Abstract
In the title molecule, C21H19FN4O, the triazole ring forms dihedral angles of 67.0 (1) and 59.6 (1)° with the phenyl and fluoro-substituted benzene rings, respectively. The dihedral angle between the phenyl ring and the fluoro-substituted benzene ring is 79.1 (1)°. The pyrrolidine ring is in a half-chair conformation. In the crystal, weak C—H⋯O and C—H⋯N hydrogen bonds connect molecules into layers parallel to (001).
Related literature
For clinical uses of triazole compounds, see: Wang & Zhou (2011 ▶); Zhou & Wang (2012 ▶); Chang et al. (2011 ▶). For the synthesis, see: Solankee et al. (2010 ▶). For related structures, see: Wang et al. (2009 ▶); Yan et al. (2009 ▶).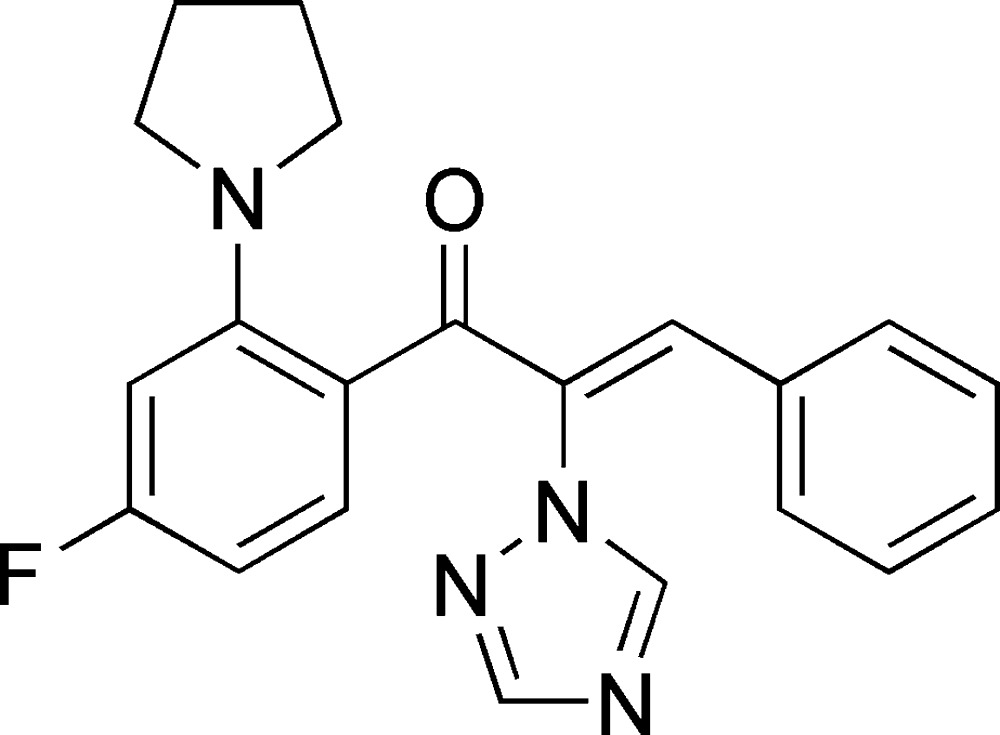
Experimental
Crystal data
C21H19FN4O
M r = 362.40
Monoclinic,

a = 11.217 (2) Å
b = 10.067 (2) Å
c = 15.793 (3) Å
β = 94.47 (3)°
V = 1778.0 (6) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.09 mm−1
T = 173 K
0.30 × 0.08 × 0.03 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996) ▶ T min = 0.973, T max = 0.997
13447 measured reflections
3403 independent reflections
2341 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.058
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.048
wR(F 2) = 0.118
S = 1.05
3403 reflections
321 parameters
2 restraints
All H-atom parameters refined
Δρmax = 0.23 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.19 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 1997 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 1997 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812018454/lh5432sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812018454/lh5432Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812018454/lh5432Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C5—H12⋯O1i | 0.981 (19) | 2.435 (19) | 3.347 (2) | 154.6 (14) |
| C16—H23⋯N1ii | 0.906 (19) | 2.525 (19) | 3.388 (3) | 159.3 (16) |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (21172181) and the Research Funds for the Central Universities, the key program of the Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing (CSTC2012jjB10026), the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (SRFDP 20110182110007) and the Research Funds for the Central Universities (XDJK2011D007, XDJK2012B026).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Chalcones are an important type of biologically active compounds with a diarylenone structural unit (Solankee et al., 2010). Triazole compounds have been shown to have clinical uses (Wang et al., 2011; Zhou et al., 2012; Chang et al., 2011). Our group have been contributing to the research and development of triazolyl chalcones as potential antimicrobial agents. Related structures of triazolylchalcones have alreay been reported (Wang et al., 2009; Yan et al., 2009). Herein we report the crystal structure of the title compound (I).
In the molecular structure (Fig. 1) the triazole ring [N1/N2/N3/C9/C10] forms dihedral angles of 67.0 (1) and 59.6 (1)° with the phenyl [C1-C6] and fluoro-substituted benzene [C12-C17] rings. The dihedral angles between the phenyl and fluoro-substituted bezene rings is 79.1 (1)°. The pyrrolidine ring [N4/C18-C21] is in a half-chair conformation. In the crystal, weak C—H···O and C—H···N hydrogen bonds connect molecules into layers parallel to (001).
Experimental
The title compound (I) was synthesized according to the procedure of Solankee et al. (2010). To a stirring mixture of 1-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-2-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)ethanone (2.23 g, 10 mmol) and benzaldehyde (1.06 g, 10 mmol) in ethanol (20 mL) in the presence of acetic acid (0.08 mL, 1.4 mmol) was added pyrrolidine (0.71 g, 10 mmol). The mixed solution was refluxed until the reaction came to the end (monitored by TLC). Subsequently, the solvent was removed under reduced pressure, and the residue was dissolved in dichloromethane (20 mL) and extracted with water (3 x 20 mL). The combined organic phase was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and concentrated under reduced pressure to produce the crude product, which was purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate (15/1:1/1, V/V) to afford the desired compound. A crystal suitable for X-ray analysis was grown from a solution of (I) in petroleum ether and ethyl acetate by slow evaporation at room temperature.
Refinement
All hydrogen atoms were refined independently with isotropic displacement parameters.
Figures
Fig. 1.
Ellipsoid plot.
Crystal data
| C21H19FN4O | Z = 4 |
| Mr = 362.40 | F(000) = 760 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Dx = 1.354 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 11.217 (2) Å | θ = 2.3–27.7° |
| b = 10.067 (2) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| c = 15.793 (3) Å | T = 173 K |
| β = 94.47 (3)° | Plate, yellow |
| V = 1778.0 (6) Å3 | 0.30 × 0.08 × 0.03 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART CCD diffractometer | 3403 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2341 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.058 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 26.0°, θmin = 3.1° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996) | h = −13→13 |
| Tmin = 0.973, Tmax = 0.997 | k = −11→12 |
| 13447 measured reflections | l = −19→19 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.048 | All H-atom parameters refined |
| wR(F2) = 0.118 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0576P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.05 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 3403 reflections | Δρmax = 0.23 e Å−3 |
| 321 parameters | Δρmin = −0.19 e Å−3 |
| 2 restraints | Extinction correction: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.0075 (13) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| F1 | 0.06331 (9) | 0.07121 (12) | 0.14879 (7) | 0.0506 (4) | |
| N3 | 0.73647 (12) | −0.01216 (15) | 0.27605 (9) | 0.0291 (4) | |
| O1 | 0.54633 (11) | 0.01888 (14) | 0.36550 (8) | 0.0389 (4) | |
| C8 | 0.62355 (15) | −0.06156 (19) | 0.24237 (11) | 0.0289 (4) | |
| C16 | 0.18387 (18) | −0.0239 (2) | 0.25987 (13) | 0.0340 (5) | |
| C17 | 0.29747 (16) | −0.06191 (18) | 0.29689 (11) | 0.0290 (4) | |
| C12 | 0.39893 (16) | −0.02771 (18) | 0.25277 (11) | 0.0290 (4) | |
| N2 | 0.76525 (14) | 0.11901 (16) | 0.27051 (10) | 0.0378 (4) | |
| N4 | 0.30375 (13) | −0.13062 (16) | 0.37147 (9) | 0.0320 (4) | |
| C13 | 0.38080 (18) | 0.02722 (19) | 0.17088 (12) | 0.0336 (5) | |
| C6 | 0.70879 (16) | −0.19160 (19) | 0.12221 (11) | 0.0291 (4) | |
| C11 | 0.52247 (16) | −0.02255 (19) | 0.29265 (12) | 0.0306 (5) | |
| C7 | 0.61641 (17) | −0.14582 (19) | 0.17621 (11) | 0.0312 (5) | |
| C3 | 0.87605 (18) | −0.2952 (2) | 0.01763 (12) | 0.0369 (5) | |
| N1 | 0.91459 (14) | 0.00330 (19) | 0.34166 (10) | 0.0422 (5) | |
| C5 | 0.68283 (18) | −0.3030 (2) | 0.07170 (11) | 0.0324 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.90214 (18) | −0.1816 (2) | 0.06478 (12) | 0.0369 (5) | |
| C1 | 0.82010 (17) | −0.1292 (2) | 0.11679 (12) | 0.0330 (5) | |
| C15 | 0.17490 (16) | 0.0344 (2) | 0.18190 (13) | 0.0363 (5) | |
| C18 | 0.19584 (18) | −0.1755 (2) | 0.41003 (13) | 0.0387 (5) | |
| C10 | 0.82587 (17) | −0.0775 (2) | 0.31872 (12) | 0.0354 (5) | |
| C9 | 0.87283 (19) | 0.1214 (2) | 0.31018 (13) | 0.0406 (5) | |
| C14 | 0.26982 (18) | 0.0594 (2) | 0.13393 (14) | 0.0365 (5) | |
| C4 | 0.76540 (19) | −0.3541 (2) | 0.01975 (12) | 0.0365 (5) | |
| C21 | 0.40905 (18) | −0.2063 (2) | 0.40537 (14) | 0.0392 (5) | |
| C20 | 0.3575 (2) | −0.3164 (2) | 0.45719 (15) | 0.0446 (6) | |
| C19 | 0.2455 (2) | −0.2535 (3) | 0.48764 (15) | 0.0477 (6) | |
| H15 | 0.5351 (16) | −0.1852 (18) | 0.1620 (10) | 0.031 (5)* | |
| H23 | 0.1166 (17) | −0.0388 (19) | 0.2867 (12) | 0.038 (6)* | |
| H3A | 0.4540 (15) | −0.2398 (18) | 0.3554 (11) | 0.037 (5)* | |
| H5 | 0.2578 (17) | 0.1005 (19) | 0.0796 (12) | 0.042 (6)* | |
| H12 | 0.6041 (17) | −0.3451 (19) | 0.0728 (11) | 0.036 (5)* | |
| H7 | 0.8209 (17) | −0.174 (2) | 0.3276 (12) | 0.044 (6)* | |
| H8A | 0.1441 (17) | −0.096 (2) | 0.4266 (11) | 0.043 (6)* | |
| H2A | 0.3393 (17) | −0.396 (2) | 0.4217 (12) | 0.044 (6)* | |
| H18 | 0.4500 (16) | 0.0451 (18) | 0.1429 (12) | 0.037 (5)* | |
| H6 | 0.9173 (18) | 0.205 (2) | 0.3160 (12) | 0.048 (6)* | |
| H4 | 0.7450 (17) | −0.432 (2) | −0.0150 (12) | 0.041 (6)* | |
| H14 | 0.9352 (18) | −0.332 (2) | −0.0180 (11) | 0.047 (6)* | |
| H11 | 0.9777 (18) | −0.1339 (19) | 0.0632 (11) | 0.039 (5)* | |
| H8B | 0.1457 (18) | −0.2321 (19) | 0.3678 (12) | 0.046 (6)* | |
| H10 | 0.8385 (17) | −0.0451 (19) | 0.1478 (12) | 0.044 (6)* | |
| H3B | 0.4656 (19) | −0.144 (2) | 0.4417 (13) | 0.057 (7)* | |
| H1A | 0.1847 (19) | −0.322 (2) | 0.5052 (13) | 0.060 (7)* | |
| H2B | 0.4184 (19) | −0.346 (2) | 0.5040 (12) | 0.049 (6)* | |
| H1B | 0.267 (2) | −0.193 (2) | 0.5352 (14) | 0.068 (8)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| F1 | 0.0285 (7) | 0.0611 (9) | 0.0608 (8) | 0.0060 (6) | −0.0043 (6) | 0.0095 (6) |
| N3 | 0.0224 (8) | 0.0345 (10) | 0.0308 (8) | −0.0006 (7) | 0.0053 (7) | −0.0009 (7) |
| O1 | 0.0283 (8) | 0.0522 (10) | 0.0372 (8) | −0.0007 (7) | 0.0075 (6) | −0.0078 (7) |
| C8 | 0.0218 (10) | 0.0320 (11) | 0.0329 (10) | 0.0000 (8) | 0.0030 (8) | 0.0016 (9) |
| C16 | 0.0223 (10) | 0.0366 (12) | 0.0439 (12) | −0.0043 (9) | 0.0078 (9) | −0.0025 (10) |
| C17 | 0.0254 (10) | 0.0299 (11) | 0.0322 (10) | −0.0002 (8) | 0.0048 (8) | −0.0047 (8) |
| C12 | 0.0236 (10) | 0.0302 (11) | 0.0337 (10) | 0.0025 (8) | 0.0058 (8) | −0.0019 (8) |
| N2 | 0.0318 (10) | 0.0360 (10) | 0.0458 (10) | −0.0048 (8) | 0.0035 (8) | −0.0013 (8) |
| N4 | 0.0231 (8) | 0.0370 (10) | 0.0367 (9) | 0.0018 (7) | 0.0083 (7) | −0.0001 (7) |
| C13 | 0.0277 (11) | 0.0356 (12) | 0.0387 (11) | −0.0006 (9) | 0.0098 (10) | 0.0000 (9) |
| C6 | 0.0257 (10) | 0.0330 (11) | 0.0288 (10) | 0.0029 (9) | 0.0035 (8) | 0.0026 (8) |
| C11 | 0.0268 (10) | 0.0327 (11) | 0.0329 (11) | 0.0002 (9) | 0.0066 (9) | 0.0015 (9) |
| C7 | 0.0235 (10) | 0.0355 (12) | 0.0355 (11) | −0.0020 (9) | 0.0070 (9) | 0.0044 (9) |
| C3 | 0.0363 (12) | 0.0447 (13) | 0.0306 (10) | 0.0121 (10) | 0.0084 (9) | 0.0003 (10) |
| N1 | 0.0268 (9) | 0.0613 (13) | 0.0389 (10) | −0.0053 (9) | 0.0053 (8) | 0.0048 (9) |
| C5 | 0.0337 (11) | 0.0331 (12) | 0.0308 (10) | −0.0020 (10) | 0.0042 (9) | 0.0042 (9) |
| C2 | 0.0249 (11) | 0.0521 (14) | 0.0341 (11) | 0.0002 (10) | 0.0048 (9) | 0.0006 (10) |
| C1 | 0.0272 (11) | 0.0398 (12) | 0.0325 (10) | 0.0008 (9) | 0.0060 (9) | −0.0008 (10) |
| C15 | 0.0219 (10) | 0.0383 (12) | 0.0480 (12) | 0.0018 (9) | −0.0028 (9) | −0.0021 (10) |
| C18 | 0.0315 (11) | 0.0439 (14) | 0.0429 (12) | −0.0019 (10) | 0.0172 (10) | 0.0001 (10) |
| C10 | 0.0260 (11) | 0.0468 (14) | 0.0340 (11) | 0.0029 (10) | 0.0068 (9) | 0.0041 (10) |
| C9 | 0.0330 (12) | 0.0464 (14) | 0.0427 (12) | −0.0101 (11) | 0.0049 (10) | −0.0016 (11) |
| C14 | 0.0358 (12) | 0.0367 (12) | 0.0371 (12) | 0.0028 (10) | 0.0032 (10) | 0.0045 (10) |
| C4 | 0.0436 (13) | 0.0345 (13) | 0.0319 (11) | 0.0027 (10) | 0.0069 (10) | −0.0014 (10) |
| C21 | 0.0328 (12) | 0.0448 (14) | 0.0409 (12) | 0.0070 (11) | 0.0086 (10) | 0.0048 (11) |
| C20 | 0.0460 (14) | 0.0441 (15) | 0.0447 (13) | 0.0036 (12) | 0.0099 (11) | 0.0071 (12) |
| C19 | 0.0506 (15) | 0.0478 (15) | 0.0471 (13) | −0.0030 (12) | 0.0187 (12) | 0.0058 (12) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| F1—C15 | 1.370 (2) | C3—H14 | 0.974 (19) |
| N3—C10 | 1.337 (2) | N1—C10 | 1.314 (3) |
| N3—N2 | 1.364 (2) | N1—C9 | 1.358 (3) |
| N3—C8 | 1.425 (2) | C5—C4 | 1.383 (3) |
| O1—C11 | 1.233 (2) | C5—H12 | 0.980 (19) |
| C8—C7 | 1.343 (3) | C2—C1 | 1.385 (3) |
| C8—C11 | 1.487 (2) | C2—H11 | 0.976 (19) |
| C16—C15 | 1.361 (3) | C1—H10 | 0.99 (2) |
| C16—C17 | 1.413 (3) | C15—C14 | 1.377 (3) |
| C16—H23 | 0.906 (19) | C18—C19 | 1.524 (3) |
| C17—N4 | 1.363 (2) | C18—H8A | 1.03 (2) |
| C17—C12 | 1.422 (2) | C18—H8B | 1.01 (2) |
| C12—C13 | 1.407 (3) | C10—H7 | 0.98 (2) |
| C12—C11 | 1.478 (3) | C9—H6 | 0.98 (2) |
| N2—C9 | 1.316 (3) | C14—H5 | 0.954 (19) |
| N4—C18 | 1.468 (2) | C4—H4 | 0.98 (2) |
| N4—C21 | 1.471 (2) | C21—C20 | 1.519 (3) |
| C13—C14 | 1.372 (3) | C21—H3A | 1.026 (18) |
| C13—H18 | 0.940 (19) | C21—H3B | 1.03 (2) |
| C6—C5 | 1.394 (3) | C20—C19 | 1.519 (3) |
| C6—C1 | 1.406 (3) | C20—H2A | 0.99 (2) |
| C6—C7 | 1.467 (2) | C20—H2B | 1.01 (2) |
| C7—H15 | 1.004 (18) | C19—H1A | 1.03 (2) |
| C3—C4 | 1.378 (3) | C19—H1B | 0.98 (2) |
| C3—C2 | 1.384 (3) | ||
| C10—N3—N2 | 109.69 (16) | C2—C1—H10 | 119.7 (11) |
| C10—N3—C8 | 128.79 (17) | C6—C1—H10 | 120.2 (11) |
| N2—N3—C8 | 121.47 (15) | C16—C15—F1 | 117.59 (17) |
| C7—C8—N3 | 120.55 (16) | C16—C15—C14 | 124.80 (18) |
| C7—C8—C11 | 125.48 (17) | F1—C15—C14 | 117.60 (17) |
| N3—C8—C11 | 113.65 (15) | N4—C18—C19 | 103.35 (17) |
| C15—C16—C17 | 119.48 (19) | N4—C18—H8A | 111.4 (10) |
| C15—C16—H23 | 119.3 (12) | C19—C18—H8A | 111.9 (10) |
| C17—C16—H23 | 121.2 (12) | N4—C18—H8B | 109.5 (11) |
| N4—C17—C16 | 118.64 (16) | C19—C18—H8B | 112.8 (11) |
| N4—C17—C12 | 123.83 (16) | H8A—C18—H8B | 107.9 (15) |
| C16—C17—C12 | 117.52 (17) | N1—C10—N3 | 110.9 (2) |
| C13—C12—C17 | 118.80 (17) | N1—C10—H7 | 128.5 (12) |
| C13—C12—C11 | 116.20 (16) | N3—C10—H7 | 120.6 (12) |
| C17—C12—C11 | 124.01 (16) | N2—C9—N1 | 115.8 (2) |
| C9—N2—N3 | 101.55 (17) | N2—C9—H6 | 120.1 (12) |
| C17—N4—C18 | 121.73 (16) | N1—C9—H6 | 124.1 (12) |
| C17—N4—C21 | 124.29 (15) | C13—C14—C15 | 115.96 (19) |
| C18—N4—C21 | 110.76 (15) | C13—C14—H5 | 123.1 (12) |
| C14—C13—C12 | 123.04 (19) | C15—C14—H5 | 120.9 (12) |
| C14—C13—H18 | 120.7 (11) | C3—C4—C5 | 120.1 (2) |
| C12—C13—H18 | 116.2 (11) | C3—C4—H4 | 120.3 (11) |
| C5—C6—C1 | 118.15 (17) | C5—C4—H4 | 119.6 (11) |
| C5—C6—C7 | 117.39 (17) | N4—C21—C20 | 104.23 (17) |
| C1—C6—C7 | 124.45 (18) | N4—C21—H3A | 108.6 (10) |
| O1—C11—C12 | 122.52 (16) | C20—C21—H3A | 113.9 (10) |
| O1—C11—C8 | 117.93 (16) | N4—C21—H3B | 109.3 (12) |
| C12—C11—C8 | 119.47 (16) | C20—C21—H3B | 112.6 (12) |
| C8—C7—C6 | 130.44 (18) | H3A—C21—H3B | 108.0 (15) |
| C8—C7—H15 | 114.9 (10) | C21—C20—C19 | 103.03 (19) |
| C6—C7—H15 | 114.6 (10) | C21—C20—H2A | 110.8 (11) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 119.69 (19) | C19—C20—H2A | 112.1 (12) |
| C4—C3—H14 | 120.5 (12) | C21—C20—H2B | 110.3 (12) |
| C2—C3—H14 | 119.8 (12) | C19—C20—H2B | 114.9 (12) |
| C10—N1—C9 | 102.06 (18) | H2A—C20—H2B | 105.9 (17) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 121.24 (19) | C20—C19—C18 | 102.69 (18) |
| C4—C5—H12 | 119.7 (11) | C20—C19—H1A | 112.8 (12) |
| C6—C5—H12 | 119.1 (11) | C18—C19—H1A | 110.9 (12) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 120.8 (2) | C20—C19—H1B | 110.2 (14) |
| C3—C2—H11 | 122.7 (11) | C18—C19—H1B | 110.3 (14) |
| C1—C2—H11 | 116.5 (12) | H1A—C19—H1B | 109.8 (18) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 120.0 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C5—H12···O1i | 0.981 (19) | 2.435 (19) | 3.347 (2) | 154.6 (14) |
| C16—H23···N1ii | 0.906 (19) | 2.525 (19) | 3.388 (3) | 159.3 (16) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, y−1/2, −z+1/2; (ii) x−1, y, z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: LH5432).
References
- Bruker (1997). SAINT and SMART Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Chang, J.-J., Wang, Y., Zhang, H.-Z., Zhou, C.-H., Geng, R.-X. & Ji, Q.-G. (2011). Chem. J. Chin. Univ. 32, 1970–1985.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1996). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Solankee, A., Kapadia, K., Ćirić, A., Soković, M., Doytchinova, I. & Geronikaki, A. (2010). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 45, 510–518. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Wang, G., Lu, Y., Zhou, C. & Zhang, Y. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o1113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y. & Zhou, C.-H. (2011). Sci. Sin. Chim, 41, 1429–1456.
- Yan, C.-Y., Wang, G.-Z. & Zhou, C.-H. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o2054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.-H. & Wang, Y. (2012). Curr. Med. Chem. 19, 239–280. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812018454/lh5432sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812018454/lh5432Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812018454/lh5432Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report



