To the Editor: The northernmost tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) focus is in Simo, Finnish Lapland. Four TBE cases were confirmed during 2008–2009. Tick-borne encephalitis virus (TBEV) is transmitted by Ixodes spp. ticks and is endemic to Eurasia from central Europe to the Far East. The virus has 3 subtypes: European (TBEV-Eur), Siberian (TBEV-Sib), and Far Eastern (TBEV-FE). TBEV-Eur is mainly transmitted by I. ricinus ticks (sheep ticks) and the 2 other subtypes by I. persulcatus ticks (taiga ticks). The range of I. ricinus ticks covers most of continental Europe and the British Isles; I. persulcatus ticks are distributed throughout eastern Europe and Asia to the People’s Republic of China and Japan.
The transmission cycle of at least TBEV-Eur in nature is fragile and depends on microclimatic conditions. Thus, within the I. ricinus distribution area, TBE is endemic merely focally (1,2). In Finland, TBE foci are located by the sea or large lakes (Figure A1). Both vector tick species are found: I. ricinus ticks in the southern and central parts of the country, but I. persulcatus ticks are in scattered foci along the western coast, including the Kokkola archipelago and Närpiö municipality, where they carry TBEV-Sib (3,4) (Figure A1).
The first human TBE cases from Simo in Lapland (65°40′N, 24°54′E; Figure A1) were reported during 2008 (n = 2) and 2009 (n = 2). On the basis of interviews with the 2 patients from 2008, we collected 97 ticks and 17 bank voles from the 2 probable sites of infection during June 2009. From the rodents, we extracted blood from the heart and performed TBEV-antibody tests by immunofluorescence assay. The ticks were placed in 51 pools (1–3 ticks/pool). We isolated RNA from tick pools and rodent lungs and brains by TriPure Isolation Reagent (Roche Diagnostics, Indianapolis, IN, USA) and performed real-time reverse transcription–PCR (5) to detect TBEV RNA. For the positive tick pools, we confirmed the identification species by Ixodes mtDNA sequencing (6).
Six of 51 tick pools (with a total of 97 I. persulcatus ticks) were positive for TBEV in real-time reverse transcription–PCR, resulting in 6% TBEV RNA prevalence. At least 1 organ was positive for TBEV RNA in as many as 15/17 bank voles, in line with our finding that TBEV RNA persists in rodents for months (7); 4 rodents had antibodies to TBEV. The TBEV RNA prevalence among ticks and rodents was relatively high, as is the incidence among humans (0.57 cases/year/1,000 inhabitants) in Simo, indicating a focus with high activity.
We isolated 6 TBEV strains from suckling mice (experimental animal permit ESLH-2008–06558/Ym-23): 2 from I. persulcatus tick pools (Simo-38 and Simo-48; pools of 2 and 3 ticks, respectively), and 4 from TBEV antibody– and RNA-positive rodent lung–brain suspensions (Simo-2, -5, -7 and -9). Partial envelope (E) and nonstructural protein 3 genes (4) of the isolated TBEV strains were sequenced (accession nos. HQ228014–HQ228024, GenBank) and subjected to phylogenetic analysis (Figure A1). Within the 1208 nt from the E gene, Simo-38 and Simo-48 from ticks and Simo-9 from a bank vole were identical. Other sequences differed for 1 nt and Simo-2 for 1 aa compared with the others. All strains were monophyletic and belonged to the TBEV-Eur subtype. The partial nonstructural protein 3 gene sequences were identical, and the phylogenetic tree showed similar topography as for the E gene (not shown).
The only tick species found in Simo was I. persulcatus, further widening its known distribution along the western coast of Finland (Figure A1). However, the virus subtype found in Simo was TBEV-Eur strain, the main vector of which is the I. ricinus tick.
TBEV-Eur strains are commonly very closely related to each other and do not form clear geographic clusters (4). Thus, it is difficult to deduce the origin of the virus. The nearest TBE-endemic focus is the Kokkola archipelago, ≈200 km south (Figure A1), but there I. persulcatus ticks carry the TBEV-Sib strain (3). The nearest areas to which the TBEV-Eur strain is endemic are in southern Finland where only I. ricinus ticks have been found.
Cattle serum samples were negative for antibodies to TBEV in the Simo area in the 1960s (8). The first human TBE cases from Simo were identified during 2008 and 2009. We isolated TBEV strains from ticks and rodents in 2009. Simo appears to be a recently established, and the northernmost, TBE focus known. TBEV may have been introduced to Simo from a geographically distinct location recently, likely within the past 50 years.
TBE seems to be moving northward in Europe (9) and shifting upward to higher elevations in the mountains (10), apparently influenced by climate change. An altered microclimate favoring TBE circulation (1), in addition to introduction of the virus, could also explain the recent emergence of TBE in Simo. In conclusion, Simo in Finnish Lapland is a new TBE-endemic focus demonstrating northward movement of foci and an unusual combination of the TBEV-Eur strain and I. persulcatus ticks in an area with no evidence of cocirculation of tick species or TBEV subtypes.
Acknowledgments
We thank Agnė Alminaitė, Miska Merentie, Maria Razzauti Sanfeliu, and Liina Voutilainen for participating in tick and rodent collection, and Eili Huhtamo and Paula Kinnunen for excellent technical assistance.
Baxter Oy, Outokumpu Stainless Oy, and the Finnish Cultural Foundation are acknowledged for financial support.
Figure A1.
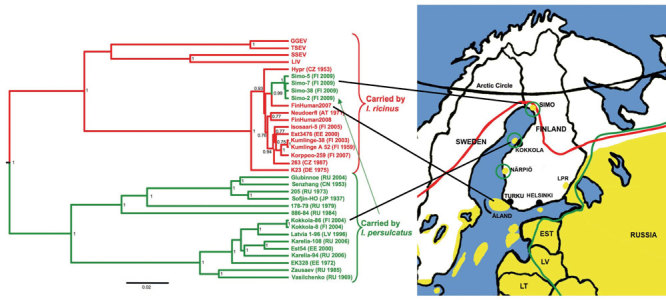
A1. Phylogenetic tree of partial E (1172-nt) gene sequences, shwoing Ixodes ricinus–transmitted strains (red) and I. persulcatus–transmitted strains (green). The tree was reconstructed by the Bayesian Markov chain Monte Carlo method in BEAST (http://beast.bio.ed.ac.uk). Maximum clade credibility tree with an arbitrary root is shown with mean branch lengths, and Bayesian posterior probabilities are given at nodes when >0.7. Country of origin and isolation year are indicated. Four strains from Simo are shown; Simo-48 and Simo-9 were identical to Simo-38. Yellow shading, tick-borne encephalitis–endemic areas; red line, I. ricinus distribution; green line, I. persulcatus distribution; LPR, Lappeenranta. Scale bar indicates number of substitutions per site.
Footnotes
Suggested citation for this article: Jääskeläinen AE, Tonteri E, Sironen T, Pakarinen L, Vaheri A, Vapalahti O. European subtype tick-borne encephalitis virus in Ixodes persulcatus Ticks [letter]. Emerg Infect Dis [serial on the Internet]. 2011 Feb [date cited]. http://dx.doi.org/10.3201/eid1702.101487
References
- 1.Randolph SE, Green RM, Peacey MF, Rogers DJ. Seasonal synchrony: the key to tick-borne encephalitis foci identified by satellite data. Parasitology. 2000;121:15–23. 10.1017/S0031182099006083 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lindquist L, Vapalahti O. Tick-borne encephalitis. Lancet. 2008;371:1861–71. 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60800-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Jääskeläinen AE, Tikkakoski T, Uzcátegui NY, Alekseev AN, Vaheri A, Vapalahti O. Siberian subtype tickborne encephalitis virus, Finland. Emerg Infect Dis. 2006;12:1568–71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Jääskeläinen AE, Sironen T, Murueva GB, Subbotina N, Alekseev AN, Castrén J, et al. Tick-borne encephalitis virus in ticks in Finland, Russian Karelia, and Buryatia. J Gen Virol. 2010;91:2706–12. 10.1099/vir.0.023663-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Schwaiger M, Cassinotti P. Development of a quantitative real-time RT-PCR assay with internal control for the laboratory detection of tick borne encephalitis virus (TBEV) RNA. J Clin Virol. 2003;27:136–45. 10.1016/S1386-6532(02)00168-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Caporale DA, Rich SM, Spielman A, Telford SR III, Kocher TD. Discriminating between Ixodes ticks by means of mitochondrial DNA sequences. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 1995;4:361–5. 10.1006/mpev.1995.1033 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Tonteri E, Jääskeläinen AE, Tikkakoski T, Voutilainen L, Niemimaa J, Henttonen H, et al. Tick-borne encephalitis virus in wild rodents in winter, Finland, 2008–2009. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011;17:72–5. 10.3201/eid1701.100051 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tuomi J, Brummer-Korvenkontio M. Antibodies against viruses of the tick-borne encephalitis group in cattle sera in Finland. Ann Med Exp Biol Fenn. 1965;43:149–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Randolph SE, Rogers DJ. Fragile transmission cycles of tick-borne encephalitis virus may be disrupted by predicted climate change. Proc Biol Sci. 2000;267:1741–4. 10.1098/rspb.2000.1204 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lukan M, Bullova E, Petko B. Climate warming and tick-borne encephalitis, Slovakia. Emerg Infect Dis. 2010;16:524–6. 10.3201/eid1603.081364 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


