Abstract
The reaction of equimolar amounts of zinc bromide and 2,9-dimethyl-1,10-phenanthroline in dry methanol provided the title compound, [ZnBr2(C14H12N2)], in good yield. The ZnII ion is coordinated in a distorted tetrahedral environment by two N atoms from the chelating 2,9-dimethyl-1,10-phenanthroline ligand and two bromide ions. There is intermolecular π–π stacking between adjacent phenanthroline units, with centroid–centroid distances of 3.594 (3) and 3.652 (3) Å.
Related literature
For similiar structures, see: Seebacher et al. (2004 ▶); Harvey et al. (1999 ▶); Jordan et al. (1991 ▶); Pallenberg et al. (1997 ▶).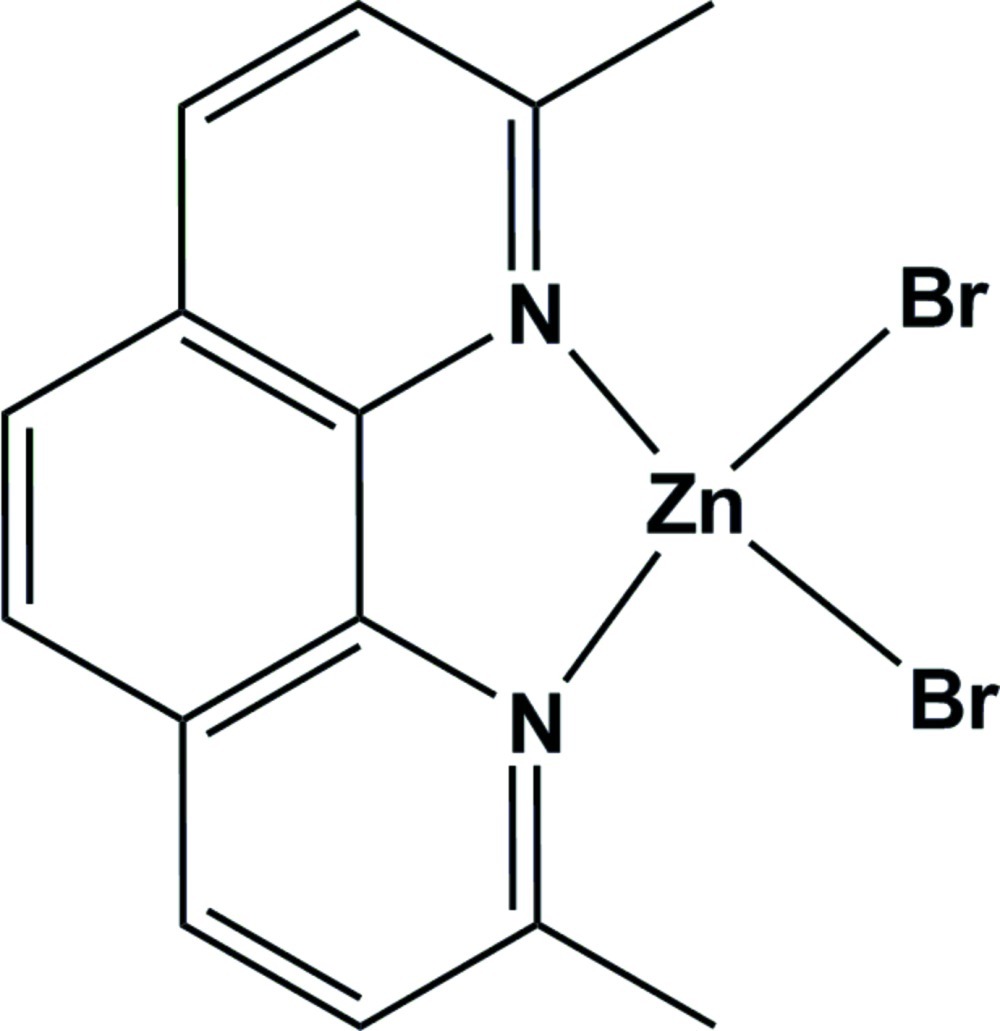
Experimental
Crystal data
[ZnBr2(C14H12N2)]
M r = 433.45
Monoclinic,
a = 9.4113 (19) Å
b = 18.424 (4) Å
c = 9.3362 (19) Å
β = 112.59 (3)°
V = 1494.6 (6) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 6.98 mm−1
T = 298 K
0.25 × 0.20 × 0.17 mm
Data collection
Stoe IPDS 2T diffractometer
Absorption correction: numerical [shape of crystal determined optically (X-RED32; Stoe & Cie, (2005 ▶)] T min = 0.274, T max = 0.383
11850 measured reflections
4014 independent reflections
2304 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.076
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.050
wR(F 2) = 0.100
S = 0.95
4014 reflections
174 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.40 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.67 e Å−3
Data collection: X-AREA (Stoe & Cie, 2005 ▶); cell refinement: X-AREA; data reduction: X-AREA; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: WinGX (Farrugia, 1999 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812022738/bt5921sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812022738/bt5921Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
We thank Shahid Beheshti University and the Iran University of Science and Technology for supporting this study.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
1,10-phenanthroline is a good bidentate chelating ligand, we present the crystal structure of the title complex based on 2,9-dimethyl-1,10-phenanthroline.
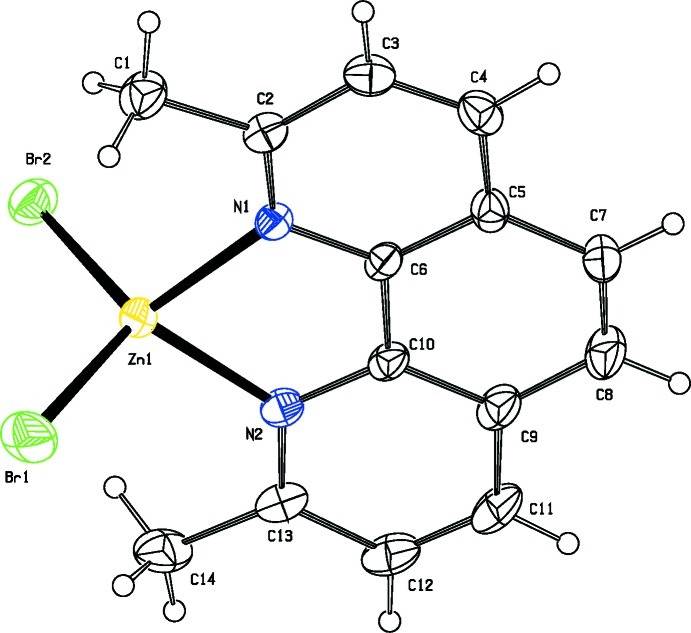
In the molecule of the title compound, (Fig. 1), the two N atoms of one phen ligand and two Br atoms are coordinated to ZnII atom in a distorted tetrahedral arrangement. The Zn—N bonds [average 2.062 Å] are somewhat shorter than the Zn—Br distances [average 2.328 Å] and they are closed to such bond lengths found in other discrete 1,10-phenanthroline derivatives of zinc complexes (Seebacher et al., (2004); Harvey et al.,(1999)). The two N atoms bite angle of phen ligand, N(2)—Zn(1)—N(1), significantly is smaller than N(2)—Zn(1)—Br(1)and N(1)—Zn(1)—Br(2). The bite angle in title complex is also similar to that of found in other zinc complexes of 1,10-phenanthroline, regardless of geometry of complex (Jordan et al.,(1991); Pallenberg et al.,(1997)).
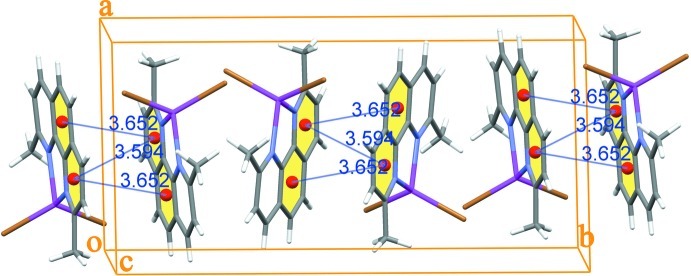
In the crystal structure, There are intermolecular π–π stacking between adjacent phenanthroline, with a centroid–centroid distances of 3.594 (3) and 3.652 (3) Å (Fig. 2). These π-π stacking interactions lead to the stabilization of the crystal structure.
Experimental
ZnBr2.2H2O (0.22 g, 1 mmol) and 2,9-dimethyl-1,10-phenanthroline (0.21, 1 mmol) were loaded in a convection tube; the tube was filled with methanol and kept at 333 K. Colorless crystals were collected from the side arm after several days(m.p. > 543 K).
Refinement
The C—H protons were positioned geometrically and refined as riding atoms with C—H = 0.93 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.2 Ueq(C) for aromatic C—H groups, C—H = 0.96 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.5 Ueq(C) for methyl groups.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound, ellipsoids drawn at 30% probability level.
Fig. 2.
The packing diagram of the title compound showing π–π stacking between adjacent 2,9-dimethyl-1,10-phenanthroline ligands.
Crystal data
| [ZnBr2(C14H12N2)] | F(000) = 840 |
| Mr = 433.45 | Dx = 1.926 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 4014 reflections |
| a = 9.4113 (19) Å | θ = 2.2–29.2° |
| b = 18.424 (4) Å | µ = 6.98 mm−1 |
| c = 9.3362 (19) Å | T = 298 K |
| β = 112.59 (3)° | Block, colorless |
| V = 1494.6 (6) Å3 | 0.25 × 0.20 × 0.17 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Stoe IPDS 2T diffractometer | 4014 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2304 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.076 |
| Detector resolution: 0.15 mm pixels mm-1 | θmax = 29.2°, θmin = 2.2° |
| rotation method scans | h = −12→12 |
| Absorption correction: numerical [shape of crystal determined optically (X-RED32; Stoe & Cie, (2005)] | k = −23→25 |
| Tmin = 0.274, Tmax = 0.383 | l = −12→12 |
| 11850 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.050 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.100 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 0.95 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0423P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 4014 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 174 parameters | Δρmax = 0.40 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.67 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Zn1 | 0.66996 (6) | 0.13233 (3) | 0.75289 (6) | 0.03618 (15) | |
| Br1 | 0.79790 (8) | 0.24221 (4) | 0.77098 (8) | 0.0667 (2) | |
| Br2 | 0.74325 (7) | 0.03299 (3) | 0.63755 (6) | 0.05122 (17) | |
| N1 | 0.6409 (4) | 0.1030 (2) | 0.9541 (4) | 0.0317 (8) | |
| N2 | 0.4348 (4) | 0.1459 (2) | 0.6749 (4) | 0.0349 (9) | |
| C1 | 0.9118 (6) | 0.0852 (3) | 1.1082 (6) | 0.0514 (14) | |
| H1A | 0.9226 | 0.0590 | 1.0240 | 0.077* | |
| H1B | 0.9740 | 0.0627 | 1.2047 | 0.077* | |
| H1C | 0.9447 | 0.1345 | 1.1074 | 0.077* | |
| C2 | 0.7466 (5) | 0.0842 (3) | 1.0900 (5) | 0.0359 (10) | |
| C3 | 0.7030 (6) | 0.0634 (3) | 1.2131 (5) | 0.0429 (12) | |
| H3 | 0.7775 | 0.0492 | 1.3077 | 0.051* | |
| C4 | 0.5507 (6) | 0.0641 (3) | 1.1932 (6) | 0.0434 (12) | |
| H4 | 0.5217 | 0.0492 | 1.2733 | 0.052* | |
| C5 | 0.4398 (6) | 0.0872 (3) | 1.0528 (5) | 0.0376 (11) | |
| C6 | 0.4904 (5) | 0.1057 (2) | 0.9352 (5) | 0.0318 (10) | |
| C7 | 0.2784 (7) | 0.0920 (3) | 1.0226 (7) | 0.0479 (13) | |
| H7 | 0.2437 | 0.0787 | 1.0996 | 0.058* | |
| C8 | 0.1774 (6) | 0.1151 (3) | 0.8858 (7) | 0.0561 (15) | |
| H8 | 0.0740 | 0.1188 | 0.8706 | 0.067* | |
| C9 | 0.2244 (6) | 0.1343 (3) | 0.7625 (6) | 0.0442 (12) | |
| C10 | 0.3796 (5) | 0.1290 (3) | 0.7864 (5) | 0.0346 (10) | |
| C11 | 0.1239 (6) | 0.1607 (3) | 0.6167 (7) | 0.0557 (14) | |
| H11 | 0.0195 | 0.1660 | 0.5956 | 0.067* | |
| C12 | 0.1803 (6) | 0.1781 (3) | 0.5082 (6) | 0.0549 (14) | |
| H12 | 0.1140 | 0.1956 | 0.4124 | 0.066* | |
| C13 | 0.3386 (6) | 0.1702 (3) | 0.5378 (6) | 0.0442 (12) | |
| C14 | 0.4045 (7) | 0.1888 (3) | 0.4201 (6) | 0.0588 (15) | |
| H14A | 0.4686 | 0.2310 | 0.4535 | 0.088* | |
| H14B | 0.3224 | 0.1985 | 0.3222 | 0.088* | |
| H14C | 0.4648 | 0.1488 | 0.4089 | 0.088* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Zn1 | 0.0290 (3) | 0.0397 (3) | 0.0402 (3) | 0.0015 (3) | 0.0137 (2) | 0.0058 (2) |
| Br1 | 0.0542 (4) | 0.0502 (4) | 0.0879 (5) | −0.0154 (3) | 0.0186 (3) | 0.0098 (3) |
| Br2 | 0.0539 (4) | 0.0554 (4) | 0.0464 (3) | 0.0142 (3) | 0.0216 (3) | 0.0027 (3) |
| N1 | 0.028 (2) | 0.032 (2) | 0.035 (2) | 0.0023 (17) | 0.0115 (17) | 0.0016 (16) |
| N2 | 0.032 (2) | 0.035 (2) | 0.0329 (19) | 0.0022 (18) | 0.0073 (16) | −0.0006 (17) |
| C1 | 0.037 (3) | 0.062 (4) | 0.050 (3) | 0.005 (3) | 0.011 (3) | 0.003 (3) |
| C2 | 0.033 (3) | 0.034 (3) | 0.035 (2) | 0.001 (2) | 0.007 (2) | −0.0042 (19) |
| C3 | 0.049 (3) | 0.041 (3) | 0.033 (2) | 0.002 (3) | 0.008 (2) | 0.000 (2) |
| C4 | 0.056 (3) | 0.041 (3) | 0.039 (3) | −0.002 (3) | 0.024 (3) | 0.000 (2) |
| C5 | 0.039 (3) | 0.032 (3) | 0.047 (3) | −0.005 (2) | 0.023 (2) | −0.005 (2) |
| C6 | 0.025 (2) | 0.027 (2) | 0.042 (2) | 0.0005 (19) | 0.012 (2) | −0.0028 (19) |
| C7 | 0.046 (3) | 0.046 (3) | 0.064 (3) | 0.000 (3) | 0.034 (3) | 0.004 (3) |
| C8 | 0.030 (3) | 0.061 (4) | 0.080 (4) | −0.004 (3) | 0.024 (3) | 0.002 (3) |
| C9 | 0.028 (2) | 0.045 (3) | 0.056 (3) | 0.001 (2) | 0.011 (2) | −0.002 (3) |
| C10 | 0.024 (2) | 0.031 (3) | 0.044 (2) | 0.000 (2) | 0.0077 (19) | −0.001 (2) |
| C11 | 0.025 (3) | 0.065 (4) | 0.066 (4) | 0.011 (3) | 0.004 (2) | −0.002 (3) |
| C12 | 0.039 (3) | 0.058 (4) | 0.047 (3) | 0.012 (3) | −0.006 (2) | 0.007 (3) |
| C13 | 0.043 (3) | 0.037 (3) | 0.044 (3) | 0.010 (2) | 0.007 (2) | −0.001 (2) |
| C14 | 0.066 (4) | 0.061 (4) | 0.039 (3) | 0.013 (3) | 0.010 (3) | 0.013 (3) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Zn1—N2 | 2.062 (4) | C5—C6 | 1.396 (6) |
| Zn1—N1 | 2.071 (3) | C5—C7 | 1.437 (7) |
| Zn1—Br1 | 2.3281 (9) | C6—C10 | 1.445 (7) |
| Zn1—Br2 | 2.3572 (8) | C7—C8 | 1.336 (8) |
| N1—C2 | 1.322 (6) | C7—H7 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C6 | 1.360 (6) | C8—C9 | 1.427 (7) |
| N2—C13 | 1.329 (6) | C8—H8 | 0.9300 |
| N2—C10 | 1.366 (5) | C9—C10 | 1.394 (7) |
| C1—C2 | 1.498 (7) | C9—C11 | 1.412 (8) |
| C1—H1A | 0.9600 | C11—C12 | 1.351 (7) |
| C1—H1B | 0.9600 | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C1—H1C | 0.9600 | C12—C13 | 1.414 (7) |
| C2—C3 | 1.414 (6) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.372 (7) | C13—C14 | 1.494 (7) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C14—H14A | 0.9600 |
| C4—C5 | 1.392 (7) | C14—H14B | 0.9600 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C14—H14C | 0.9600 |
| N2—Zn1—N1 | 81.63 (14) | N1—C6—C5 | 122.8 (4) |
| N2—Zn1—Br1 | 112.03 (11) | N1—C6—C10 | 117.8 (4) |
| N1—Zn1—Br1 | 113.94 (11) | C5—C6—C10 | 119.4 (4) |
| N2—Zn1—Br2 | 113.29 (11) | C8—C7—C5 | 121.2 (4) |
| N1—Zn1—Br2 | 112.05 (11) | C8—C7—H7 | 119.4 |
| Br1—Zn1—Br2 | 118.32 (3) | C5—C7—H7 | 119.4 |
| C2—N1—C6 | 119.7 (4) | C7—C8—C9 | 121.5 (5) |
| C2—N1—Zn1 | 128.7 (3) | C7—C8—H8 | 119.2 |
| C6—N1—Zn1 | 111.5 (3) | C9—C8—H8 | 119.2 |
| C13—N2—C10 | 119.5 (4) | C10—C9—C11 | 116.8 (4) |
| C13—N2—Zn1 | 128.5 (3) | C10—C9—C8 | 118.9 (5) |
| C10—N2—Zn1 | 112.0 (3) | C11—C9—C8 | 124.2 (5) |
| C2—C1—H1A | 109.5 | N2—C10—C9 | 123.0 (4) |
| C2—C1—H1B | 109.5 | N2—C10—C6 | 117.1 (4) |
| H1A—C1—H1B | 109.5 | C9—C10—C6 | 119.9 (4) |
| C2—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C12—C11—C9 | 119.6 (5) |
| H1A—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C12—C11—H11 | 120.2 |
| H1B—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C9—C11—H11 | 120.2 |
| N1—C2—C3 | 120.3 (4) | C11—C12—C13 | 121.1 (5) |
| N1—C2—C1 | 118.1 (4) | C11—C12—H12 | 119.5 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 121.6 (4) | C13—C12—H12 | 119.5 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 120.1 (5) | N2—C13—C12 | 120.0 (5) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.0 | N2—C13—C14 | 117.6 (5) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.0 | C12—C13—C14 | 122.4 (5) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 119.8 (4) | C13—C14—H14A | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.1 | C13—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.1 | H14A—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 117.1 (4) | C13—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—C7 | 123.9 (4) | H14A—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—C7 | 119.0 (5) | H14B—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| N2—Zn1—N1—C2 | −177.9 (4) | C7—C5—C6—C10 | −0.1 (7) |
| Br1—Zn1—N1—C2 | −67.4 (4) | C4—C5—C7—C8 | 179.4 (5) |
| Br2—Zn1—N1—C2 | 70.3 (4) | C6—C5—C7—C8 | −1.5 (8) |
| N2—Zn1—N1—C6 | 1.1 (3) | C5—C7—C8—C9 | 1.7 (9) |
| Br1—Zn1—N1—C6 | 111.6 (3) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | −0.3 (9) |
| Br2—Zn1—N1—C6 | −110.7 (3) | C7—C8—C9—C11 | −178.5 (6) |
| N1—Zn1—N2—C13 | 176.8 (4) | C13—N2—C10—C9 | 1.5 (7) |
| Br1—Zn1—N2—C13 | 64.3 (4) | Zn1—N2—C10—C9 | 179.4 (4) |
| Br2—Zn1—N2—C13 | −72.7 (4) | C13—N2—C10—C6 | −177.5 (4) |
| N1—Zn1—N2—C10 | −0.8 (3) | Zn1—N2—C10—C6 | 0.4 (5) |
| Br1—Zn1—N2—C10 | −113.3 (3) | C11—C9—C10—N2 | −1.9 (8) |
| Br2—Zn1—N2—C10 | 109.7 (3) | C8—C9—C10—N2 | 179.8 (5) |
| C6—N1—C2—C3 | 3.3 (7) | C11—C9—C10—C6 | 177.1 (5) |
| Zn1—N1—C2—C3 | −177.8 (3) | C8—C9—C10—C6 | −1.3 (8) |
| C6—N1—C2—C1 | −177.3 (4) | N1—C6—C10—N2 | 0.6 (6) |
| Zn1—N1—C2—C1 | 1.7 (7) | C5—C6—C10—N2 | −179.5 (4) |
| N1—C2—C3—C4 | −1.5 (7) | N1—C6—C10—C9 | −178.4 (4) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 179.1 (5) | C5—C6—C10—C9 | 1.4 (7) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −1.7 (8) | C10—C9—C11—C12 | 1.0 (8) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 2.8 (7) | C8—C9—C11—C12 | 179.2 (6) |
| C3—C4—C5—C7 | −178.0 (5) | C9—C11—C12—C13 | 0.2 (9) |
| C2—N1—C6—C5 | −2.0 (7) | C10—N2—C13—C12 | −0.2 (7) |
| Zn1—N1—C6—C5 | 178.9 (4) | Zn1—N2—C13—C12 | −177.7 (4) |
| C2—N1—C6—C10 | 177.8 (4) | C10—N2—C13—C14 | 179.4 (4) |
| Zn1—N1—C6—C10 | −1.3 (5) | Zn1—N2—C13—C14 | 1.9 (7) |
| C4—C5—C6—N1 | −1.1 (7) | C11—C12—C13—N2 | −0.7 (9) |
| C7—C5—C6—N1 | 179.8 (5) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 179.8 (6) |
| C4—C5—C6—C10 | 179.1 (4) |
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: BT5921).
References
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst. 32, 837–838.
- Harvey, M., Baggio, S., Baggio, R. & Mombrú, A. W. (1999). Acta Cryst. C55, 308–310.
- Jordan, K. J., Wacholtz, W. F. & Crosby, G. A. (1991). Inorg. Chem. 30, 4588–4593.
- Pallenberg, A. J., Marschner, T. M. & Barnhart, D. M. (1997). Polyhedron, 16, 2711–2719.
- Seebacher, J., Mian, J. & Vahrenkamp, H. (2004). Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. pp. 409–417.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Stoe & Cie (2005). X-AREA and X-RED32 Stoe & Cie, Darmstadt, Germany.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812022738/bt5921sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812022738/bt5921Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report