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| arm | duk | fas | fle | gib | gut | jak | lie | och | ram | vol | This study | |
| arm | 100 | 94.03 | 91.54 | 91.54 | 92.04–92.53 | 86.07–92.54 | 92.04 | 91.54–92.54 | 89.55–93.03 | 81.59 | 93.03–94.03 | 92.04 |
| duk | 100 | 94.53 | 92.54 | 96.51–97.01 | 92.04–96.51 | 94.53 | 97.51–98.51 | 95.02–97.01 | 82.59 | 98.01–99.00 | 92.02 | |
| fas | 100 | 89.05 | 92.04–92.53 | 88.56–94.03 | 94.53 | 95.02–96.02 | 92.04–95.52 | 82.59 | 93.53–94.53 | 94.53 | ||
| fle | 100 | 93.03–95.03 | 86.57–92.04 | 91.04 | 91.04–92.04 | 90.55–92.04 | 82.09 | 92.53–93.53 | 91.04 | |||
| gib | 99.5 | 90.05–95.02 | 92.04–92.54 | 94.03–95.52 | 94.03–95.52 | 84.08–84.58 | 95.52–97.01 | 92.04–93.54 | ||||
| gut | 90.55–97.51 | 89.05–94.53 | 91.54–96.02 | 91.04–95.52 | 79.10–82.59 | 91.04–96.52 | 89.05–94.53 | |||||
| jak | 100 | 94.53–95.52 | 92.54–95.02 | 82.09 | 94.03–95.02 | 100 | ||||||
| lie | 98.51–100 | 94.53–98.51 | 83.08–84.08 | 96.52–98.51 | 94.53–95.52 | |||||||
| ochi | 94.53–100 | 81.59–84.58 | 94.03–98.01 | 92.54–95.02 | ||||||||
| ram | 100 | 83.58–84.08 | 82.09 | |||||||||
| vol | 98.51–100 | 94.03–95.02 | ||||||||||
| This study | 100 | |||||||||||
*arm, armillata; duk, dukei; fas, fassiata; fle, flexuosa; gib, gibsoni; gut, gutturosa; jak, jakutensis; lie, lienalis; och, ochegni; ram, ramachandrini; vol, volvulus.
Table 2. Sequence similarities in the mitochondrial 16S rRNA gene in the Onchocera sp. isolated in this study and other Onchocherca spp.*.
| Species | % Sequence similarity |
|||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| arm | duk | fas | fle | gib | gut | jak | lie | och | ram | vol | This study | |
| arm | 100 | 91.56 | 96.00 | 96.00 | 94.67 | 93.78–94.22 | 94.22 | 93.33-93.78 | 93.33–93.78 | 93.33 | 91.55–92.00 | 93.78 |
| duki | 100 | 95.56 | 92.00 | 95.56 | 94.67–95.11 | 94.67 | 95.11 | 96.89–97.33 | 91.11 | 96.89–97.33 | 91.11 | |
| fas | 100 | 95.56 | 96.89 | 96.00–96.44 | 96.44 | 96.44–96.88 | 95.56–96.00 | 93.33 | 94.66–95.11 | 96.00 | ||
| fle | 100 | 94.22 | 94.22–94.66 | 95.56 | 93.78–94.22 | 92.40–92.88 | 93.78 | 92.44–92.89 | 95.11 | |||
| gib | 100 | 97.78–98.22 | 97.78 | 96.89–97.33 | 94.67 | 93.78 | 93.77–94.22 | 97.33 | ||||
| gut | 99.10–100 | 96.89–97.33 | 96.00–96.89 | 93.33–93.77 | 91.56–92.00 | 93.33–93.78 | 96.89–97.33 | |||||
| jak | 100 | 98.22–98.67 | 92.88–93.33 | 92.44 | 92.00–92.44 | 99.56 | ||||||
| lie | 99.56–100 | 93.33–93.78 | 92.44–92.88 | 92.44–92.88 | 97.78–98.22 | |||||||
| och | 99.56–100 | 91.11–91.55 | 97.33–98.22 | 93.33–93.78 | ||||||||
| ram | 100 | 90.22–90.67 | 92.00 | |||||||||
| vol | 99.56–100 | 92.44–92.89 | ||||||||||
| This study | 100 | |||||||||||
*arm, armillata; duk, dukei; fas, fassiata; fle, flexuosa; gib, gibsoni; gut, gutturosa; jak, jakutensis; lie, lienalis; och, ochegni; ram, ramachandrini; vol, volvulus.
Conclusions
The limiting factor in identifying the causative agent in our patient was the nature of the sample material. Because only a few formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded sections were available, morphologic identification was not possible. PCR-based identification was restricted because DNA has a tendency to degrade when stored in formalin, which limits the length of the target sequence to ≈300 bp and limits its discriminatory power (9). A different approach with 3 PCRs, 1 for genus identification and 2 for species identification, and primers for highly variable multicopy targets enabled us to accurately identify the causative agent as O. jakutensis.
To our knowledge, O. jakutensis has never been identified as an agent of human filariasis. It has been identified as a rare parasite of red deer in Germany, Poland, and Russia, and may also be found in other northern European countries (10). Our patient came from the United States and had traveled all over Europe. She could thus have acquired the infection in several different locations.
Two findings for this patient were particularly unusual and obscured the identification of the parasite. The first finding was that she had, in contrast to all previous human cases of zoonotic onchocercosis, multiple nodules. The second finding was that her face (periorbital and buccal), neck, and scalp were affected, although zoonotic filariae are typically found in similar or identical tissues as in their natural hosts (11). O. jakutensis is usually found in tissues of the outer thigh and caudal part of the back; >2 nodules per infected host are rare (12,13).
It is unlikely that these findings are associated with greater virulence of O. jakutensis than of other zoonotic Onchocerca spp. However, parasite virulence might be related to the patient having had autoimmune disease since childhood and as a result having received long-term immunosuppressive therapy. The immune status of the patient was further impaired by renal insufficiency for >10 years. However, no data exist on the immune status of patients in any of the previously reported cases of infection with zoonotic Onchocerca spp. For other nematodes, e.g., Strongyloides stercoralis, a correlation between immune status of the patient and severity of disease is well established. One report describes more severe skin manifestations caused by O. volvulus in HIV patients (14).
We have identified a zoonotic infestation with an Onchocerca sp. that can cause disease in humans. The combination of impaired immunity and unusually progressing infestation highlights a new aspect of zoonotic filariasis.
Acknowledgments
We thank Odile Bain and Silvio Pampiglione for helpful comments.
Biography
Ms Koehsler is a research assistant and a doctoral student at the Department of Medical Parasitology of the Medical University of Vienna. Her research interests include the molecular biology of parasites.
Footnotes
Suggested citation for this article: Koehsler M, Soleiman A, Aspöck H, Auer H, Walochnik J. Onchocerca jakutensis as a causative agent of human filariasis. Emerg Infect Dis [serial on the Internet]. 2007 Nov [date cited]. Available from http://www.cdc.gov/eid/content/13/11/1749.htm
References
- 1.Siegenthaler R, Gubler R. Paraarticulares Nematodengranulom (einheimische Onchocerca). Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1965;95:1102–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Beaver PC, Horner GS, Bilos JZ. Zoonotic onchocercosis in a resident of Illinois and observations on the identification of Onchocerca species. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1974;23:595–607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Takaoka H, Bain O, Uni S, Korenaga M, Tada K, Ichikawa H, et al. Human infection with Onchocerca dewittei japonica, a parasite from wild boar in Oita, Japan. Parasite. 2001;8:261–3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Pampiglione S, Vakalis N, Lyssimachou A, Kouppari G, Orihel TC. Subconjunctival zoonotic Onchocerca in an Albanian man. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 2001;95:827–32. 10.1080/00034980120111163 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Köhsler M, Leitner B, Blaschitz M, Michel R, Aspoeck H, Walochnik J. ITS1 sequence variabilities correlate with 18S rDNA sequence types in the genus Acanthamoeba (Protozoa: Amoebozoa). Parasitol Res. 2006;98:86–93. 10.1007/s00436-005-0022-x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Morales-Hojas R, Post RJ, Shelley AJ, Maia-Herzog M, Coscaron S, Cheke RA. Characterisation of nuclear ribosomal DNA sequences from Onchocerca volvulus and Mansonella ozzardi (Nematoda: Filarioidea) and development of a PCR-based method for their detection in skin biopsies. Int J Parasitol. 2001;31:169–77. 10.1016/S0020-7519(00)00156-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Morales-Hojas R, Cheke RA, Post RJ. Molecular systematics of five Onchocerca species (Nematoda: Filarioidea) including the human parasite, O. volvulus, suggest sympatric speciation. J Helminthol. 2006;80:281–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Krueger A, Fischer P, Morales-Hojas R. Molecular phylogeny of the filaria genus Onchocerca with special emphasis on Afrotropical human and bovine parasites. Acta Trop. 2007;101:1–14. 10.1016/j.actatropica.2006.11.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.An SF, Fleming KA. Removal of inhibitor(s) of the polymerase chain reaction from formalin fixed, paraffin wax embedded tissues. J Clin Pathol. 1991;44:924–7. 10.1136/jcp.44.11.924 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Bain O, Schulz-Key H. The species of Onchocerca in the red deer: redescription of O. flexuosa (Wedl, 1856) and description of O. tubingensis n.sp. and O. tarsicola n.sp [in French]. Tropenmed Parasitol. 1974;25:437–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Demiaszkiewicz AW. Redescription of Onchocerca jakutensis (Gubanov, 1964) (Nematoda, Filaroideaea). Acta Parasitologica Polonica. 1993;38:124–7. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Schulz-Key H. Studies on the Filariidae of Cervidae in southern Germany. 2. Filariidae of the red deer (Cervus elaphus) [in German]. Tropenmed Parasitol. 1975;26:348–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Plenge-Bonig A, Kromer M, Buttner DW. Light and electron microscopy studies on Onchocerca jakutensis and O. flexuosa of red deer show different host-parasite interactions. Parasitol Res. 1995;81:66–73. 10.1007/BF00932419 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kipp W, Bamuhiiga J, Rubaale T. Simulium neavei–transmitted onchocerciasis: HIV infection increases severity of onchocercal skin disease in a small sample of patients. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2003;97:310–1. 10.1016/S0035-9203(03)90157-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]