SUMMARY
Alzheimer's disease (AD) results in cognitive decline and altered network activity, but the mechanisms are unknown. To identify such mechanisms, we studied human amyloid precursor protein (hAPP) transgenic mice, which simulate key aspects of AD. Electroencephalographic recordings in hAPP mice revealed spontaneous epileptiform discharges, indicating network hypersynchrony, primarily during reduced gamma oscillatory activity. Because this oscillatory rhythm is generated by inhibitory parvalbumin (PV) cells, network dysfunction in hAPP mice might arise from impaired PV cells. Supporting this hypothesis, hAPP mice and AD patients had decreased levels of the interneuron-specific and PV cell–predominant voltage-gated sodium channel subunit Nav1.1. Restoring Nav1.1 levels in hAPP mice by Nav1.1-BAC expression increased inhibitory synaptic activity and gamma oscillations and reduced hypersynchrony, memory deficits, and premature mortality. We conclude that reduced Nav1.1 levels and PV cell dysfunction critically contribute to abnormalities in oscillatory rhythms, network synchrony, and memory in hAPP mice and possibly in AD.
INTRODUCTION
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is incurable and increasing in prevalence in aging populations. Diverse lines of evidence suggest that amyloid-β (Aβ) peptides contribute to AD pathogenesis (Hardy and Selkoe, 2002). Pathological levels of Aβ enhance synaptic depression and impair synaptic plasticity at glutamatergic synapses (Hsieh et al., 2006; Kamenetz et al., 2003; Walsh et al., 2002). However, its effects on circuits and network activity in humans and mouse models are poorly understood (Palop and Mucke, 2010). Besides synaptic depression, human amyloid precursor protein (hAPP) transgenic lines with high Aβ levels show evidence of altered network activity, reflected in abnormal expression of activity-regulated genes, clusters of hyperactive and hypoactive neurons, network hyperexcitability, and spontaneous epileptiform activity (Busche et al., 2008; Harris et al., 2010; Minkeviciene et al., 2009; Palop et al., 2007; Roberson et al., 2011). In AD patients and nondemented humans, amyloid deposits are predominately distributed along networks with aberrant neuronal activity (Buckner et al., 2005; Sperling et al., 2009), suggesting activity-driven pathology (Bero et al., 2011). Thus, network abnormalities leading to, or induced by, Aβ accumulation may be a relatively early pathogenic event in AD (Sperling et al., 2009). The incidence of epileptic activity is also increased in sporadic AD (Amatniek et al., 2006), but is particularly high in pedigrees with early-onset autosomal dominant AD (Cabrejo et al., 2006; Larner and Doran, 2006; Palop and Mucke, 2009; Snider et al., 2005). Therefore, determining the mechanisms of AD-related network dysfunction and its relation to cognitive decline is an important objective.
hAPP mice are experimental models of cerebral Aβ amyloidosis and of synaptic and cognitive dysfunctions. hAPPJ20 mice simulate several key aspects of sporadic and autosomal dominant AD, including deficits in learning and memory, behavioral abnormalities, synaptic alterations, amyloid plaques, and gliosis (Cheng et al., 2007; Cisse et al., 2011; Palop et al., 2007; Palop et al., 2003; Roberson et al., 2007). Previously, we discovered spontaneous epileptic activity, indicating network hypersynchrony, in cortical and hippocampal EEG recordings of hAPPJ20 mice (Palop et al., 2007). Here, we determined if these large-scale events of network hypersynchronization are linked to specific abnormalities in oscillatory rhythmic activity (“brain waves”). Interestingly, network hypersynchrony emerged during reduced gamma activity, a high-frequency oscillatory rhythm that depends on the synaptic activity of parvalbumin-positive inhibitory interneurons (PV cells) and contributes to cognitive functions (Cardin et al., 2009; Korotkova et al., 2010; Mann and Paulsen, 2007; Sohal et al., 2009). We therefore tested the hypothesis that abnormalities in network synchrony, oscillatory rhythms, and cognitive functions in hAPP mice arise from impaired PV cells.
Voltage-gated sodium channels (VGSC) control cellular and network excitability by modulating synaptic activity in specific neuronal subtypes (Meisler and Kearney, 2005). Sporadic loss-of-function mutations or haploinsufficiency of the VGSC subunit Nav1.1 due to genomic microdeletions cause epilepsy syndromes (Catterall et al., 2010; Suls et al., 2006). Since Nav1.1 is expressed predominantly in PV cells (Ogiwara et al., 2007; Wang et al., 2011), network hypersynchrony in these epilepsies may arise from impaired PV cells (Ogiwara et al., 2007; Yu et al., 2006). Dysfunction of PV cells has also been implicated in cognitive alterations and psychiatric symptoms in other disorders associated with altered network activity, including schizophrenia and autism (Fazzari et al., 2010; Sohal et al., 2009).
Consistent with a critical role for altered Nav1.1 levels and PV cell–dependent activity in the pathogenesis of network and cognitive dysfunction of hAPP mice, reversing Nav1.1 reductions in hAPPJ20 mice by Nav1.1-BAC transgene expression restored PV cell–dependent gamma oscillations and inhibitory synaptic currents and reduced premature mortality, network hypersynchrony, and memory deficits in these mice. Thus, Nav1.1 depletion in PV cells may contribute to network dysfunction and cognitive deficits in hAPP mice and possibly in AD. Improving the function of PV cells and gamma activity may be of therapeutic benefit in AD and other brain disorders associated with altered network activity and cognitive impairments.
RESULTS
Network Hypersynchrony Emerges during Reduced Gamma Activity in hAPPJ20 Mice
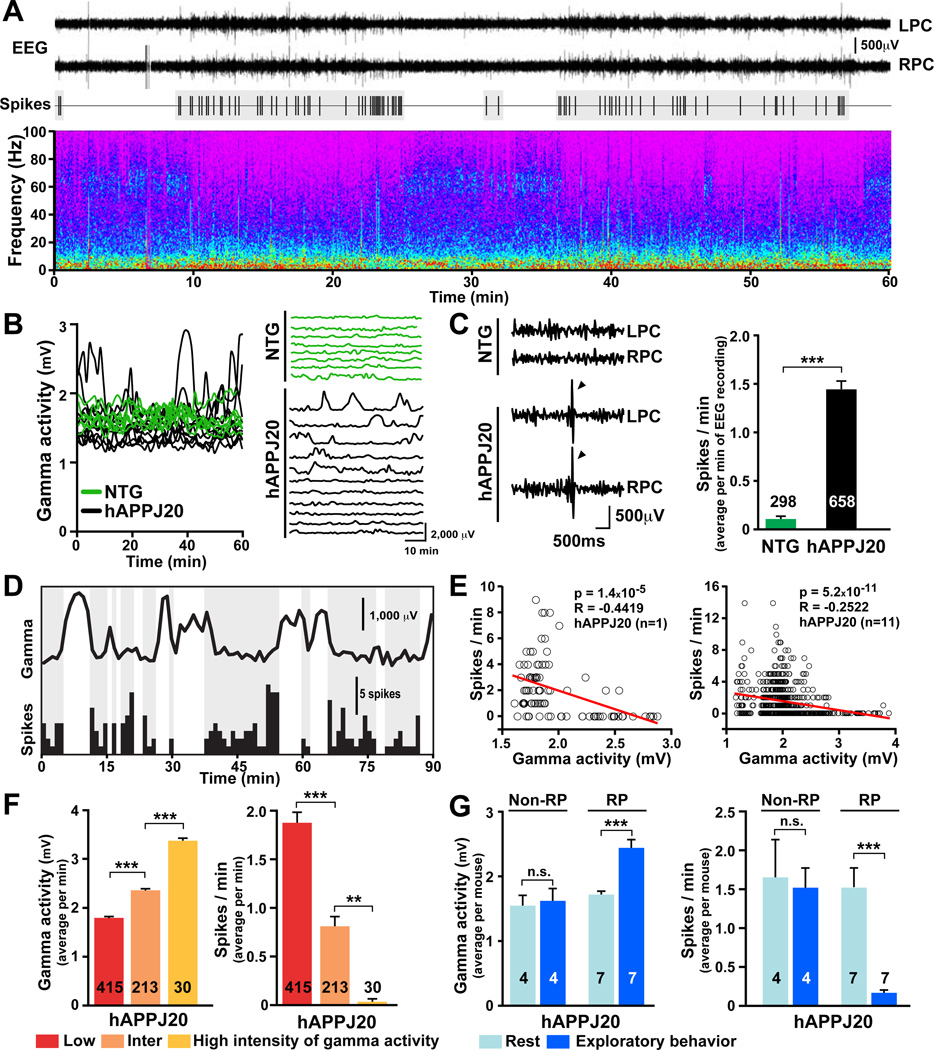
The combined activity of neural networks generates specific oscillatory patterns that can be measured by EEG recordings. We first determine if any patterns of abnormal EEG activity are associated with spontaneous epileptiform discharges (spikes) in hAPPJ20 mice. Oscillations of 0–100 Hz and spikes were monitored in 1-min intervals for 60 min over the parietal cortex of nontransgenic (NTG) and hAPPJ20 mice. hAPPJ20 mice had prominent abnormalities in the intensity of gamma oscillations (20–80 Hz; Figure 1A), including abrupt fluctuations and depressed intensity of gamma activity (Figure 1A, B). Consistent with previous findings (Harris et al., 2010; Minkeviciene et al., 2009; Palop et al., 2007; Roberson et al., 2011), hAPPJ20 mice had frequent spikes (Figure 1A, C). Spikes occurred in clusters and were closely related to the intensity of gamma oscillations (Figure 1A, D). Linear regression analyses within individual and among hAPPJ20 mice revealed an inverse relationship between the intensity of gamma activity and the spike rate (Figure 1E). Across hAPPJ20 mice, spikes were absent during periods of high-intensity gamma activity, common during intermediate-intensity gamma activity, and frequent during low-intensity gamma activity (Figure 1F). Thus, network hypersynchrony emerges during reduced gamma activity. Equivalent results were found when periods of high- and low-intensity gamma activity were compared in each hAPPJ20 mouse (Figure S1A, B). Because gamma oscillations are generated by the synaptic activity of PV cells (Cardin et al., 2009; Sohal et al., 2009), we hypothesized that the above network alterations arise from PV cell impairments and that enhancing gamma activity or PV cell function would be of benefit in hAPPJ20 mice.
Figure 1. Network Hypersynchrony Emerges during Reduced Intensity of Gamma Activity in hAPPJ20 Mice.
EEG recordings from the left (L) and right (R) parietal cortex (PC) in NTG (n=8) and hAPPJ20 (n=11) mice. The intensity of gamma activity (20–80 Hz), frequency of epileptiform discharges (spikes), and exploratory activity were measured in 1-min intervals for 60 min. Numbers in bars are minutes of EEG recording (C, F) or mice (G).
(A) EEG recordings (top), spike distribution (middle), and full frequency range (0–100 Hz) spectrogram (bottom) from an hAPPJ20 mouse. Spike rate increases during periods of reduced gamma intensity.
(B) Longitudinal quantifications of gamma activity in hAPPJ20 (black) and NTG (green) mice illustrating abnormal patterns of gamma activity in hAPPJ20 mice. Each trace represents a mouse.
(C) hAPPJ20 mice, but not NTG controls, displayed frequent spikes (arrowheads).
(D) Longitudinal quantification of gamma activity (top trace) and spike rate (bottom histogram).
(E) Linear regression analyses revealed an inverse relationship between intensity of gamma activity and spike rate in individual (left) and among (right) hAPPJ20 mice.
(F) Minutes with low, intermediate (inter), or high intensity of gamma activity (left) had high, intermediate, or low spike rates (right), respectively.
(G) Only hAPPJ20 mice with increased gamma activity during exploration (responders, RP) (left) had reductions in spikes (right). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 by unpaired (C) or paired (G) two-sample t test, or ANOVA and Tukey test (F). Bars represent mean ± SEM. See Figure S1 for supporting data.
In support of the latter possibility, exploratory behavior was associated with increased gamma activity and fewer spikes in hAPPJ20 mice (Figure S1C). Interestingly, only hAPPJ20 mice with increased gamma activity during exploration had reductions in spikes (Figure 1G). Thus, gamma activity, but not exploratory behavior per se, modulates epileptiform discharges in these mice.
Inhibitory Synaptic Impairments and PV Cell Dysfunction in hAPPJ20 Mice
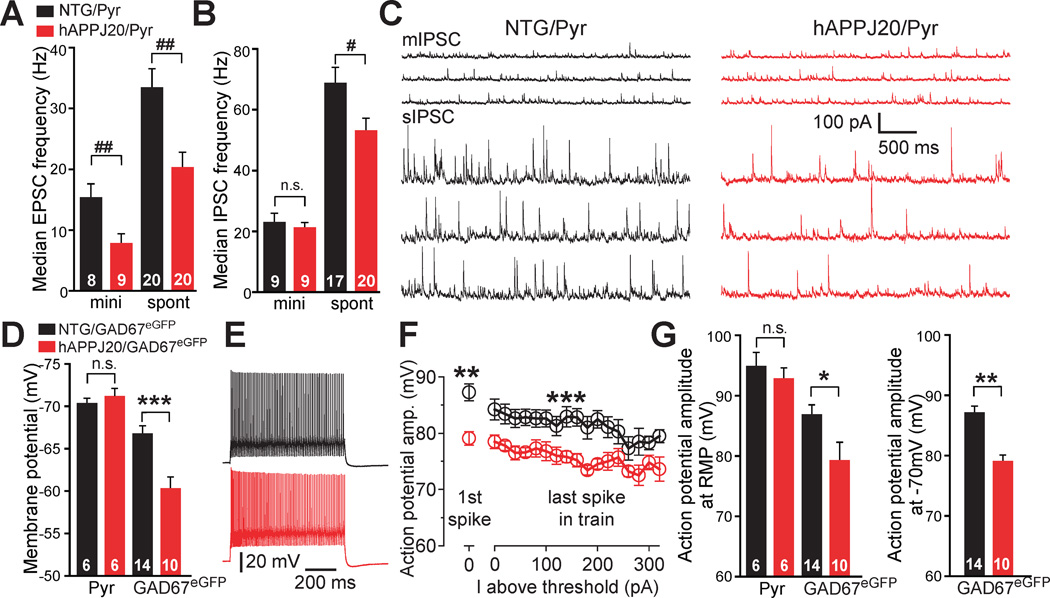
In agreement with previous findings (Roberson et al., 2011), hAPPJ20 mice had reduced glutamatergic transmission in the parietal cortex (Figure 2A). To explore whether GABAergic function is altered in hAPPJ20 mice, we recorded miniature and spontaneous inhibitory postsynaptic currents (mIPSC vs sIPSC, respectively) from layer II/III pyramidal neurons. When action potential–driven neuronal activity was blocked, hAPPJ20 and NTG mice had similar amplitudes and frequencies of mIPSCs (Figure 2B, C), suggesting a normal number of functional GABAergic synapses. However, when action potential–driven neuronal activity was present, hAPPJ20 mice had significant reductions in sIPSC frequency (Figure 2B, C), indicating activity-dependent impairment in GABAergic function. Thus, interneuronal excitability is likely compromised by intrinsic or circuit alterations in hAPPJ20 mice (Roberson et al., 2011).
Figure 2. Inhibitory Synaptic Impairments and PV Cell Dysfunction in hAPPJ20 Mice.
(A–C) Synaptic alterations in layer II/III pyramidal neurons (Pyr) of the parietal cortex in hAPPJ20 (hAPPJ20/Pyr; red) and NTG (NTG/Pyr; black) mice. (A, B) Frequency of miniature (mini, m) and spontaneous (spont, s) excitatory (A) and inhibitory (B) postsynaptic currents (mIPSC, sIPSC, mEPSC, and sEPSC). #p<0.05, ##p<0.01 (Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney two-sample rank test). (C) Recordings of mIPSCs (upper panels) and sIPSCs (lower panels). (D–G) Synaptic alterations in fast-spiking GABAergic cells of the parietal cortex in GAD67eGFP transgenic mice without (NTG/GAD67eGFP; black) or with hAPP (hAPPJ20/GAD67eGFP; red) expression. (D) Resting membrane potential (RMP) of pyramidal cells and fast-spiking GABAergic cells. ***p<0.001 (t test). (E) Spike traces from fast-spiking GABAergic cells (red) evoked by 800-ms current of 380 pA. (F) Mean action potential amplitudes for the first spike at threshold and for the last spike of the train at each 20-pA-current step above threshold. Neurons were held at −70 mV between current steps (n=10–14 cells per genotype). **p<0.01 (t test), ***p<0.001 (two-way ANOVA). (G) Reduced action potential amplitudes for the first spike at threshold in fast-spiking GABAergic cells of hAPPJ20/GAD67eGFP mice. Neurons were at RMP (left) or held at −70 mV (right) between current steps. *p<0.05, **p<0.01 (t test). Numbers in bars are cells (A, B, D, G). Values are mean ± SEM. See Figure S2 and Table S1 for supporting data.
To determine if intrinsic properties of fast-spiking PV cells are altered in hAPPJ20 mice, we crossed hAPPJ20 mice with bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) transgenic mice expressing enhanced GFP (eGFP) directed by GAD67 regulatory sequences (GAD67eGFP) (Chattopadhyaya et al., 2004) to produce GAD67eGFP mice without or with hAPP expression (NTG/GAD67eGFP and hAPPJ20/GAD67eGFP, respectively). eGFP-labeled fast-spiking GABAergic interneurons and nonlabeled pyramidal cells were assessed by patch-clamp recordings. Fast-spiking interneurons, but not pyramidal cells, had more depolarized resting membrane potentials in hAPPJ20/GAD67eGFP mice than in NTG/GAD67eGFP mice (Figure 2D and Table S1). Action potential properties were examined using current steps of increasing amplitude (800 ms, 20 pA steps). Although the pattern and frequency of action potentials across different stimulus intensities (0–320 pA above threshold) did not differ between genotypes (Figures 2E and S2A–C), fast-spiking interneurons had smaller action-potential amplitudes in hAPPJ20/GAD67eGFP mice than in NTG/GAD67eGFP mice both at resting membrane potentials and when resting membrane potentials were held constant at −70 mV (Figure 2F, G and Table S1). No differences in action potential amplitudes were found in layer II/III pyramidal cells (Figure 2G).
Reduced VGSC Levels in PV Cells of hAPPJ20 Mice and in AD Brains
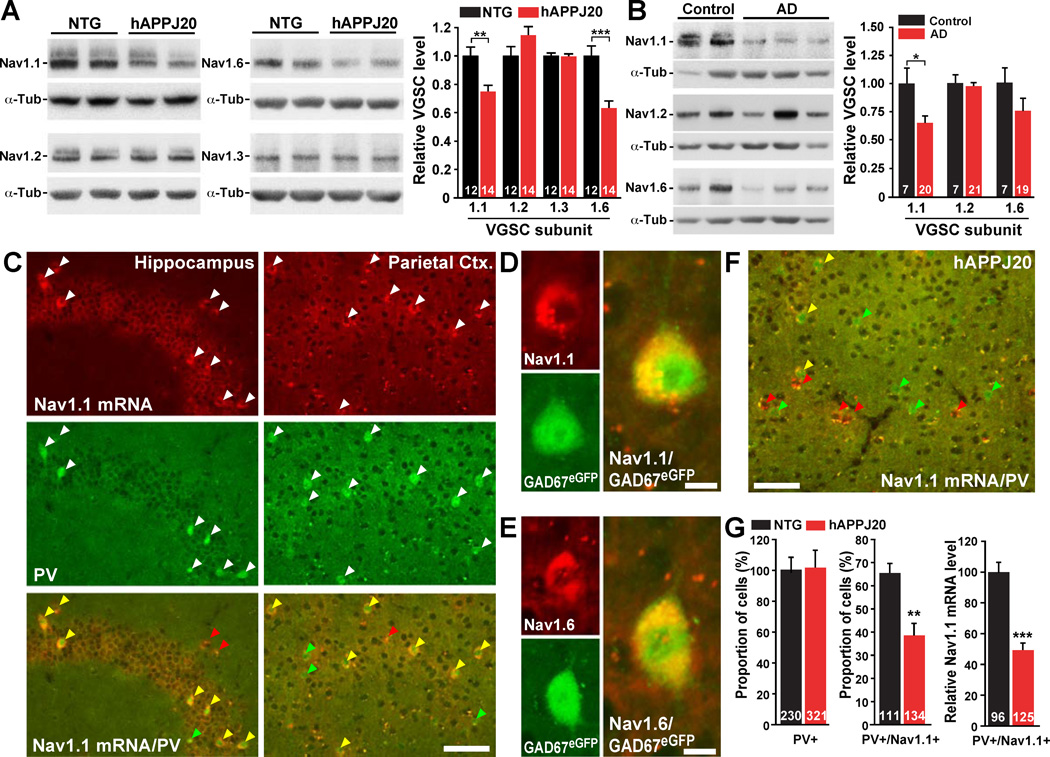
Because action potential–driven synaptic activity depends on VGSCs (Catterall et al., 2010; Meisler and Kearney, 2005) (Figure S2D–F), we measured the levels of the four main VGSC subunits expressed in the central nervous system (Nav1.1, Nav1.2, Nav1.3, and Nav1.6) (Meisler and Kearney, 2005). hAPPJ20 mice had reduced levels of Nav1.1 and Nav1.6, but not Nav1.2 and Nav1.3, in the parietal cortex (Figure 3A). We also analyzed Nav1.1, Nav1.2, and Nav1.6 levels in the inferior parietal cortex of patients with AD and nondemented controls. In the AD cases, Nav1.1 levels were significantly depleted, Nav1.6 levels showed a clear trend toward depletion, and Nav1.2 levels were unchanged (Figure 3B).
Figure 3. Reduced Nav1.1 Levels in PV Cells of hAPPJ20 Mice and in AD Brains.
(A–B) Parietal cortex from mice and inferior parietal cortex from humans was dissected and VGSC levels were determined by western blot analyses. (A) Representative western blots and quantification of Nav1.1, Nav1.2, Nav1.3, and Nav1.6 in hAPPJ20 and NTG mice. (B) Representative western blots and quantification of Nav1.1, Nav1.2, and Nav1.6 levels in nondemented controls and AD cases.
(C–G) Double fluorescence in situ hybridization for Nav1.1 (red) and immunohistochemistry for PV (green) on cryosections from NTG, hAPPJ20, and GAD67eGFP mice. (C) In NTG mice, Nav1.1 mRNA was expressed at high levels by PV cells. Arrowheads in bottom panels (merged) indicate single- (PV; green, Nav1.1; red) or double-labeled (yellow) cells. (D, E) In GAD67eGFP mice, Nav1.1 (D) and Nav1.6 (E) mRNAs were highly expressed by GAD67eGFP-positive (green) cells. (F) In hAPPJ20 mice, Nav1.1 mRNA expression was reduced in the parietal cortex (compare with C). (G) hAPPJ20 mice had no reductions of PV cells in the parietal cortex (left) but had fewer Nav1.1-positive PV cells (middle) and lower Nav1.1 mRNA expression in PV cells (right) than controls. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 (t test). Scale bars: 50 µm (C, F); 5 µm (D, E). Values are mean ± SEM. Numbers in bars are mice (A), human cases (B), or cells (G). See Figure S3 for supporting data.
VGSCs show distinct patterns of expression across neuronal populations (Lorincz and Nusser, 2008; Meisler and Kearney, 2005; Ogiwara et al., 2007), and the effects of reduced VGSC expression on network activity depend on the type of neuron affected. In agreement with previous reports (Lorincz and Nusser, 2008; Meisler and Kearney, 2005; Ogiwara et al., 2007), Nav1.1 mRNA was highly expressed by a small subset of neurons in the hippocampus and parietal cortex (Figures 3C and S3A). Double-labeling for Nav1.1 mRNA and PV showed near complete co-location of these gene products (Figures 3C and S3A). Nav1.6 mRNA was highly expressed by the majority of hippocampal neurons and a small subset in the parietal cortex (Figure S3B). Double-labeling for Nav1.6 mRNA and PV revealed near complete co-location in the parietal cortex (Figure S3B). Consistent with these results and the expression of eGFP in PV cells in line G42 (Chattopadhyaya et al., 2004), Nav1.1 and Nav1.6 were expressed by green fluorescent cells in the parietal cortex of GAD67eGFP mice (Figure 3D, E). Thus, Nav1.1 and Nav1.6 expression in the parietal cortex is restricted primarily to PV cells. Similar results were found in primary cell cultures (Figure S3C).
Similar expression patterns were found in hAPPJ20 mice (Figure 3F). However, quantification of PV- and Nav1.1-positive cells and Nav1.1 mRNA signals in PV cells showed reduced numbers of Nav1.1-positive PV cells and reduced Nav1.1 mRNA expression in PV cells in the parietal cortex of hAPPJ20 mice (Figure 3G), indicating reduced Nav1.1 levels in PV cells in hAPPJ20 mice.
Inhibiting VGSCs Reduces Gamma Activity and Enhances Network Hypersynchronization and Learning/Memory Impairments in hAPPJ20 Mice
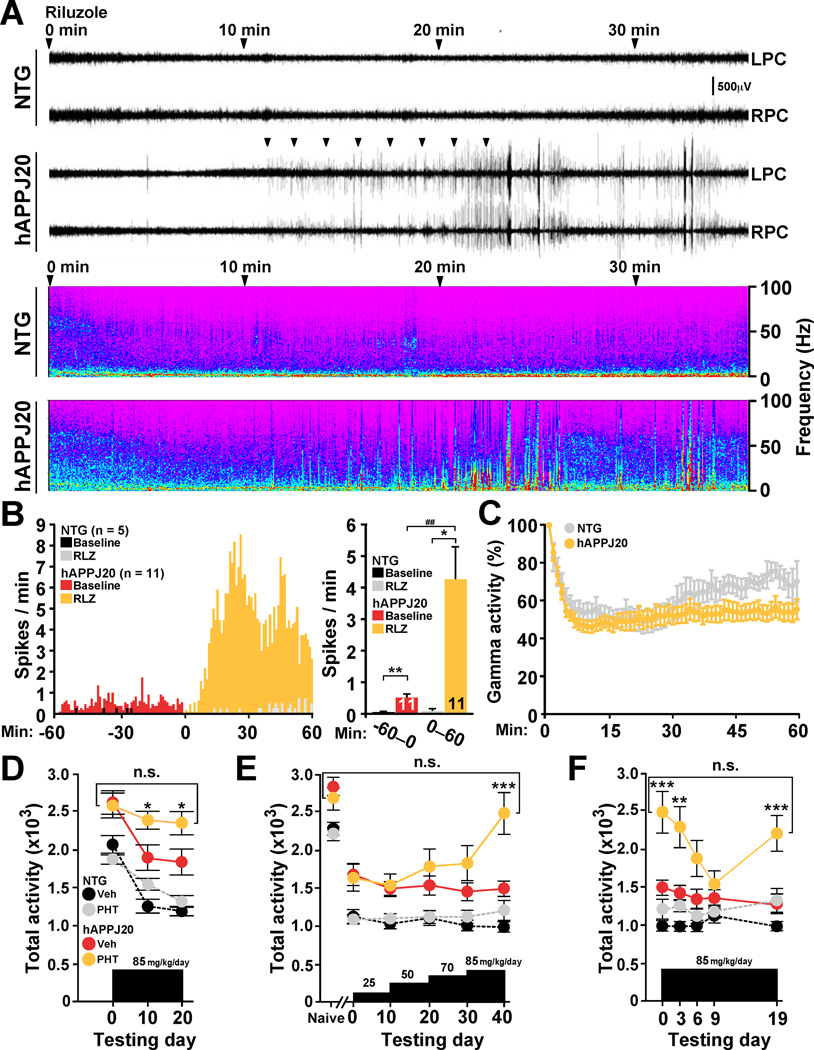
To explore potential relations among VGSCs, gamma oscillations, and network hypersynchronization in hAPP mice, we inhibited VGSC function with riluzole or phenytoin (Spadoni et al., 2002) and monitored neural network activity by EEG. Riluzole reduced the intensity of gamma oscillations within minutes and triggered intense epileptiform activity in hAPPJ20 mice but not in NTG controls (Figure 4A–C). These effects were independent of exploratory activity (Figure S4A). Phenytoin had similar effects (Figure S4B, C). These results strongly suggest VGSC hypofunction is causally linked to abnormal gamma activity and network hypersynchrony in hAPPJ20 mice. In agreement with our results, VGSC blockers also exacerbate seizure activity in human epilepsies due to Nav1.1 loss-of-function mutations (Liao et al., 2010; Striano et al., 2008).
Figure 4. Inhibition of VGSCs Reduces Gamma Activity and Enhances Hypersynchrony and Context-Dependent Memory Deficits in hAPPJ20 Mice.
(A–C) EEG recordings from the left (L) and right (R) parietal cortex (PC) were performed in hAPPJ20 (n=11) and NTG (n=5) mice before and after injection of the VGSC blocker riluzole (RZL, 20 mg/kg, i.p.). (A) In hAPPJ20 mice, but not in NTG controls, riluzole induced intense epileptiform activity (spikes) within 10–15 min (arrowheads). Lower panels show the full frequency range spectrograms of the corresponding EEG recordings. (B) 1-min (left) and 60-min (right) interval quantifications of spikes 60 min before and after riluzole injection. Two-way repeated-measures ANOVA revealed significant effects of treatment (p<0.001), genotype (p<0.01), and treatment × genotype interaction (p<0.001) (left). (C) Intensity of gamma activity after riluzole treatment normalized to gamma intensity during the first minute of recording (100%). Riluzole reduced gamma activity more prominently in hAPPJ20 mice than in NTG controls. Treatment (p<0.001) and treatment × genotype interaction (p<0.001) effects by two-way repeated-measures ANOVA.
(D–F) hAPPJ20 (n=15–16 per group) and NTG (n=12–15 per group) mice were treated with the VGSC blocker phenytoin (PHT) or vehicle (Veh) and tested to assess context-dependent habituation and dishabituation to a novel environment. (D) Phenytoin (85 mg/kg/day for 10 days) prevented habituation only in hAPPJ20 mice. *p<0.05 vs vehicle-treated hAPPJ20 mice (twoway repeated-measures ANOVA and Bonferroni test). (E) Phenytoin also increased dishabituation in hAPPJ20 mice. ***p<0.001 vs vehicle-treated hAPPJ20 mice (two-way repeated-measures ANOVA and Bonferroni test). (F) Phenytoin-treated hAPPJ20 mice fully habituated to the environment when they were exposed to it more frequently. However, after 10 days, phenytoin-treated hAPPJ20 mice showed increased dishabituation. *p<0.05, **p<0.01 (unpaired t test), ##p<0.01 (paired t test) (B). *p<0.05, ***p<0.001 vs vehicle-treated hAPPJ20 mice (ANOVA and Bonferroni test) (D–F). Bar or line graphs represent mean ± SEM. See Figure S4 for supporting data.
Aberrant network activity may contribute to cognitive deficits in hAPP mice (Ittner et al., 2010; Palop et al., 2007; Roberson et al., 2011). Consistent with this notion and the above data, inhibiting VGSC function in hAPPJ20 mice also increased context-dependent memory deficits (Figure 4D–F). We measured context-dependent habituation (“learning”) and dishabituation (“forgetting”) to a novel environment. Inhibiting VGSCs with phenytoin markedly impaired context-dependent habituation to a novel environment in hAPPJ20 mice but not in NTG controls (Figure 4D). Phenytoin also caused profound dishabituation in hAPPJ20 mice but not in NTG controls (Figure 4E). Thus, inhibition of VGSCs in hAPPJ20 mice, but not in NTG mice, disrupts context-dependent learning and memory.
To ensure that these behavioral effects in hAPPJ20 mice were not due to motor dysfunction, we increased trial frequency to enhance learning. Under these conditions, we observed no abnormalities in habituation and dishabituation in phenytoin- and vehicle-treated hAPPJ20 mice (Figure 4F), suggesting that their increased exploratory behavior in our original paradigm was related to cognitive impairment rather than abnormal motor function. Retesting of fully habituated phenytoin-treated hAPPJ20 mice 10 days later again revealed prominent dishabituation (Figure 4F), suggesting enhanced forgetting. These results are consistent with other data indicating that aberrant network activity contributes to cognitive deficits in hAPP mice (Palop et al., 2007; Roberson et al., 2011; Roberson et al., 2007).
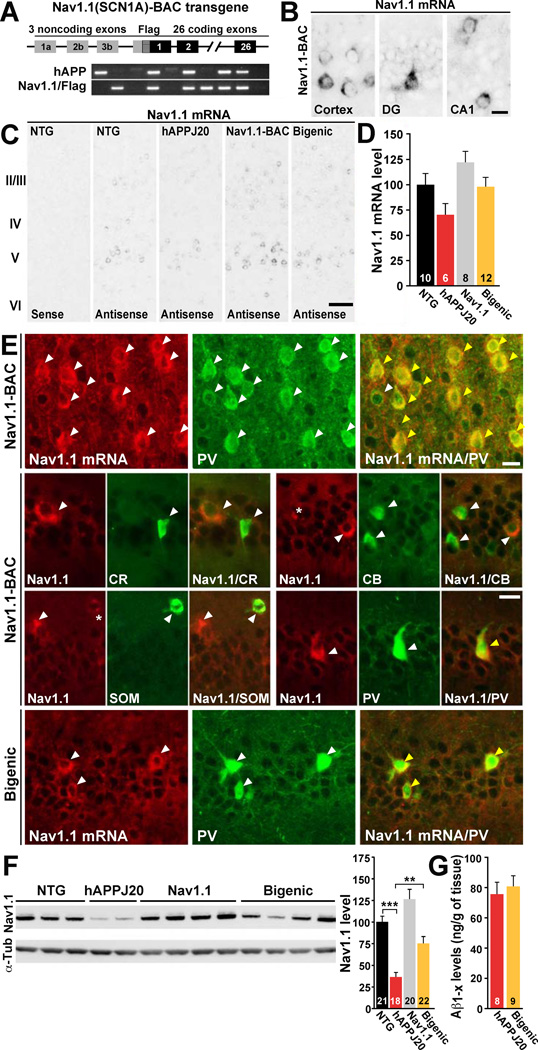
Increasing Nav1.1 Levels in hAPPJ20 Mice by Nav1.1-BAC Transgene Overexpression
To test whether reduced Nav1.1 levels cause abnormalities in oscillatory rhythms, network synchronization and cognitive functions in hAPPJ20 mice, we increased Nav1.1 levels by crossing them with Nav1.1-BAC transgenic mice (Figure 5A) (Tang et al., 2009). The following genotypes were generated: NTG, singly transgenic (hAPPJ20 or Nav1.1), and doubly transgenic (hAPPJ20/Nav1.1, “bigenic”). As in NTG mice (Figures 3C and S3A), Nav1.1 mRNA was highly expressed by a subset of neurons in Nav1.1-BAC transgenic mice (Figure 5B). Nav1.1-BAC transgenic mice, including Nav1.1 and hAPPJ20/Nav1.1 mice, had Nav1.1 expression patterns like those of NTG and hAPPJ20 mice, but higher levels of expression (Figure 5C, D). Similar to NTG and hAPPJ20 mice (Figure 3C, F), Nav1.1 and hAPPJ20/Nav1.1 mice had high levels of Nav1.1 mRNA expression in PV cells but not in other types of interneurons or pyramidal cells, as shown by double-labeling for Nav1.1 mRNA and immunohistochemistry for PV, calretinin, calbindin, and somatostatin (Figure 5E) (Ogiwara et al., 2009; Wang et al., 2011). Nav1.1-BAC expression also increased Nav1.1 protein levels in Nav1.1 and hAPPJ20/Nav1.1 mice (Figure 5F). Nav1.1 levels were much lower in hAPPJ20 mice than NTG mice but were nearly normal in hAPPJ20/Nav1.1 mice (Figure 5F). Increasing Nav1.1 levels in hAPPJ20 mice did not alter total Aβ levels at 3 month of age (Figure 5G).
Figure 5. Increasing Levels of Nav1.1 in hAPPJ20 Mice by Nav1.1-BAC Transgene Overexpression.
(A) Nav1.1(SCN1A)-BAC transgene construct and PCR detection of genotypes.
(B–E) Single bright-field in situ hybridization for Nav1.1 (B, C) and double fluorescence in situ hybridization for Nav1.1 (red) and immunohistochemistry (green) (E) for parvalbumin (PV), calretinin (CR), calbindin (CB), or somatostatin (SOM) on cryosections from NTG, hAPPJ20, Nav1.1, and hAPPJ20/Nav1.1 (bigenic) mice. (B) As in NTG mice (Figure S3A), Nav1.1 mRNA expression in Nav1.1 mice was restricted to a few cells. (C) Nav1.1 mRNA expression patterns were similar in all genotypes. (D) Densitometric analysis of Nav1.1 mRNA signals in the parietal cortex (C) revealed that Nav1.1-BAC transgene expression increased Nav1.1 mRNA levels in mice with (p=0.018) or without (p=0.028) hAPP expression (two-way ANOVA). (E) In Nav1.1 and bigenic mice, Nav1.1 mRNA was highly expressed by PV cells but not by other interneuronal populations. Arrowheads indicate single- (white) or double-labeled (yellow) cells. Asterisks indicate very low or putative expression.
(F) Representative western blots (left) and quantification (right) of Nav1.1 levels in the parietal cortex. Nav1.1 levels were increased by Nav1.1-BAC transgene expression in mice with (p<0.001) or without (p<0.001) hAPP (two-way ANOVA). **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 (one-way ANOVA and Tukey test).
(G) Cortical Aβ1-x levels in 3-month-old hAPPJ20 and bigenic mice determined by ELISA. Scale bars: 10 µm (B, E); 50 µm (C). Numbers in bars are mice (D, F, G). Bars represent mean ± SEM.
Increasing Nav1.1 Levels Increases Inhibitory Synaptic Currents and Gamma Activity and Decreases Epileptiform Activity
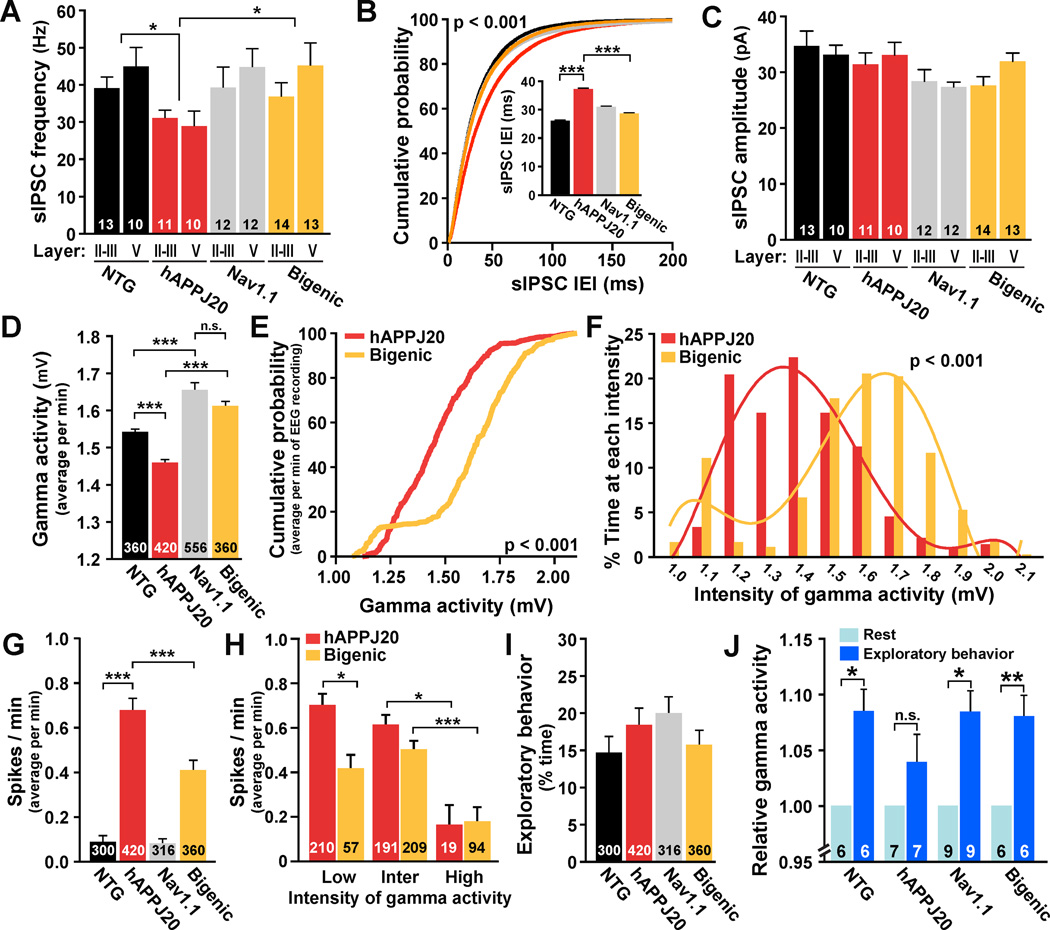
Consistent with the prominent expression of Nav1.1 and Nav1.1-BAC in PV cells and the involvement of these cells in inhibition of cortical pyramidal cells and generation of gamma oscillations (Cardin et al., 2009; Ogiwara et al., 2007; Sohal et al., 2009), increasing Nav1.1 expression prevented abnormalities in spontaneous IPSCs and gamma activity in hAPPJ20 mice (Figure 6). In agreement with results shown in Figure 2B, hAPPJ20 mice had reduced frequencies, but not amplitudes, of sIPSCs in layer III/III and V pyramidal neurons of the parietal cortex (Figure 6A–C). BAC-Nav1.1 expression prevented this deficit in hAPPJ20/Nav1.1 mice (Figure 6A, B), indicating that it depends on Nav1.1 levels.
Figure 6. Enhancing Nav1.1 Levels Increases Inhibitory Synaptic Currents and Gamma Activity and Reduces Epileptiform Discharges in hAPPJ20 Mice.
(A–C) Average frequency (A) and amplitude (C) of sIPSCs and cumulative probability of sIPSC interevent intervals (IEI) (B) recorded from layer II/III and V pyramidal cells. For statistical analyses, data from cells in layers II/III and V were combined (n=21–27 cells per genotype). Nav1.1-BAC expression prevented sIPCS frequency deficits in hAPPJ20 mice. *p<0.05, ***p<0.001 (ANOVA and Tukey test).
(D–J) EEG recordings from parietal cortex in NTG (n=6), hAPPJ20 (n=7), Nav1.1 (n=9), and bigenic (n=6) mice. The intensity of gamma activity (20–80 Hz) and epileptiform discharges were measured in 1-min intervals for 60 min. (D) Intensity of gamma activity. (E, F) Cumulative probability of gamma intensity (E) and proportion of time spent at each gamma intensity (F) in hAPPJ20 and bigenic mice. Nav1.1-BAC transgene expression increased the intensity of gamma activity in hAPPJ20 mice. p<0.001 (two-sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov test). (G) Spike frequency. Nav1.1-BAC transgene expression reduced spike frequency in hAPPJ20 mice. (H) Spike frequency in hAPPJ20 and bigenic mice during periods of low, intermediate (inter) or high intensity of gamma activity. (I) Exploratory activity during EEG recording. (J) Significant increases in gamma activity during exploratory behavior (dark blue) were found in bigenic mice but not in hAPPJ20 mice. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 (ANOVA and Tukey test) (D, G, H). *p<0.05, **p<0.01 (paired t test) (J). Numbers in bars are cells (A, C), minutes of recording (D, G–I) or mice (J). Bars represent mean ± SEM.
Higher Nav1.1 expression also increased the intensity of gamma activity in mice with or without hAPP (Figure 6D). Cumulative frequency analysis of the gamma intensity during all minutes recorded showed a significant shift to higher intensity values in hAPPJ20/Nav1.1 mice compared with hAPPJ20 mice (Figure 6E). hAPPJ20/Nav1.1 mice also spent more time at higher intensity values of gamma activity than hAPPJ20 mice (Figure 6F). Thus, increasing Nav1.1 levels in hAPPJ20 mice counteracts their gamma intensity deficits.
Since network hypersynchrony decreases during high-intensity gamma activity in unmanipulated hAPPJ20 mice (Figure 1), we tested whether Nav1.1-BAC-dependent increases in gamma activity are associated with reduced epileptic activity. Increasing Nav1.1 levels in hAPPJ20 mice indeed reduced their epileptiform discharges (Figure 6G). hAPPJ20/Nav1.1 mice had fewer spikes than hAPPJ20 mice during low-intensity gamma activity, but both groups had similar spike activity during intermediate- and high-intensity gamma activity (Figure 6H), suggesting that increased Nav1.1 levels primary reduce epileptiform discharges by modulating gamma activity. Mice of all genotypes showed similar levels of exploratory behavior during the EEG recordings (Figure 6I).
As predicted from the results in Figure 1G, hAPPJ20 mice had smaller increases of gamma activity during exploratory activity than NTG mice (Figure 6J). This deficit was also ameliorated by Nav1.1-BAC expression (Figure 6J). Thus, increasing Nav1.1 levels restores baseline gamma activity and increases of gamma activity associated with exploratory behaviors.
Increasing Nav1.1 Levels Reduces Learning and Memory Deficits and Premature Mortality in hAPPJ20 Mice
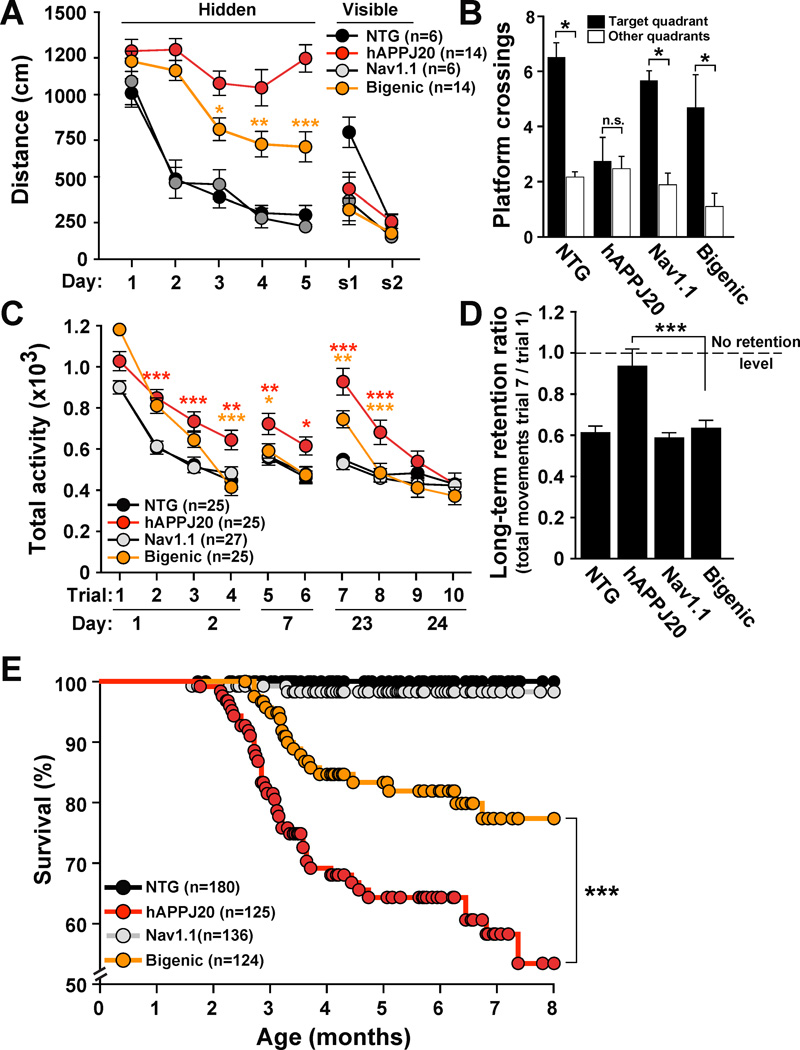
To determine if Nav1.1 alterations in hAPPJ20 mice contribute to cognitive decline, we assessed spatial learning and memory of mice in the Morris water maze. Compared with NTG controls, hAPPJ20 mice were severely impaired in the hidden platform component (days 1–5), but not the visible platform component (s1 and s2) of the test (Figure 7A), indicating specific spatial learning deficits. Increasing Nav1.1 levels by Nav1.1-BAC expression reduced these spatial learning impairments in hAPPJ20 mice and did not affect the performance of NTG mice (Figure 7A). In the probe trial (platform removed), only hAPPJ20 mice failed to cross the original platform location more often than equivalent locations in non-target quadrants (Figure 7B). hAPPJ20/Nav1.1 mice performed at control levels, indicating improved spatial learning and/or memory retention.
Figure 7. Increasing Nav1.1 Levels Ameliorates Spatial and Context-Dependent Learning and Memory Deficits in hAPPJ20 Mice.
NTG, hAPPJ20, Nav1.1, and hAPPJ20/Nav1.1 (bigenic) mice were tested to assess spatial learning and memory in the Morris water maze and context-dependent habituation and dishabituation to a novel environment in the open field.
(A) Distance swum in the hidden (spatial) and visible (cued) platform components of the Morris water maze test. In the spatial component, bigenic mice performed better than hAPPJ20 mice. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 (two-way repeated-measures ANOVA and Bonferroni test).
(B) Platform crossings during the probe trial (platform removed). Only hAPPJ20 mice had memory retention deficits. *p<0.05 vs. nontarget locations (paired two-tailed t test).
(C) Activity of mice in an open field was assessed on days 1–2, 7, and 23–24. In these three sessions, bigenic mice habituated faster and more completely than hAPPJ20 mice. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001 (two-way repeated-measures ANOVA and Bonferroni test). Red asterisks indicate differences between NTG and hAPPJ20 mice, and yellow asterisks differences between hAPPJ20 and bigenic mice.
(D) Only hAPPJ20 mice had memory retention deficits. ***p<0.001 by ANOVA and Tukey test.
(E) Survival curves. Nav1.1-BAC expression reduced premature mortality of hAPPJ20 mice. ***p<0.001 (Kaplan-Meier test). Values are mean ± SEM. See Figure S5 for supporting data.
Context-dependent habituation and dishabituation to a novel environment were assessed in the open field. hAPPJ20/Nav1.1 mice habituated faster and more completely than hAPPJ20 mice (Figure 7C; trials 1–4), suggesting improved contextual learning. After four trials of testing, hAPPJ20/Nav1.1 mice, but not hAPPJ20 mice, were completely habituated and indistinguishable in their activity from NTG and Nav1.1 mice. Mice were retested in the same environment 5 and 15 days later to assess contextual memory. NTG and Nav1.1 mice had persistently low levels of activity at 5 and 15 days (Figure 7C), indicating normal contextual memory. Compared with these groups, hAPPJ20 mice showed increased activity at 5 days and a marked increase in activity at 15 days (Figure 7C), indicating profound dishabituation (forgetting). The activity of hAPPJ20/Nav1.1 mice was indistinguishable from that of controls at 5 days and intermediate between the activities of controls and hAPPJ20 mice at 15 days. Only hAPPJ20 mice had impaired memory retention (Figure 7D). Additional training revealed again that hAPPJ20/Nav1.1 mice habituated better than hAPPJ20 mice (Figure 7C; trials 7–10). After 10 trials, all genotypes were fully habituated and indistinguishable from each other. Thus, deficits in contextual learning and memory of hAPPJ20 mice depend on time and experience. Overall, our data show that increasing Nav1.1 levels in hAPPJ20 mice enhances their capacity for learning and memory.
hAPP mouse lines often die prematurely, likely from epileptic activity (Hsiao et al., 1995; Ittner et al., 2010; Minkeviciene et al., 2009; Palop et al., 2007; Roberson et al., 2011; Roberson et al., 2007). Increasing Nav1.1 levels in hAPPJ20 mice markedly improved their survival (Figure 7E).
DISCUSSION
This study identified alterations in the VGSC Nav1.1 subunit as a novel mechanism of hAPP/Aβ-induced aberrant network activity and cognitive decline. hAPP mice and humans with AD had reduced levels of Nav1.1. Restoring Nav1.1 levels in hAPP mice by Nav1.1-BAC expression had profound and beneficial effects on inhibitory synaptic currents, oscillatory rhythms, network synchrony, cognitive functions, and premature mortality, highlighting the pathophysiological relevance of Nav1.1 depletion in vivo. Since Nav1.1 is prominently expressed in inhibitory PV cells in rodents and humans (Ogiwara et al., 2007; Wang et al., 2011), our data suggest that dysfunction of PV cells and inhibitory functions contribute to AD-related functional impairments. Multiple lines of evidence support this conclusion: (1) hAPP mice had decreased Nav1.1 levels in PV cells and altered PV cell–dependent synaptic and network activity (gamma oscillations), (2) network hypersynchronization intensified during depressed gamma oscillations and diminished during increased gamma activity, (3) inhibiting VGSCs and gamma oscillations with VGSC blockers enhanced network hypersynchronization and memory deficits in hAPP mice, and (4) increasing Nav1.1 expression enhanced inhibitory synaptic currents and gamma activity and reduced network hypersynchronization and memory deficits in hAPP mice. These results pinpoint Nav1.1 reductions as a key molecular mechanism, PV cells as a primary cellular substrate, and PV cell–dependent alterations in gamma activity and inhibitory deficits as functional mechanisms of network and cognitive dysfunction in hAPP mice.
Nav1.1 Deficiency, Inhibitory Synaptic Dysfunction, and Epilepsy
VGSCs control cellular excitability and produce sodium currents involved in action potential generation (Meisler and Kearney, 2005). Loss-of-function mutations in Nav1.1 (SCN1A gene) or microdeletions in one SCN1A allele cause epilepsy syndromes in humans, ranging from benign febrile seizures to severe myoclonic epilepsy of infancy (Catterall et al., 2010; Meisler and Kearney, 2005; Suls et al., 2006). Inducing Nav1.1 haploinsufficiency in rodents causes severe epileptic activity and premature mortality (Ogiwara et al., 2007; Yu et al., 2006). The degree of loss-of-function in Nav1.1 mutations appears to determine the clinical severity of the epilepsy syndromes (Catterall et al., 2010). The epileptogenic mechanism underlying these conditions is closely related to the restricted expression of the Nav1.1 subunit in inhibitory interneurons, particularly PV cells (Lorincz and Nusser, 2008; Ogiwara et al., 2007; Wang et al., 2011), and their specific impairments in action potential–driven activity (Ogiwara et al., 2007; Yu et al., 2006). Consistent with these observations, hAPP mice had reduced action potential-driven inhibitory synaptic activity (sIPSCs) (Roberson et al., 2011). Increasing Nav1.1 expression prevented sIPCS deficits in hAPP mice, indicating that Nav1.1 depletion contributes to activity-dependent inhibitory synaptic deficits. We could not obtain conclusive evidence that action potential amplitude deficits in hAPP mice are caused by reduced Nav1.1 levels. Additional alterations in other ion channels, such as Nav1.6, and more depolarized resting membrane potentials, which could result in larger steady-state inactivation of VGSCs, may contribute to the amplitude deficits.
PV Cell-Dependent Gamma Activity and Network Stability
Fast-spiking PV- and non-fast-spiking cholecystokinin (CCK)-containing basket cells are the two major sources of perisomatic inhibition in the cerebral cortex and are specialized for the primary control and fine-tuning of neuronal network oscillations, respectively (Freund and Katona, 2007). Reflecting this functional dichotomy PV cells are involved in disorders of abnormal rhythmic synchrony, such as epilepsy, whereas CCK cells are involved in mood disorders and anxiety (Freund and Katona, 2007). Fast-spiking inhibitory PV basket cells represent around 40% of inhibitory interneurons and provide strong somatic and perisomatic inhibition to excitatory pyramidal cells. PV cells are electrically coupled by gap junctions and, therefore, form a tightly connected interneuronal network. Their combined fast-spiking inhibitory synaptic activity onto pyramidal cells generates a high-frequency oscillatory signature in the gamma range (20–80 Hz). Increasing the firing of PV cells by optogenetic stimulation increases the intensity of gamma oscillatory activity (Cardin et al., 2009; Sohal et al., 2009). Therefore, gamma activity likely reflects the inhibitory synaptic activity of fast-spiking PV cells in vivo. Cell-autonomous impairments of PV cell development reduce gamma activity and cause network instability and epilepsy (Wang et al., 2010), indicating that PV cells are critical in maintaining network stability.
Consistent with PV cell dysfunction, behaving hAPP mice had abnormal gamma activity. Notably, reduced gamma activity correlated with increased epileptiform discharges, suggesting a causal link between dysfunction of PV cells, reduced gamma activity, and epileptiform activity in hAPP mice. Several lines of evidence support this notion. Pharmacological inhibition of VGSCs further reduced gamma activity and proportionally increased spike frequency. Increases in gamma activity during exploratory behavior were associated with reduction of spike frequency. And Nav1.1-BAC transgene expression increased gamma activity in Nav1.1 and hAPP/Nav1.1 mice and reduced spike frequency in hAPP/Nav1.1 mice. Thus, pharmacological, behavioral, and genetic manipulations of gamma activity consistently modulated spike frequency in the opposite direction, suggesting that these network alterations are causally related and mediated by Nav1.1 depletions. Since increased spike activity could further reduce gamma activity (Medvedev, 2002), this phenomenon could create a vicious cycle in hAPP mice. However, specific manipulations of gamma activity and epileptic spikes would be needed to establish causal relations between these two abnormalities.
Gamma Activity, Epileptiform Discharges, and Cognitive Functions
Hippocampal and neocortical gamma activity is increased during attention and learning, and such increases predict successful memory formation in humans (Sederberg et al., 2007). The importance of PV cell–mediated gamma activity for cognitive function is strongly supported by the finding that enhancing gamma activity by optogenetic stimulation of PV cells increased performance of circuit processing by increasing signal/noise ratio (Sohal et al., 2009). Gamma activity is reduced in AD patients (Herrmann and Demiralp, 2005). Similarly, hAPP mice had reduced gamma activity at baseline and diminished inductions during exploratory activity. Increasing Nav1.1 levels prevented gamma activity deficits and ameliorated deficits in contextual and spatial learning and memory, indicating a causal role of Nav1.1 depletion in these deficits. Interestingly, Nav1.1-BAC expression in hAPPJ20 mice had stronger beneficial effects in memory or retrieval (e.g., water maze probe trials or retrieval 2-week trial in the open field) than in learning (e.g., water maze hidden training or habituation in the open field), possibly reflecting improvements in neocortical functions.
Altered gamma activity may relate to interneuronal dysfunction and cognitive alterations in other psychiatric and neurological disorders, including epilepsy, autism, schizophrenia, and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (Cardin et al., 2009; Fazzari et al., 2010; Herrmann and Demiralp, 2005). These and our findings suggest that abnormal gamma activity directly contributes to cognitive impairments and that PV cell dysfunction is an important underlying mechanism.
Seizure activity is increased in AD (Amatniek et al., 2006), particularly in early-onset familial AD (FAD) (Palop and Mucke, 2009). Convulsive seizures occur in 7–21% of sporadic AD patients (Amatniek et al., 2006; Hauser et al., 1986; Mendez and Lim, 2003), ~30% of pedigrees carrying FAD PS1 mutations (Larner and Doran, 2006), 31% of patients with PS2 mutations (Jayadev et al., 2010), 56% of patients with APP duplications (Cabrejo et al., 2006), and ~83% of pedigrees with very early-onset AD (Snider et al., 2005). Behavioral or EEG epileptic activity is also common in transgenic mouse lines expressing FAD-mutant hAPP, including Tg2576 (Hsiao et al., 1995), hAPPJ20 (Palop et al., 2007), APP/PS1 (Minkeviciene et al., 2009), ECAPP (Harris et al., 2010), hAPPJ9/FYN (Roberson et al., 2011), and APP23 mice (Lalonde et al., 2005). Increasing Nav1.1 levels in hAPPJ20 mice reduced epileptic activity and improved cognitive functions, suggesting that epileptic activity may contribute to cognitive impairments in hAPP mice.
Potential Clinical and Therapeutic Implications
Cortical and hippocampal hyperactivity of neuronal networks is an early event in AD pathogenesis and is associated with early amyloid deposition in nondemented humans with or without mild cognitive impairment (MCI) (Sperling et al., 2009). Impaired inhibition has been suggested as a potential mechanism of network hyperactivity (Busche et al., 2008; Palop et al., 2007; Palop and Mucke, 2010; Sperling et al., 2009). Our findings support this notion and suggest that behavioral interventions or pharmacological manipulations that increase gamma activity and/or reduce network hyperactivity have beneficial effects on cognitive functions in the presence of pathologically elevated Aβ levels. They also suggest that pharmacological interventions that reduce gamma activity (e.g., antiepileptic drugs affecting sodium channel function) could impair cognitive function in patients with AD or related disorders. In support of this observation, phenytoin increases AD risk in nondemented elderly people (Carter et al., 2007) and causes acute cognitive decline in Down’s syndrome patients with AD (Tsiouris et al., 2002). It needs to be determined whether these mechanisms of cognitive dysfunction are playing critical roles in all or only a subset of AD patients. Mouse and human data suggest that early-onset FAD patients with seizures might be particularly affected by these alterations.
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
Transgenic Mice
We studied transgenic C57BL/6J mice expressing hAPP with the Swedish and Indiana FAD mutations and NTG littermate controls from line J20 (hAPPJ20 mice) (Mucke et al., 2000). For some experiments, hAPPJ20 mice were crossed with BAC transgenic C57BL/6J mice expressing eGFP directed by GAD67 regulatory sequences (Jackson Laboratory; strain: CB6-Tg(Gad1-EGFP)G42Zjh/J, line G42) (Chattopadhyaya et al., 2004) or BAC-Nav1.1 transgenic FVB/N mice from line 1 overexpressing wildtype murine Nav1.1 (Tang et al., 2009). Unless indicated otherwise, measurements were performed in 4–7-month-old mice.
Human Tissues
Inferior parietal cortex was dissected from frozen brains of 22 AD cases (age 78.4±10.8 years, mean±SD) and seven nondemented controls (age 83.5±15.3 years) from the Alzheimer’s Disease Research Center, University of California, San Diego. See extended experimental procedures.
Immunohistochemistry
Tissue preparation and immunohistochemistry were performed as described (Palop et al., 2007; Palop et al., 2003). Primary antibodies used included rabbit anti-parvalbumin (Swant), rabbit anti-Nav1.1 (Alomone Labs), rabbit anti-Nav1.6 (Alomone), and mouse anti-GAD67 (Chemicon). Primary antibodies were detected with biotinylated goat anti-rabbit (Vector Laboratories) or with fluorescein-labeled donkey anti-rabbit (Jackson ImmunoResearch), Alexa 594 donkey antimouse (Invitrogen), or Alexa 488 donkey anti-rabbit (Invitrogen). See extended experimental procedures.
In Situ Hybridization
Tissue preparation and in situ hybridization were performed as described (Palop et al., 2007). Antisense and sense RNA digoxigenin-labeled probes were generated from EST clones (Open Byosystems) (NCBI#: BE944238 for Nav1.1 and AI839069 for Nav1.6). Digoxigenin-labeled probes were detected with the HNPP fluorescent detection set (Roche), followed by standard fluorescence immunohistochemistry with polyclonal anti-PV (Swant) or anti-GFP (Molecular Probes) antibodies. Nav1.1- and PV-positive neurons were quantified in two sections, 100 µm apart. In all, 551 neurons positive for PV and/or Nav1.1 were identified and analyzed. The proportion of PV-positive cells expressing Nav1.1 mRNA (PV+/Nav1.1+) and the relative Nav1.1 mRNA signal intensity in PV cells were calculated for each genotype.
Western Blot Analysis
Microdissections and western blot analysis were performed as described (Palop et al., 2005). Primary antibodies included rabbit anti-Nav1.1 (Alomone), rabbit anti-Nav1.2 (Alomone), rabbit anti-Nav1.3 (Alomone), rabbit anti-Nav1.6 (Alomone), rabbit anti-GAD67 (Millipore), rabbit anticalretinin (Swant), rabbit anti-parvalbumin (Swant), rabbit anti-calbindin (Swant), mouse antireelin (Millipore), and mouse anti-α-tubulin (Sigma). Primary antibodies were detected with horseradish peroxidase–conjugated secondary anti-mouse IgG antibody (Calbiochem) or HRPconjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG (Calbiochem). Bands were visualized by ECL and quantitated densitometrically with ImageQuant software (Molecular Dynamics). See extended experimental procedures.
Slice Electrophysiology
sIPSCs were recorded at the reversal potential of ionotropic glutamate receptors (0 mV); sEPSCs were recorded at the reversal potential of GABAA receptors (−65 mV); mIPSCs and mEPSCs were recorded in the presence of 0.5 µM tetrodotoxin and 50 µM CdCl2. Signals were acquired with Axoclamp 2A, MultiClamp 700B, or Axopatch 200A amplifiers (Molecular Devices). Voltage- and current-clamp recordings were analyzed in Igor Pro (Wavemetrics) with custom-written procedures. For detection of synaptic events in voltage-clamp recordings, events were detected as deflections exceeding 5–7 pA above baseline mean. From each recording, 500–1000 consecutive events were sampled.
To analyze the intrinsic properties of neurons recorded in current-clamp mode, the input resistance was estimated at the resting membrane potential in response to 500-ms hyperpolarizing current steps of 20–40 pA. The membrane time constant and capacitance were estimated by fitting single exponentials to initial phases of these voltage responses. For analysis of action potential properties, neurons were recorded at resting or at −70 mV membrane potentials and depolarized with 800-ms current steps in 20-pA increments. See extended experimental procedures.
EEG Recordings
EEG activity in freely moving mice was recorded with the Harmonie 5.0b software (Stellate). Sharp-wave discharges were automatically detected by the Gotman spike detectors (Harmonie, Stellate). Spectral analysis was analyzed using a custom-written procedure running under IGOR Pro v6.12A. The gamma frequency band (gamma activity) represents the average of the spectral values in the 20–80-Hz range (Barth and Mody, 2011). Low, intermediate and high intensity of gamma activities were defined as minutes with values <30%, 30–60%, >60% of the total amplitude of the gamma activity. See extended experimental procedures.
Drug Treatments
For acute treatments, riluzole was dissolved at 2 mg/ml in 50% polyethylene glycol 400 in distilled water and injected IP at 20 mg/kg, and phenytoin was dissolved at 10 mg/ml in phosphate-buffered saline and injected IP at 100 mg/kg. For chronic treatment, phenytoin was dissolved daily in the drinking water at 0.15–0.75 mg/ml to reach final doses of 25, 50, 70, and 85 mg/kg/day.
Morris Water Maze
Mice were trained to locate the hidden platform over 5 consecutive days (two sessions of two trials per day, 4 h apart). Four hours after the last training session, the platform was removed, and a 60-sec probe trial was performed. Two days later, mice were trained to locate the visible platform over two sessions of two trials each. Performance was monitored with an EthoVision video tracking system (Noldus Information Technology). See extended experimental procedures.
Open Field Behavior
Exploratory locomotor activity was measured in an open field (automated Flex-Field/Open Field Photobeam Activity System). Mice were placed in one of four identical clear plastic chambers (40 × 40 × 30 cm) for 5 min (Figure 7) or 15 min (Figure 4). Total movements in the open field were reported. See extended experimental procedures.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were performed with SPSS 10.0, STATA 11.2, or Prism 5.0. Experimenters were blinded with respect to genotype and treatment of mice and to diagnosis of human cases. See extended experimental procedures.
HIGHLIGHTS.
Network hypersynchrony emerges during reduced gamma oscillatory activity in hAPP mice
PV cells in hAPP mice have reduced Nav1.1 levels and impaired functions
Inhibiting VGSCs enhances network hypersynchrony and memory deficits in hAPP mice
Restoring Nav1.1 levels improves network and memory functions in hAPP mice
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by a Stephen D. Bechtel, Jr. Foundation Young Investigator Award to J.J.P.; National Institutes of Health Grants AG022074, AG011385 and NS065780 to L.M., NS002808, NS030549, AG5131, and AG18440 to E.M.; the Philippe Foundation Award to L.V.; the Coelho Endowment to I.M.; Pew and McKnight Foundations to A.C.K.; Epilepsy Foundation Postdoctoral Fellowship to E.O.M.; and facilities grants from Stephen D. Bechtel, Jr. and the National Center for Research Resources. We thank A. Escayg for the Nav1.1-BAC transgenic mice; J. Noebles and A. Gittis for helpful comments; G.Q. Yu, X. Wang, W. Guo, E. Pham, K. Bummer, I. Lo and D.H. Kim for excellent technical support; and G. Howard and S. Ordway for editorial review.
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA
The supplemental material includes five supplemental figures, one supplemental table, and extended experimental procedures.
REFERENCES
- Amatniek JC, Hauser WA, DelCastillo-Castaneda C, Jacobs DM, Marder K, Bell K, Albert M, Brandt J, Stern Y. Incidence and predictors of seizures in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Epilepsia. 2006;47:867–872. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2006.00554.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barth AM, Mody I. Changes in hippocampal neuronal activity during and after unilateral selective hippocampal ischemia in vivo. J Neurosci. 2011;31:851–860. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5080-10.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bero AW, Yan P, Roh JH, Cirrito JR, Stewart FR, Raichle ME, Lee JM, Holtzman DM. Neuronal activity regulates the regional vulnerability to amyloid-beta deposition. Nat Neurosci. 2011;14:750–756. doi: 10.1038/nn.2801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckner RL, Snyder AZ, Shannon BJ, LaRossa G, Sachs R, Fotenos AF, Sheline YI, Klunk WE, Mathis CA, Morris JC, et al. Molecular, structural, and functional characterization of Alzheimer’s disease: Evidence for a relationship between default activity, amyloid, and memory. J Neurosci. 2005;25:7709–7717. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2177-05.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busche MA, Eichhoff G, Adelsberger H, Abramowski D, Wiederhold KH, Haass C, Staufenbiel M, Konnerth A, Garaschuk O. Clusters of hyperactive neurons near amyloid plaques in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Science. 2008;321:1686–1689. doi: 10.1126/science.1162844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabrejo L, Guyant-Maréchal L, Laquerriére A, Vercelletto M, De La Fourniére F, Thomas-Antérion C, Verny C, Letournel F, Pasquier F, Vital A, et al. Phenotype associated with APP duplication in five families. Brain. 2006;129:2966–2976. doi: 10.1093/brain/awl237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardin JA, Carlen M, Meletis K, Knoblich U, Zhang F, Deisseroth K, Tsai LH, Moore CI. Driving fast-spiking cells induces gamma rhythm and controls sensory responses. Nature. 2009;459:663–667. doi: 10.1038/nature08002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter MD, Weaver DF, Joudrey HR, Carter AO, Rockwood K. Epilepsy and antiepileptic drug use in elderly people as risk factors for dementia. J Neurol Sci. 2007;252:169–172. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2006.11.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall WA, Kalume F, Oakley JC. NaV1.1 channels and epilepsy. J Physiol. 2010;588:1849–1859. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2010.187484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyaya B, Di Cristo G, Higashiyama H, Knott GW, Kuhlman SJ, Welker E, Huang ZJ. Experience and activity-dependent maturation of perisomatic GABAergic innervation in primary visual cortex during a postnatal critical period. J Neurosci. 2004;24:9598–9611. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1851-04.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng I, Scearce-Levie K, Legleiter J, Palop J, Gerstein H, Bien-Ly N, Puoliväli J, Lesné S, Ashe K, Muchowski P, et al. Accelerating amyloid-β fibrillization reduces oligomer levels and functional deficits in Alzheimer disease mouse models. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:23818–23828. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M701078200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cisse M, Halabisky B, Harris JA, Devidze N, Dubal D, Lotz G, Kim DH, Hamto T, Ho K, Yu G-Q, et al. Reversing EphB2 depletion rescues cognitive functions in Alzheimer model. Nature. 2011;469:47–52. doi: 10.1038/nature09635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fazzari P, Paternain AV, Valiente M, Pla R, Lujan R, Lloyd K, Lerma J, Marin O, Rico B. Control of cortical GABA circuitry development by Nrg1 and ErbB4 signalling. Nature. 2010;464:1376–1380. doi: 10.1038/nature08928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund TF, Katona I. Perisomatic inhibition. Neuron. 2007;56:33–42. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2007.09.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy J, Selkoe DJ. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: Progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science. 2002;297:353–356. doi: 10.1126/science.1072994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris JA, Devidze N, Verret L, Ho K, Hamto T, Lo I, Yu G-Q, Palop JJ, Masliah E, Mucke L. Transsynaptic progression of amyloid-β-induced neuronal dysfunction within the entorhinal-hippocampal network. Neuron. 2010;68:428–441. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.10.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser WA, Morris ML, Heston LL, Anderson VE. Seizures and myoclonus in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology. 1986;36:1226–1230. doi: 10.1212/wnl.36.9.1226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann CS, Demiralp T. Human EEG gamma oscillations in neuropsychiatric disorders. Clin Neurophysiol. 2005;116:2719–2733. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2005.07.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiao KK, Borchelt DR, Olson K, Johannsdottir R, Kitt C, Yunis W, Xu S, Eckman C, Younkin S, Price D, et al. Age-related CNS disorder and early death in transgenic FVB/N mice overexpressing Alzheimer amyloid precursor proteins. Neuron. 1995;15:1203–1218. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90107-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh H, Boehm J, Sato C, Iwatsubo T, Tomita T, Sisodia S, Malinow R. AMPAR removal underlies Aβ-induced synaptic depression and dendritic spine loss. Neuron. 2006;52:831–843. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2006.10.035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ittner LM, Ke YD, Delerue F, Bi M, Gladbach A, van Eersel J, Wolfing H, Chieng BC, Christie MJ, Napier IA, et al. Dendritic function of tau mediates amyloid-beta toxicity in Alzheimer’s disease mouse models. Cell. 2010;142:387–397. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.06.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayadev S, Leverenz JB, Steinbart E, Stahl J, Klunk W, Yu CE, Bird TD. Alzheimer’s disease phenotypes and genotypes associated with mutations in presenilin 2. Brain. 2010;133:1143–1154. doi: 10.1093/brain/awq033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamenetz F, Tomita T, Hsieh H, Seabrook G, Borchelt D, Iwatsubo T, Sisodia S, Malinow R. APP processing and synaptic function. Neuron. 2003;37:925–937. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(03)00124-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korotkova T, Fuchs EC, Ponomarenko A, von Engelhardt J, Monyer H. NMDA receptor ablation on parvalbumin-positive interneurons impairs hippocampal synchrony, spatial representations, and working memory. Neuron. 2010;68:557–569. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.09.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalonde R, Dumont M, Staufenbiel M, Strazielle C. Neurobehavioral characterization of APP23 transgenic mice with the SHIRPA primary screen. Behav Brain Res. 2005;157:91–98. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2004.06.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larner AJ, Doran M. Clinical phenotypic heterogeneity of Alzheimer’s disease associated with mutations of the presenilin-1 gene. J Neurol. 2006;253:139–158. doi: 10.1007/s00415-005-0019-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao WP, Shi YW, Long YS, Zeng Y, Li T, Yu MJ, Su T, Deng P, Lei ZG, Xu SJ, et al. Partial epilepsy with antecedent febrile seizures and seizure aggravation by antiepileptic drugs: Associated with loss of function of Na(v) 1.1. Epilepsia. 2010;51:1669–1678. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2010.02645.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorincz A, Nusser Z. Cell-type-dependent molecular composition of the axon initial segment. J Neurosci. 2008;28:14329–14340. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4833-08.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann EO, Paulsen O. Role of GABAergic inhibition in hippocampal network oscillations. Trends Neurosci. 2007;30:343–349. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2007.05.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medvedev AV. Epileptiform spikes desynchronize and diminish fast (gamma) activity of the brain. An "anti-binding" mechanism? Brain Res Bull. 2002;58:115–128. doi: 10.1016/s0361-9230(02)00768-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisler MH, Kearney JA. Sodium channel mutations in epilepsy and other neurological disorders. J Clin Invest. 2005;115:2010–2017. doi: 10.1172/JCI25466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendez M, Lim G. Seizures in elderly patients with dementia: Epidemiology and management. Drugs Aging. 2003;20:791–803. doi: 10.2165/00002512-200320110-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minkeviciene R, Rheims S, Dobszay MB, Zilberter M, Hartikainen J, Fulop L, Penke B, Zilberter Y, Harkany T, Pitkanen A, et al. Amyloid beta-induced neuronal hyperexcitability triggers progressive epilepsy. J Neurosci. 2009;29:3453–3462. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5215-08.2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mucke L, Masliah E, Yu G-Q, Mallory M, Rockenstein EM, Tatsuno G, Hu K, Kholodenko D, Johnson-Wood K, McConlogue L. High-level neuronal expression of Aβ1–42 in wild-type human amyloid protein precursor transgenic mice: Synaptotoxicity without plaque formation. J Neurosci. 2000;20:4050–4058. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-11-04050.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogiwara I, Miyamoto H, Morita N, Atapour N, Mazaki E, Inoue I, Takeuchi T, Itohara S, Yanagawa Y, Obata K, et al. Na(v)1.1 localizes to axons of parvalbumin-positive inhibitory interneurons: A circuit basis for epileptic seizures in mice carrying an Scn1a gene mutation. J Neurosci. 2007;27:5903–5914. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5270-06.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palop JJ, Chin J, Bien-Ly N, Massaro C, Yeung BZ, Yu G-Q, Mucke L. Vulnerability of dentate granule cells to disruption of Arc expression in human amyloid precursor protein transgenic mice. J Neurosci. 2005;25:9686–9693. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2829-05.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palop JJ, Chin J, Roberson ED, Wang J, Thwin MT, Bien-Ly N, Yoo J, Ho KO, Yu G-Q, Kreitzer A, et al. Aberrant excitatory neuronal activity and compensatory remodeling of inhibitory hippocampal circuits in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron. 2007;55:697–711. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2007.07.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palop JJ, Jones B, Kekonius L, Chin J, Yu G-Q, Raber J, Masliah E, Mucke L. Neuronal depletion of calcium-dependent proteins in the dentate gyrus is tightly linked to Alzheimer’s disease-related cognitive deficits. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:9572–9577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1133381100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palop JJ, Mucke L. Epilepsy and cognitive impairments in Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol. 2009;66:435–440. doi: 10.1001/archneurol.2009.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palop JJ, Mucke L. Amyloid-beta-induced neuronal dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease: From synapses toward neural networks. Nat Neurosci. 2010;13:812–818. doi: 10.1038/nn.2583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberson ED, Halabisky B, Yoo JW, Yao J, Chin J, Yan F, Wu T, Hamto P, Devidze N, Yu G-Q, et al. Amyloid-β/Fyn-induced synaptic, network, and cognitive impairments depend on Tau levels in multiple mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci. 2011;31:700–711. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4152-10.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberson ED, Scearce-Levie K, Palop JJ, Yan F, Cheng IH, Wu T, Gerstein H, Yu G-Q, Mucke L. Reducing endogenous tau ameliorates amyloid β-induced deficits in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. Science. 2007;316:750–754. doi: 10.1126/science.1141736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sederberg PB, Schulze-Bonhage A, Madsen JR, Bromfield EB, McCarthy DC, Brandt A, Tully MS, Kahana MJ. Hippocampal and neocortical gamma oscillations predict memory formation in humans. Cereb Cortex. 2007;17:1190–1196. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhl030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider BJ, Norton J, Coats MA, Chakraverty S, Hou CE, Jervis R, Lendon CL, Goate AM, McKeel DW, Jr, Morris JC. Novel presenilin 1 mutation (S170F) causing Alzheimer disease with Lewy bodies in the third decade of life. Arch Neurol. 2005;62:1821–1830. doi: 10.1001/archneur.62.12.1821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sohal VS, Zhang F, Yizhar O, Deisseroth K. Parvalbumin neurons and gamma rhythms enhance cortical circuit performance. Nature. 2009;459:698–702. doi: 10.1038/nature07991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spadoni F, Hainsworth AH, Mercuri NB, Caputi L, Martella G, Lavaroni F, Bernardi G, Stefani A. Lamotrigine derivatives and riluzole inhibit INa,P in cortical neurons. Neuroreport. 2002;13:1167–1170. doi: 10.1097/00001756-200207020-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperling RA, Laviolette PS, O'Keefe K, O'Brien J, Rentz DM, Pihlajamaki M, Marshall G, Hyman BT, Selkoe DJ, Hedden T, et al. Amyloid deposition is associated with impaired default network function in older persons without dementia. Neuron. 2009;63:178–188. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.07.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Striano P, Striano S, Minetti C, Zara F. Refractory, life-threatening status epilepticus in a 3-year-old girl. Lancet Neurol. 2008;7:278–284. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(08)70043-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suls A, Claeys KG, Goossens D, Harding B, Van Luijk R, Scheers S, Deprez L, Audenaert D, Van Dyck T, Beeckmans S, et al. Microdeletions involving the SCN1A gene may be common in SCN1A-mutation-negative SMEI patients. Hum Mutat. 2006;27:914–920. doi: 10.1002/humu.20350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang B, Dutt K, Papale L, Rusconi R, Shankar A, Hunter J, Tufik S, Yu FH, Catterall WA, Mantegazza M, et al. A BAC transgenic mouse model reveals neuron subtype-specific effects of a Generalized Epilepsy with Febrile Seizures Plus (GEFS+) mutation. Neurobiol Dis. 2009;35:91–102. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2009.04.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsiouris JA, Patti PJ, Tipu O, Raguthu S. Adverse effects of phenytoin given for late-onset seizures in adults with Down syndrome. Neurology. 2002;59:779–780. doi: 10.1212/wnl.59.5.779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh DM, Klyubin I, Fadeeva JV, Cullen WK, Anwyl R, Wolfe MS, Rowan MJ, Selkoe DJ. Naturally secreted oligomers of amyloid β protein potently inhibit hippocampal long-term potentiation in vivo. Nature. 2002;416:535–539. doi: 10.1038/416535a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang WZ, Takashima S, Segawa Y, Itoh M, Shi XY, Hwang SK, Nabeshima K, Takeshita M, Hirose S. The developmental changes of Na(v)1.1 and Na(v)1.2 expression in the human hippocampus and temporal lobe. Brain Res. 2011;1389:61–70. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2011.02.083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y, Dye CA, Sohal V, Long JE, Estrada RC, Roztocil T, Lufkin T, Deisseroth K, Baraban SC, Rubenstein JL. Dlx5 and Dlx6 regulate the development of parvalbumin-expressing cortical interneurons. J Neurosci. 2010;30:5334–5345. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5963-09.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu FH, Mantegazza M, Westenbroek RE, Robbins CA, Kalume F, Burton KA, Spain WJ, McKnight GS, Scheuer T, Catterall WA. Reduced sodium current in GABAergic interneurons in a mouse model of severe myoclonic epilepsy in infancy. Nat Neurosci. 2006;9:1142–1149. doi: 10.1038/nn1754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.