Abstract
Single-stranded DNA (ssDNA)-binding proteins play an essential role in DNA replication and repair. They use oligonucleotide/oligosaccharide-binding (OB)-folds, a five-stranded β-sheet coiled into a closed barrel, to bind to ssDNA thereby protecting and stabilizing the DNA. In eukaryotes the ssDNA-binding protein (SSB) is known as replication protein A (RPA) and consists of three distinct subunits that function as a heterotrimer. The bacterial homolog is termed SSB and functions as a homotetramer. In the archaeon Haloferax volcanii there are three genes encoding homologs of RPA. Two of the rpa genes (rpa1 and rpa3) exist in operons with a novel gene specific to Euryarchaeota; this gene encodes a protein that we have termed RPA-associated protein (rpap). The rpap genes encode proteins belonging to COG3390 group and feature OB-folds, suggesting that they might cooperate with RPA in binding to ssDNA. Our genetic analysis showed that rpa1 and rpa3 deletion mutants have differing phenotypes; only Δrpa3 strains are hypersensitive to DNA damaging agents. Deletion of the rpa3-associated gene rpap3 led to similar levels of DNA damage sensitivity, as did deletion of the rpa3 operon, suggesting that RPA3 and RPAP3 function in the same pathway. Protein pull-downs involving recombinant hexahistidine-tagged RPAs showed that RPA3 co-purifies with RPAP3, and RPA1 co-purifies with RPAP1. This indicates that the RPAs interact only with their respective associated proteins; this was corroborated by the inability to construct rpa1 rpap3 and rpa3 rpap1 double mutants. This is the first report investigating the individual function of the archaeal COG3390 RPA-associated proteins (RPAPs). We have shown genetically and biochemically that the RPAPs interact with their respective RPAs, and have uncovered a novel single-stranded DNA-binding complex that is unique to Euryarchaeota.
Keywords: archaea, Haloferax volcanii, RPA single-strand DNA-binding protein, COG3390 RPA-associated protein, DNA repair, protein overexpression, Cdc48d
Introduction
Genomic DNA must be unwound in order to be replicated or repaired, leaving it vulnerable to nuclease and chemical attack as well as open to the possibility of forming secondary structures. Binding of the single-stranded DNA (ssDNA)-binding proteins (SSB) RPA and SSB prevents any of these events from occurring (Lu et al., 2009). The SSB is denominated SSB in bacteria and replication protein A (RPA) in eukaryotes; they bind to ssDNA with high affinity and to dsDNA and RNA with low affinity (Wobbe et al., 1987; Wold et al., 1989; Kim et al., 1992). They play a vital organizational role in the central genome maintenance of the cell, providing docking platforms for a wide range of enzymes to gain access to genomic substrates (Lu and Keck, 2008). The bacteriophage T4 gene 32 monomer was the first SSB to be identified (Alberts and Frey, 1970). RPA was first identified as an essential protein for DNA replication in the eukaryotic simian virus (SV40; Wobbe et al., 1987) by stimulating the T antigen-mediated unwinding of the SV40 origin of replication (Kenny et al., 1989). RPA and SSB have now been established as essential proteins for DNA metabolism including DNA replication, recombination, and repair in all domains of life (Wobbe et al., 1987; Heyer et al., 1990; Coverley et al., 1991, 1992; Moore et al., 1991; Wold, 1997). The basic architecture of RPA and SSB is based on the oligonucleotide/oligosaccharide-binding (OB)-fold, a five-stranded β-sheet coiled into a closed barrel, but the number of OB-folds present varies from species to species (Bochkarev and Bochkareva, 2004; Fanning et al., 2006).
Unlike in bacteria and eukaryotes, the architecture of SSBs present in archaea is not uniform. There is wide diversity of SSBs in the two main archaeal phyla, Euryarchaea, and Crenarchaea. Crenarchaea possess SSBs similar to those of bacteria, consisting of a single subunit with one OB-fold and an acidic C-terminus tail (Rolfsmeier and Haseltine, 2010). Euryarchaea have RPA-like proteins that show homology with the eukaryotic RPA, but from species to species the architecture of euryarchaeal RPAs varies dramatically from a single polypeptide RPA to an RPA made up of several subunits. Each of these RPAs can contain up to four OB-folds as well as a zinc finger motif (Rolfsmeier and Haseltine, 2010).
Pyrococcus furiosus RPA consists of three subunits RPA41, 14, and 32, denominated RPA1, 2, and 3, respectively, which form a heterotrimer as seen in eukaryotes. Strand exchange and immunoprecipitation assays have shown that P. furiosus heterotrimeric RPA stimulates strand exchange, and interacts with the clamp loader RFC and both DNA polymerases B and D (Komori and Ishino, 2001). The heterotrimeric complex seen in P. furiosus is also found in P. abyssi and P. horikoshii. However, in other archaeal species the rpa genes have undergone lineage-specific duplications, resulting in differing numbers of SSBs with diverse structures. Unlike the RPA complex found in Pyrococcus spp., or eukaryotic RPA, these do not form trimeric complexes (Robbins et al., 2004).
Methanosarcina acetivorans possesses three RPA subunits, MacRPA1, 2, and 3, which are unlikely to form a heterotrimeric complex as seen in P. furiosus and in eukaryotes. MacRPA1 contains four DNA-binding domains (DBD) containing OB-folds, MacRPA2 and 3 both have two OB-fold containing DBDs. Each of the three MacRPAs can function as SSBs, and are able to stimulate primer extension by M. acetivorans DNA polymerase BI (Robbins et al., 2004, 2005). This demonstrates an element of redundancy between the three MacRPAs, and suggests that the heterotrimeric RPA structure observed in P. furiosus is the exception and not the rule. Lin et al. (2008) suggest that intramolecular recombination between RPA homologs may have led to the diversity of RPAs found in euryarchaea, which can function in different pathways or cellular processes.
A similar pattern of lineage-specific gene duplication is seen with the archaeal MCM helicase, where the number and type of MCM subunits that make up the hexameric helicase differ between archaeal species. The genes encoding the MCM subunits fall into distinct phylogenetic clades, but these do not correspond to specific subunits of eukaryotic MCM. Instead they have arisen through lineage-specific gene family expansion (Chia et al., 2010). Such gene duplication might allow different archaeal species to refine the structure and function of MCM (and potentially RPA) for differing conditions and specialized roles.
Sulfolobus solfataricus has a bacterial-like SSB consisting of a small 20 kDa peptide containing one OB-fold and an acidic C-terminus tail (Haseltine and Kowalczykowski, 2002; Rolfsmeier and Haseltine, 2010). The S. solfataricus SSB quaternary structure is similar to that of E. coli SSB, however the primary structure of the OB-fold shows greater homology to that of the eukaryotic RPA70 DNA-binding domain B (DBDB). This suggests that crenarchaeal SSBs may be structurally similar to bacterial SSB but at a protein sequence level show homology to the eukaryotic RPA (Haseltine and Kowalczykowski, 2002; Kerr et al., 2003). In S. solfataricus there is an absence of DNA damage recognition proteins such as homologs of XPA or XPC to initiate NER. The ability of S. solfataricus SSB to specifically bind and melt damaged duplex DNA in vitro suggests SSB may play a role in the identification and binding of damaged DNA, followed by the subsequent recruitment of NER repair proteins (Cubeddu and White, 2005).
Haloferax volcanii encodes three RPA genes rpa1, rpa2, and rpa3 (Hartman et al., 2010). Recent studies have shown RPA2 to be essential while RPA1 and RPA3 are not (Skowyra and MacNeill, 2012). Note that these authors used the nomenclature rpaA1, A2, B1, B2, B3, and C to refer to rpa3, rpap3, rpa1, rpap1, rpe, and rpa2, respectively, while we have chosen to maintain the official nomenclature as described in Table 4 of the H. volcanii genome paper (Hartman et al., 2010). Both rpa1 and rpa3 are in operons with other genes; rpa1 is in an operon with genes encoding an OB-fold containing protein (hereby designated RPA-associated protein or RPAP) and a calcineurin-like phosphoesterase, while only one OB-fold rpa-associated protein (rpap) gene is present in the rpa3 operon (Figure 1). The presence of an rpap gene in the same operon as rpa can be found in other euryarchaeota, including Halobacterium marismortui, Halobacterium salinarum, and Natronomonas pharaonis, as well as in M. mazei and M. barkeri. The rpap gene has been assigned to the cluster of orthologous groups (COG) 3390 (Berthon et al., 2008).
Figure 1.
Operon and domain structures of H. volcanii single-stranded DNA-binding proteins. Genes for RPA1 and RPA3 are in operons with genes for RPA-associated proteins, RPAP1 and RPAP3, respectively. The gene for RPA1 phosphoesterase (RPE) is present in the rpa1 operon. Domains (not to scale) comprising OB-folds, zinc fingers and a phosphoesterase motif are shown.
To examine if RPA1 and 3, as well as RPAP1 and RPAP3 play a role in DNA repair, as is true for both the bacterial SSB and eukaryotic RPA, DNA damage assays were performed using the single and operon deletion mutants. Cells with deletions of the rpa1 and rpa3 operons had previously been examined by Skowyra and MacNeill (2012). However, this is the first report investigating the individual function of the archaeal COG3390 RPAP. We show genetically and biochemically that the RPAPs interact with their respective RPAs, and have thereby uncovered a novel SSB complex that is unique to Euryarchaeota.
Materials and Methods
All chemicals were from Sigma and restriction enzymes from New England Biolabs, unless stated otherwise. Standard molecular techniques were used (Sambrook and Russell, 2001).
Strains and plasmids
Haloferax volcanii strains (Table 1) were grown at 45°C on complete (Hv-YPC), casamino acids (Hv-Ca), or minimal (Hv-Min) agar, or in Hv-YPC or Hv-Ca broth as described previously. Isolation of genomic and plasmid DNA, as well as transformation of H. volcanii were carried out as described previously (Allers et al., 2004).
Table 1.
Haloferax volcanii strains.
| Strain | Relevant genotype* | Source or reference |
|---|---|---|
| DS2 | Wild-type | Mullakhanbhai and Larsen (1975) |
| H195 | ΔpyrE2 bgaHa-Bb leuB-Ag1 ΔtrpA ΔhdrB | Guy et al. (2006) |
| H1209 | ΔpyrE2 ΔhdrB Nph-pitA Δmrr | Allers et al. (2010) |
| H1216 | ΔpyrE2 bgaHa-Bb leuB-Ag1 ΔtrpA ΔhdrB Δrpap1::trpA+ | H195 pTA1170 |
| H1217 | ΔpyrE2 bgaHa-Bb leuB-Ag1 ΔtrpA ΔhdrB Δrpa1::trpA+ | H195 pTA1166 |
| H1244 | ΔpyrE2 bgaHa-Bb leuB-Ag1 ΔtrpA ΔhdrB Δrpa3::trpA+ | H195 pTA1174 |
| H1246 | ΔpyrE2 bgaHa-Bb leuB-Ag1 ΔtrpA ΔhdrB Δrpa1 operon | H195 pTA1189 |
| H1260 | ΔpyrE2 ΔhdrB bgaHa-Bb Δrpa3 operon::trpA+ leuB-Ag1 ΔtrpA | H195 pTA1207 |
| H1280 | ΔpyrE2 bgaHa-Bb leuB-Ag1 ΔtrpA ΔhdrB Δrpap1 | H1216 pTA1217 |
| H1281 | ΔpyrE2 bgaHa-Bb leuB-Ag1 ΔtrpA ΔhdrB Δrpa1 | H1217 pTA1141 |
| H1282 | ΔpyrE2 bgaHa-Bb leuB-Ag1 ΔtrpA ΔhdrB Δrpa1 operon rpa3 operon+::[Δrpa3 operon::trpA+, pyrE2+] | H1246 pTA1207 pop-in |
| H1326 | ΔpyrE2 bgaHa-Bb leuB-Ag1 ΔtrpA ΔhdrB Δrpap1 rpa3+::[Δrpa3::trpA+ pyrE2+] | H1280 pTA1174 pop-in |
| H1333 | ΔpyrE2 ΔhdrB Nph-pitA Δmrr Hsa-cdc48d | H1209 pTA1240 |
| H1390 | ΔpyrE2 bgaHa-Bb leuB-Ag1 ΔtrpA ΔhdrB Δrpa1 operon rpa3 operon+::[Δrpa3 operon::trpA+, pyrE2+] <rpa1 operon+hdrB+pyrE2> | H1282 pTA1265 pop-in |
| H1410 | ΔpyrE2 bgaHa-Bb leuB-Ag1 ΔtrpA ΔhdrB Δrpap3 | H195 pTA1284 |
| H1424 | ΔpyrE2 ΔhdrB Nph-pitA Δmrr cdc48d-Ct | H1333 pTA1294 |
| H1430 | ΔpyrE2 ΔhdrB Nph-pitA Δmrr cdc48d-Ct <p.tna::his tag + pyrE2+ hdrB+> | H1424 pTA963 |
| H1473 | ΔpyrE2 bgaHa-Bb leuB-Ag1 ΔtrpA ΔhdrB Δrpa1 rpap3+::[Δrpap3::trpA+ pyrE2+] | H1281 pTA1284 pop-in |
| H1480 | ΔpyrE2 ΔhdrB Nph-pitA Δmrr cdc48d-Ct <p.tnaA::his tag-rpa3 rpap3 pyrE2+ hdrB+> | H1424 pTA1280 |
| H1481 | ΔpyrE2 ΔhdrB Nph-pitA Δmrr cdc48d-Ct <p.tnaA::rpa3 his tag-rpap3 pyrE2+ hdrB+> | H1424 pTA1281 |
| H1482 | ΔpyrE2 ΔhdrB Nph-pitA Δmrr cdc48d-Ct <p.tnaA::his tag-rpa1 rpap1 pyrE2+ hdrB+> | H1424 pTA1326 |
| H1483 | ΔpyrE2 ΔhdrB Nph-pitA Δmrr cdc48d-Ct <p.tnaA::rpa1 his tag-rpap1 pyrE2+ hdrB+> | H1424 pTA1327 |
*Genes shown within <> are present on an episomal plasmid, genes shown within [] are present on an integrated plasmid (pop-in).
Construction of mutant strains
Deletion mutants were constructed as described previously (Allers et al., 2004). Plasmids for gene deletion are shown in Table 2, and were generated by PCR using oligonucleotides shown in Table 3. Template DNA for the PCRs was isolated from genomic DNA.
Table 2.
Plasmids.
| Plasmid | Relevant properties | Source or reference |
|---|---|---|
| pBluescript II SK+ | Standard cloning vector | Stratagene |
| pTA131 | Integrative vector based on pBluescript II, with pyrE2 marker | Allers et al. (2004) |
| pTA409 | Shuttle vector containing ampicillin, pyrE2 and hdrB markers, and pHV1/4 replication origin | Delmas et al. (2009) |
| pTA884 | pBluescript II with H. volcanii 5,038-bp EcoRI/NotI genomic fragment containing rpa3 operon | This study |
| pTA898 | pBluescript II with H. volcanii 7,335-bp EcoRI/NotI genomic fragment containing rpa2 | This study |
| pTA937 | pBluescript II with H. volcanii 8,565-bp BspEI genomic fragment containing rpa1 operon | This study |
| pTA963 | Overexpression vector with 6xHis-tag, pyrE2 and hdrB markers, and pHV2 origin | Allers et al. (2010) |
| pTA1141 | pTA131 containing rpa1 deletion construct inserted at KpnI and XbaI sites, contains an internal NdeI site | This study |
| pTA1142 | pTA131 containing rpa3 deletion construct inserted at EcoRI and KpnI sites, contains an internal NdeI site | This study |
| pTA1166 | rpa1 deletion construct pTA1141 with trpA marker, amplified from pTA298 introducing NdeI restriction sites to insert at internal NdeI restriction site in pTA1141 | This study |
| pTA1170 | Deletion construct of rpap1 containing trpA marker from pTA298 inserted at EcoRI and KpnI sites in pTA131 | This study |
| pTA1174 | rpa3 deletion construct containing trpA marker from pTA1166 inserted at NdeI restriction site | This study |
| pTA1180 | pTA131 with cdc48d deletion construct | Allers et al. (2010) |
| pTA1189 | pTA131 with rpa1 operon deletion construct inserted at restriction sites XbaI and EcoRI with an internal NdeI site | This study |
| pTA1196 | rpa3 operon deletion construct, using NdeI/EcoRI downstream fragment from pTA1282 (rpap3 deletion construct) inserted at NdeI/EcoRI sites in pTA1142 (rpa3 deletion construct), to replace the downstream fragment of the rpa3 deletion construct | This study |
| pTA1207 | Deletion construct of rpa3 operon pTA1196 with insertion of the trpA marker from pTA1166 at internal NdeI site | This study |
| pTA1217 | RPAP1 deletion construct pTA1170 with upstream and trpA fragment replaced with the upstream fragment amplified from pTA937 by PCR, to introduce compatible SphI sites, generating non-trpA-marked deletion construct | This study |
| pTA1218 | pTA963 with rpa3 inserted downstream of His-tag. AseI inserted after rpa3 stop codon to allow insertion of His-tagged rpa3 upstream of His-tagged rpap3 (AseI is NdeI compatible) | This study |
| pTA1222 | pTA963 with rpa1 N-terminally His-tagged, has an AseI site downstream of rpa1 to allow insertion of rpap1 (NdeI compatible) | This study |
| pTA1223 | pTA963 overexpression vector with rpap1 N-terminally His-tagged inserted at PsiI and BamHI sites. rpap1 was amplified by PCR from pTA937 introducing BspHI and BamHI sites | This study |
| pTA1224 | pTA963 with rpap3 N-terminally His-tagged inserted at PsiI and EcoRI sites. RPAP3 was amplified by PCR from pTA884 introducing BspHI and EcoRI sites | This study |
| pTA1240 | Gene replacement construct with insertion of 896 bp Hsa-cdc48d gene (amplified from H. salinarum DNA) between upstream and downstream flanking regions of H. volcanii cdc48d deletion construct pTA1180 | This study |
| pTA1265 | pTA409 with insertion of rpa1 operon from pTA937 at EcoRV site | This study |
| pTA1280 | pTA1218 with rpap3 amplified from pTA884 by PCR and inserted at BstEII and EcoRI sites after the N-terminally His-tagged rpa3, maintaining reading frame | This study |
| pTA1281 | pTA1224 with rpa3 amplified from pTA884 by PCR and inserted upstream of N-terminally His-tagged rpap3 at NdeI site | This study |
| pTA1282 | rpap3 deletion construct with upstream and downstream regions amplified from genomic clone pTA884, introducing external KpnI and EcoRI sites, used to ligate into pTA131, and internal NdeI site | This study |
| pTA1284 | rpap3 deletion construct pTA1282 with trpA marker digested from pTA1166 using NdeI and inserted at NdeI site in pTA1282, generating trpA-marked rpap3 deletion construct | This study |
| pTA1288 | pBluescript II with H. volcanii 3,299-bp SalI/BspHI genomic fragment containing cdc48d gene | This study |
| pTA1294 | pTA131 with 2,247 bp Hvo-cdc48d-Ct gene replacement construct amplified from pTA1288: 1,797 bp EcoRI-NheI fragment with C-terminally truncated cdc48d plus upstream region, ligated to 485 bp NheI-KpnI fragment with downstream region of cdc48d, inserted at EcoRI and KpnI sites | This study |
| pTA1326 | pTA1222 with rpap1, amplified from pTA937 introducing BstEII and BamHI sites, and inserted downstream of His-tagged rpa1 at BstEII and BamHI sites | This study |
| pTA1327 | pTA1223 with rpa1 inserted upstream of His-tagged rpap1 at NdeI site. rpa1 was amplified from pTA937 introducing NdeI and AseI (NdeI compatible) sites | This study |
Table 3.
Oligonucleotides.
| Oligonucleotide | Sequence (5′–3′) | Relevant properties | Use (plasmid generated) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rpa1CF DS | GTTCGAGGTACCGTTCGGGGAGC | Δrpa1 external downstream primer, KpnI site | pTA1141 |
| Rpa1CR DS | AGGTGCGCATATGAGCGCCTCGC | Δrpa1 internal downstream primer, NdeI site | pTA1141 |
| Rpa1 CR US | TACTACGTCTAGACGGACCTGTTCG | Δrpa1 external upstream primer, XbaI site | pTA1141 |
| Rpa1 CF US | GGTCGAGTTCCATATGGTCGGGATTCGCC | Δrpa1 internal upstream primer, NdeI site | pTA1141 |
| Rpa3KpnI F | GCCGGTGGTACCACAGCCTC | Δrpa3 external upstream primer, KpnI site | pTA1142 |
| Rpa3NdeIR | GCAAATCAGTCATATGCTACCTCGCC | Δrpa3 internal upstream primer, NdeI site | pTA1142 |
| Rpa3EcoRIR | GACGGTGGAATTCGGCCGTCG | Δrpa3 external downstream primer, EcoRI site | pTA1142 |
| Rpa3NdeI FC | GCGAGGTCGATGCATATGAGTTCCAACG | Δrpa3 internal downstream primer, NdeI site | pTA1142 |
| trpANdeIF | CTCTGCACATATGTCGCTCGAAGACGC | trpA forward primer containing NdeI site | pTA1166 |
| trpANdeIR | TGCATGCCATATGCGTTATGTGCG | trpA reverse primer containing NdeI | pTA1166 |
| RPAP11kpnIus | CCGCGAGTGGTACCGCAAGCCCG | Δrpap1 external upstream primer, KpnI site | pTA1170 |
| RPAP11nsiIus | CGACGACCGGCGATGCATTCATGCGCGC | Δrpap1 internal upstream primer, NsiI site | pTA1170 |
| RPAP11sphIds | GCTGAAGGGCATGCGAGGCCGTGC | Δrpap1 internal downstream primer, SphI site | pTA1170 |
| RPAP11ecoRIds | CGGCGAGAGAATTCCCTGCCCGGG | Δrpap1 external downstream primer, EcoRI site | pTA1170 |
| PEecorI F | GCCCGAATTCCGTCTGATTG | Δrpa1 operon external downstream primer, EcoRI site | pTA1189 |
| Rpa1CR US | TACTACGTCTAGACGGACCTGTTCG | Δrpa1 operon external upstream primer, XbaI site | pTA1189 |
| RPEndeI R DS | CTACCGGAACATATGACTCGGGTCG | Δrpa1 operon internal downstream primer, NdeI site | pTA1189 |
| Rpa1ndeI F2 | GTTGGACCCATATGTCGAACGACG | Δrpa1 operon internal upstream primer, NdeI site | pTA1189 |
| RPAP11SphI US | GCGATTTCCCGCATGCCGACGACCG | Δrpap1 internal upstream primer, SphI site | pTA1217 |
| RPAP11 kpnI us | CCGCGAGTGGTACCGCAAGCCCG | Δrpap1 external upstream primer, KpnI site | pTA1217 |
| Rpa3BspHI F | AGGTAGATCATGACTGATTTGC | rpa3 forward primer, BspHI site | pTA1218 |
| Rpa3 RAsel | CGAGTGGGGAATTCGTTGGAATTAATTTACATC | rpa3 reverse primer, AseI site | pTA1218 |
| Rpa1F NcoI | CCCGACTCCATGGAACTCGACC | rpa1 forward primer, NcoI site | pTA1222 |
| Rpa1AseI/EcoRI | CGGCGGCGAATTCGCGGTAGGCGATTAATCGCGTGC | rpa1 reverse primer, AseI and EcoRI sites | pTA1222 |
| pTA1327 | |||
| RPAP1F BspHI | GGTGCGCTCATGAGCGCCTCG | rpap1 forward primer, BspHI site | pTA1223 |
| RPAP1BamHI | CGTTCGGGGGATCCGCGCCTGC | rpap1 reverse primer, BamHI site | pTA1223 |
| pTA1326 | |||
| RPAP3BspHI F | GTCGATGTTCATGAGTTCCAACG | rpap3 forward primer, BspHI site | pTA1224 |
| RPAP3EcoRI R | CGGTCGGAATTCAGGCCGAC | rpap3 reverse primer, EcoRI site | pTA1224 |
| pTA1280 | |||
| HsaCdc48F | GTTCTTGGCATATGACCGAGGCTCTC | Forward primer for Hsa-cdc48d, NdeI site | pTA1240, Probe Figure 5B |
| HsaCdc48R | CTGACAGATCTCGCAGTCACAGC | Reverse primer for Hsa-cdc48d, BgIII site | pTA1240, Probe Figure 5B |
| Rpa3BstEII | GATGCGCGGTGACCTCGTGG | rpap3 forward primer, native BstEII site | pTA1280 |
| Rpa3NdeI | CGAGGTAGCATATGACTGATTTGCG | rpa3 forward primer, NdeI site | pTA1281 |
| RPAP3 gitF | CTCCCAATGGGTACCAAGGTGGAGGC | Δrpap3 internal upstream primer, NdeI site | pTA1282 |
| RPAP3 gitR | TCGTTGGACATATGTTACATCGACCTCGC | Δrpap3 external upstream primer, KpnI site | pTA1282 |
| RPAP3 F DS | CTCGCTGAATTCGGTGGGTGC | Δrpap3 external downstream primer, EcoRI site | pTA1282 |
| RPAP3 R DS | CTGAGCGCATATGCGGGCGTCTCG | Δrpap3 internal downstream primer, NdeI site | pTA1282 |
| cdc48dUF | ACGGGTACCCACGTTGCTGG | Hvo-cdc48d external upstream primer, KpnI site | pTA1294 |
| cdc48dDR | GCCGAATTCGAGCCGAGGTGG | Hvo-cdc48d external downstream primer, EcoRI site | pTA1294 |
| cdc48d-CtrR | CGGCGCGCTAGCCGGACCGGTTACGC | Internal reverse primer to generate C-terminally truncated Hvo-cdc48d, NheI site at cdc48d stop codon | pTA1294 |
| cdc48d-CtrF | CTGTGGTGCTAGCCGTCGTCCGACCCCG | Internal forward primer to generate C-terminal truncated Hvo-cdc48d, NheI site at cdc48d stop codon | pTA1294 |
| cdc48dSeqF | GGAAAAAGGGGCAGATGGTG | Forward primer to downstream flanking region of Hvo-cdc48d | PCR Figure 5C |
| cdc48dHvSeqR | CGACGACATCTCGCTGATTCG | Reverse primer to Hvo-cdc48d gene | PCR Figure 5C |
| cdc48dHsalSeqR | GGTCAACACGCTGCTGAAGTCC | Reverse primer to Hsa-cdc48d gene | PCR Figure 5C |
| Rpa1BstEII | CCGGCACGGTGACCGCCATCC | rpap1 forward primer, native BstEII site | pTA1326 |
| Rpa1NdeI | CCCGACCATATGGAACTCGACC | rpa1 forward primer, NdeI site | pTA1327 |
Construction of protein overexpression strains
Protein overexpression strains were constructed by transformation with episomal overexpression plasmids as described previously (Allers et al., 2010). Plasmids for protein expression are shown in Table 2, and were generated by PCR using oligonucleotides shown in Table 3. Template DNA for the PCRs was isolated from genomic DNA.
UV irradiation assays
UV irradiation assays were carried out as described previously (Delmas et al., 2009).
Mitomycin C assays
Mitomycin C (MMC) assays were carried out as described previously (Lestini et al., 2010).
Protein overexpression and purification
Protein overexpression was carried out as described previously (Allers et al., 2010) with the following amendments: cultures were incubated at 45°C overnight to an OD650 of 0.5, when protein expression was induced by adding 3 mM Trp to the culture followed by incubation at 45°C, with shaking for a further 1 h until OD650 ≈ 0.7.
Protein precipitation
Deoxycholate was added to 0.015%, vortexed, and incubated for 10 min at room temperature. Trichloroacetic acid was added to 7.2% and incubated at room temperature for 5 min. Samples were centrifuged at 14,000 × g at room temperature for 8 min. Supernatant was removed and precipitated protein resuspended in 15 μl resuspension buffer (330 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.2, 2.6% SDS, 17 mM NaOH, 5% glycerol, 0.25 mg/ml bromophenol blue). Samples were heated for 10 min at 94°C and cooled on ice before loading onto an SDS-PAGE gel.
Mass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry of excised protein bands was carried out as described previously (Allers et al., 2010). Details of protein identification are given in the Table A1 in Appendix.
Results
RPA3 but not RPA1 functions in DNA repair
In eukaryotes, specifically Saccharomyces cerevisiae, all three RPA subunits have been shown to be essential for cell survival (Brill and Stillman, 1991). Work by Skowyra and MacNeill (2012) has shown that H. volcanii rpa2 is essential, which is in agreement with our fruitless attempts to delete rpa2 (data not shown). To examine if the other rpa genes of H. volcanii are also essential, genomic deletions of rpa1 and rpa3 were generated using the counter selective pop-in/pop-out method (Allers et al., 2004). To generate the deletion constructs by PCR, rpa1 and rpa3 operons were first isolated from wild-type (WT) H. volcanii using native BspEI and EcoRI/NotI restriction sites, respectively, to generate genomic libraries. These were then screened for the presence of the rpa1 and rpa3 operons, individually, using colony hybridization. The isolated plasmids, pTA937 (rpa1 operon) and pTA884 (rpa3 operon) were confirmed by DNA sequencing. Deletion constructs for rpa1 and rpa3 were designed to avoid polar effects on the expression of the downstream rpap genes by maintaining the reading frame. Genomic deletions of both rpa1 and rpa3 (trpA-marked) were successful, generating strains H1217 and H1244, respectively (Figures 2 and 3, respectively). The ability to delete both rpa1 and rpa3 with relative ease, but not rpa2, indicates that the cellular requirement for each RPA is not equal, making it unlikely that they function collectively.
Figure 2.
(A) Map of rpa1 operon indicating location of Δrpa1, Δrpap1, and Δrpa1 operon deletions, as well as the BspEI and NruI sites, and probes used to verify the deletions. (B) Southern blot of genomic DNA cut with BspEI and probed with flanking regions of rpa1 and rpap1, as shown in (A), to indicate deletion of rpa1 and rpap1, respectively. (C) Southern blot of genomic DNA cut with NruI and probed with flanking regions of rpa1 operon (rpa1 op.), as shown in (A), to indicate deletion of the rpa1 operon.
Figure 3.
(A) Map of rpa3 operon indicating location of Δrpa3, Δrpap3, and Δrpa3 operon deletions, as well as the AscI, MluI, StuI, and XhoI sites and probes used to verify the deletions. (B) Southern blot of genomic DNA cut with StuI and XhoI, and probed with flanking regions of rpa3, as shown in Figure 2A, to indicate deletion of rpa3. (C) Southern blot of genomic DNA cut with AscI and StuI, and probed with flanking regions of rpap3, as shown in Figure 2A, to indicate deletion of the rpap3. (D) Southern blot of genomic DNA cut with MluI and probed with flanking regions of rpa3 operon (rpa3 op.), as shown in Figure 2A, to indicate deletion of the rpa3 operon.
Both eukaryotic and bacterial SSB are involved in DNA repair. To examine if H. volcanii RPA1 and RPA3 function in DNA repair, the effects of DNA damage on cell survival of H1217 and H1244 were examined. UV irradiation results in the formation of cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers and 6-4 pyrimidine-pyrimidone dimer photoproducts, as well as ssDNA nicks that indirectly generate double-stranded DNA breaks (DSBs). The latter require repair by homologous recombination (HR) or single-strand DNA annealing (Fousteri and Mullenders, 2008; Rouillon and White, 2011). MMC is a chemotherapeutic agent that reacts with DNA generating covalent interstrand cross-links, requiring removal by nucleotide excision repair (NER) and HR (Tomasz et al., 1987). The Δrpa1 mutant H1217 was no more sensitive than the WT to UV and MMC-induced DNA damage, however the Δrpa3 mutant H1244 exhibited moderate sensitivity to both UV and MMC-induced DNA damage (Figure 4).
Figure 4.
(A) Wild-type (WT), rpa1, rpap1, rpa1 operon, rpa3, rpap3, rpa3 operon (H195, H1217, H1216, H1246, H1244, H1410, and H1260, respectively), were plated out and exposed to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. The average and standard error (SE) of three experiments are shown. (B) The strains shown in (A) were plated out and exposed to mitomycin C (MMC). The average and SE of three experiments are shown.
RPAP3 but not RPAP1 functions in DNA repair
Analysis of predicted protein domains indicates that RPA1 and RPA3 both possess zinc finger domains, and that RPA1 has three OB-folds compared to the single OB-fold present in RPA3 (Figure 1). Both COG3390 RPAPs RPAP1 and RPAP3 possess a single OB-fold suggesting a possible role in DNA binding. The RPA1 phosphoesterase (RPE) has a calcineurin-like phosphoesterase domain, and was not investigated individually. However, our results and those of Skowyra and MacNeill (2012) show that rpe is a non-essential gene.
To study the roles of RPAP1 and RPAP3 in DNA repair, Δrpap1 (H1216) and Δrpap3 (H1410) mutants were generated, both using trpA-marked deletion constructs (Figures 2 and 3, respectively). As with Δrpa1 strain H1217, the Δrpap1 mutant H1216 showed no increased sensitivity to UV irradiation or to MMC-induced DNA damage. However, the Δrpap3 deletion mutant H1410 was hypersensitive to both types of DNA damage, and the level of sensitivity was similar to that exhibited by the Δrpa3 mutant H1244.
We examined whether the absence of both RPA and RPAP results in a synergistic deficiency in DNA repair. Genomic deletions of the rpa1 and rpa3 operons were generated in strains H1246 and H1260, respectively, with only the latter being a trpA-marked deletion (Figures 2 and 3, respectively); deletions of the rpa1 and rpa3 operons have previously been reported by Skowyra and MacNeill (2012). The Δrpa1 operon mutant showed no increased sensitivity to UV irradiation or to MMC-induced DNA damage. However the Δrpa3 operon deletion mutant was hypersensitive to both types of DNA damage, and the level of sensitivity was similar to that exhibited by the single Δrpa3 and Δrpap3 mutants H1244 and H1410, respectively (Figure 4). This result suggests that RPA3 and RPAP3 function in the same pathway(s) of DNA repair.
Redundancy between rpa1 and rpa3 operons
In order to test for redundancy between the two RPAs, an attempt was made to generate a double Δrpa1 operon Δrpa3 operon deletion. This involved constructing the strain H1282, which contained the pop-in of a trpA-marked Δrpa3 operon construct (pTA1207) in an unmarked Δrpa1 operon background (H1246). An episomal plasmid (pTA1265), marked with pyrE2 and providing in trans expression of the rpa1 operon was used for complementation during the pop-out step (note that this episomal plasmid is lost during counter-selection with 5-FOA). Neither of the two pop-outs generated from this strain (H1390) yielded the desired Δrpa1 operon Δrpa3 operon mutant (see Figure A1 in Appendix). This indicates that the cell requires either RPA1 or RPA3 (and/or their respective RPAPs) for survival.
Next we attempted to generate Δrpa1 Δrpap3 and Δrpa3 Δrpap1 deletion mutants. This would test whether the RPAPs can complement each other, or whether they are instead specific for their respective RPAs. The trpA-marked Δrpap3 construct (pTA1284) was used in an unmarked Δrpa1 background (H1280), and the trpA-marked Δrpa3 construct (pTA1207) was used in an unmarked Δrpap1 background (H1281). In both cases two pop-outs were generated but none proved to be the desired deletions (see Figure 1 in Appendix). This suggests that the putative RPA:RPAP complex is dependent upon specific RPA:RPAP interactions for functionality.
Construction of protein overexpression strain with C-terminal truncation of Cdc48d
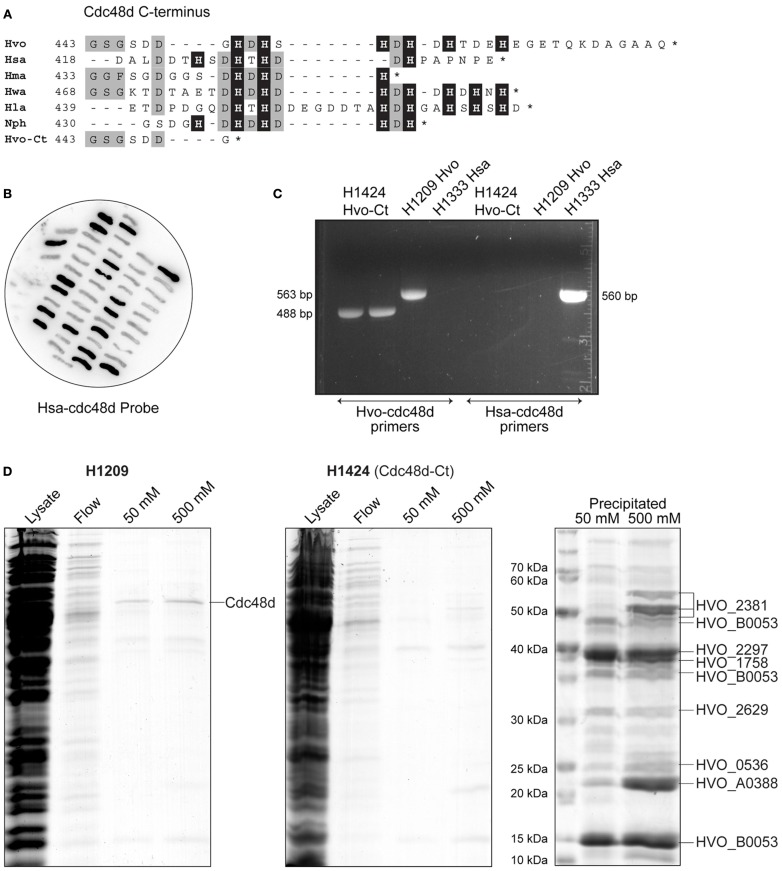
In a previous publication (Allers et al., 2010), we constructed a strain of H. volcanii where the histidine-rich pitA gene is replaced by the ortholog from N. pharaonis. The latter protein lacks the histidine-rich linker region found in H. volcanii PitA and does not co-purify with His-tagged recombinant proteins. The absence of Hvo-PitA revealed an additional co-purifying protein, which we identified as Cdc48d (HVO_1907) and features a histidine-rich C-terminus (Figure 5A). We were unable to delete cdc48d, indicating that this gene is essential (Allers et al., 2010). The presence of this contaminating protein was problematic for purification of His-tagged RPA1 and RPAP1, due to similar molecular weights (Cdc48d, 53 kDa; RPA1, 46 kDa; RPAP1, 65 kDa).
Figure 5.
(A) Protein sequence alignment of C-terminus of Cdc48d from selected species of haloarchaea (Hvo, H. volcanii; Hsa, Halobacterium salinarum; Hma, Haloarcula marismortui; Hwa, Haloquadratum walsbyi; Hla, Halorubrum lacusprofundi; Nph, N. pharaonis; Hvo-Ct, H. volcanii C-terminal truncation Cdc48d-Ct). Histidine residues are indicated by a black background. (B) Colony hybridization of 5-FOA-resistant clones of H. volcanii H1333, after pop-in/pop-out gene replacement with pTA1294. H. salinarum cdc48d sequences (Hsa-cdc48d) were used as a probe, clones failing to hybridize therefore carry the truncated H. volcanii cdc48d-Ct allele present in pTA1294. (C) Verification of truncated cdc48d-Ct allele in H1424 by PCR (488 bp product), with primers specific to either H. volcanii or H. salinarum genes. H1209 genomic DNA was used as a control for wild-type H. volcanii cdc48d (563 bp product), and H1333 was used as a control for H. salinarum cdc48d (560 bp product). (D) H. volcanii strains H1209 and H1424 containing empty vector pTA963 (Allers et al., 2010) were used in mock protein overexpression. Histidine-rich cellular proteins were purified from the soluble fraction (lysate) by affinity chromatography on a Ni2+ chelating column, samples were taken from the flow-through (flow) and bound proteins were eluted using 50 and 500 mM imidazole. Precipitation using trichloroacetic acid and deoxycholate was used to enhance visualization and identification of the eluted proteins by mass spectrometry. Cdc48d (HVO_1907) eluted from cell extracts of H1209 but not from H1424 (cdc48d-Ct).
All orthologs of Cdc48d from haloarchaea feature a histidine-rich C-terminus, however Cdc48d from Haloarcula marismortui and H. salinarum have only three and four histidines, respectively, compared to six in H. volcanii (Figure 5A). Therefore, we replaced the H. volcanii cdc48d gene in H1209 (Allers et al., 2010) with orthologous genes from H. marismortui and H. salinarum, generating H. volcanii strains H1405 and H1333, respectively. Unfortunately these strains grew poorly and were not suitable for recombinant protein overexpression. Instead, we generated a truncated allele of H. volcanii cdc48d, encoding a Cdc48d protein lacking the histidine-rich C-terminus (Cdc48d-Ct; Figure 5A). The cdc48d-Ct allele was used to replace the H. salinarum cdc48d gene in H. volcanii H1333, generating H1424 (Figures 5B,C). This strain exhibits normal cell growth and the Cdc48d-Ct protein no longer co-purifies with His-tagged recombinant proteins (Figure 5D). A number of minor histidine-rich contaminants are now apparent, which have been identified by mass spectrometry.
Direct RPAP interaction with respective RPA
The genetic analysis of rpa1 and rpa3 and their respective rpap genes indicates not only that RPA3 and RPAP3 function in the same DNA repair pathway(s), but also that they function together as a specific RPA:RPAP complex. To establish whether this is achieved via a direct RPA:RPAP interaction, affinity pull-downs were employed (Allers et al., 2010). The rpa1 and rpa3 operons were cloned under control of the tryptophanase promoter in plasmid pTA963, where either the RPA or the RPAP was tagged with a hexahistidine tag.
Histidine-tagged RPA1 and RPA3 pulled down their respective RPAPs, and histidine-tagged RPAP1 and RPAP3 pulled down their respective RPAs (Figure 6). However, histidine-tagged RPA1 did not pull down RPAP3, and vice versa. This confirms that the RPAs interact specifically with their respective RPAPs, supporting our conclusions based on the failure to generate Δrpa1 Δrpap3 and Δrpa3 Δrpap1 deletion mutants. Neither RPA1 nor RPA3 pulled down RPA2, and histidine-tagged RPA2 did not pull down RPA1 or 3, or either of the RPAPs (data not shown). This supports the suggestion that the three RPAs of H. volcanii do not form a heterotrimer as observed in eukaryotes and P. furiosus, but instead form three separate ssDNA-binding factors.
Figure 6.
H. volcanii strains containing (A) histidine-tagged RPA1 (H1482), (B) histidine-tagged RPAP1 (H1483), (C) histidine-tagged RPA3 (H1480), and (D) histidine-tagged RPAP3 (H1481) were used in protein overexpression. The histidine-tagged recombinant proteins were purified from the soluble fraction (lysate) by affinity chromatography on a Ni2+ chelating column, samples were taken from the flow-through (FT) and bound proteins were eluted using 50 and 500 mM imidazole. Precipitation using trichloroacetic acid and deoxycholate was used to enhance visualization and identification of the eluted proteins by mass spectrometry. Stars denote contaminants shown in Figure 5D.
Discussion
There is a unifying theme in archaea of a great variety in the number and type of proteins involved in DNA replication, and repair, whose counterparts in eukaryotes are much more uniform. This has been shown to be the case for RPA, where eukaryotes possess three subunits that all form unified clades in a phylogenetic analysis, but in archaea the number and structure of subunits varies widely. Some euryarchaea possess differing numbers of RPA subunits and some possess differing numbers of RPAs and RPAPs. Crenarchaea also possess varying numbers of SSB, however in both euryarchaea and crenarchaea none of the RPAs, RPAPs, or SSBs fall into unified clades. Again this is seen in the case of MCM, where eukaryotes possess six MCM subunits that each form unified clades, but in archaea there is a vast range in the number of MCM subunits, differing between individual species, and none of which fall into uniform clades (Chia et al., 2010). Characterizing the RPA-RPAP complexes of H. volcanii will shed light on how the RPAs and RPAPs function together in binding and stabilizing ssDNA. This in turn will provide insight for other RPAs and RPAPs in archaea, but also offer reasoning behind the driving force of such non-uniform evolution of archaea.
The genetic and biochemical analysis presented here indicates the three RPAs of H. volcanii do not form a heterotrimeric complex as in P. furiosus and eukaryotes. Instead, RPA1 and RPA3 form complexes with their respective RPAPs. Unlike rpa2, both rpa1 and rpa3 genomic deletions were generated with relative ease, showing that the latter are not essential for cell survival and supporting the hypothesis that the three RPAs do not form a heterotrimeric complex.
The ease at which the rpa1, rpap1, and rpa1 operon deletion mutants were made, coupled with a lack DNA damage sensitivity, signifies the rpa1 operon does not play a major role in DNA replication or repair. The moderate DNA damage sensitivity shown by the individual rpa3, rpap3, and the rpa3 operon mutants indicates that the efficient repair of UV and MMC-induced DNA damage requires the products of the rpa3 operon but not the rpa1 operon. However, it proved impossible to generate a double Δrpa1 operon Δrpa3 operon deletion, showing that cellular growth requires either RPA1 or RPA3.
Both single Δrpa3 and Δrpap3 mutants showed a similar DNA damage sensitivity to each other, and to the rpa3 operon mutant, providing genetic evidence that RPA3 and RPAP3 act in the same DNA repair pathway. Furthermore, we were unable to generate Δrpa1 Δrpap3 and Δrpa3 Δrpap1 deletion mutants, indicating that RPAP1 could not substitute for RPAP3 (and vice versa), and suggesting that the RPA3 interacts specifically with RPAP3 (and likewise for RPA1 and RPAP1). However it is unclear what role the associated proteins play, since the presence of an OB-fold does not necessarily indicate direct ssDNA binding. Instead, the RPAPs may provide a platform for protein:protein interactions. This is seen in eukaryotes, where the RPA 14 kDa subunit possesses a single OB-fold, this subunit is essential for formation of the RPA heterotrimer by facilitating protein:protein interactions (Fanning et al., 2006).
The co-purification of histidine-tagged RPA1 and RPA3 with their respective untagged RPAPs (and vice versa) supports our hypothesis that H. volcanii RPA1 and RPA3 form complexes with their respective RPAPs. This observation, and the differing outcomes of rpa1, rpa2, and rpa3 deletions, indicates that the three RPAs of H. volcanii do not function as a heterotrimer. Similar results have been obtained in M. acetivorans, where the three RPAs are able to bind ssDNA individually, in addition to stimulating primer extension by M. acetivorans DNA polymerase BI in vitro. (Robbins et al., 2004).
This study has shown genetically and biochemically that RPAPs interact with RPAs, and that this interaction is RPA-specific. This is the first report investigating the function of the archaeal COG3390RPA-associated proteins (RPAPs), thus providing an important insight of the structure and function of H. volcanii single-strand DNA-binding proteins.
Author Contributions
Amy Stroud and Thorsten Allers wrote the paper; Amy Stroud and Thorsten Allers designed the experiments; Amy Stroud and Thorsten Allers performed the microbiological and biochemical experiments; Susan Liddell carried out the mass spectrometry; Amy Stroud, Susan Liddell, and Thorsten Allers analyzed the data.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the BBSRC for a PhD studentship awarded to Amy Stroud and the Royal Society for a University Research Fellowship awarded to Thorsten Allers. We thank Kayleigh Wardell for help with strain construction, and Ed Bolt, Geoff Briggs, and Karen Bunting for their advice.
Appendix
Table A1.
Identification of proteins present in cellular soluble fraction after purification by affinity chromatography on a Ni2+ chelating column.
| Prot accession | Protein name | HVO_# | Predicted MW | Observed MW | MASCOT score | Number of peptides | % coverage | Peptide sequences |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| gi[292655491] | RPAP1 | 1337 | 64,829 | 57,781 | 671 | 12 | 18 | 8 |
| gi[292655492] | RPA1 | 1338 | 45,954 | 36,960 | 940 | 15 | 40 | 11 |
| gi[292655491] | RPAP1 | 1337 | 64,829 | 62,780 | 578 | 10 | 21 | 9 |
| gi[292655492] | RPA1 | 1338 | 45,954 | 45,686 | 808 | 15 | 40 | 12 |
| gi[292654471] | RPAP3 | 0291 | 21,979 | 15,074 | 435 | 10 | 53 | 7 |
| gi[292654471] | RPAP3 | 0291 | 21,979 | 16,217 | 484 | 10 | 59 | 8 |
| gi[292654472] | RPA3 | 0292 | 34,562 | 28,262 | 796 | 13 | 43 | 10 |
| gi[292654472] | RPA3 | 0292 | 34,562 | 31,741 | 735 | 13 | 48 | 11 |
| gi[292656508] | Hypothetical protein | 2381 | 52,319 | 55,300/50,200 | 240 | 5 | 11 | 5 |
| gi[292493992] | Hypothetical protein | B0053 | 13,897 | 4,73,600 | 259 | 4 | 33 | 3 |
| gi[292656425] | Deoxyhypusine synthase | 2297 | 38,616 | 39,500 | 451 | 7 | 25 | 4 |
| gi[292655899] | Thioredoxin reductase | 1758 | 36,505 | 38,000 | 312 | 6 | 21 | 6 |
| gi[292493992] | Hypothetical protein | B0053 | 13,897 | 36,300 | 208 | 6 | 40 | 4 |
| gi[292656748] | Htr-like protein | 2629 | 30,266 | 31,700 | 93 | 4 | 17 | 4 |
| gi[292654704] | Ferritin | 0536 | 19,892 | 24,900 | 66 | 1 | 6 | 1 |
| gi[292653937] | Transcriptional regulator | A0388 | 20,201 | 22,300 | 586 | 15 | 54 | 8 |
| gi[292493992] | Hypothetical protein | B0053 | 13,897 | 13,500 | 170 | 3 | 33 | 3 |
Prot Accession, the database entry, e.g., gi|292655491; predicted MW, predicted molecular weight (Da) of the protein sequence identified by MASCOT; observed MW, molecular weight estimated from migration on SDS-PAGE; MASCOT score, MASCOT score associated with protein identification; number of peptides, no. of peptides associated with protein identification by MASCOT; % coverage, % of the database sequence entry that is covered by the peptides matched to it in the MASCOT data. Peptide sequences, the number of distinct peptide sequences associated with the protein identified by MASCOT.
Figure A1.
(A) Map of rpa3 operon indicating location of Δrpa3, Δrpap3, and Δrpa3 operon deletions, as well as the AscI and StuI sites and the probe used to verify the deletions. The size of this fragment in the wild-type (H195) is 8 kb. (B) Southern blot of genomic DNA cut with AscI and StuI, and probed with flanking regions of rpa3 operon (rpa3 op.), as shown in (A), indicates failure to generate Δrpa1 Δrpap3 mutant as bands of the expected size for deletion are not seen (3.4 and 4.4 kb). (C) Southern blot of genomic DNA cut with AscI and StuI, and probed with flanking regions of rpa3 op., as shown in (A), indicates failure to generate Δrpap1 Δrpa3 mutant as bands of the expected size for deletion are not seen (2.8 and 5 kb). (D) Southern blot of genomic DNA cut with AscI and StuI, and probed with flanking regions of rpa3 op., as shown in (A) indicates failure to generate Δrpa1 operon Δrpa3 operon mutant as bands of the expected size for deletion are not seen (2.8 and 3.4 kb).
References
- Alberts B. M., Frey L. (1970). T4 bacteriophage gene 32: a structural protein in the replication and recombination of DNA. Nature 227, 1313–1318 10.1038/2271313a0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allers T., Barak S., Liddell S., Wardell K., Mevarech M. (2010). Improved strains and plasmid vectors for conditional overexpression of His-tagged proteins in Haloferax volcanii. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 76, 1759–1769 10.1128/AEM.02670-09 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allers T., Ngo H. P., Mevarech M., Lloyd R. G. (2004). Development of additional selectable markers for the halophilic archaeon Haloferax volcanii based on the leuB and trpA genes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 70, 943–953 10.1128/AEM.70.2.943-953.2004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berthon J., Cortez D., Forterre P. (2008). Genomic context analysis in Archaea suggests previously unrecognized links between DNA replication and translation. Genome Biol. 9, R71. 10.1186/gb-2008-9-4-r71 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bochkarev A., Bochkareva E. (2004). From RPA to BRCA2: lessons from single-stranded DNA binding by the OB-fold. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 14, 36–42 10.1016/j.sbi.2004.01.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brill S. J., Stillman B. (1991). Replication factor-A from Saccharomyces cerevisiae is encoded by three essential genes coordinately expressed at S phase. Genes Dev. 5, 1589–1600 10.1101/gad.5.9.1589 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chia N., Cann I., Olsen G. J. (2010). Evolution of DNA replication protein complexes in eukaryotes and Archaea. PLoS ONE 5, e10866 10.1371/journal.pone.0010866 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coverley D., Kenny M. K., Lane D. P., Wood R. D. (1992). A role for the human single-stranded DNA binding protein HSSB/RPA in an early stage of nucleotide excision repair. Nucleic Acids Res. 20, 3873–3880 10.1093/nar/20.15.3873 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coverley D., Kenny M. K., Munn M., Rupp W. D., Lane D. P., Wood R. D. (1991). Requirement for the replication protein SSB in human DNA excision repair. Nature 349, 538–541 10.1038/349538a0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cubeddu L., White M. F. (2005). DNA damage detection by an archaeal single-stranded DNA-binding protein. J. Mol. Biol. 353, 507–516 10.1016/j.jmb.2005.08.050 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delmas S., Shunburne L., Ngo H. P., Allers T. (2009). Mre11-Rad50 promotes rapid repair of DNA damage in the polyploid archaeon Haloferax volcanii by restraining homologous recombination. PLoS Genet. 5, e1000552. 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000552 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning E., Klimovich V., Nager A. R. (2006). A dynamic model for replication protein A (RPA) function in DNA processing pathways. Nucleic Acids Res. 34, 4126–4137 10.1093/nar/gkl550 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fousteri M., Mullenders L. H. (2008). Transcription-coupled nucleotide excision repair in mammalian cells: molecular mechanisms and biological effects. Cell Res. 18, 73–84 10.1038/cr.2008.163 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy C. P., Haldenby S., Brindley A., Walsh D. A., Briggs G. S., Warren M. J., Allers T., Bolt E. L. (2006). Interactions of RadB, a DNA repair protein in Archaea, with DNA and ATP. J. Mol. Biol. 358, 46–56 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.02.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman A. L., Norais C., Badger J. H., Delmas S., Haldenby S., Madupu R., Robinson J., Khouri H., Ren Q., Lowe T. M., Maupin-Furlow J., Pohlschroder M., Daniels C., Pfeiffer F., Allers T., Eisen J. A. (2010). The complete genome sequence of Haloferax volcanii DS2, a model archaeon. PLoS ONE 5, e9605 10.1371/journal.pone.0015856 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haseltine C. A., Kowalczykowski S. C. (2002). A distinctive single-strand DNA-binding protein from the archaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus. Mol. Microbiol. 43, 1505–1515 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.02807.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyer W. D., Rao M. R., Erdile L. F., Kelly T. J., Kolodner R. D. (1990). An essential Saccharomyces cerevisiae single-stranded DNA binding protein is homologous to the large subunit of human RP-A. EMBO J. 9, 2321–2329 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny M. K., Lee S. H., Hurwitz J. (1989). Multiple functions of human single-stranded-DNA binding protein in simian virus 40 DNA replication: single-strand stabilization and stimulation of DNA polymerases alpha and delta. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 86, 9757–9761 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9757 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr I. D., Wadsworth R. I., Cubeddu L., Blankenfeldt W., Naismith J. H., White M. F. (2003). Insights into ssDNA recognition by the OB fold from a structural and thermodynamic study of Sulfolobus SSB protein. EMBO J. 22, 2561–2570 10.1093/emboj/cdg272 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim C., Snyder R. O., Wold M. S. (1992). Binding properties of replication protein A from human and yeast cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 12, 3050–3059 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komori K., Ishino Y. (2001). Replication protein A in Pyrococcus furiosus is involved in homologous DNA recombination. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 25654–25660 10.1074/jbc.M102423200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lestini R., Duan Z., Allers T. (2010). The archaeal Xpf/Mus81/FANCM homolog Hef and the Holliday junction resolvase Hjc define alternative pathways that are essential for cell viability in Haloferax volcanii. DNA Repair (Amst.) 9, 994–1002 10.1016/j.dnarep.2010.06.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y., Lin L. J., Sriratana P., Coleman K., Ha T., Spies M., Cann I. K. (2008). Engineering of functional replication protein a homologs based on insights into the evolution of oligonucleotide/oligosaccharide-binding folds. J. Bacteriol. 190, 5766–5780 10.1128/JB.00846-07 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu D., Keck J. L. (2008). Structural basis of Escherichia coli single-stranded DNA-binding protein stimulation of exonuclease I. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 105, 9169–9174 10.1073/pnas.0810041106 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu D., Windsor M. A., Gellman S. H., Keck J. L. (2009). Peptide inhibitors identify roles for SSB C-terminal residues in SSB/exonuclease I complex formation. Biochemistry 48, 6764–6771 10.1021/bi900814c [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore S. P., Erdile L., Kelly T., Fishel R. (1991). The human homologous pairing protein HPP-1 is specifically stimulated by the cognate single-stranded binding protein hRP-A. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 9067–9071 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9067 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullakhanbhai M. F., Larsen H. (1975). Halobacterium volcanii spec. nov., a Dead Sea halobacterium with a moderate salt requirement. Arch. Microbiol. 104, 207–214 10.1007/BF00447326 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. B., McKinney M. C., Guzman C. E., Sriratana B., Fitz-Gibbon S., Ha T., Cann I. K. (2005). The euryarchaeota, nature’s medium for engineering of single-stranded DNA-binding proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 15325–15339 10.1074/jbc.M412870200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. B., Murphy M. C., White B. A., Mackie R. I., Ha T., Cann I. K. (2004). Functional analysis of multiple single-stranded DNA-binding proteins from Methanosarcina acetivorans and their effects on DNA synthesis by DNA polymerase BI. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 6315–6326 10.1074/jbc.M304491200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolfsmeier M. L., Haseltine C. A. (2010). The single-stranded DNA binding protein of Sulfolobus solfataricus acts in the presynaptic step of homologous recombination. J. Mol. Biol. 397, 31–45 10.1016/j.jmb.2010.01.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouillon C., White M. F. (2011). The evolution and mechanisms of nucleotide excision repair proteins. Res. Microbiol. 162, 19–26 10.1016/j.resmic.2010.09.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook J., Russell D. W. (2001). Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press [Google Scholar]
- Skowyra A., MacNeill S. A. (2012). Identification of essential and non-essential single-stranded DNA-binding proteins in a model archaeal organism. Nucleic Acids Res. 40, 1077–1090 10.1093/nar/gkr913 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz M., Lipman R., Chowdary D., Pawlak J., Verdine G. L., Nakanishi K. (1987). Isolation and structure of a covalent cross-link adduct between mitomycin C and DNA. Science 235, 1204–1208 10.1126/science.3103215 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wobbe C. R., Weissbach L., Borowiec J. A., Dean F. B., Murakami Y., Bullock P., Hurwitz J. (1987). Replication of simian virus 40 origin-containing DNA in vitro with purified proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84, 1834–1838 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1834 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold M. S. (1997). Replication protein A: a heterotrimeric, single-stranded DNA-binding protein required for eukaryotic DNA metabolism. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 66, 61–92 10.1146/annurev.biochem.66.1.61 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold M. S., Weinberg D. H., Virshup D. M., Li J. J., Kelly T. J. (1989). Identification of cellular proteins required for simian virus 40 DNA replication. J. Biol. Chem. 264, 2801–2809 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]