Abstract
The title compound, [CdBr2(C13H12N4O)], was obtained from the reaction of Cd(NO3)2·4H2O with methyl(pyridin-2-yl)methanone picolinoylhydrazone and sodium bromide. The Cd2+ cation is ligated by one O atom and two N atoms of the tridentate ligand and two bromide anions, forming a Br2CdN2O polyhedron with a distorted trigonal–bipyramidal coordination geometry. In the crystal, non-classical C—H⋯Br hydrogen bonds are observed. In addition, π–π stacking interactions [centroid–centroid distance = 3.7455 (19) Å] contribute to the stabilization of the crystal structure.
Related literature
For related complexes with similar tridentate ligands, see: Kasuga et al. (2001 ▶); Chen et al. (2005 ▶); Datta et al. (2011 ▶).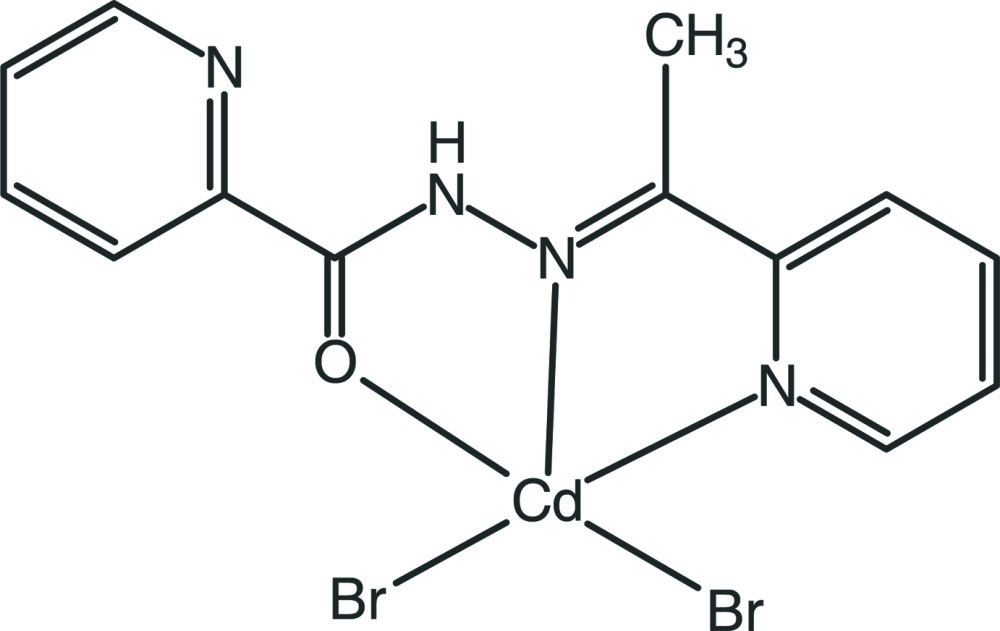
Experimental
Crystal data
[CdBr2(C13H12N4O)]
M r = 512.48
Monoclinic,
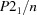
a = 8.1336 (3) Å
b = 13.6111 (5) Å
c = 14.6102 (5) Å
β = 90.550 (1)°
V = 1617.38 (10) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 6.29 mm−1
T = 296 K
0.32 × 0.18 × 0.16 mm
Data collection
Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2005 ▶) T min = 0.267, T max = 0.365
15317 measured reflections
3874 independent reflections
2859 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.032
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.028
wR(F 2) = 0.062
S = 1.02
3874 reflections
195 parameters
1 restraint
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.47 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.54 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2009 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2009 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶) and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: WinGX (Farrugia, 1999 ▶) and PLATON.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812023185/vm2176sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812023185/vm2176Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C7—H7C⋯Br2i | 0.96 | 2.91 | 3.810 (4) | 157 |
Symmetry code: (i) 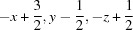 .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the provision of funds for the purchase of a diffractometer and encouragement by Dr Muhammad Akram Chaudhary, Vice Chancellor, University of Sargodha, Pakistan.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Schiff base complexes have attracted much attention due to their interesting structures and wide potential applications. Recently, the relative unsymmetrical tridentate Schiff base ligands and their hydrogenated derivatives have been introduced into the coordination chemistry to assemble polymers with beautiful molecular structures. Some organic N-donor ligands are often chosen to fabricate these various complexes. In this connection, some complexes with similar tridentate ligands have been studied (Kasuga et al., 2001; Chen et al., 2005; Datta et al., 2011). Herein, we report the structure of a new cadmium complex based on a pyridine based tridentate Schiff base ligand.
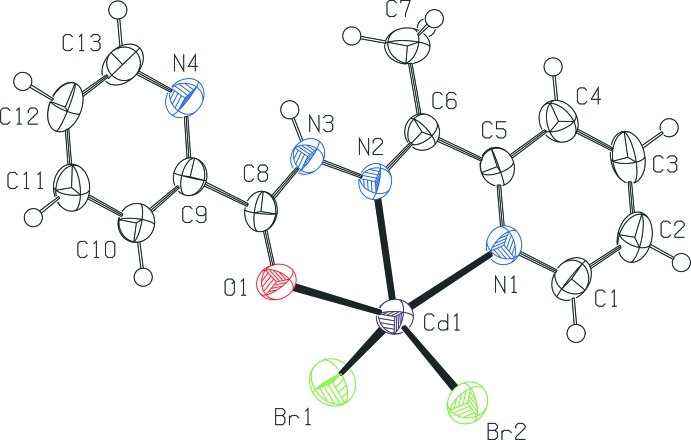
The molecular structure of title compound is shown in Fig. 1. The Cd ion is five coordinated forming a distorted trigonal-bipyramidal coordination sphere, in which three positions are occupied by two N atoms and one O atom from the tridentate Schiff base ligand, and two positions coming from two bromide ions. As can be seen in Fig. 1, all non-H atoms of the tridentate Schiff base ligand are nearly coplanar, with maximum deviations of -0.053 (4) Å for C7 and 0.049 (2) Å for N2.
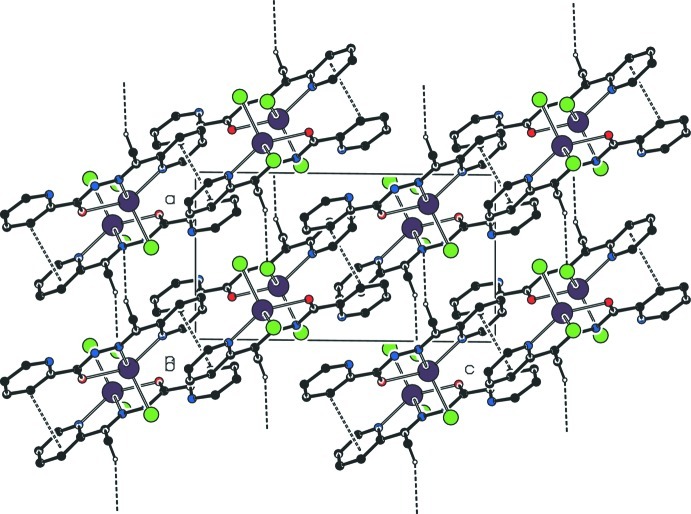
Molecules are linked to each other, via weak C—H···Br intermolecular hydrogen bonds along the crystallographic a axis (Table 1, Fig. 2). In the crystal, weak π-π stacking interactions also contribute to the stabilization: [Cg3···Cg3(1 - x, -y, 1 - z) = 3.7455 (19) Å; where Cg3 is the centroid of the N1/C1–C5 ring].
Experimental
The potentially tridenatate ligand methyl-2-pyridyl ketone picolinoyl hydrazone was obtained by condensation of methyl-2-pyridyl ketone and picolinic acid hydrazide with the ratio 1:1 in methanol. The title compound C13H12Br2CdN4O has been synthesized by the reaction of methanolic solution of the ligand and Cd(NO3)2.4H2O in the presence of excess amount of NaBr. The ligand (1 mmol, 0.240 g) and cadmium nitrate (1 mmol, 279 g) were placed in main arm of a branched tube; sodium bromide (2 mmol, 0.206 g) was added to the mixture too. Methanol was carefully added to fill the arms. The tube was sealed and the ligand-containing arm was immersed in an oil bath at 333 K while the branched arm was kept at ambient temperature. After five days, suitable single crystals, were deposited in the cooler arm which were isolated, filtered off, washed with acetone and ether and air dried.
Refinement
H atoms bonded to C atoms were positioned geometrically and treated as riding with C—H = 0.93 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) for aromatic H, and C—H = 0.96 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(C) for methyl H. The amine H atom was located in difference Fourier map and refined freely [N—H = 0.86 (2) Å].
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound with the atom numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids for non-H atoms are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.
View of the intermolecular C—H···Br hydrogen bonds and π-π stacking interactions of the title compound. H atoms not involved in hydrogen bonding are omitted.
Crystal data
| [CdBr2(C13H12N4O)] | F(000) = 976 |
| Mr = 512.48 | Dx = 2.105 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2yn | Cell parameters from 545 reflections |
| a = 8.1336 (3) Å | θ = 4.2–18.3° |
| b = 13.6111 (5) Å | µ = 6.29 mm−1 |
| c = 14.6102 (5) Å | T = 296 K |
| β = 90.550 (1)° | Prism, colourless |
| V = 1617.38 (10) Å3 | 0.32 × 0.18 × 0.16 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer | 3874 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2859 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.032 |
| ω scans | θmax = 28.1°, θmin = 2.9° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2005) | h = −10→10 |
| Tmin = 0.267, Tmax = 0.365 | k = −17→18 |
| 15317 measured reflections | l = −19→18 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.028 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.062 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.02 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0245P)2 + 0.5132P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3874 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 195 parameters | Δρmax = 0.47 e Å−3 |
| 1 restraint | Δρmin = −0.54 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. Bond distances, angles etc. have been calculated using the rounded fractional coordinates. All su's are estimated from the variances of the (full) variance-covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account in the estimation of distances, angles and torsion angles |
| Refinement. Refinement on F2 for ALL reflections except those flagged by the user for potential systematic errors. Weighted R-factors wR and all goodnesses of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The observed criterion of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating -R-factor-obs etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R-factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cd1 | 0.32238 (3) | 0.16938 (2) | 0.27655 (2) | 0.0429 (1) | |
| Br1 | 0.04606 (5) | 0.15378 (3) | 0.35202 (3) | 0.0626 (1) | |
| Br2 | 0.42596 (5) | 0.34049 (2) | 0.23982 (3) | 0.0550 (1) | |
| O1 | 0.2555 (3) | 0.10824 (15) | 0.12175 (14) | 0.0493 (8) | |
| N1 | 0.5195 (3) | 0.12698 (18) | 0.38976 (17) | 0.0438 (9) | |
| N2 | 0.4511 (3) | 0.02135 (16) | 0.24438 (15) | 0.0370 (8) | |
| N3 | 0.4106 (3) | −0.02318 (18) | 0.16427 (17) | 0.0401 (8) | |
| N4 | 0.3565 (3) | −0.11450 (19) | 0.01147 (18) | 0.0495 (10) | |
| C1 | 0.5632 (5) | 0.1867 (2) | 0.4579 (2) | 0.0555 (11) | |
| C2 | 0.6781 (5) | 0.1618 (3) | 0.5230 (2) | 0.0585 (11) | |
| C3 | 0.7498 (4) | 0.0712 (3) | 0.5186 (2) | 0.0585 (14) | |
| C4 | 0.7079 (4) | 0.0090 (2) | 0.4477 (2) | 0.0487 (11) | |
| C5 | 0.5925 (4) | 0.0390 (2) | 0.3832 (2) | 0.0385 (9) | |
| C6 | 0.5464 (3) | −0.0217 (2) | 0.3021 (2) | 0.0377 (9) | |
| C7 | 0.6137 (5) | −0.1226 (2) | 0.2915 (2) | 0.0577 (11) | |
| C8 | 0.3114 (4) | 0.0268 (2) | 0.1050 (2) | 0.0392 (9) | |
| C9 | 0.2810 (4) | −0.0274 (2) | 0.01743 (19) | 0.0381 (9) | |
| C10 | 0.1844 (4) | 0.0113 (2) | −0.0505 (2) | 0.0473 (11) | |
| C11 | 0.1592 (4) | −0.0425 (2) | −0.1296 (2) | 0.0523 (11) | |
| C12 | 0.2361 (5) | −0.1319 (2) | −0.1370 (2) | 0.0543 (11) | |
| C13 | 0.3333 (5) | −0.1652 (2) | −0.0658 (2) | 0.0569 (13) | |
| H1 | 0.51340 | 0.24800 | 0.46140 | 0.0660* | |
| H2 | 0.70680 | 0.20560 | 0.56930 | 0.0700* | |
| H3 | 0.82590 | 0.05170 | 0.56290 | 0.0700* | |
| H3N | 0.434 (4) | −0.0819 (15) | 0.150 (2) | 0.056 (10)* | |
| H4 | 0.75670 | −0.05260 | 0.44310 | 0.0580* | |
| H7A | 0.54530 | −0.15920 | 0.24990 | 0.0860* | |
| H7B | 0.61610 | −0.15480 | 0.34990 | 0.0860* | |
| H7C | 0.72320 | −0.11890 | 0.26780 | 0.0860* | |
| H10 | 0.13630 | 0.07280 | −0.04360 | 0.0570* | |
| H11 | 0.09200 | −0.01880 | −0.17650 | 0.0630* | |
| H12 | 0.22280 | −0.16960 | −0.18970 | 0.0650* | |
| H13 | 0.38510 | −0.22580 | −0.07180 | 0.0680* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cd1 | 0.0474 (1) | 0.0383 (1) | 0.0428 (1) | 0.0045 (1) | −0.0051 (1) | −0.0016 (1) |
| Br1 | 0.0532 (2) | 0.0726 (3) | 0.0622 (2) | −0.0011 (2) | 0.0063 (2) | 0.0021 (2) |
| Br2 | 0.0638 (2) | 0.0413 (2) | 0.0598 (2) | −0.0049 (2) | −0.0091 (2) | 0.0024 (2) |
| O1 | 0.0616 (15) | 0.0432 (13) | 0.0429 (12) | 0.0105 (11) | −0.0085 (11) | −0.0083 (10) |
| N1 | 0.0503 (16) | 0.0397 (14) | 0.0412 (15) | −0.0023 (12) | −0.0086 (12) | 0.0021 (11) |
| N2 | 0.0393 (14) | 0.0367 (13) | 0.0350 (14) | −0.0022 (11) | −0.0031 (11) | −0.0016 (10) |
| N3 | 0.0476 (15) | 0.0354 (14) | 0.0373 (14) | −0.0005 (12) | −0.0045 (11) | −0.0063 (11) |
| N4 | 0.0654 (19) | 0.0394 (15) | 0.0436 (16) | 0.0006 (13) | −0.0089 (13) | −0.0043 (12) |
| C1 | 0.075 (2) | 0.0403 (18) | 0.051 (2) | −0.0047 (17) | −0.0117 (18) | −0.0030 (15) |
| C2 | 0.071 (2) | 0.061 (2) | 0.0433 (19) | −0.0144 (19) | −0.0141 (17) | −0.0057 (16) |
| C3 | 0.056 (2) | 0.073 (3) | 0.046 (2) | −0.0134 (18) | −0.0175 (17) | 0.0083 (17) |
| C4 | 0.0471 (19) | 0.0505 (19) | 0.0483 (19) | −0.0019 (15) | −0.0065 (15) | 0.0107 (15) |
| C5 | 0.0371 (16) | 0.0401 (16) | 0.0381 (16) | −0.0056 (13) | −0.0025 (13) | 0.0074 (13) |
| C6 | 0.0359 (16) | 0.0361 (16) | 0.0411 (17) | −0.0045 (13) | 0.0005 (13) | 0.0033 (13) |
| C7 | 0.065 (2) | 0.0458 (19) | 0.062 (2) | 0.0137 (17) | −0.0072 (18) | −0.0003 (17) |
| C8 | 0.0396 (16) | 0.0418 (17) | 0.0362 (16) | −0.0092 (14) | −0.0016 (13) | 0.0004 (13) |
| C9 | 0.0384 (16) | 0.0383 (16) | 0.0376 (16) | −0.0058 (13) | 0.0000 (13) | −0.0005 (12) |
| C10 | 0.0495 (19) | 0.0458 (18) | 0.0464 (19) | 0.0008 (15) | −0.0065 (15) | −0.0043 (15) |
| C11 | 0.056 (2) | 0.057 (2) | 0.0437 (19) | −0.0102 (17) | −0.0101 (16) | 0.0044 (15) |
| C12 | 0.069 (2) | 0.053 (2) | 0.0408 (19) | −0.0194 (18) | −0.0046 (17) | −0.0082 (15) |
| C13 | 0.075 (3) | 0.0397 (18) | 0.056 (2) | −0.0021 (17) | −0.0054 (19) | −0.0107 (16) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Cd1—Br1 | 2.5218 (5) | C5—C6 | 1.490 (4) |
| Cd1—Br2 | 2.5359 (4) | C6—C7 | 1.487 (4) |
| Cd1—O1 | 2.466 (2) | C8—C9 | 1.495 (4) |
| Cd1—N1 | 2.364 (2) | C9—C10 | 1.366 (4) |
| Cd1—N2 | 2.321 (2) | C10—C11 | 1.382 (4) |
| O1—C8 | 1.224 (4) | C11—C12 | 1.373 (4) |
| N1—C1 | 1.331 (4) | C12—C13 | 1.377 (5) |
| N1—C5 | 1.341 (4) | C1—H1 | 0.9300 |
| N2—N3 | 1.356 (3) | C2—H2 | 0.9300 |
| N2—C6 | 1.282 (4) | C3—H3 | 0.9300 |
| N3—C8 | 1.360 (4) | C4—H4 | 0.9300 |
| N4—C9 | 1.338 (4) | C7—H7A | 0.9600 |
| N4—C13 | 1.335 (4) | C7—H7B | 0.9600 |
| N3—H3N | 0.85 (2) | C7—H7C | 0.9600 |
| C1—C2 | 1.370 (5) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.366 (6) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.378 (4) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C5 | 1.385 (4) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| Br1—Cd1—Br2 | 117.98 (2) | O1—C8—N3 | 123.0 (3) |
| Br1—Cd1—O1 | 100.54 (6) | O1—C8—C9 | 124.0 (3) |
| Br1—Cd1—N1 | 105.95 (6) | C8—C9—C10 | 121.4 (3) |
| Br1—Cd1—N2 | 114.91 (6) | N4—C9—C8 | 114.9 (3) |
| Br2—Cd1—O1 | 100.76 (5) | N4—C9—C10 | 123.8 (3) |
| Br2—Cd1—N1 | 98.50 (6) | C9—C10—C11 | 118.9 (3) |
| Br2—Cd1—N2 | 127.09 (6) | C10—C11—C12 | 118.1 (3) |
| O1—Cd1—N1 | 134.55 (8) | C11—C12—C13 | 119.4 (3) |
| O1—Cd1—N2 | 67.49 (8) | N4—C13—C12 | 123.0 (3) |
| N1—Cd1—N2 | 68.01 (8) | N1—C1—H1 | 118.00 |
| Cd1—O1—C8 | 114.21 (19) | C2—C1—H1 | 119.00 |
| Cd1—N1—C1 | 123.3 (2) | C1—C2—H2 | 121.00 |
| Cd1—N1—C5 | 117.77 (19) | C3—C2—H2 | 121.00 |
| C1—N1—C5 | 118.9 (3) | C2—C3—H3 | 120.00 |
| Cd1—N2—N3 | 117.17 (17) | C4—C3—H3 | 120.00 |
| Cd1—N2—C6 | 122.33 (18) | C3—C4—H4 | 120.00 |
| N3—N2—C6 | 120.3 (2) | C5—C4—H4 | 120.00 |
| N2—N3—C8 | 117.6 (2) | C6—C7—H7A | 109.00 |
| C9—N4—C13 | 116.9 (3) | C6—C7—H7B | 109.00 |
| C8—N3—H3N | 117 (2) | C6—C7—H7C | 109.00 |
| N2—N3—H3N | 126 (2) | H7A—C7—H7B | 109.00 |
| N1—C1—C2 | 123.0 (3) | H7A—C7—H7C | 109.00 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 118.7 (3) | H7B—C7—H7C | 109.00 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 119.2 (3) | C9—C10—H10 | 121.00 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 119.4 (3) | C11—C10—H10 | 121.00 |
| N1—C5—C4 | 120.8 (3) | C10—C11—H11 | 121.00 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 122.8 (3) | C12—C11—H11 | 121.00 |
| N1—C5—C6 | 116.4 (3) | C11—C12—H12 | 120.00 |
| N2—C6—C7 | 125.1 (3) | C13—C12—H12 | 120.00 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 120.3 (2) | N4—C13—H13 | 119.00 |
| N2—C6—C5 | 114.6 (2) | C12—C13—H13 | 119.00 |
| N3—C8—C9 | 113.0 (2) | ||
| Br1—Cd1—O1—C8 | −107.6 (2) | Cd1—N2—C6—C7 | 170.9 (2) |
| Br2—Cd1—O1—C8 | 131.0 (2) | Cd1—N2—N3—C8 | 6.6 (3) |
| N1—Cd1—O1—C8 | 17.6 (3) | Cd1—N2—C6—C5 | −11.0 (3) |
| N2—Cd1—O1—C8 | 5.2 (2) | N3—N2—C6—C7 | −3.4 (4) |
| Br1—Cd1—N1—C1 | −76.1 (3) | N3—N2—C6—C5 | 174.8 (2) |
| Br2—Cd1—N1—C1 | 46.4 (3) | N2—N3—C8—O1 | −1.5 (4) |
| O1—Cd1—N1—C1 | 160.7 (2) | N2—N3—C8—C9 | 177.5 (2) |
| N2—Cd1—N1—C1 | 173.0 (3) | C9—N4—C13—C12 | −0.5 (5) |
| Br1—Cd1—N1—C5 | 105.4 (2) | C13—N4—C9—C8 | −179.7 (3) |
| Br2—Cd1—N1—C5 | −132.2 (2) | C13—N4—C9—C10 | −0.4 (5) |
| O1—Cd1—N1—C5 | −17.9 (3) | N1—C1—C2—C3 | −0.8 (6) |
| N2—Cd1—N1—C5 | −5.6 (2) | C1—C2—C3—C4 | 1.8 (5) |
| Br1—Cd1—N2—N3 | 85.55 (18) | C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.9 (5) |
| Br2—Cd1—N2—N3 | −92.50 (19) | C3—C4—C5—N1 | −1.0 (5) |
| O1—Cd1—N2—N3 | −5.94 (17) | C3—C4—C5—C6 | 177.0 (3) |
| N1—Cd1—N2—N3 | −176.5 (2) | N1—C5—C6—N2 | 5.2 (4) |
| Br1—Cd1—N2—C6 | −88.8 (2) | C4—C5—C6—C7 | 5.3 (4) |
| Br2—Cd1—N2—C6 | 93.1 (2) | C4—C5—C6—N2 | −172.9 (3) |
| O1—Cd1—N2—C6 | 179.7 (2) | N1—C5—C6—C7 | −176.6 (3) |
| N1—Cd1—N2—C6 | 9.2 (2) | O1—C8—C9—N4 | 178.4 (3) |
| Cd1—O1—C8—C9 | 177.1 (2) | N3—C8—C9—C10 | −179.9 (3) |
| Cd1—O1—C8—N3 | −4.0 (4) | O1—C8—C9—C10 | −1.0 (5) |
| Cd1—N1—C5—C6 | 2.6 (3) | N3—C8—C9—N4 | −0.6 (4) |
| Cd1—N1—C1—C2 | −179.7 (3) | N4—C9—C10—C11 | 1.4 (5) |
| C1—N1—C5—C4 | 2.0 (4) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | −179.3 (3) |
| C1—N1—C5—C6 | −176.1 (3) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | −1.5 (5) |
| C5—N1—C1—C2 | −1.1 (5) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 0.7 (5) |
| Cd1—N1—C5—C4 | −179.3 (2) | C11—C12—C13—N4 | 0.3 (6) |
| C6—N2—N3—C8 | −178.9 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C7—H7C···Br2i | 0.96 | 2.91 | 3.810 (4) | 157 |
Symmetry code: (i) −x+3/2, y−1/2, −z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: VM2176).
References
- Bruker (2005). SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Bruker (2009). APEX2 and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Chen, L., Zhang, W., Huang, S., Jin, X. & Sun, W.-H. (2005). Inorg. Chem. Commun. 8, 41–43.
- Datta, A., Das, K., Jhou, Y.-M., Huang, J.-H. & Lee, H. M. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, m123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst. 32, 837–838.
- Kasuga, N. C., Sekino, K., Koumo, C., Shimada, N., Ishikawa, M. & Nomia, K. (2001). J. Inorg. Biochem. 84, 55–65. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812023185/vm2176sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812023185/vm2176Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report