Abstract
In the title compound, C26H28N4 2+·2PF6 −, the complete cation is generated by a crystallographic twofold axis. The benzimidazole ring is almost planar (r.m.s. deviation = 0.0207 Å) and makes dihedral angles of 50.12 (2)° with its symmetry-related component and 65.81 (2)° with the central benzene ring. In the crystal, molecules are linked into a three-dimensional network by C—H⋯F interactions. A π–π interaction with a centroid–centroid distance of 3.530 (1) Å is observed. Four F atoms of the hexafluorophosphate anion are disordered over two sets of sites in a 0.889 (6):0.111 (6) ratio.
Related literature
For the biological applications of benzimidazoles, see: Narasimhan et al. (2012 ▶). For a related structure, see: Haque et al. (2012 ▶).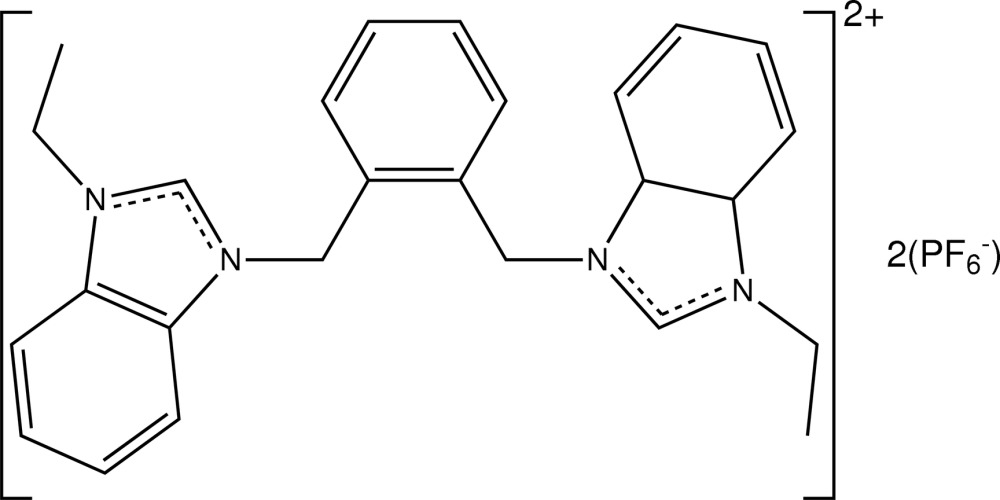
Experimental
Crystal data
C26H28N4 2+·2PF6 −
M r = 686.46
Monoclinic,
a = 23.2016 (5) Å
b = 8.1526 (2) Å
c = 16.9992 (4) Å
β = 121.274 (1)°
V = 2748.23 (11) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.27 mm−1
T = 100 K
0.26 × 0.26 × 0.14 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2009 ▶) T min = 0.933, T max = 0.963
14787 measured reflections
3921 independent reflections
3156 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.037
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.046
wR(F 2) = 0.098
S = 1.05
3921 reflections
217 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.48 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.35 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2009 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2009 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXTL; molecular graphics: SHELXTL; software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812019344/hb6760sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812019344/hb6760Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1—H1A⋯F6i | 0.95 | 2.42 | 3.142 (3) | 133 |
| C3—H3A⋯F5ii | 0.95 | 2.45 | 3.374 (2) | 166 |
| C5—H5A⋯F5iii | 0.95 | 2.52 | 3.420 (3) | 159 |
| C6—H6A⋯F4iv | 0.95 | 2.53 | 3.392 (2) | 151 |
| C8—H8B⋯F1i | 0.99 | 2.39 | 3.350 (3) | 164 |
| C13—H13C⋯F1v | 0.98 | 2.55 | 3.523 (2) | 174 |
| C13—H13C⋯F5v | 0.98 | 2.50 | 3.166 (2) | 125 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 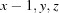 ; (ii)
; (ii) 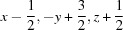 ; (iii)
; (iii) 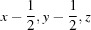 ; (iv)
; (iv) 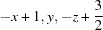 ; (v)
; (v) 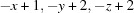 .
.
Acknowledgments
RAH thanks Universiti Sains Malaysia (USM) for the Research University (RU) grants (1001/PKIMIA/811157 and 304/PKIMIA/6511123). MAI is grateful to (IPS) USM for financial support [fellowship: USM·IPS/JWT/1/19 (JLD 6)] and the research attachment fund [P-KM0018/10(R) − 308/AIPS/415401]. HKF thanks USM for the Research University Grant No. 1001/PFIZIK/811160.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Benzimidazole-constituted compounds are known as bioactive heterocyclic compounds that are of wide interest for biological and clinical applications (Narasimhan et al., 2012). As a part of our ongoing studies in this area (Haque et al., 2012), we now describe the title compound.
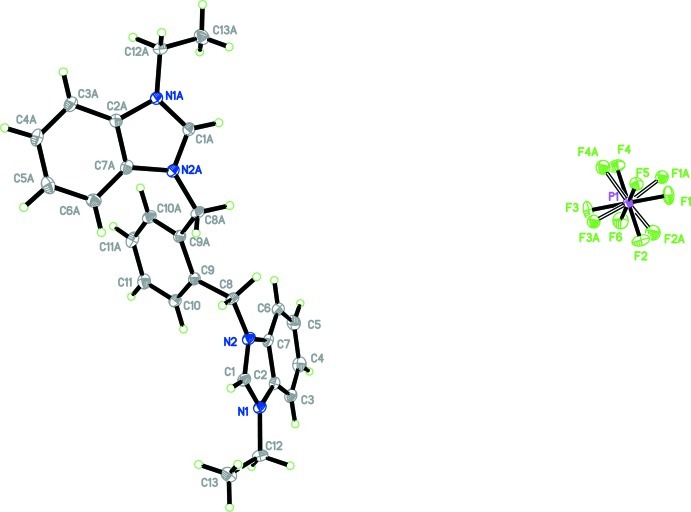
All parameters in the title compound (Fig. 1) are within normal ranges. The complete molecule is generated by a crystallographic two-fold axis. The benzimidazole (N1—N2/C1—C7) ring is planar with the r.m.s 0.0207 Å. It makes a dihedral angle of 50.12 (2)° with its symmetrical component and 65.81 (2) Å with the central benzene ring (C9—C11/C9A—C11A). Four fluorine atoms (F1—F4) of the hexafluorophosphate cation are disordered over two positions with the final refined occupancies of 0.889 (6):0.111 (6).
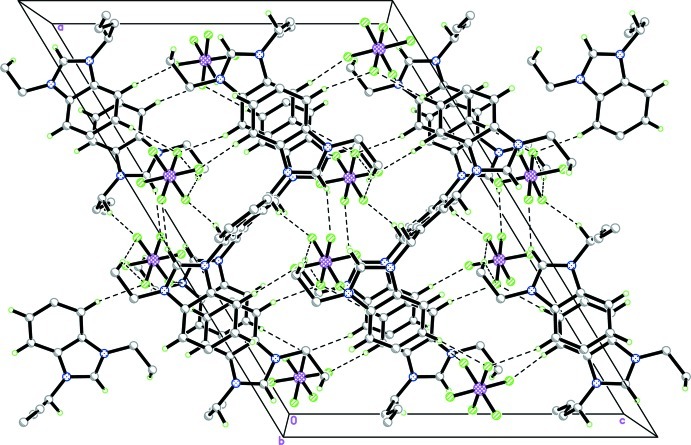
In the crystal structure, (Fig. 2), the molecules are linked into a three-dimensional network through intermolecular C—H···F hydrogen bonds (Table 1). A π-π interaction with centroid-centroid distance of 3.530 (1) Å is observed (Cg1 = C2—C7).
Experimental
A mixture of benzimidazole (1.18 g, 10 mmol) and potassium hydroxide (1.18 g, 15 mmol) in 30 ml of DMSO was stirred at room temperature (27–28°C) for 30 min. Ethyl bromide (0.75 ml, 10 mmol) was added drop-wise into this consistently stirring mixture and it was further stirred for 2 h at same temperature, then poured into water (150 ml) and was extracted by chloroform (3 × 20 ml). The extract was filtered by five plies of filter papers with medium porosity to collect a crystal-clear solution which was evaporated under vacuum to get N-ethylbenzimidazole (I) as a thick yellowish fluid. Then, a mixture of I (0.73 g, 5 mmol) and 1,2- bis(bromomethyl)benzene (0.66 g, 2.5 mmol) in 1,4-dioxane (20 ml) was refluxed at 110°C for 12 h. The bromide salt of title compound appeared as beige-colored precipitates in a dark brown solution. The mixture was filtered and the precipitates were washed by fresh 1,4-dioxane (3 x 5 ml) and dried at room temperature for 24 h. The soft lumps so obtained were dissolved in methanol (30 ml) along with KPF6 (1.84 g, 10 mmol) and stirred for 3 h at room temperature. The white solid that appeared was filtered, washed by fresh methanol followed by water. The compound was dried at room temperature (1.53 g, 89.5%). A saturated solution of 2.2PF6 dissolved in acetonitrile (1 ml) was prepared. The compound was dissolved in it and the solution was evaporated at room temperature to collect colourless blocks of the title compound.
Refinement
All H atoms attached to C atoms were fixed geometrically and refined as riding with C—H = 0.95–0.99 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) or 1.5Ueq(C-methyl). A rotating group model was applied to the methyl group. Four fluorine atoms (F1—F4) of the hexafluorophosphate cation are disordered over two positions with the final refined occupancies of 0.889 (6):0.111 (6).The minor component was refined isotropically.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure, showing 50% probability displacement ellipsoids. Hydrogen atoms are shown as spheres of arbitrary radius.
Fig. 2.
The crystal packing of (I). Dashed lines indicate hydrogen bonds. H atoms not involved in the hydrogen bond interactions have been omitted for clarity.
Crystal data
| C26H28N42+·2PF6− | F(000) = 1400 |
| Mr = 686.46 | Dx = 1.659 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, C2/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -C 2yc | Cell parameters from 3899 reflections |
| a = 23.2016 (5) Å | θ = 2.5–29.7° |
| b = 8.1526 (2) Å | µ = 0.27 mm−1 |
| c = 16.9992 (4) Å | T = 100 K |
| β = 121.274 (1)° | Block, colourless |
| V = 2748.23 (11) Å3 | 0.26 × 0.26 × 0.14 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEXII CCD diffractometer | 3921 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 3156 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.037 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 29.8°, θmin = 2.1° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2009) | h = −32→31 |
| Tmin = 0.933, Tmax = 0.963 | k = −11→9 |
| 14787 measured reflections | l = −23→23 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.046 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.098 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.05 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0339P)2 + 4.2095P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3921 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 217 parameters | Δρmax = 0.48 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.35 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Experimental. The crystal was placed in the cold stream of an Oxford Cryosystems Cobra open-flow nitrogen cryostat (Cosier & Glazer, 1986) operating at 100.0 (1) K. |
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| P1 | 0.89811 (2) | 0.80829 (6) | 0.89390 (3) | 0.01579 (11) | |
| F5 | 0.84112 (5) | 0.94532 (13) | 0.83897 (7) | 0.0220 (2) | |
| F6 | 0.95467 (6) | 0.67136 (15) | 0.94831 (8) | 0.0323 (3) | |
| F1 | 0.95400 (8) | 0.92423 (17) | 0.89472 (17) | 0.0309 (5) | 0.889 (6) |
| F2 | 0.91321 (10) | 0.8889 (2) | 0.98909 (10) | 0.0303 (5) | 0.889 (6) |
| F3 | 0.84260 (11) | 0.6929 (2) | 0.8940 (2) | 0.0311 (5) | 0.889 (6) |
| F4 | 0.88302 (12) | 0.7290 (2) | 0.79927 (10) | 0.0314 (5) | 0.889 (6) |
| F1A | 0.9350 (7) | 0.9043 (15) | 0.8457 (11) | 0.024 (3)* | 0.111 (6) |
| F2A | 0.9323 (8) | 0.9133 (18) | 0.9770 (10) | 0.032 (4)* | 0.111 (6) |
| F4A | 0.8573 (8) | 0.7032 (18) | 0.7950 (10) | 0.029 (3)* | 0.111 (6) |
| F3A | 0.8547 (9) | 0.713 (2) | 0.9237 (11) | 0.024 (4)* | 0.111 (6) |
| N1 | 0.16728 (7) | 0.66335 (17) | 1.09095 (9) | 0.0146 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.10920 (7) | 0.67626 (18) | 0.94040 (9) | 0.0154 (3) | |
| C1 | 0.10867 (8) | 0.7060 (2) | 1.01737 (11) | 0.0157 (3) | |
| H1A | 0.0717 | 0.7513 | 1.0192 | 0.019* | |
| C2 | 0.20844 (8) | 0.5997 (2) | 1.06084 (11) | 0.0142 (3) | |
| C3 | 0.27289 (8) | 0.5312 (2) | 1.10913 (12) | 0.0174 (3) | |
| H3A | 0.2982 | 0.5254 | 1.1744 | 0.021* | |
| C4 | 0.29766 (9) | 0.4723 (2) | 1.05606 (13) | 0.0206 (4) | |
| H4A | 0.3410 | 0.4226 | 1.0859 | 0.025* | |
| C5 | 0.26085 (9) | 0.4833 (2) | 0.95923 (13) | 0.0212 (4) | |
| H5A | 0.2802 | 0.4424 | 0.9257 | 0.025* | |
| C6 | 0.19723 (9) | 0.5525 (2) | 0.91211 (12) | 0.0174 (3) | |
| H6A | 0.1723 | 0.5610 | 0.8469 | 0.021* | |
| C7 | 0.17168 (8) | 0.6091 (2) | 0.96517 (11) | 0.0150 (3) | |
| C8 | 0.05184 (8) | 0.6967 (2) | 0.84619 (11) | 0.0163 (3) | |
| H8A | 0.0663 | 0.7624 | 0.8105 | 0.020* | |
| H8B | 0.0157 | 0.7582 | 0.8480 | 0.020* | |
| C9 | 0.02370 (8) | 0.5336 (2) | 0.79767 (11) | 0.0151 (3) | |
| C10 | 0.04406 (8) | 0.3851 (2) | 0.84445 (12) | 0.0178 (3) | |
| H10A | 0.0740 | 0.3845 | 0.9093 | 0.021* | |
| C11 | 0.02104 (9) | 0.2372 (2) | 0.79734 (12) | 0.0200 (4) | |
| H11A | 0.0342 | 0.1364 | 0.8301 | 0.024* | |
| C12 | 0.18631 (9) | 0.6741 (2) | 1.18835 (11) | 0.0186 (3) | |
| H12A | 0.2176 | 0.7675 | 1.2179 | 0.022* | |
| H12B | 0.2104 | 0.5727 | 1.2208 | 0.022* | |
| C13 | 0.12542 (9) | 0.6968 (2) | 1.19816 (13) | 0.0212 (4) | |
| H13A | 0.1402 | 0.7015 | 1.2636 | 0.032* | |
| H13B | 0.0944 | 0.6044 | 1.1692 | 0.032* | |
| H13C | 0.1024 | 0.7992 | 1.1681 | 0.032* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| P1 | 0.0129 (2) | 0.0162 (2) | 0.0174 (2) | 0.00054 (16) | 0.00725 (17) | 0.00099 (17) |
| F5 | 0.0197 (5) | 0.0208 (5) | 0.0221 (5) | 0.0054 (4) | 0.0084 (4) | 0.0053 (4) |
| F6 | 0.0233 (6) | 0.0279 (6) | 0.0390 (7) | 0.0116 (5) | 0.0115 (5) | 0.0080 (5) |
| F1 | 0.0212 (8) | 0.0261 (7) | 0.0505 (14) | −0.0047 (6) | 0.0224 (9) | −0.0001 (7) |
| F2 | 0.0303 (9) | 0.0381 (9) | 0.0169 (6) | 0.0070 (7) | 0.0083 (6) | −0.0039 (6) |
| F3 | 0.0263 (9) | 0.0207 (8) | 0.0519 (15) | −0.0042 (7) | 0.0244 (11) | 0.0045 (10) |
| F4 | 0.0382 (11) | 0.0331 (9) | 0.0228 (7) | 0.0058 (8) | 0.0157 (7) | −0.0062 (6) |
| N1 | 0.0127 (6) | 0.0161 (7) | 0.0134 (6) | 0.0006 (5) | 0.0056 (5) | −0.0010 (5) |
| N2 | 0.0112 (6) | 0.0185 (7) | 0.0137 (6) | 0.0007 (5) | 0.0044 (5) | −0.0010 (6) |
| C1 | 0.0122 (7) | 0.0179 (8) | 0.0151 (7) | 0.0008 (6) | 0.0057 (6) | −0.0011 (6) |
| C2 | 0.0126 (7) | 0.0133 (7) | 0.0157 (7) | −0.0015 (6) | 0.0067 (6) | −0.0014 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0132 (8) | 0.0175 (8) | 0.0175 (8) | 0.0002 (6) | 0.0051 (7) | 0.0007 (7) |
| C4 | 0.0131 (8) | 0.0216 (9) | 0.0238 (9) | 0.0034 (7) | 0.0074 (7) | 0.0021 (7) |
| C5 | 0.0198 (9) | 0.0219 (9) | 0.0268 (9) | 0.0000 (7) | 0.0155 (8) | −0.0023 (8) |
| C6 | 0.0168 (8) | 0.0189 (8) | 0.0161 (8) | −0.0025 (6) | 0.0082 (7) | −0.0023 (7) |
| C7 | 0.0112 (7) | 0.0142 (8) | 0.0165 (8) | −0.0017 (6) | 0.0050 (6) | −0.0009 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0117 (7) | 0.0202 (8) | 0.0114 (7) | −0.0004 (6) | 0.0022 (6) | 0.0006 (6) |
| C9 | 0.0102 (7) | 0.0201 (8) | 0.0143 (8) | −0.0008 (6) | 0.0059 (6) | −0.0009 (6) |
| C10 | 0.0117 (8) | 0.0235 (9) | 0.0147 (8) | −0.0010 (6) | 0.0045 (6) | 0.0018 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0146 (8) | 0.0191 (8) | 0.0227 (9) | 0.0014 (6) | 0.0072 (7) | 0.0042 (7) |
| C12 | 0.0193 (8) | 0.0216 (9) | 0.0121 (7) | 0.0021 (7) | 0.0062 (7) | −0.0011 (7) |
| C13 | 0.0260 (9) | 0.0195 (9) | 0.0227 (9) | 0.0017 (7) | 0.0158 (8) | 0.0017 (7) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| P1—F2A | 1.481 (14) | C4—C5 | 1.410 (3) |
| P1—F3A | 1.552 (19) | C4—H4A | 0.9500 |
| P1—F4 | 1.5947 (14) | C5—C6 | 1.382 (2) |
| P1—F3 | 1.5957 (18) | C5—H5A | 0.9500 |
| P1—F1 | 1.5987 (13) | C6—C7 | 1.390 (2) |
| P1—F6 | 1.6011 (12) | C6—H6A | 0.9500 |
| P1—F2 | 1.6077 (15) | C8—C9 | 1.522 (2) |
| P1—F5 | 1.6082 (11) | C8—H8A | 0.9900 |
| P1—F1A | 1.656 (11) | C8—H8B | 0.9900 |
| P1—F4A | 1.674 (14) | C9—C10 | 1.390 (2) |
| N1—C1 | 1.330 (2) | C9—C9i | 1.409 (3) |
| N1—C2 | 1.397 (2) | C10—C11 | 1.391 (3) |
| N1—C12 | 1.478 (2) | C10—H10A | 0.9500 |
| N2—C1 | 1.337 (2) | C11—C11i | 1.383 (3) |
| N2—C7 | 1.395 (2) | C11—H11A | 0.9500 |
| N2—C8 | 1.467 (2) | C12—C13 | 1.518 (2) |
| C1—H1A | 0.9500 | C12—H12A | 0.9900 |
| C2—C7 | 1.392 (2) | C12—H12B | 0.9900 |
| C2—C3 | 1.395 (2) | C13—H13A | 0.9800 |
| C3—C4 | 1.383 (2) | C13—H13B | 0.9800 |
| C3—H3A | 0.9500 | C13—H13C | 0.9800 |
| F2A—P1—F3A | 95.5 (8) | N1—C1—H1A | 124.8 |
| F2A—P1—F4 | 157.6 (7) | N2—C1—H1A | 124.8 |
| F3A—P1—F4 | 106.7 (6) | C7—C2—C3 | 121.92 (15) |
| F2A—P1—F3 | 111.9 (7) | C7—C2—N1 | 106.67 (14) |
| F4—P1—F3 | 90.44 (11) | C3—C2—N1 | 131.37 (15) |
| F2A—P1—F1 | 67.6 (7) | C4—C3—C2 | 115.88 (16) |
| F3A—P1—F1 | 162.7 (6) | C4—C3—H3A | 122.1 |
| F4—P1—F1 | 90.05 (9) | C2—C3—H3A | 122.1 |
| F3—P1—F1 | 179.50 (11) | C3—C4—C5 | 122.29 (16) |
| F2A—P1—F6 | 88.8 (6) | C3—C4—H4A | 118.9 |
| F3A—P1—F6 | 86.5 (7) | C5—C4—H4A | 118.9 |
| F4—P1—F6 | 89.14 (8) | C6—C5—C4 | 121.35 (16) |
| F3—P1—F6 | 90.47 (9) | C6—C5—H5A | 119.3 |
| F1—P1—F6 | 89.39 (7) | C4—C5—H5A | 119.3 |
| F3A—P1—F2 | 73.4 (6) | C5—C6—C7 | 116.48 (16) |
| F4—P1—F2 | 179.76 (10) | C5—C6—H6A | 121.8 |
| F3—P1—F2 | 89.66 (11) | C7—C6—H6A | 121.8 |
| F1—P1—F2 | 89.86 (9) | C6—C7—C2 | 122.06 (15) |
| F6—P1—F2 | 91.07 (7) | C6—C7—N2 | 131.37 (16) |
| F2A—P1—F5 | 91.4 (6) | C2—C7—N2 | 106.53 (14) |
| F3A—P1—F5 | 93.4 (7) | N2—C8—C9 | 112.54 (14) |
| F4—P1—F5 | 90.69 (7) | N2—C8—H8A | 109.1 |
| F3—P1—F5 | 89.39 (9) | C9—C8—H8A | 109.1 |
| F1—P1—F5 | 90.75 (7) | N2—C8—H8B | 109.1 |
| F6—P1—F5 | 179.78 (9) | C9—C8—H8B | 109.1 |
| F2—P1—F5 | 89.10 (7) | H8A—C8—H8B | 107.8 |
| F2A—P1—F1A | 92.3 (7) | C10—C9—C9i | 119.25 (10) |
| F3A—P1—F1A | 171.2 (7) | C10—C9—C8 | 121.89 (14) |
| F4—P1—F1A | 65.9 (5) | C9i—C9—C8 | 118.85 (9) |
| F3—P1—F1A | 154.6 (5) | C9—C10—C11 | 120.70 (15) |
| F6—P1—F1A | 97.8 (4) | C9—C10—H10A | 119.6 |
| F2—P1—F1A | 114.0 (5) | C11—C10—H10A | 119.7 |
| F5—P1—F1A | 82.2 (4) | C11i—C11—C10 | 119.87 (10) |
| F2A—P1—F4A | 175.5 (8) | C11i—C11—H11A | 120.1 |
| F3A—P1—F4A | 86.9 (7) | C10—C11—H11A | 120.1 |
| F3—P1—F4A | 70.3 (5) | N1—C12—C13 | 112.13 (14) |
| F1—P1—F4A | 110.2 (5) | N1—C12—H12A | 109.2 |
| F6—P1—F4A | 95.2 (5) | C13—C12—H12A | 109.2 |
| F2—P1—F4A | 159.0 (6) | N1—C12—H12B | 109.2 |
| F5—P1—F4A | 84.6 (5) | C13—C12—H12B | 109.2 |
| F1A—P1—F4A | 85.1 (6) | H12A—C12—H12B | 107.9 |
| C1—N1—C2 | 108.21 (13) | C12—C13—H13A | 109.5 |
| C1—N1—C12 | 127.07 (14) | C12—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| C2—N1—C12 | 124.68 (14) | H13A—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| C1—N2—C7 | 108.18 (14) | C12—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C1—N2—C8 | 125.72 (14) | H13A—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C7—N2—C8 | 125.88 (14) | H13B—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| N1—C1—N2 | 110.39 (14) | ||
| C2—N1—C1—N2 | −0.89 (19) | N1—C2—C7—C6 | −178.67 (15) |
| C12—N1—C1—N2 | −178.83 (15) | C3—C2—C7—N2 | 177.24 (15) |
| C7—N2—C1—N1 | 0.45 (19) | N1—C2—C7—N2 | −0.69 (18) |
| C8—N2—C1—N1 | 175.33 (15) | C1—N2—C7—C6 | 177.89 (18) |
| C1—N1—C2—C7 | 0.97 (18) | C8—N2—C7—C6 | 3.0 (3) |
| C12—N1—C2—C7 | 178.98 (15) | C1—N2—C7—C2 | 0.18 (18) |
| C1—N1—C2—C3 | −176.69 (18) | C8—N2—C7—C2 | −174.70 (15) |
| C12—N1—C2—C3 | 1.3 (3) | C1—N2—C8—C9 | −109.15 (18) |
| C7—C2—C3—C4 | −0.5 (2) | C7—N2—C8—C9 | 64.8 (2) |
| N1—C2—C3—C4 | 176.88 (17) | N2—C8—C9—C10 | 9.8 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 1.2 (3) | N2—C8—C9—C9i | −169.32 (17) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.8 (3) | C9i—C9—C10—C11 | 3.6 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −0.4 (3) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | −175.57 (16) |
| C5—C6—C7—C2 | 1.2 (3) | C9—C10—C11—C11i | 1.8 (3) |
| C5—C6—C7—N2 | −176.25 (17) | C1—N1—C12—C13 | 15.8 (2) |
| C3—C2—C7—C6 | −0.7 (3) | C2—N1—C12—C13 | −161.87 (15) |
Symmetry code: (i) −x, y, −z+3/2.
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C1—H1A···F6ii | 0.95 | 2.42 | 3.142 (3) | 133 |
| C3—H3A···F5iii | 0.95 | 2.45 | 3.374 (2) | 166 |
| C5—H5A···F5iv | 0.95 | 2.52 | 3.420 (3) | 159 |
| C6—H6A···F4v | 0.95 | 2.53 | 3.392 (2) | 151 |
| C8—H8B···F1ii | 0.99 | 2.39 | 3.350 (3) | 164 |
| C13—H13C···F1vi | 0.98 | 2.55 | 3.523 (2) | 174 |
| C13—H13C···F5vi | 0.98 | 2.50 | 3.166 (2) | 125 |
Symmetry codes: (ii) x−1, y, z; (iii) x−1/2, −y+3/2, z+1/2; (iv) x−1/2, y−1/2, z; (v) −x+1, y, −z+3/2; (vi) −x+1, −y+2, −z+2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HB6760).
References
- Bruker (2009). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Haque, R. A., Iqbal, M. A., Fun, H.-K. & Arshad, S. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o924–o925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Narasimhan, B., Sharma, D. & Kumar, P. (2012). Med. Chem. Res. 21, 269–283.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812019344/hb6760sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812019344/hb6760Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report